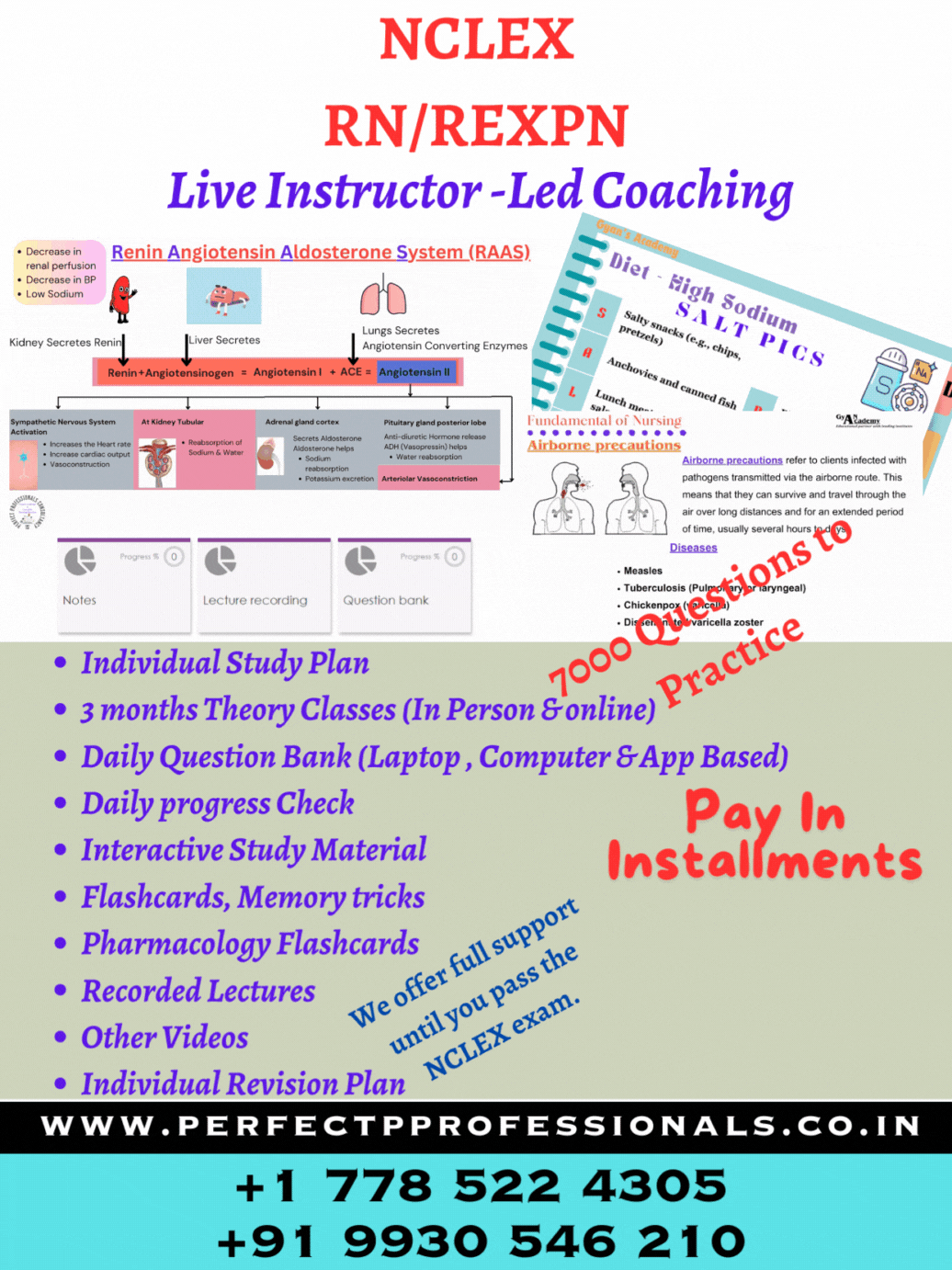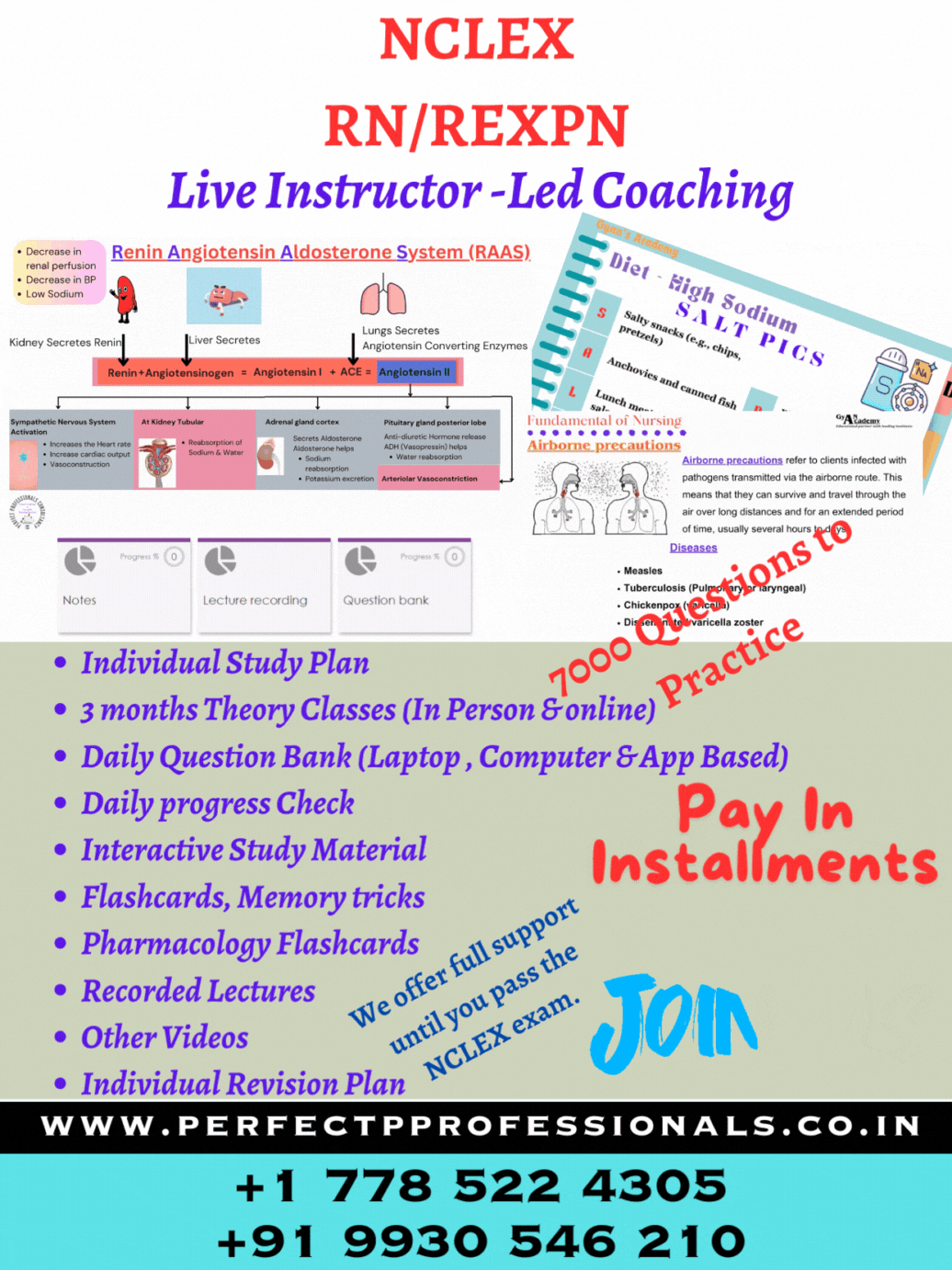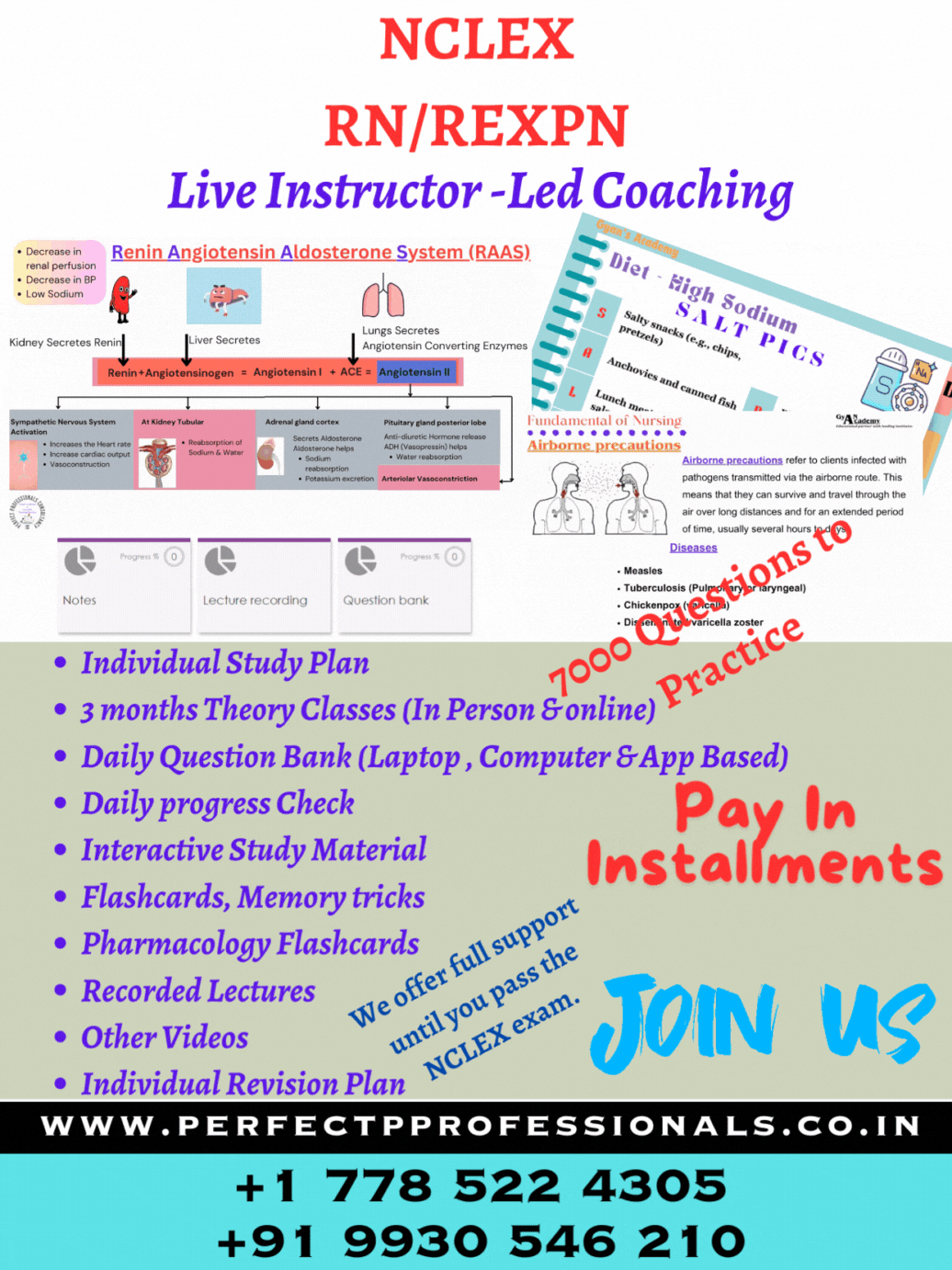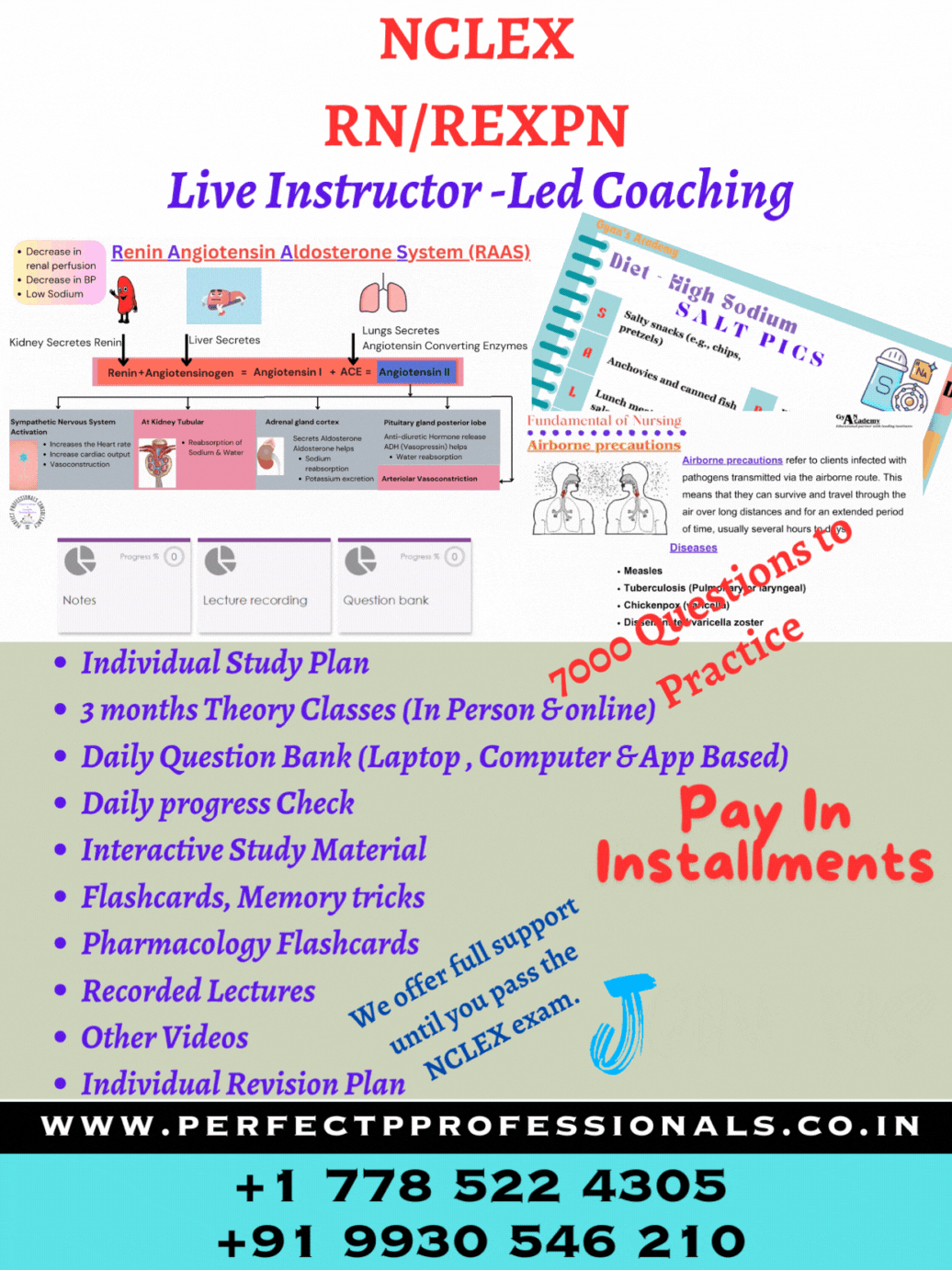
Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) contains sulfapyridine and aspirin (5-ASA) and is used as a topical gastrointestinal anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory agent in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). When the 5-ASA is combined with the sulfa preparation, the drug does not become absorbed until it reaches the colon. Dehydration is a risk with IBD as the client can have up to 20 diarrheal stools a day. The client usually does not feel thirsty until after there is a fluid volume deficit. Sulfa can crystallize in the kidney if the client is dehydrated. Normal urine specific gravity is 1.003-1.030. Elevated specific gravity can indicate concentrated urine and be a sign of dehydration (Option 4).
(Option 1) Due to the inflammatory nature of IBD, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C reactive protein, and white blood cells can be elevated. This is an expected finding during an exacerbation.
(Option 2) Mild to moderate anemia (normal hemoglobin 13.2-17.3 g/dL [132-173 g/L] for males, 11.7-15.5 g/dL [117-155 g/L] for females) is common with most chronic inflammatory conditions (eg, rheumatoid arthritis, IBD) as the body cannot use the available iron in bone marrow with active inflammation. In addition, IBD exacerbation usually includes bloody stools, resulting in blood loss iron deficiency anemia. This needs follow-up but is not a priority.
(Option 3) Yellow-orange discoloration of the client's skin and urine is an expected side effect from the drug.
Educational objective: Dehydration is a concem with sulfasalazine and most other "sulfa" medications due to the risk of crystal formation in the kidney. It is also a potential complication of inflammatory bowel disease
Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) contains sulfapyridine and aspirin (5-ASA) and is used as a topical gastrointestinal anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory agent in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). When the 5-ASA is combined with the sulfa preparation, the drug does not become absorbed until it reaches the colon. Dehydration is a risk with IBD as the client can have up to 20 diarrheal stools a day. The client usually does not feel thirsty until after there is a fluid volume deficit. Sulfa can crystallize in the kidney if the client is dehydrated. Normal urine specific gravity is 1.003-1.030. Elevated specific gravity can indicate concentrated urine and be a sign of dehydration (Option 4).
(Option 1) Due to the inflammatory nature of IBD, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C reactive protein, and white blood cells can be elevated. This is an expected finding during an exacerbation.
(Option 2) Mild to moderate anemia (normal hemoglobin 13.2-17.3 g/dL [132-173 g/L] for males, 11.7-15.5 g/dL [117-155 g/L] for females) is common with most chronic inflammatory conditions (eg, rheumatoid arthritis, IBD) as the body cannot use the available iron in bone marrow with active inflammation. In addition, IBD exacerbation usually includes bloody stools, resulting in blood loss iron deficiency anemia. This needs follow-up but is not a priority.
(Option 3) Yellow-orange discoloration of the client's skin and urine is an expected side effect from the drug.
Educational objective: Dehydration is a concem with sulfasalazine and most other "sulfa" medications due to the risk of crystal formation in the kidney. It is also a potential complication of inflammatory bowel disease
Thanks for sharing. It’s acme quality.
I am in truth thrilled to gleam at this blog posts which consists of tons of profitable facts, thanks for providing such data.
Deference to website author, some wonderful selective information.
You completed several fine points there. I did a search on the theme and found a good number of people will have the same opinion with your blog.
I think this is among the most important info for me. And i am glad reading your article. But wanna remark on some general things, The website style is ideal, the articles is really excellent : D. Good job, cheers
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..extra wait .. …
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back frequently!
Would love to constantly get updated outstanding weblog! .
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your site is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you have on this site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for more articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found just the info I already searched all over the place and simply couldn’t come across. What an ideal site.
I needed to create you that bit of remark so as to give many thanks as before regarding the lovely knowledge you’ve provided in this case. It is really particularly open-handed of you to offer publicly what a few individuals would have made available for an e-book to help with making some profit for themselves, notably given that you might have done it in the event you considered necessary. These ideas as well served like the fantastic way to be certain that some people have the same fervor the same as my own to know a lot more with regards to this issue. I believe there are a lot more pleasant instances in the future for folks who browse through your website.
Just wanna comment that you have a very decent internet site, I love the style and design it actually stands out.
Excellent analysis
Thought-provoking
Great line up. We will be linking to this great article on our site. Keep up the good writing.
It’s appropriate time to make some plans for the longer term and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this submit and if I may just I want to suggest you few fascinating issues or advice. Perhaps you could write next articles referring to this article. I desire to read more issues about it!
Hierzu zählt beispielsweise auch eine einfache grafische Darstellung eines Balkens
in Form eines Raumschiffs, der bis zu einem zufälligen Punkt aufsteigt und
damit den jeweiligen Multiplikator auf den Einsatz gewährt.
Somit bietet die Demoversion nicht nur für Anfänger, die ein neues Spiel kennenlernen wollen, sondern auch für fortgeschrittene Nutzer eine gute Chance, um neue Slots zu erleben und
dabei qualitativen Spielspaß ohne finanzielles Risiko
genießen zu können. Dennoch bietet die Demoversion vor allem für neue Nutzer eine gute Gelegenheit, sich zunächst
mit einem Spiel und dessen Mechanik vertraut machen zu können, ehe das Abenteuer
mit echtem Geld beginnen kann.
Aus diesem Grund finden Sie auf unserer Plattform verschiedene Möglichkeiten, um mit kompetenten Mitarbeitern aus dem Kundenservice in Kontakt treten zu können. Die entsprechenden Links finden Sie am unteren Ende der Homepage im Fußbereich
der Website. Wer möglicherweise ein problematisches Spielverhalten aufweist, kann hier entsprechende Kontaktangebote wahrnehmen und sich über weitere Schritte informieren. Hierzu zählt beispielsweise die uns vorliegende Lizenz, welche uns vorliegt und eine
allgemeine Sicherheit bietet.
Wir bieten sowohl für unsere Neu- als auch für unsere treuen Bestandskunden Aktionen und Bonusprogramme an. Die Spiele im
Live Casino können nicht ohne den Einsatz von Echtgeld gespielt werden.
Der Spieler ist also live dabei, wenn der Spielleiter die Karten austeilt oder
die Kugel in den Kessel schnippt.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/jet-casino-cashback-ihr-weg-zu-verlorenen-einsatzen-zuruck/
Microsoft 365 seamlessly tracks updates, tasks, and comments across all your files so you can pick up right
where you left off. Anyone in your organization can quickly create documents,
presentations, and worksheets within a single, unified app experience.
Also, depending on the user’s country/region,
the daily and weekly purchase limit will vary.
After the stream ends, viewers can still see the leaderboard during replay.
Click it to see the leaderboard and where you rank among the top 50 most
engaged viewers. This reflects the points you’ve earned during the live stream.
Clicking on this icon will take viewers directly to the leaderboard to
see the top 50 engaged viewers.
In February 2006, Microsoft announced that it intended to expand its
Redmond campus by 1,100,000 square feet (100,000 m2) at a cost of
$1 billion and said that this would create space for between 7,000 and
15,000 new employees over the following three years. The more viewers engage
(for example, via live chat messages, Super Chat, Super Stickers, or gifts) the
higher they may rank on the leaderboard. As you engage in the live
stream, keep an eye out for the crown icon at the top of the live chat.
The top 3 engaged viewers even get a special badge next to their name in the live chat!
The first major expansion of the campus came in 1992, bringing the total amount of office space
to 1.7 million square feet (160,000 m2) on 260 acres (110 ha) of land.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/monte-casino-overview/
The links on our site are for entertainment and informational purposes
only. There are thousands of jurisdictions worldwide with access to the internet.
You can look forward to the most accurate directory of casino data on the internet.
Welcome to World Casino Directory’s global directory of casino companies,
operators and owners. The city of Sydney sparkles during the festive
and summer holiday season.
Built in 2015,Rydges Australia Square offers stylish accommodation in the heart of
Sydney CBD (Central Business District). Tucked behind a storied sandstone facade—once home to
Sydney’s Fairfax newspaper empire and the venerable Bank of
New South Wales—Paradox Sydney pens a fresh chapter on a timeless page.
Located in Sydney CBD (Central Business District), next to bustling Martin Place, The Fullerton Hotel Sydney features an à la carte restaurant, a bar and access to a fitness centre.
To top off your luxury experience, relax, refresh and
be pampered, why not visit the Darling Spa? With
panoramic views over Darling Harbour, the city’s most iconic landmarks, glamorous and indulgent rooms,
and Sydney’s most attentive service, this is the
pinnacle of hospitality. It’s home to four unique hotels and residences, including Sydney’s first and only Forbes five-star
boutique hotel and urban resort – The Darling.
The complex is home to over a dozen of Sydney’s best restaurants,
from elegant fine dining to unfussy quick bites
and comfort food. It features over 100,000 sqm of poker tables, table
games, dice games, gaming machines and more spread over two expansive
levels. With an array of treatments and spa experiences available,
finish your spa day feeling nothing but rejuvenated.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/mega-moolah-reviews-gambling-plays-for-big-wins/
paypal casino canada
References:
http://www.joblagbe.com
casino online uk paypal
References:
https://www.dynamicviewpoint.co.uk/employer/online-casino-mit-paypal-einzahlung-die-top-casinos-im-vergleich
I like this web blog its a master peace ! Glad I detected this on google .
I haven¦t checked in here for some time as I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I will add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Whats Taking place i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I am hoping to give a contribution & assist different customers like its aided me. Great job.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/zh-TC/register-person?ref=DCKLL1YD
I love the efforts you have put in this, appreciate it for all the great articles.