NCLEX RN Exam #02
NCLEX RN Exam #1 The NCLEX-RN practice exam is a free resource that you should use before starting your preparation. Make sure you have approximately 5 hours available to complete it.
This practice exam will evaluate your knowledge and help you determine whether you are adequately prepared for the actual NCLEX-RN exam.
NCLEX RN Exam #01
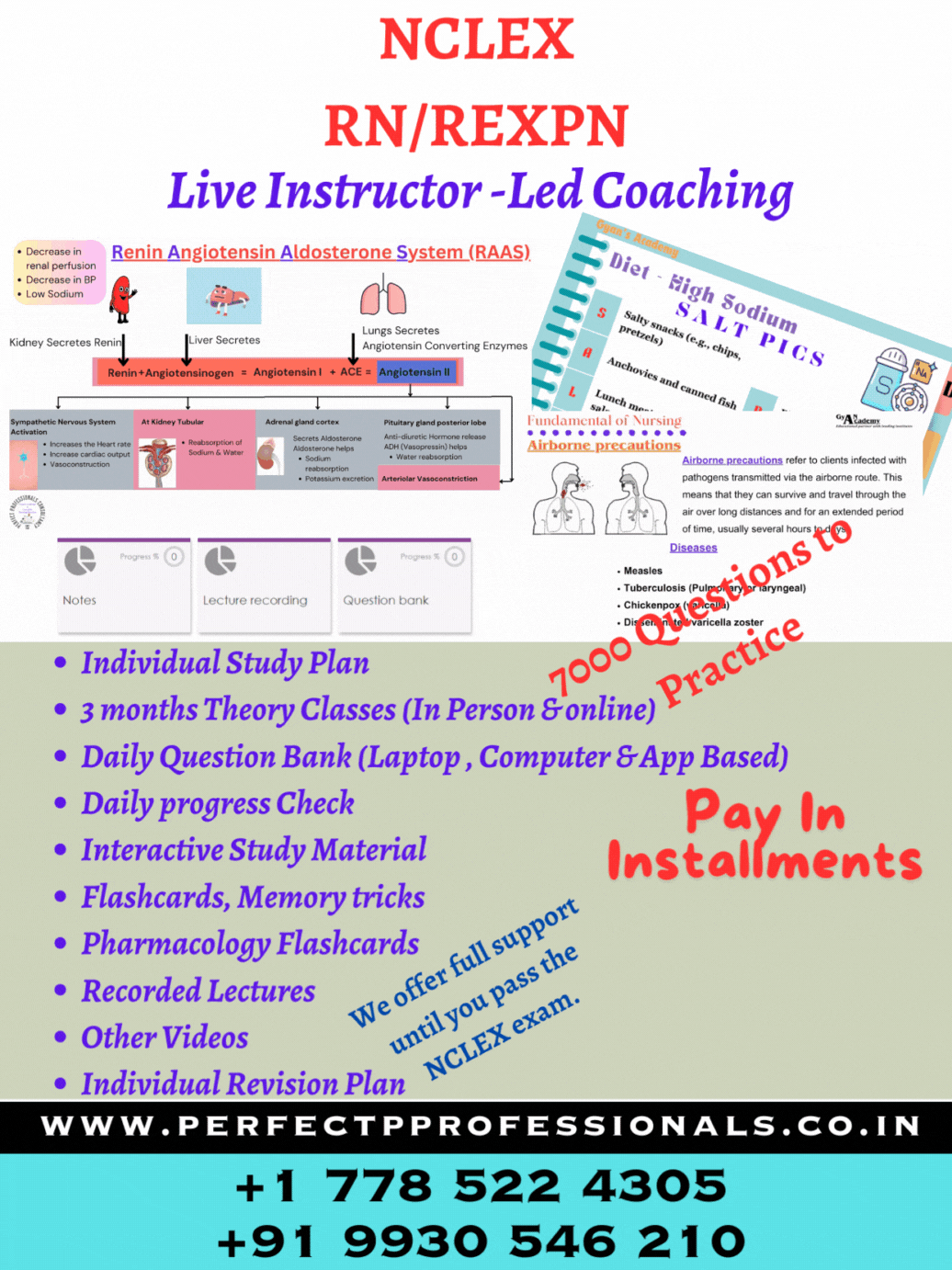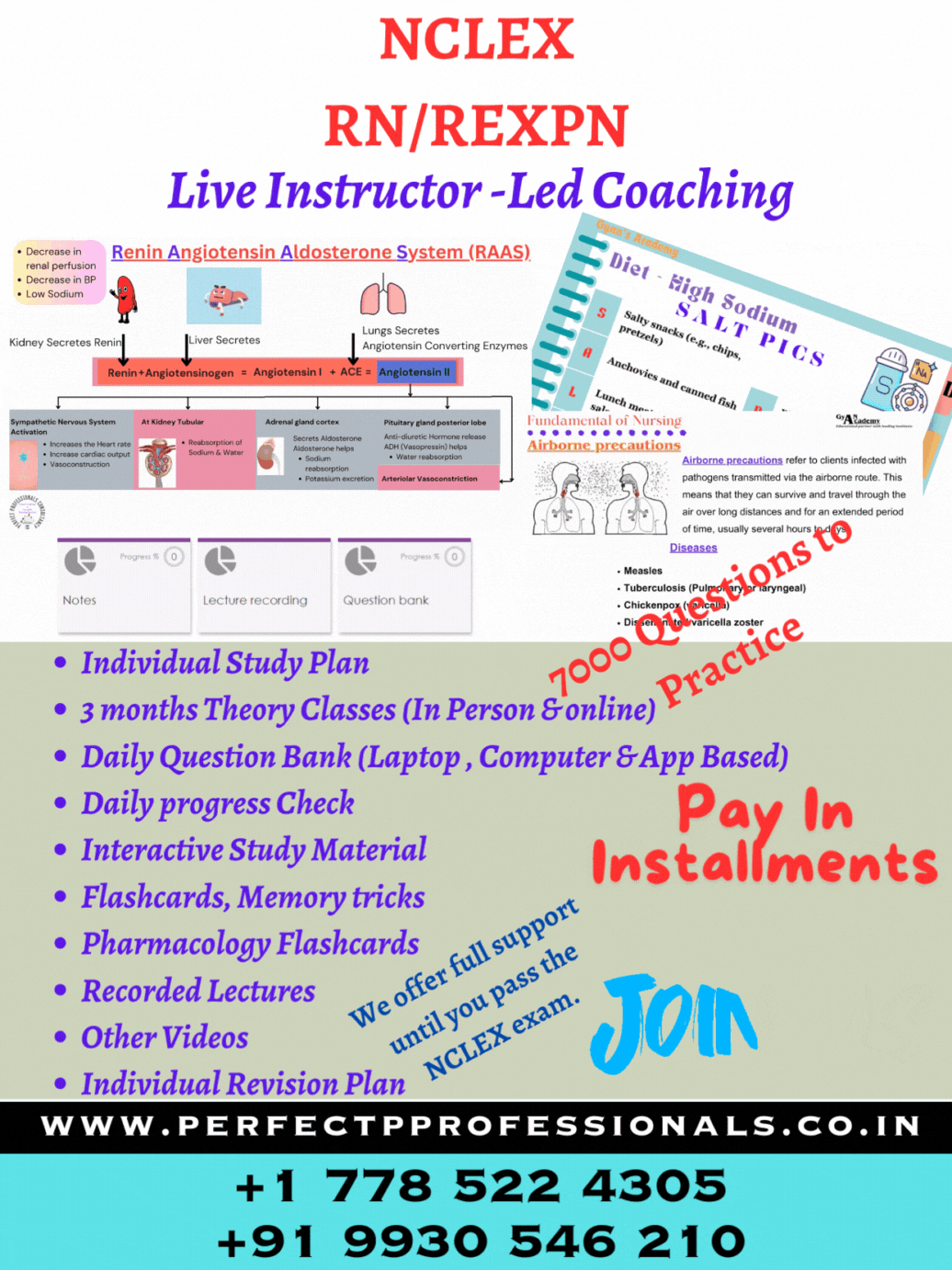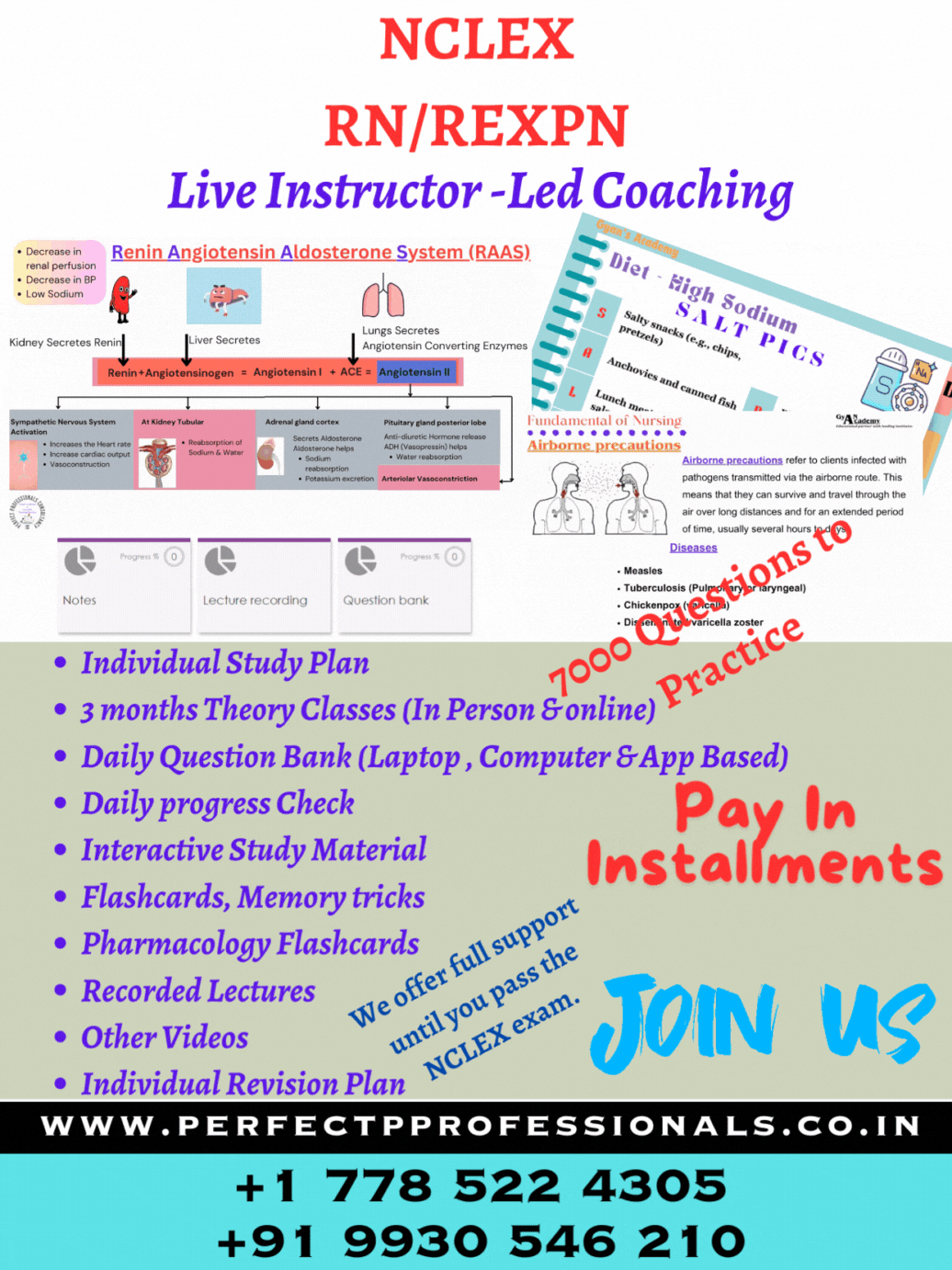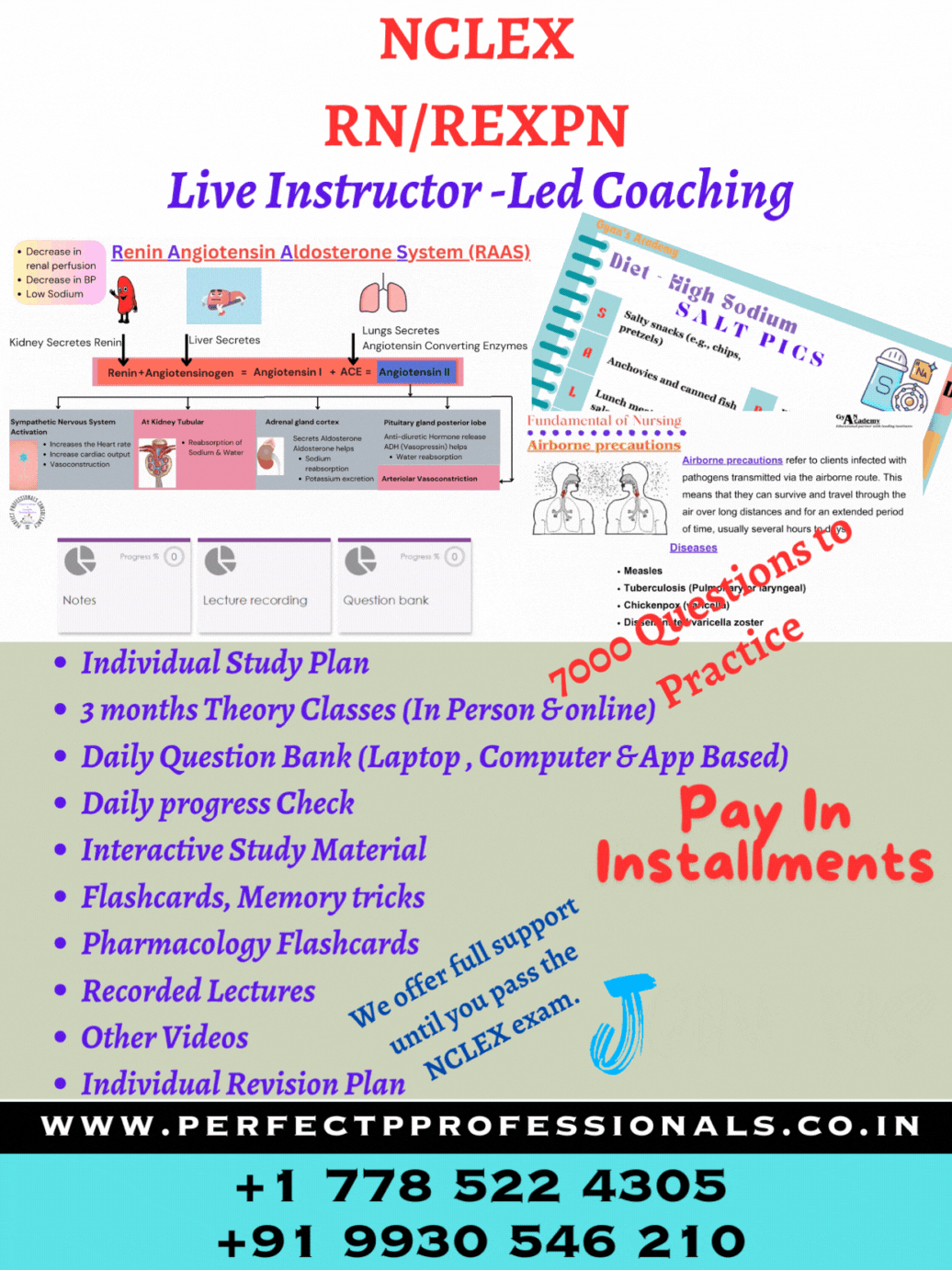
NCLEX RN Exam #1
NCLEX Exam Prep Questions
Check NCLEX Practice Questions with Answers on www.completenursingsolution.in
NCLEX RN Exam #02
Daily NXLEX RN practice questions free of cost
Discover more from Complete Nursing Solution
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


Trustworthy regular service, makes busy NYC life manageable. Can’t recommend highly enough. Thanks for everything.
Dry Cleaning in New York city by Sparkly Maid NYC
Thankyou for this post, I am a big fan of this website would like to keep updated.
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
I like what you guys are up also. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my website 🙂
Somebody necessarily help to make severely articles I would state. This is the first time I frequented your website page and up to now? I surprised with the research you made to make this particular put up extraordinary. Great task!
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thanks, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your site?
Some really excellent posts on this website, appreciate it for contribution. “He that falls in love with himself will have no rivals.” by Benjamin Franklin.
What¦s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I’m hoping to give a contribution & assist different users like its helped me. Good job.
Hello! Would you mind if I share your blog with my myspace group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thank you
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem with your web site in internet explorer, would test this… IE still is the market leader and a huge portion of people will miss your wonderful writing because of this problem.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.com/pt-BR/register?ref=GJY4VW8W
You have remarked very interesting details ! ps nice site.
Die exklusive Auswahl an Tischspielen in der Spielbank Amsterdam Sloterdijk begeistert Casino-Fans mit klassischen und innovativen Spielangeboten. In der Spielbank Amsterdam Sloterdijk erwartet
Besucher eine beeindruckende Auswahl an Automatenspielen. Besucher können auch das spannende
Money Wheel erleben oder an einem der vielen Multi Games-Terminals spielen, die
private Spielfreude mit der Dynamik des Tisches verbinden. Das
Holland Casino bietet klassische Spiele wie Roulette, Black Jack und Punto Banco – alle unter der Leitung erfahrener Croupiers.
Ob Sie zum Spiel, zur Atmosphäre oder einfach nur für einen unterhaltsamen Abend kommen, Holland Casino
Amsterdam bietet eine stilvolle und aufregende Umgebung.
Ob Sie ein erfahrener Spieler sind oder zum ersten Mal ein Casino besuchen, Holland Casino Amsterdam sorgt für einen unvergesslichen Abend.
Joods Historisch Museum liegt in einer 7
km Entfernung und Eremitage Amsterdam ist innerhalb
von 15 Minuten mit dem Auto vom Holiday Inn Amsterdam – Arena Towers aus zu erreichen. Van-Gogh-Museum liegt in nur 17 Gehminuten Entfernung und Anne-Frank-Haus ist in einem 25-minütigen Spaziergang von diesem
3-Sterne Hotel V Frederiksplein Amsterdam aus zu erreichen. Van-Gogh-Museum liegt in einer 2 km Entfernung und Nieuwe Kerk ist innerhalb von 5 Gehminuten von dem
5-Sterne-Hotel Hotel W Amsterdam aus zu erreichen.
Wer Online Casinospiele genießen möchte, wird feststellen, dass jedes seriöse Online-Casino ein festgelegtes Casino Alter verlangt.
Anderswo kann das Casino Amerika Alter bereits ab 18 Jahren gelten, abhängig von den regionalen Gesetzen. Portugiesische Casinos sind
zudem bekannt für ihre strengen Kontrollen, um sicherzustellen, dass diese
Altersgrenze stets eingehalten wird. Das Portugal Casino Alter beträgt 18
Jahre, was Volljährigen den Zutritt zu Spielbanken erlaubt.
Alle Spielbanken kontrollieren streng, sodass ein Altersnachweis bei jedem
Besuch erforderlich ist. Diese Regelung macht Monaco einzigartig, da Monegassen selbst die berühmten Casinos des Landes nicht betreten dürfen.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/der-legiano-casino-login-ihr-weg-zum-online-glucksspiel/
Whats Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It positively helpful and it has helped me out loads. I’m hoping to contribute & aid other customers like its aided me. Good job.
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending way to much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
Very great visual appeal on this website , I’d rate it 10 10.
Your home is valueble for me. Thanks!…
You are my inhalation, I own few blogs and infrequently run out from to post .
Some truly nice and utilitarian info on this website, likewise I think the design holds good features.