The nurse should assess first the newly admitted client with gastroenteritis as prolonged vomiting increases the risk for dehydration, acid-base and electrolyte disturbances (eg, orthostatic hypotension, acid loss, hypokalemia, hyponatremia), and potential cardiac dysrthythmias. The client is exhibiting manifestations of hypokalemia, including muscle cramps and muscle weakness. Hypokalemia can lead to dangerous cardiac arrhythmias (Option 2).
(Option 1) Ahistamine-related reaction (eg, pruritus) is an expected adverse effect associated with the administration of epidural morphine (Astramorph), so this client does not need to be assessed first. An antihistamine such as IV diphenhydramine (Benadryl) may be prescribed to help alleviate itching.
(Option 3) This client may have been excessively diuresed (eg, with bumetanide [Bumex]) and could have orthostatic hypotension. This client is the second priority. Because the client is in the hospital, the risk of severe hypokalemia is low (as most clients receive potassium supplements), and the client is not exhibiting symptoms of hypokalemia.
(Option 4) Gross hematuria is an expected manifestation of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. It is usually mild and does not require urgent attention.
Educational objective: A newly admitted client with gastroenteritis and prolonged vomiting is at risk for acid-base, fluid, and electrolyte disturbances and dehydration related to body fluid and acid loss. The nurse should assess the client for orthostatic hypotension, manifestations of metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, and cardiac dysrhythmias.
The nurse should assess first the newly admitted client with gastroenteritis as prolonged vomiting increases the risk for dehydration, acid-base and electrolyte disturbances (eg, orthostatic hypotension, acid loss, hypokalemia, hyponatremia), and potential cardiac dysrthythmias. The client is exhibiting manifestations of hypokalemia, including muscle cramps and muscle weakness. Hypokalemia can lead to dangerous cardiac arrhythmias (Option 2).
(Option 1) Ahistamine-related reaction (eg, pruritus) is an expected adverse effect associated with the administration of epidural morphine (Astramorph), so this client does not need to be assessed first. An antihistamine such as IV diphenhydramine (Benadryl) may be prescribed to help alleviate itching.
(Option 3) This client may have been excessively diuresed (eg, with bumetanide [Bumex]) and could have orthostatic hypotension. This client is the second priority. Because the client is in the hospital, the risk of severe hypokalemia is low (as most clients receive potassium supplements), and the client is not exhibiting symptoms of hypokalemia.
(Option 4) Gross hematuria is an expected manifestation of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. It is usually mild and does not require urgent attention.
Educational objective: A newly admitted client with gastroenteritis and prolonged vomiting is at risk for acid-base, fluid, and electrolyte disturbances and dehydration related to body fluid and acid loss. The nurse should assess the client for orthostatic hypotension, manifestations of metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, and cardiac dysrhythmias.
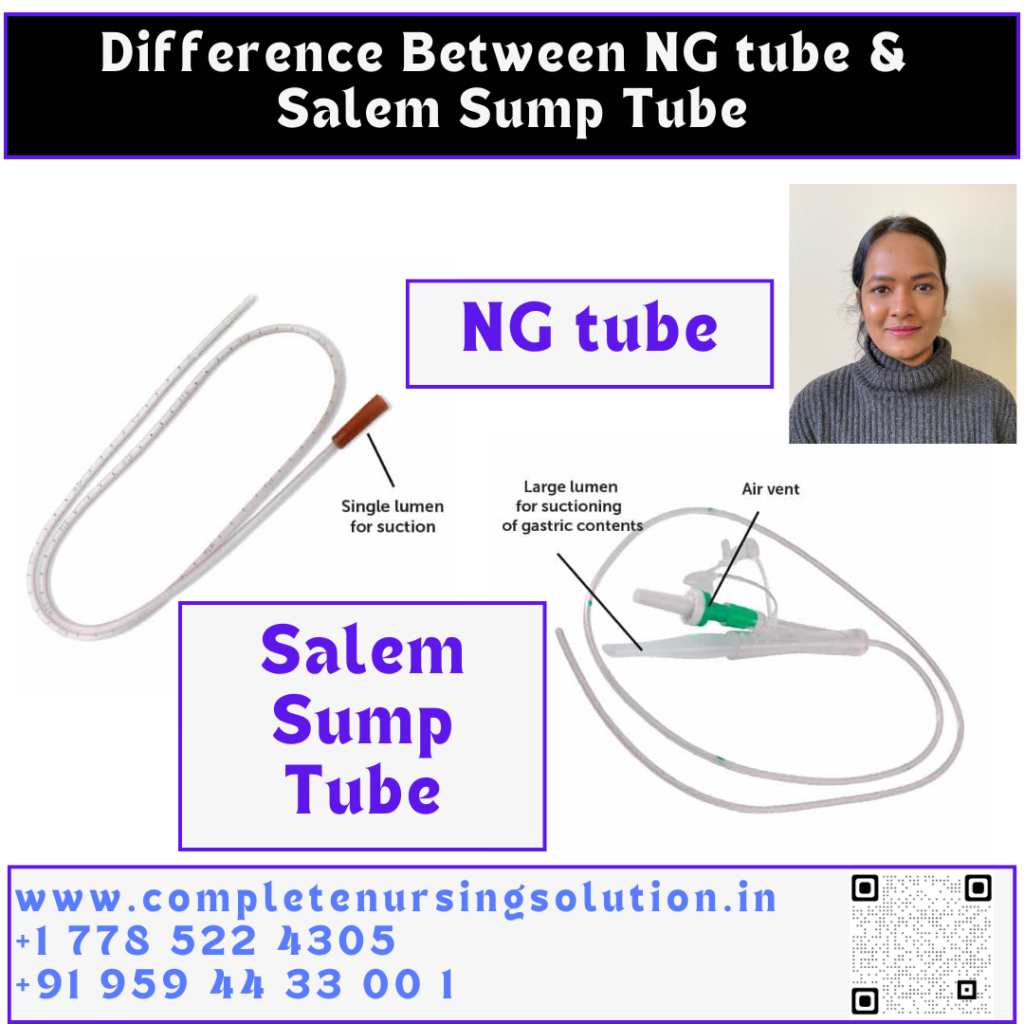
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
tg77com https://www.tg77com.org
I have recently started a site, the information you provide on this site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
Thanks for sharing superb informations. Your website is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you’ve on this blog. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched all over the place and simply could not come across. What an ideal web site.