Elevating Patient Care Through Comprehensive In-service Training
Achieve NCLEX Excellence March 27
Achieve NCLEX Excellence March 27
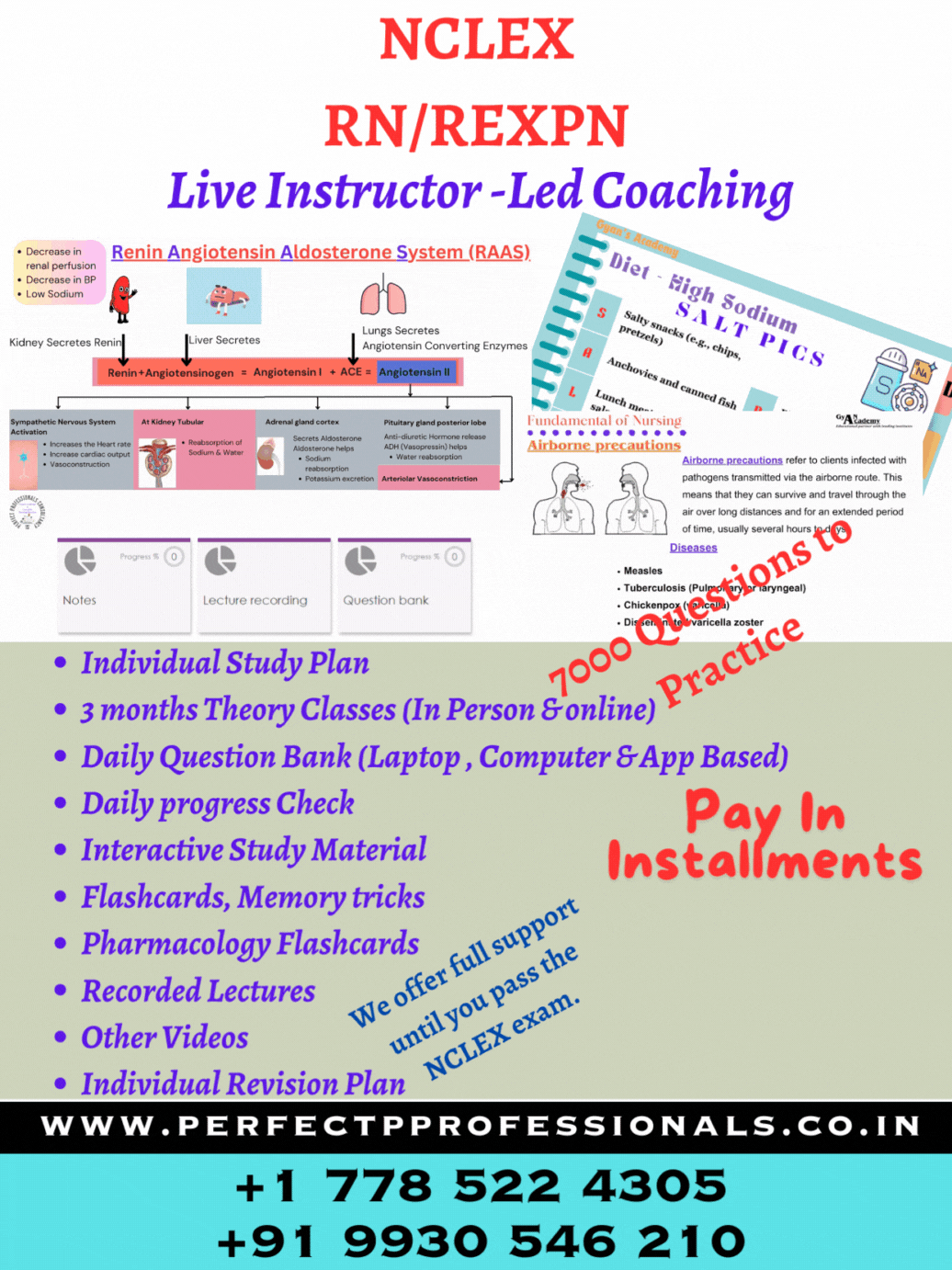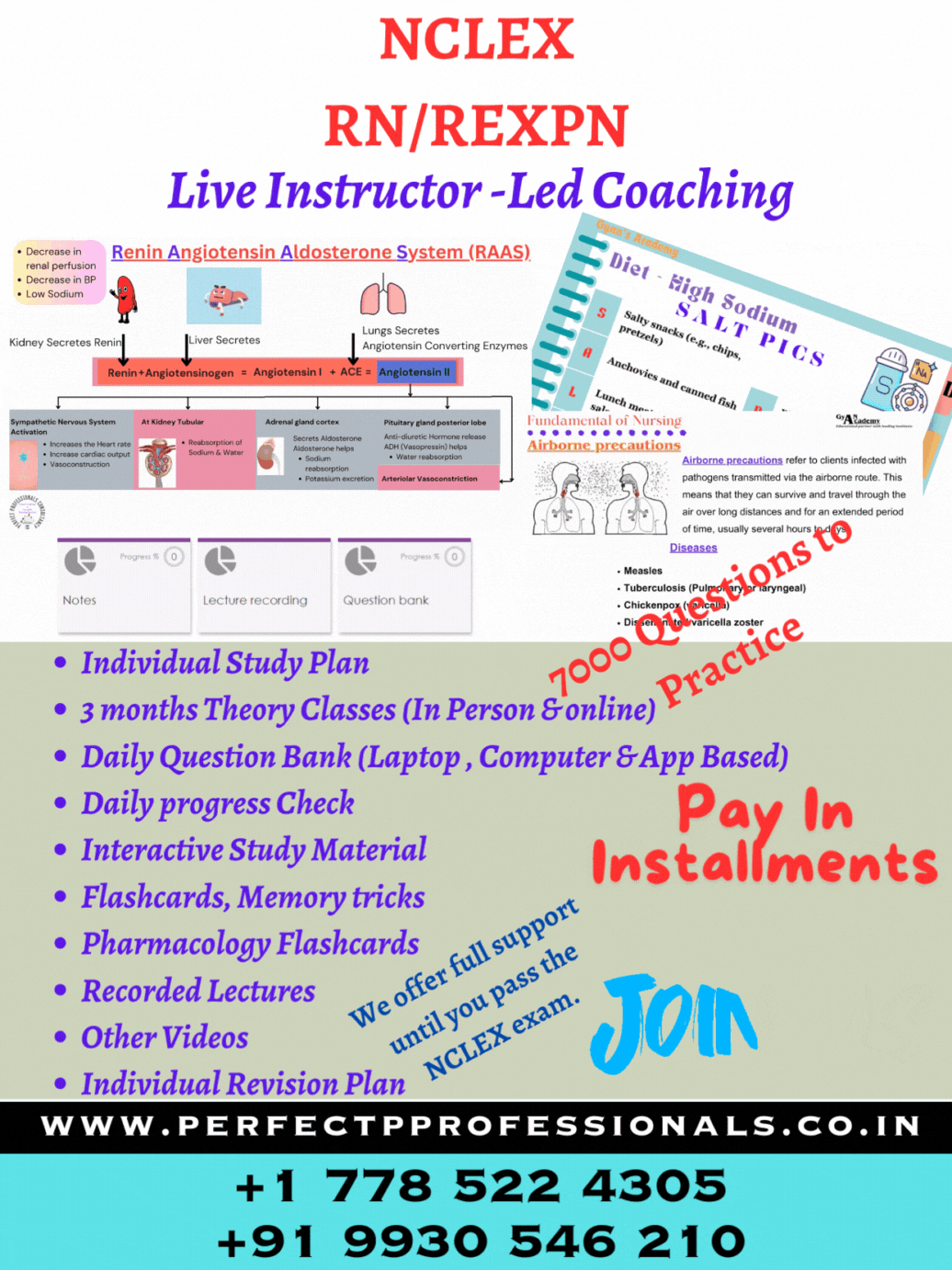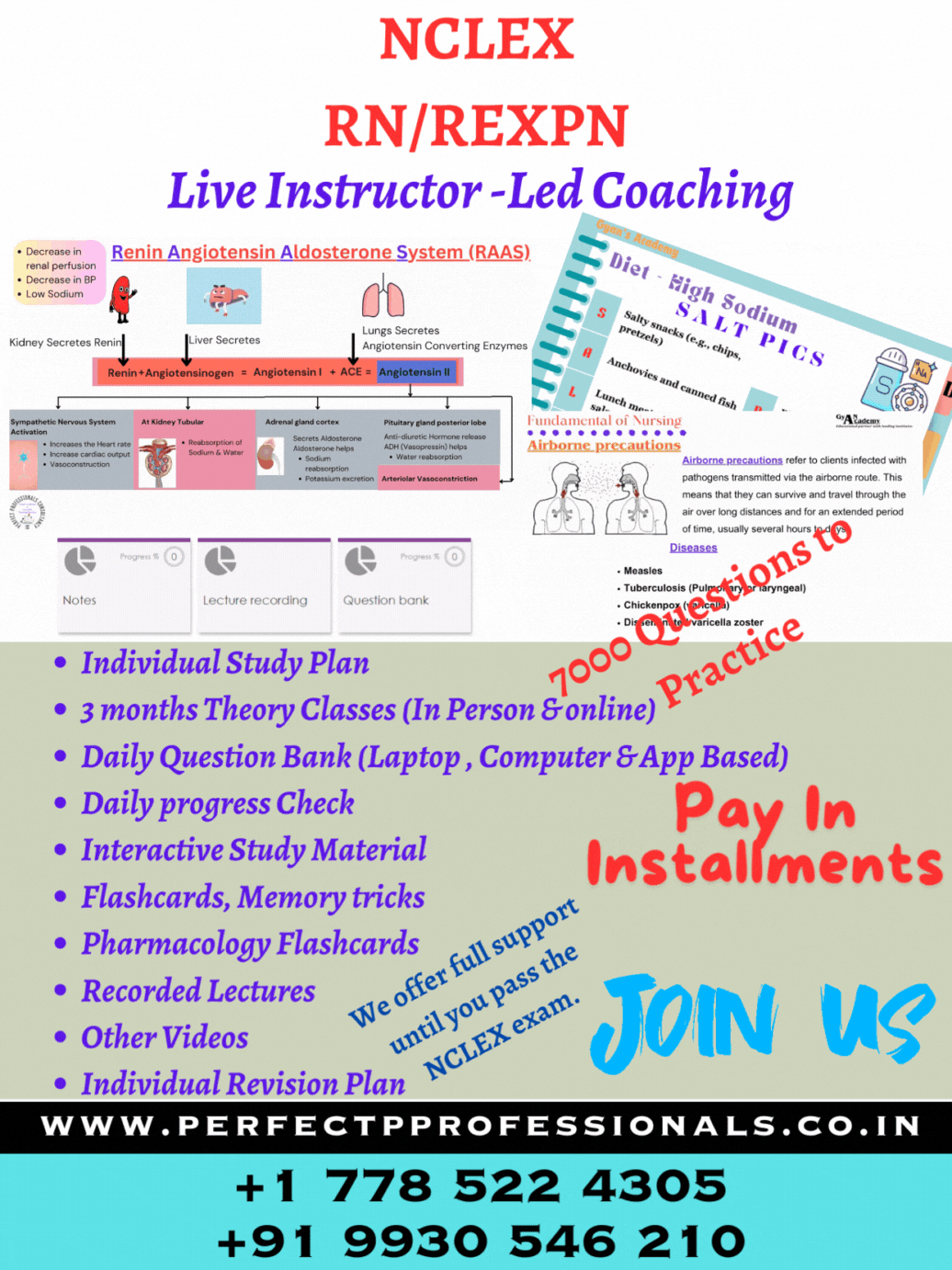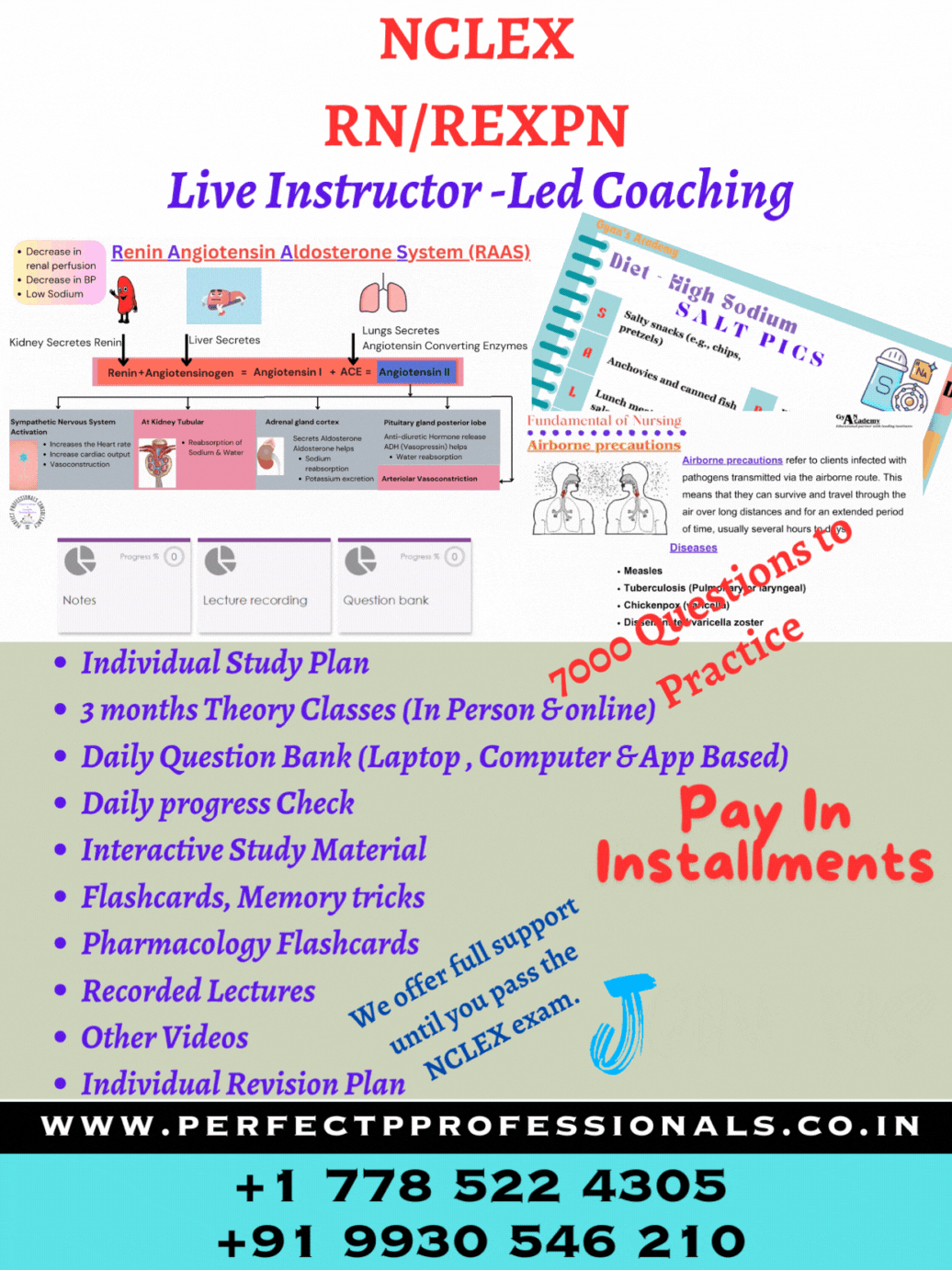
ABC Priority for NCLEX RN exam
Achieve NCLEX Excellence March 27
Achieve NCLEX Excellence March 26
NCLEX Exam Prep Questions
Check NCLEX Practice Questions with Answers on www.completenursingsolution.in
Best NCLEX Practice Questions
Daily NXLEX RN practice questions free of cost
Achieve NCLEX Excellence
To receive daily NCLEX practice questions on your mobile, please join us!
NCLEX (National Council Licensure Examination)
The NCLEX (National Council Licensure Examination) is a standardized exam that nurses must pass in order to obtain a nursing license in the United States and Canada. There are two types of NCLEX exams:
- NCLEX-RN: This is the exam for Registered Nurses (RNs).
- NCLEX-PN: This is the exam for Practical Nurses (LPNs) or Licensed Vocational Nurses (LVNs).
The purpose of the NCLEX is to ensure that nurses have the necessary knowledge, skills, and abilities to provide safe and effective care to patients. The exam is created by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN), and each state or province in the U.S. or Canada has its own licensing board that requires the NCLEX for licensure.
Key points about the NCLEX:
- Content: The exam covers topics like patient care, safety, pharmacology, mental health, and more. It’s designed to assess the clinical judgment and decision-making skills of nursing candidates.
- Format: The NCLEX is a computerized adaptive test (CAT), meaning the difficulty of questions adjusts based on the answers you provide. The test can have anywhere from 75 to 265 questions, and you need to correctly answer enough questions to pass.
- Passing Criteria: The exam doesn’t have a fixed number of correct answers; it uses a statistical model to determine whether you are consistently performing above the passing standard.
Achieve NCLEX Excellence March 27
Discover more from Complete Nursing Solution
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.