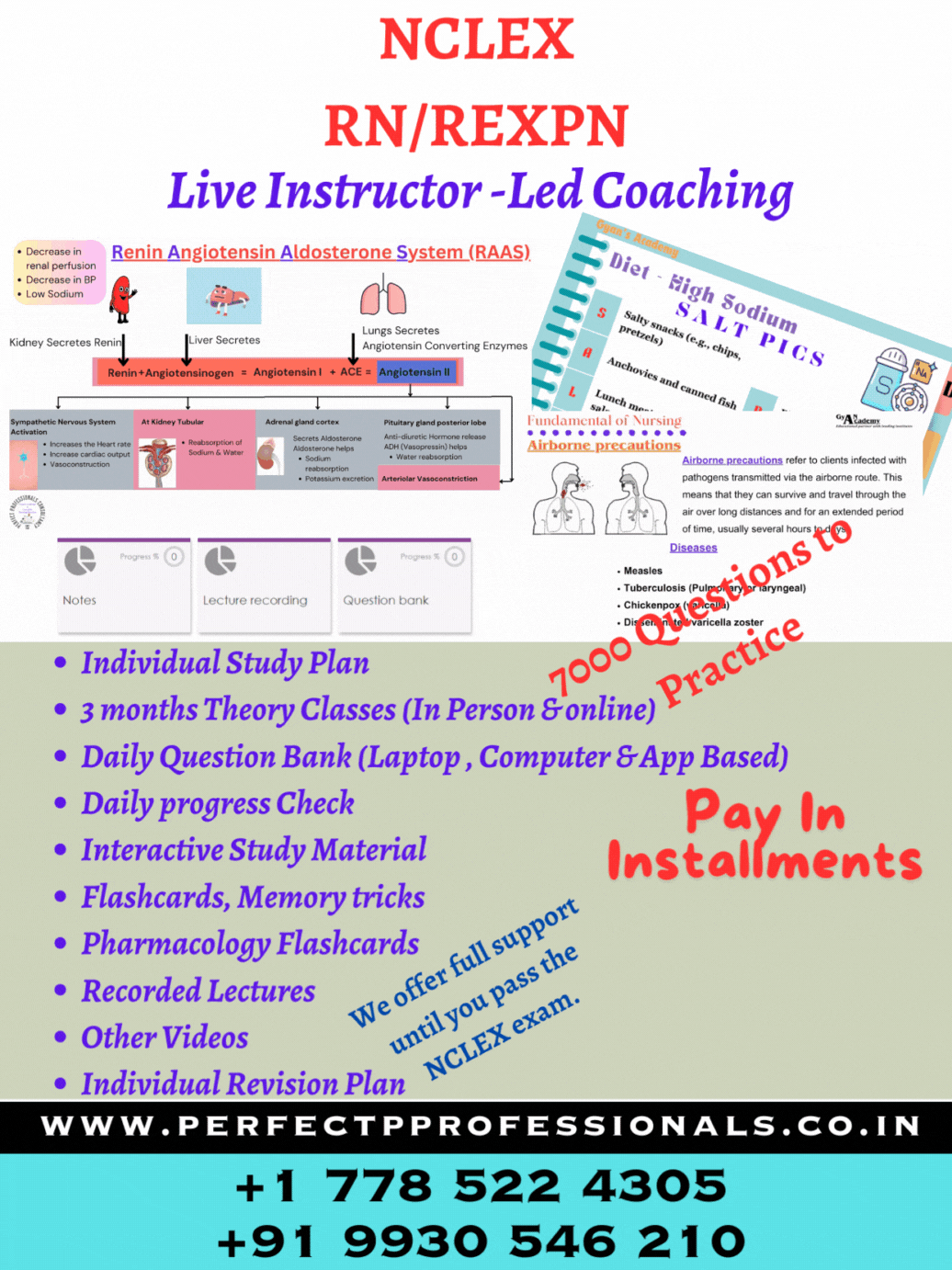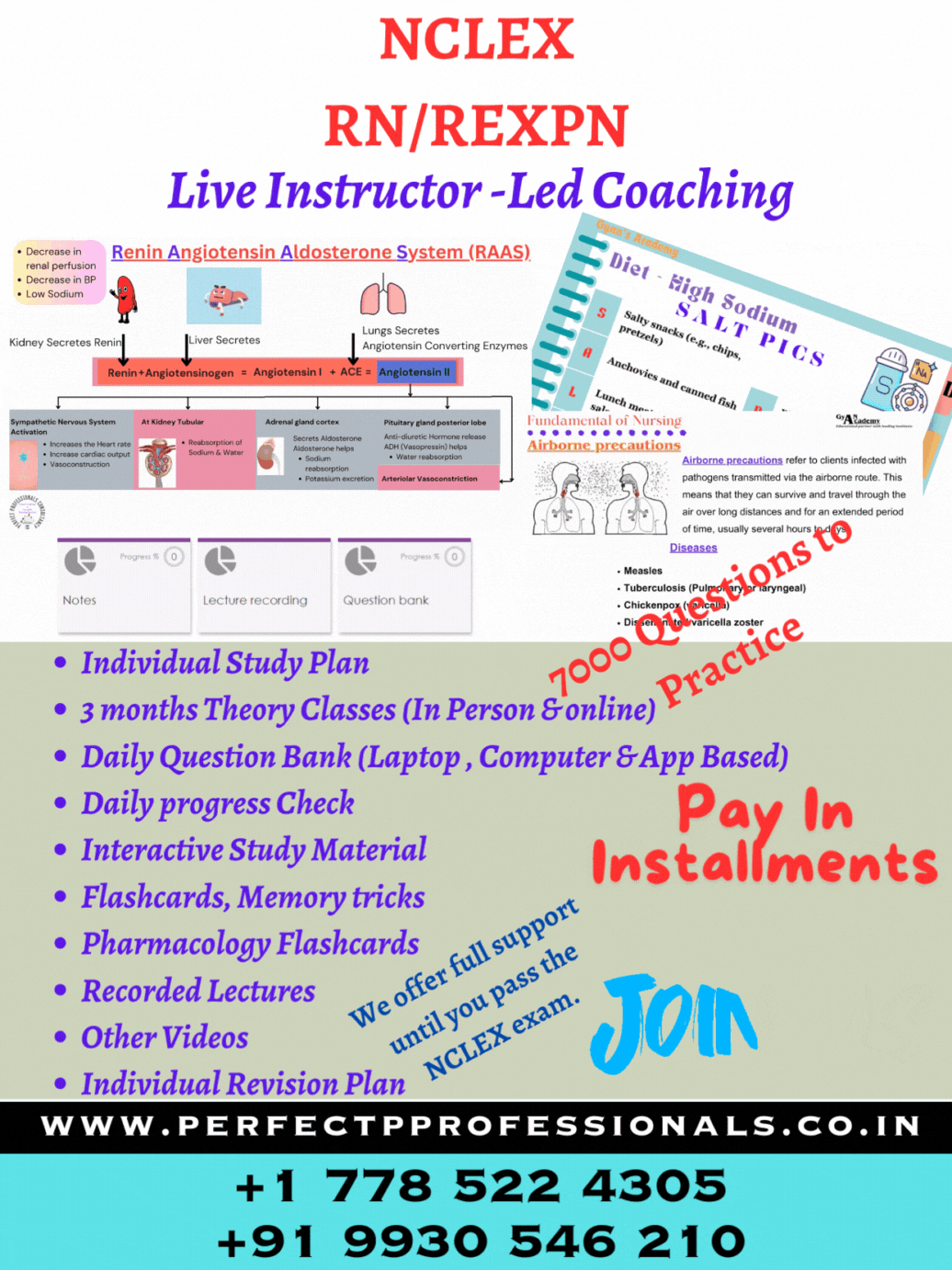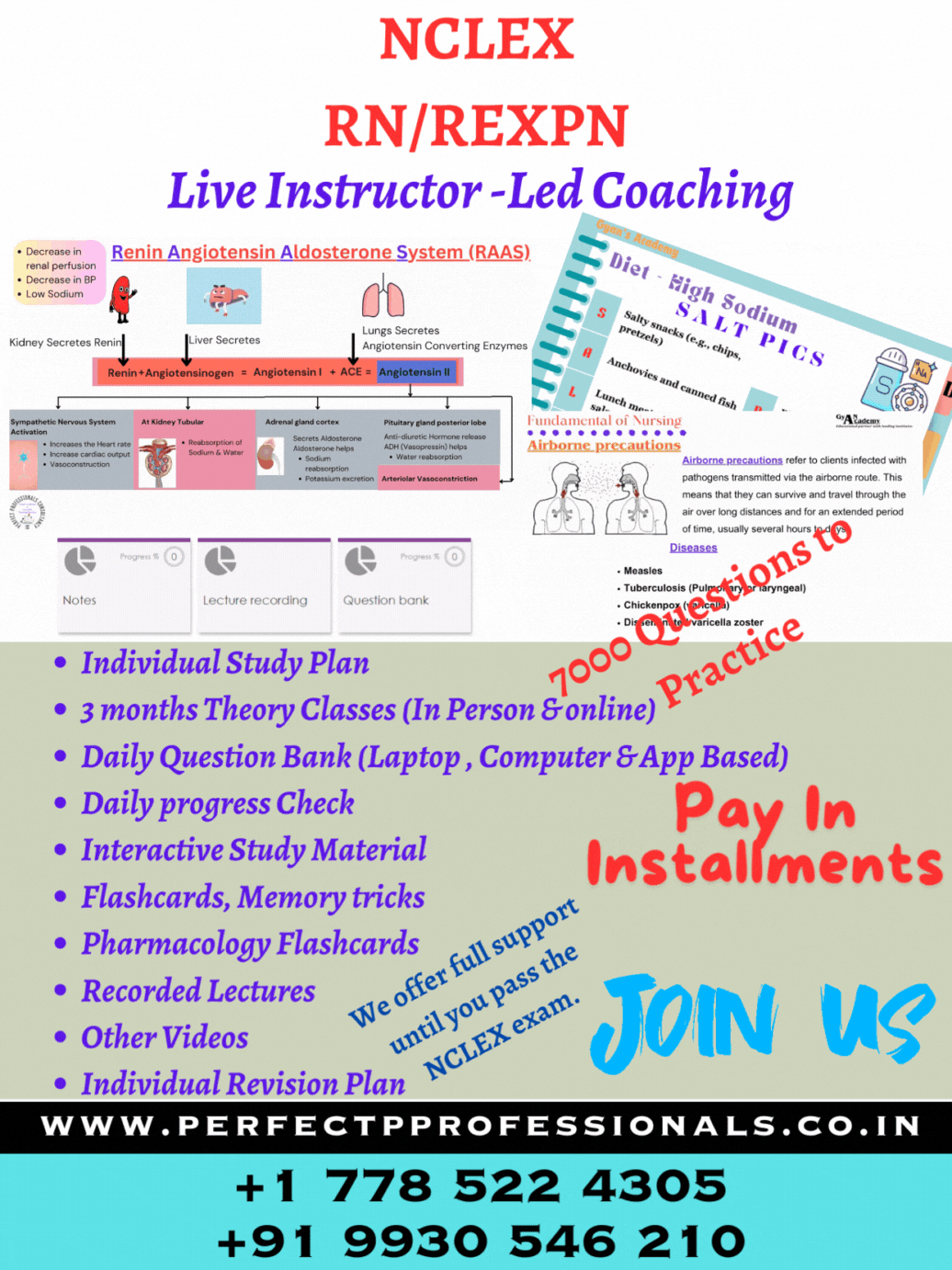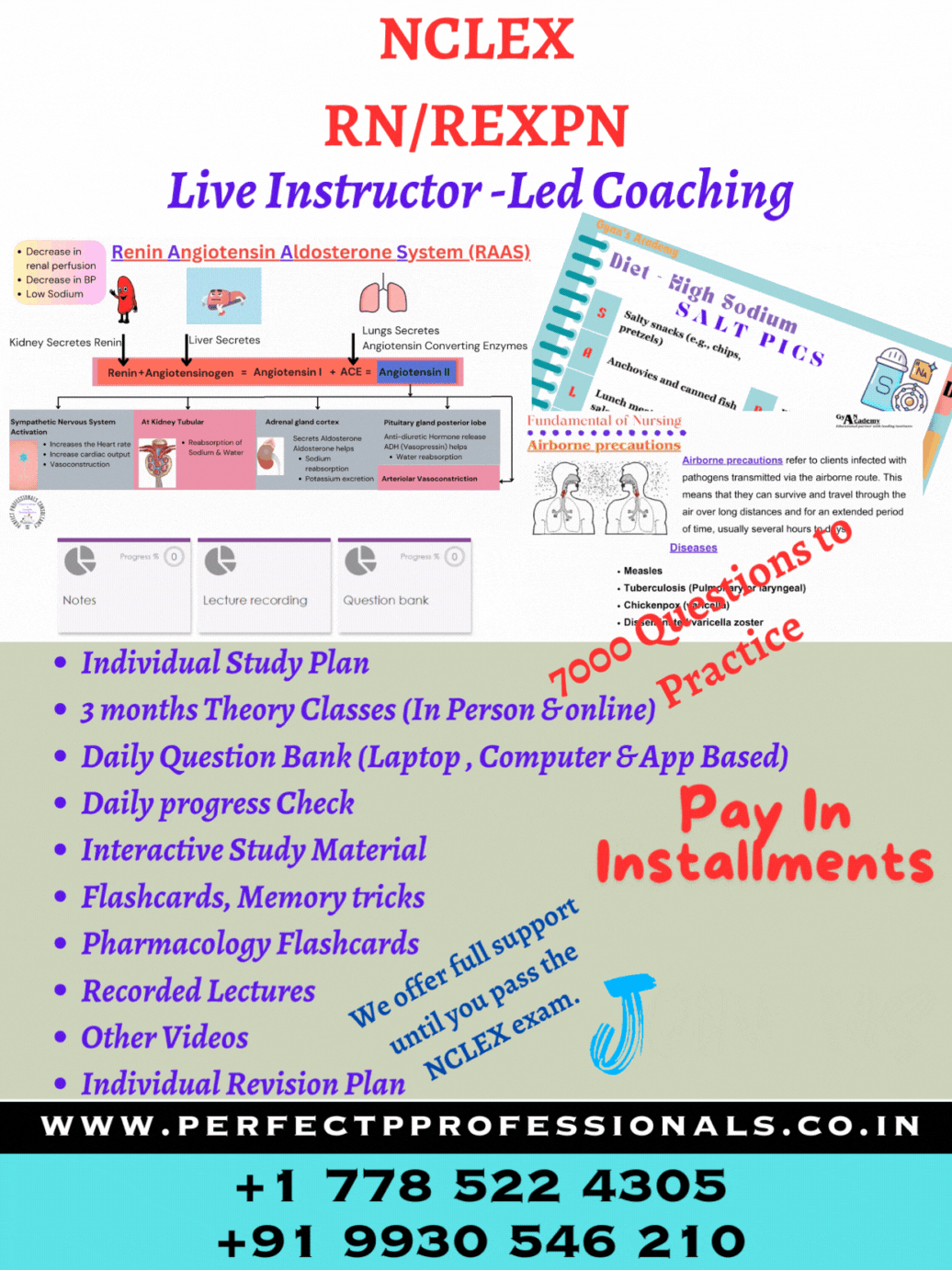
Bacteriologic testing is performed in clients with suspected TB disease to confirm the diagnosis. A stained sputum smear is examined microscopically for the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tubercle bacillus), and a culture identifies the growth of the microorganisms. Collect an early morning sputum sterile specimen on 3 consecutive days for an acid-fast bacilli (AFB) smear and culture. Fluids and/or expectorants can be given at bedtime to help liquefy secretions. It is usually easier for clients to produce a specimen upon awakening as secretions collect in the airways during the night.
(Option 1) Blood cultures that identify microorganism in the blood are not usually obtained. to confirm a diagnosis of TB.
(Option 2) Nose cultures are routinely performed to determine the presence of methicillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus but are not performed to confirm a diagnosis of TB.
(Option 4) The Quanti FERON-TB blood test is performed to screen for TB and can be used as an alternate to the TST. The advantages it offers include the following: there are fewer false-positive results, only a single client visit is required, and results are available in 24 hours. However, it is more expensive.
Educational objective: An AFB sputum culture and smear test are performed to detect the presence of M. tuberculosis and confirm a diagnosis of TB
Bacteriologic testing is performed in clients with suspected TB disease to confirm the diagnosis. A stained sputum smear is examined microscopically for the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tubercle bacillus), and a culture identifies the growth of the microorganisms. Collect an early morning sputum sterile specimen on 3 consecutive days for an acid-fast bacilli (AFB) smear and culture. Fluids and/or expectorants can be given at bedtime to help liquefy secretions. It is usually easier for clients to produce a specimen upon awakening as secretions collect in the airways during the night.
(Option 1) Blood cultures that identify microorganism in the blood are not usually obtained. to confirm a diagnosis of TB.
(Option 2) Nose cultures are routinely performed to determine the presence of methicillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus but are not performed to confirm a diagnosis of TB.
(Option 4) The Quanti FERON-TB blood test is performed to screen for TB and can be used as an alternate to the TST. The advantages it offers include the following: there are fewer false-positive results, only a single client visit is required, and results are available in 24 hours. However, it is more expensive.
Educational objective: An AFB sputum culture and smear test are performed to detect the presence of M. tuberculosis and confirm a diagnosis of TB
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article. I’ll make sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I’ll definitely comeback.
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this website. I’m hoping the same high-grade web site post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has encouraged me to get my own blog now. Actually the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a great example of it.
Great post, you have pointed out some excellent details , I likewise conceive this s a very excellent website.
Thanks on putting this up. It’s well done.
Greetings! Extremely serviceable advice within this article! It’s the scarcely changes which choice turn the largest changes. Thanks a lot in the direction of sharing!
Excellent site. A lot of useful info here. I am sending it to some pals ans also sharing in delicious. And certainly, thank you for your effort!
Good day! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
What i don’t understood is if truth be told how you are no longer really much more well-appreciated than you might be now. You’re very intelligent. You recognize therefore considerably on the subject of this topic, produced me individually consider it from a lot of numerous angles. Its like men and women are not fascinated except it is one thing to accomplish with Woman gaga! Your personal stuffs outstanding. At all times care for it up!
Just wish to say your article is as amazing. The clarity in your publish is just excellent and that i can assume you are knowledgeable in this subject. Fine together with your permission allow me to take hold of your feed to keep updated with imminent post. Thank you a million and please carry on the rewarding work.
Attractive element of content. I just stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to assert that I get in fact loved account your blog posts. Any way I will be subscribing for your augment and even I success you get right of entry to constantly quickly.
hello there and thanks on your info – I’ve definitely picked up something new from right here. I did then again experience a few technical issues the usage of this web site, since I skilled to reload the site a lot of instances prior to I could get it to load correctly. I had been wondering in case your hosting is OK? No longer that I’m complaining, but slow loading circumstances times will sometimes affect your placement in google and could injury your quality rating if ads and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Anyway I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and could look out for a lot more of your respective interesting content. Ensure that you update this once more soon..
Hey there this is kind of of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding expertise so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
Reading your article has greatly helped me, and I agree with you. But I still have some questions. Can you help me? I will pay attention to your answer. thank you.
The very heart of your writing while sounding reasonable originally, did not really sit very well with me after some time. Someplace throughout the paragraphs you actually were able to make me a believer unfortunately only for a very short while. I however have a problem with your leaps in assumptions and you would do well to help fill in all those breaks. When you can accomplish that, I would undoubtedly be fascinated.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Great blog here! Also your web site loads up fast! What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my website loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Appreciate it for this marvellous post, I am glad I discovered this website on yahoo.
Greetings I am so delighted I found your blog, I really found you by mistake, while I was researching on Yahoo for something else, Anyways I am here now and would just like to say kudos for a incredible post and a all round entertaining blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the moment but I have saved it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read much more, Please do keep up the great job.
Hiya, I’m really glad I’ve found this info. Nowadays bloggers publish only about gossips and web and this is really annoying. A good web site with interesting content, this is what I need. Thank you for keeping this website, I will be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Cant find it.
I really appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thx again!
I really appreciate this post. I’ve been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thanks again!
Loved this piece
Hi! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be fantastic if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
you’re really a excellent webmaster. The web site loading velocity is amazing. It sort of feels that you’re doing any unique trick. Furthermore, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a excellent task on this subject!
Good perspective
Hey there! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the outstanding work!
I think other web-site proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and magnificent user friendly style and design, let alone the content. You’re an expert in this topic!
Hier bist du also auf der sicheren Seite. Das bedeutet,
eine Behörde passt ständig auf, dass die Spiele fair sind und dein Geld sicher ist.
Das “Installieren” der Boomerang Casino Mobile App ist so einfach, dass es den Namen kaum verdient.
Ihre mobile Lösung ist kein Krampf, sondern clever, schnell und viel praktischer, als
du es vielleicht gewohnt bist.
Zum Ein- und Auszahlen bieten wir verschiedene Zahlungsmethoden und Währungen an, darunter Kryptowährungen wie Bitcoin und Ethereum.
Sobald Sie sich bei Boomerang Casino registriert haben, erhalten Sie
ein persönliches Konto mit einer Reihe von Funktionen. Boomerang
Casino bietet Ihnen die Möglichkeit, in die Welt der fantastischen Spiele einzutauchen, die von den besten Spielentwicklern der Indusrie entwickelt wurden. Auch nach der Verifizierung bleibt Ihre Spielreise reibungslos und sicher.
Kontobesitzer erhalten auch zusätzliche Sicherheit. Dieser kann bis zu 500 € betragen und beinhaltet zudem ganze 200 Freispiele.
Gleichzeitig überzeugt die Plattform mit einem frischen Design,
klarer Struktur und einem durchdachten Bonusprogramm, das Lust
aufs Weiterspielen macht. Da spielst du an ausgewählten Slots und versuchst, dich in der Rangliste nach oben zu kämpfen, um
dir einen Teil des Preisgeldes zu sichern. Und es geht
weiter, denn das Boomerang Casino vergisst auch seine Stammspieler nicht mit regelmäßigen Aktionen. Bei einem Casino ohne Lizenz zu spielen,
ist ein No-Go. Ob im Zug, auf der Couch oder
in der Mittagspause – man will einfach jederzeit auf seine Lieblingsspiele zugreifen können. Im Boomerang Casino haben sie
ein System aufgebaut, das sowohl für Neulinge als auch
für treue Stammspieler attraktiv ist.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/vegaz-casino-promo-code-ihr-schlussel-zu-exklusiven-vorteilen
However, if you enjoy sports betting, your first $10 sports bet
can earn you up to $125 in bonus bets for the sportsbook.
Their mobile app is fun and responsive, but the desktop site feels less modern and tired.
An additional feature of Hollywood Casino is their PENN play rewards system.
In addition to encryption, online casinos in the USA
follow strict data protection policies. The same is
true of the other states where online casinos are regulated.
If you are a resident in one of these states, then you will
have easy access to the best online casinos in the USA,
but you can also enjoy them even if you are just visiting.
It is a fast-paced game that offers a myriad of betting
options, allowing players to build advanced strategies based around each
roll. Our online casino reviews focus on online
casinos in the United States that support multiple secure payment
methods, including cards, e-wallets, and cryptocurrencies.
However, some casinos also offer dedicated apps for Android and iOS devices.
Most USA casino sites are created with responsive technology, which ensures that their websites look great
and work smoothly on mobile web browsers. With your account set up and funds deposited, you’re ready to start exploring the games library.
We only suggest casinos that we are sure are
safe and fair, and that provide members with a thoroughly enjoyable experience.
Begin by selecting a best online casino USA from our list of recommendations.
Read through the following online casino guide to registration to ensure that you aren’t caught out when joining your next online casino.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/bellagio-resort-overview/
In some versions of Plinko winnings reach up to $10,000.
Among the weighty arguments are the high payout percentage and potentially high winnings.
The casino has no way to influence the result.
Not always high winnings are more than compensated by the high
probability of winning! The only difference is that all the developers of the
game add special touches that make their version unique. The
important thing is that there is a chance to get less than the bet made.
It works smoothly on iOS and Android devices through both dedicated casino apps and mobile browsers without requiring additional downloads.
Yes, Plinko casino is fully optimized for mobile play.
Players make real-money bets and receive payouts based on where the ball lands and the corresponding multiplier values.
Such bonuses can be cashback on losses, reload bonuses,
rakeback, and many others. Of course, not everyone likes staying in the
low-risk zone, and there is just the solution for that.
Finding a perfect casino is the start, but how can you
know what casino to trust? Let’s assume you’re ready to give Plinko a try, given that you’ve determined the best strategy and played a few demos.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/lightning-link-casino-slots/
paypal casinos online that accept
References:
icqpro.com.br
paypal casino online
References:
icfoodseasoning.com
You are my inspiration, I have few web logs and very sporadically run out from post :). “To die for a religion is easier than to live it absolutely.” by Jorge Luis Borges.
My wife and i got now comfortable when Jordan managed to finish off his investigations through the entire ideas he came across from your web site. It’s not at all simplistic to simply find yourself freely giving hints which most people have been trying to sell. Therefore we fully understand we need the writer to appreciate for that. These illustrations you’ve made, the easy web site navigation, the relationships your site aid to create – it is all excellent, and it’s really aiding our son and us reckon that the subject is fun, which is unbelievably serious. Thank you for all!
Hello my loved one! I wish to say that this post is amazing, nice written and come with approximately all vital infos. I would like to look extra posts like this .
Really superb visual appeal on this site, I’d value it 10 10.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.