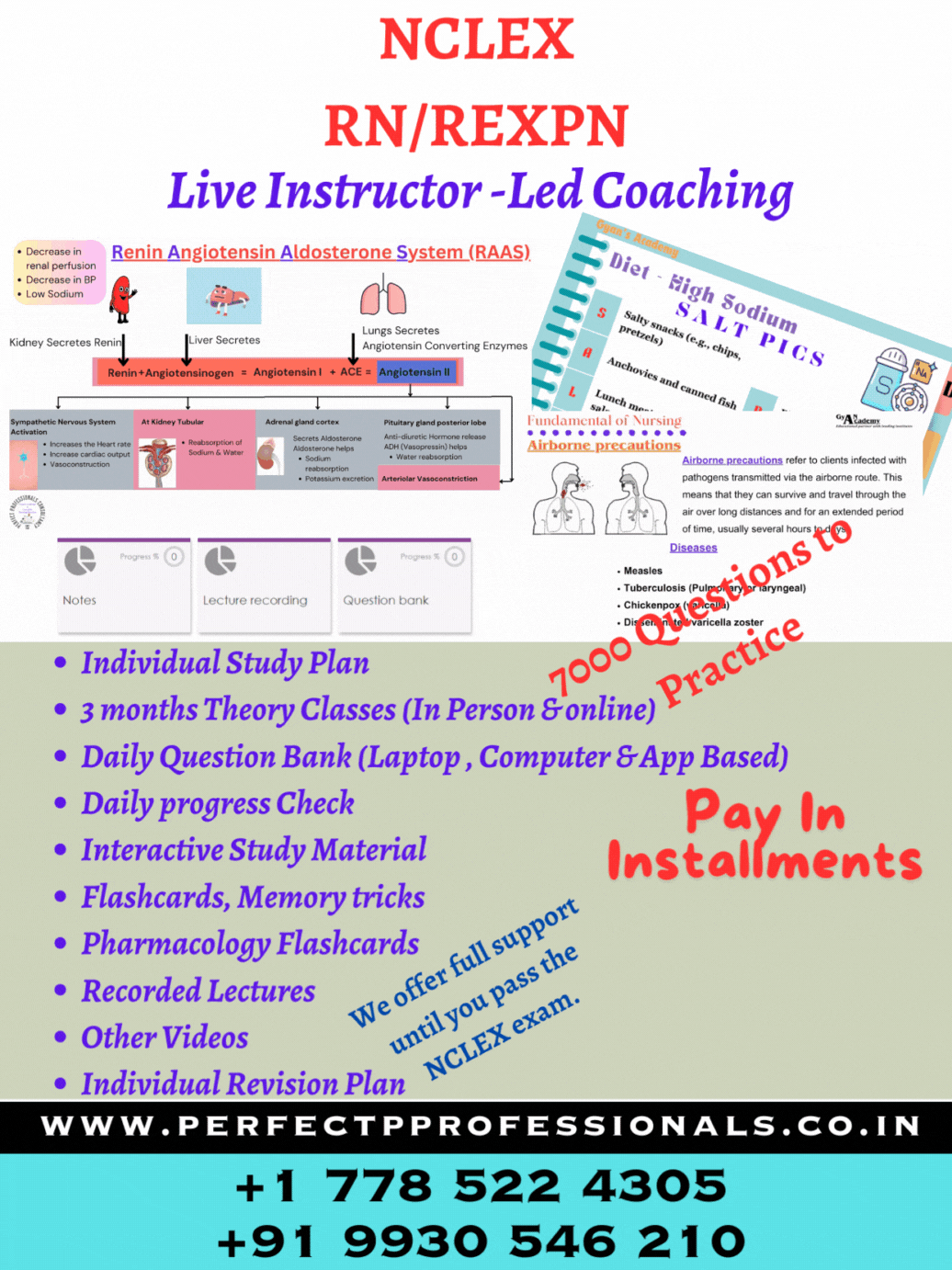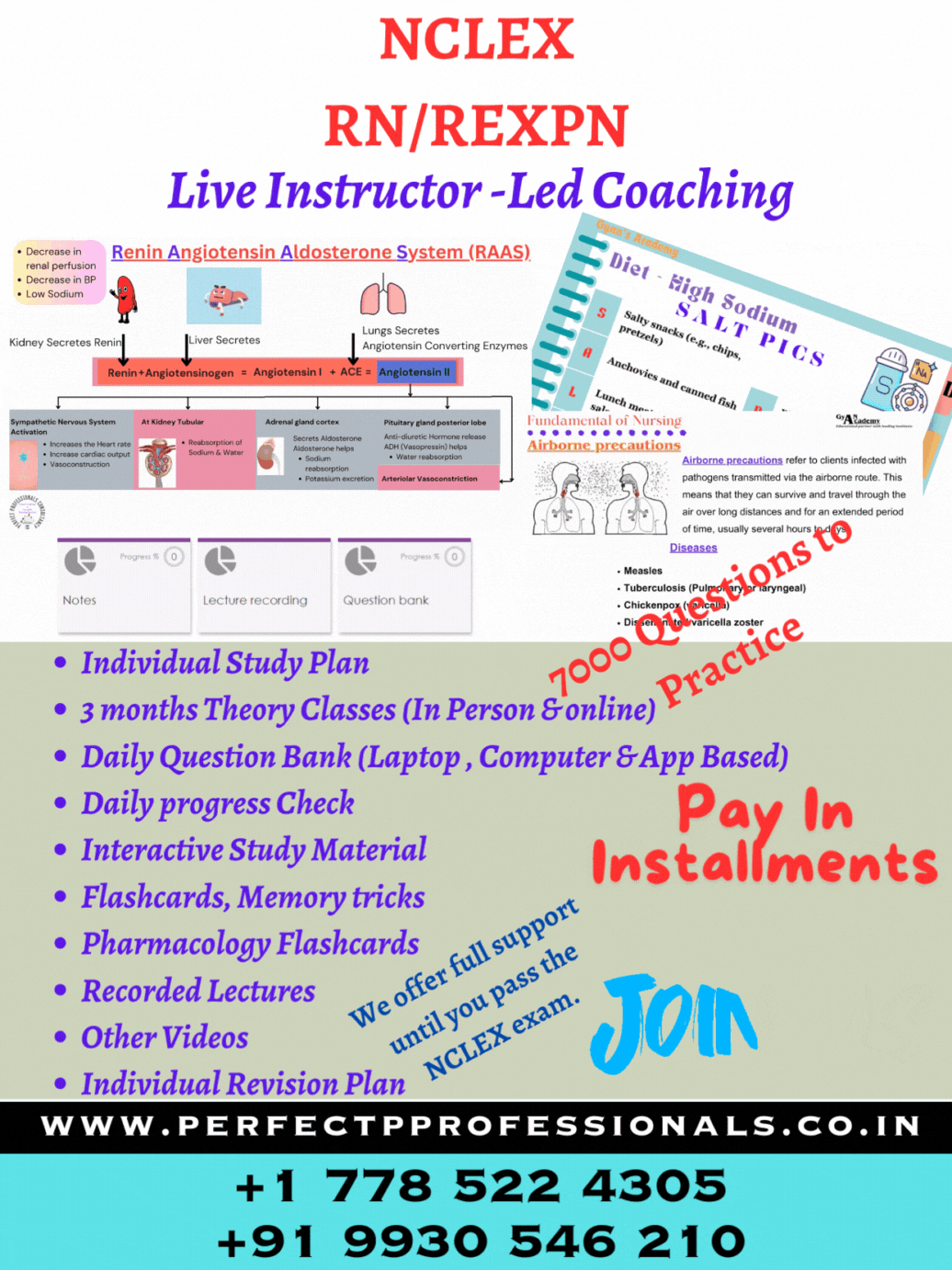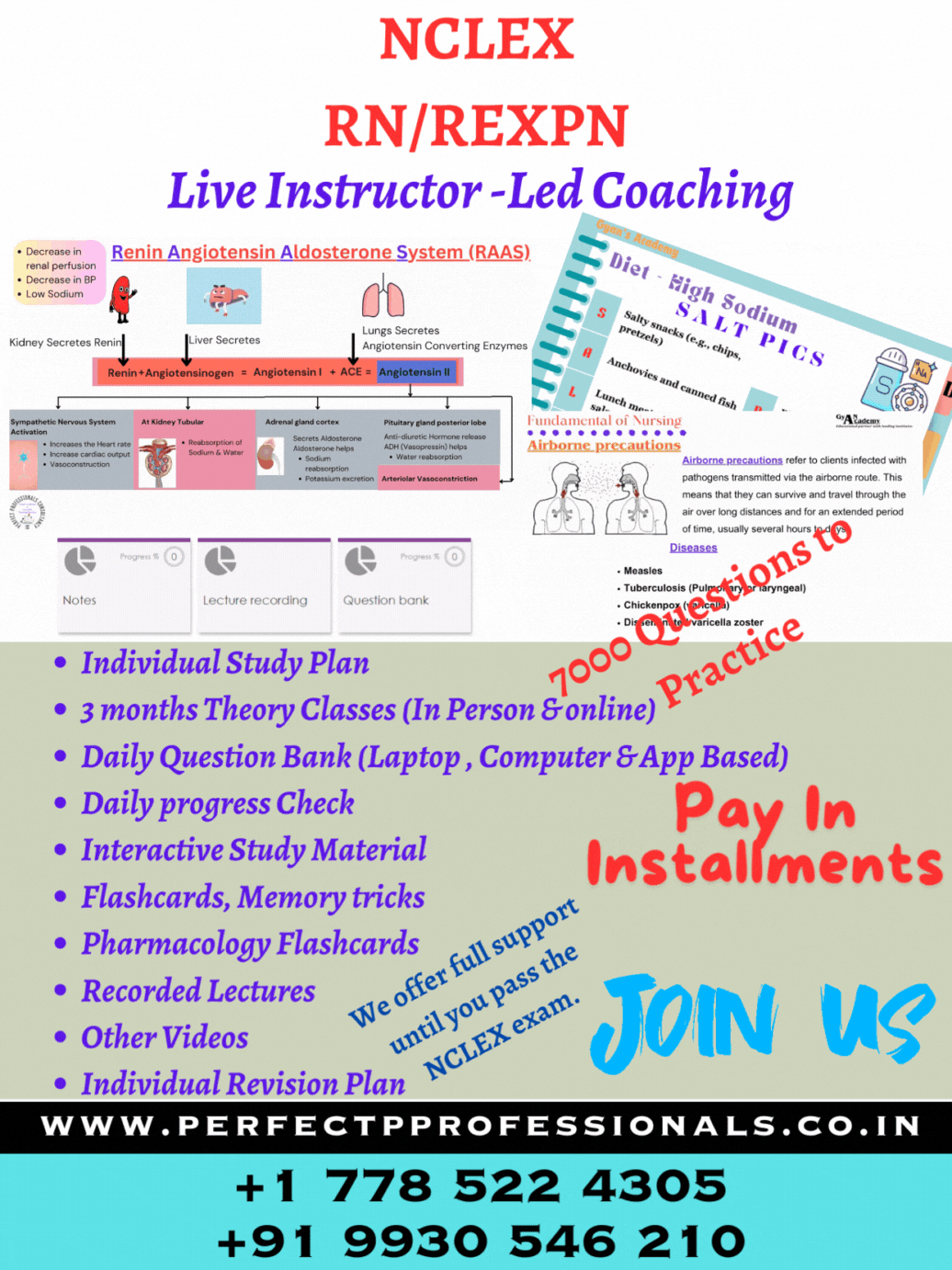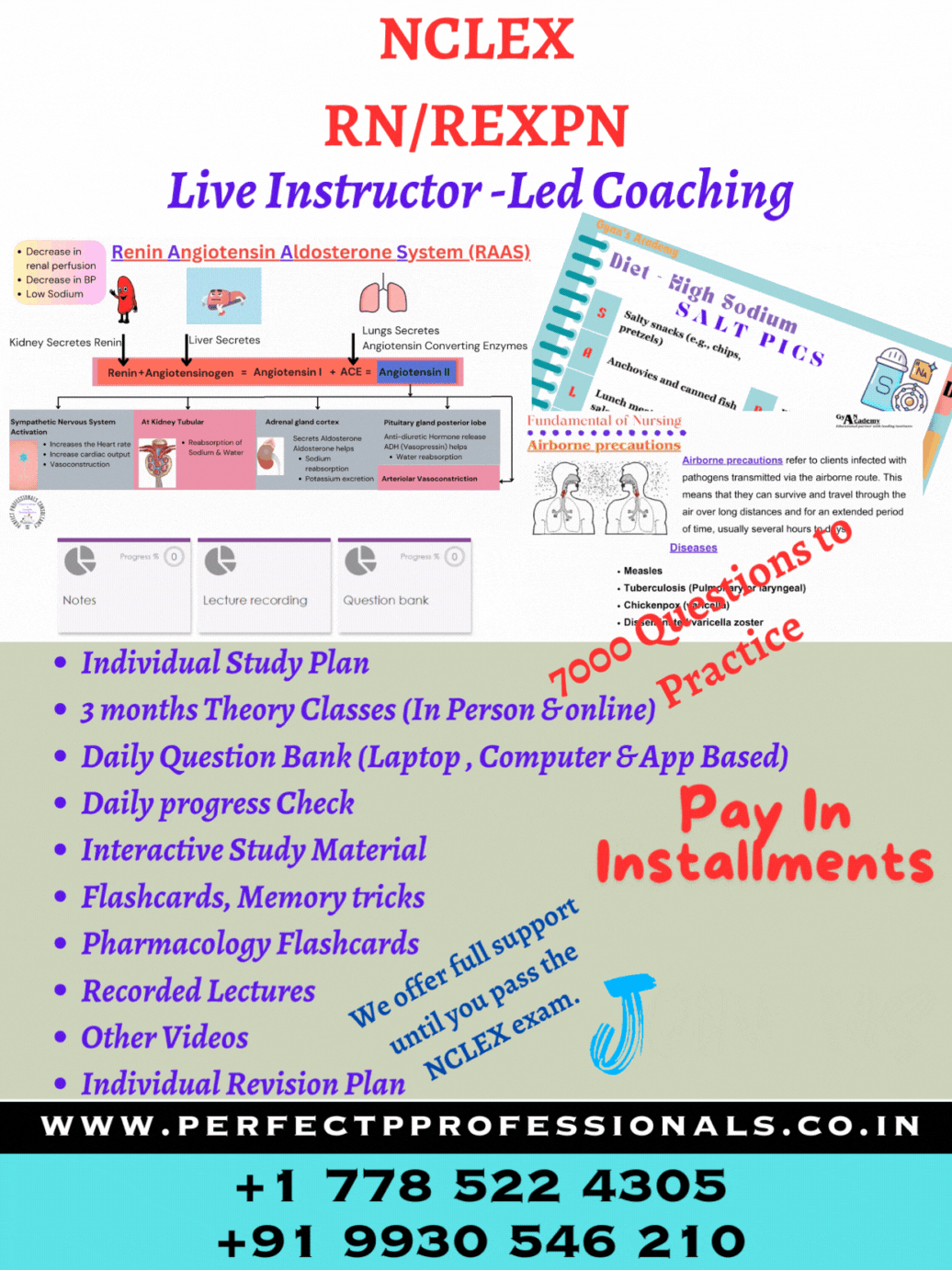
In this scenario, a client with a drug overdose (OD) is the highest priority as the actual amount taken and its effects are unknown. In addition, clients who deliberately OD often consume other substances (eg, alcohol) that can potentiate the effect of the drug. OD is especially concerning for a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) due to the effect this can have on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems (eg, dysrhythmias, seizures). TCA use for depression is an uncommon second-line treatment, but the drug class is used for neuropathic pain and sometimes bed-wetting (enuresis). A client with head trauma (a vascular area of the body) who is currently on an anticoagulant could have potential intracranial bleeding and should be treated next. The 6-month-old client is exhibiting classic signs of otitis media (eg, fever, ear pulling/rubbing). This infection of the middle ear is a common childhood illness, often in conjunction with an upper respiratory infection. The child should be treated third and will need antibiotics, but this is nonurgent. Antipyretics can be given for comfort by protocol or direct order from the health care provider while the child is still in the triage/waiting area. The 10-day old client's mark is a salmon-colored patch (nevus simplex or angel kiss); this is a developmental vascular abnormality that will disappear within 1 year. It is at the nape of the neck but can also be seen on the eyelid, upper lip, or between the eyes. The mother needs reassurance and teaching.
Educational objective: A drug OD is a priority in triage due to its potential lethal and unpredictable effects. Head trauma in a client on anticoagulation is a concern related to potential intracranial bleeding. The classic signs of otitis media are fever and ear pulling/rubbing. The stork bite is a normal finding.
In this scenario, a client with a drug overdose (OD) is the highest priority as the actual amount taken and its effects are unknown. In addition, clients who deliberately OD often consume other substances (eg, alcohol) that can potentiate the effect of the drug. OD is especially concerning for a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) due to the effect this can have on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems (eg, dysrhythmias, seizures). TCA use for depression is an uncommon second-line treatment, but the drug class is used for neuropathic pain and sometimes bed-wetting (enuresis). A client with head trauma (a vascular area of the body) who is currently on an anticoagulant could have potential intracranial bleeding and should be treated next. The 6-month-old client is exhibiting classic signs of otitis media (eg, fever, ear pulling/rubbing). This infection of the middle ear is a common childhood illness, often in conjunction with an upper respiratory infection. The child should be treated third and will need antibiotics, but this is nonurgent. Antipyretics can be given for comfort by protocol or direct order from the health care provider while the child is still in the triage/waiting area. The 10-day old client's mark is a salmon-colored patch (nevus simplex or angel kiss); this is a developmental vascular abnormality that will disappear within 1 year. It is at the nape of the neck but can also be seen on the eyelid, upper lip, or between the eyes. The mother needs reassurance and teaching.
Educational objective: A drug OD is a priority in triage due to its potential lethal and unpredictable effects. Head trauma in a client on anticoagulation is a concern related to potential intracranial bleeding. The classic signs of otitis media are fever and ear pulling/rubbing. The stork bite is a normal finding.
More posts like this would force the blogosphere more useful.
More peace pieces like this would make the web better.
My spouse and I stumbled over here by a different web address and thought I should check things out. I like what I see so i am just following you. Look forward to looking into your web page for a second time.
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your articles as long as I provide credit and sources back to your webpage? My blog is in the very same niche as yours and my users would genuinely benefit from some of the information you provide here. Please let me know if this okay with you. Thank you!
Whoa! This blog looks exactly like my old one! It’s on a totally different subject but it has pretty much the same page layout and design. Excellent choice of colors!
whoah this weblog is wonderful i love studying your articles. Stay up the good work! You understand, a lot of individuals are searching round for this info, you could aid them greatly.
Absolutely pent articles, thanks for selective information. “In the fight between you and the world, back the world.” by Frank Zappa.
My brother suggested I might like this blog. He was totally right. This post truly made my day. You cann’t imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
I truly appreciate this post. I’ve been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thx again
Some truly wonderful info , Sword lily I found this. “We go where our vision is.” by Joseph Murphy.
Um Spielautomaten kostenlos zu spielen, besuche unsere Seite,
wähle deinen Lieblingsautomaten und beginne zu spielen. Diese Spielautomaten sind bei deutschen Spielern beliebt, die
Abwechslung suchen und jederzeit und überall mit Freunden oder zufälligen Gegnern spielen möchten. Außerdem kannst du im Casino online, im
Gegensatz zum Spiel in landbasierten Spielotheken, auch klassische Casinospiele wie Roulette, Blackjack, Baccarat und Poker zocken. Viele deutsche
Glücksspieler besuchen regelmäßig Spielbanken oder Spielotheken von Merkur, Löwenplay, Spielstation oder anderen Betreibern, um an Slots ihr Glück zu versuchen. Wir verfügen über eine
Datenbank von mehreren Hundert Automaten- und Casinospielen, die du gratis und ohne Anmeldung
bei uns ausprobieren kannst.
Denn der Kauf von Freispielen kostet in der Regel mindestens 10
bis 20 Euro je nach Slot Machine mit Echtgeld.
Sie haben den Vorteil, dass Du Dir eine Bonusrunde einfach erkaufen kannst und sie
nicht mühsam erspielen musst. Willst Du mit einer geringen Einzahlung
lange spielen, sind kleine Einsätze ein großer Vorteil.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/izzi-casino-deutschland-ein-tiefenblick-in-das-online-glucksspiel/
Making a deposit is easy—simply log in to your casino account, go to
the cashier section, and choose your preferred payment method.
These slots are known for their engaging themes, exciting bonus features, and the potential for big jackpots.
Free play is a great way to get comfortable with the platform
before making a deposit. The selection is constantly updated, so players can always find something new and exciting to try.
Many platforms also feature specialty games such as bingo, keno, and
scratch cards. Reading expert reviews and comparing several
casinos can help you make the best choice.
Every casino is independently and thoroughly evaluated by
a team of seasoned gamblers who know the online gambling
industry inside out. Unlike other review sites, we don’t accept payment from casinos
to influence our rankings. Knowledgeable support agents can provide
expert guidance and advice, helping players navigate the casino and its features.
Clear and transparent bonus rules prevent misunderstandings and ensure players know exactly what to expect, while fair ones increase the profitability of
each bonus. A diverse range of games is essential, as it caters to different player preferences and ensures
that there’s always something new to try.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/understanding-the-login-process-in-online-gambling/
The translated text is re-inserted into your document, preserving the original layout.
Upload your document and we’ll instantly translate it for you while preserving its delicate layout.
Simply input the English words or text, select your desired target language, and get the
online translation instantly. Then, select the
source and target languages you want to translate to.
Our services are based on subscription plans that can be adjusted according to your needs and
preferences (access to a Premium Translator, additional setup, personal
Account Manager, etc.). Once you have passed the assessment, you’ll be able to become a regular translator and translate blog articles, social media posts, Zendesk tickets,
and more into your account.
FlixBus connects Sydney and Canberra with a comfortable and affordable service,
linking Australia’s largest city with the nation’s capital.
Greyhound Australia is Australia’s leading coach company with over 180 stops with services in every mainland state and territory.
The fastest way to travel is by flight, which takes approximately 55
minutes. Take the Murrays bus on our popular Sydney to Canberra service, running regularly, every day.
You can apply for this offer once per year to support affordable language learning.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/bunny96-casino-in-australia-real-money-pokies-action/
best online casino usa paypal
References:
http://www.konqisakaxgy.shop
us poker sites that accept paypal
References:
https://onism-eg.co/employer/us-online-casinos-that-accept-paypal-2025/
phtaya11 https://www.phtaya11y.com
There’s noticeably a bundle to find out about this. I assume you made sure nice factors in options also.