Acute epiglottitis is a supraglottic inflammatory process that occurs most commonly in children with Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) infection. Inflammation of the epiglottis can cause airway obstruction and is a medical emergency. Common signs of impending airway obstruction include restlessness, stridor, and drooling due to dysphagia. The nurse should prepare to assist with emergent endotracheal intubation.
(Option 2) If left untreated, the inflamed appendix may rupture, causing peritonitis, major abscess, or partial bowel obstruction. The client with acute appendicitis may require antibiotic administration and emergent surgical appendectomy. Although appendicitis is an emergent condition, a client with impending airway obstruction from epiglottitis must be seen immediately
(Option 3) Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an acquired disorder in which antibodies cause decreased platelet survival and production. Petechiae, pinpoint lesions on the skin from capillary hemorrhages, are a common sign of ITP. Acute ITP usually resolves spontaneously without complications, and management is primarily supportive (eg, platelet monitoring, corticosteroids, IV immunoglobulin).
(Option 4) Cystic fibrosis affects the secretory glands, resulting in thick sputum that may become blood-tinged from frequent coughing. A client with cystic fibrosis who has blood- tinged sputum should be evaluated but is not a priority.
Educational objective: Acute epiglottitis is a life-threatening emergency due to possible airway obstruction from severe swelling of the epiglottis. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, stridor, drooling. restlessness, and tripod positioning. The nurse should prepare to assist with emergent endotracheal intubation.
Acute epiglottitis is a supraglottic inflammatory process that occurs most commonly in children with Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) infection. Inflammation of the epiglottis can cause airway obstruction and is a medical emergency. Common signs of impending airway obstruction include restlessness, stridor, and drooling due to dysphagia. The nurse should prepare to assist with emergent endotracheal intubation.
(Option 2) If left untreated, the inflamed appendix may rupture, causing peritonitis, major abscess, or partial bowel obstruction. The client with acute appendicitis may require antibiotic administration and emergent surgical appendectomy. Although appendicitis is an emergent condition, a client with impending airway obstruction from epiglottitis must be seen immediately
(Option 3) Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an acquired disorder in which antibodies cause decreased platelet survival and production. Petechiae, pinpoint lesions on the skin from capillary hemorrhages, are a common sign of ITP. Acute ITP usually resolves spontaneously without complications, and management is primarily supportive (eg, platelet monitoring, corticosteroids, IV immunoglobulin).
(Option 4) Cystic fibrosis affects the secretory glands, resulting in thick sputum that may become blood-tinged from frequent coughing. A client with cystic fibrosis who has blood- tinged sputum should be evaluated but is not a priority.
Educational objective: Acute epiglottitis is a life-threatening emergency due to possible airway obstruction from severe swelling of the epiglottis. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, stridor, drooling. restlessness, and tripod positioning. The nurse should prepare to assist with emergent endotracheal intubation.
![Boost Skills: NCLEX Daily Questions #12 [ays_quiz id="160"]](https://completenursingsolution.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/01-Nov.-NCLEX-Practice-Questions.png)
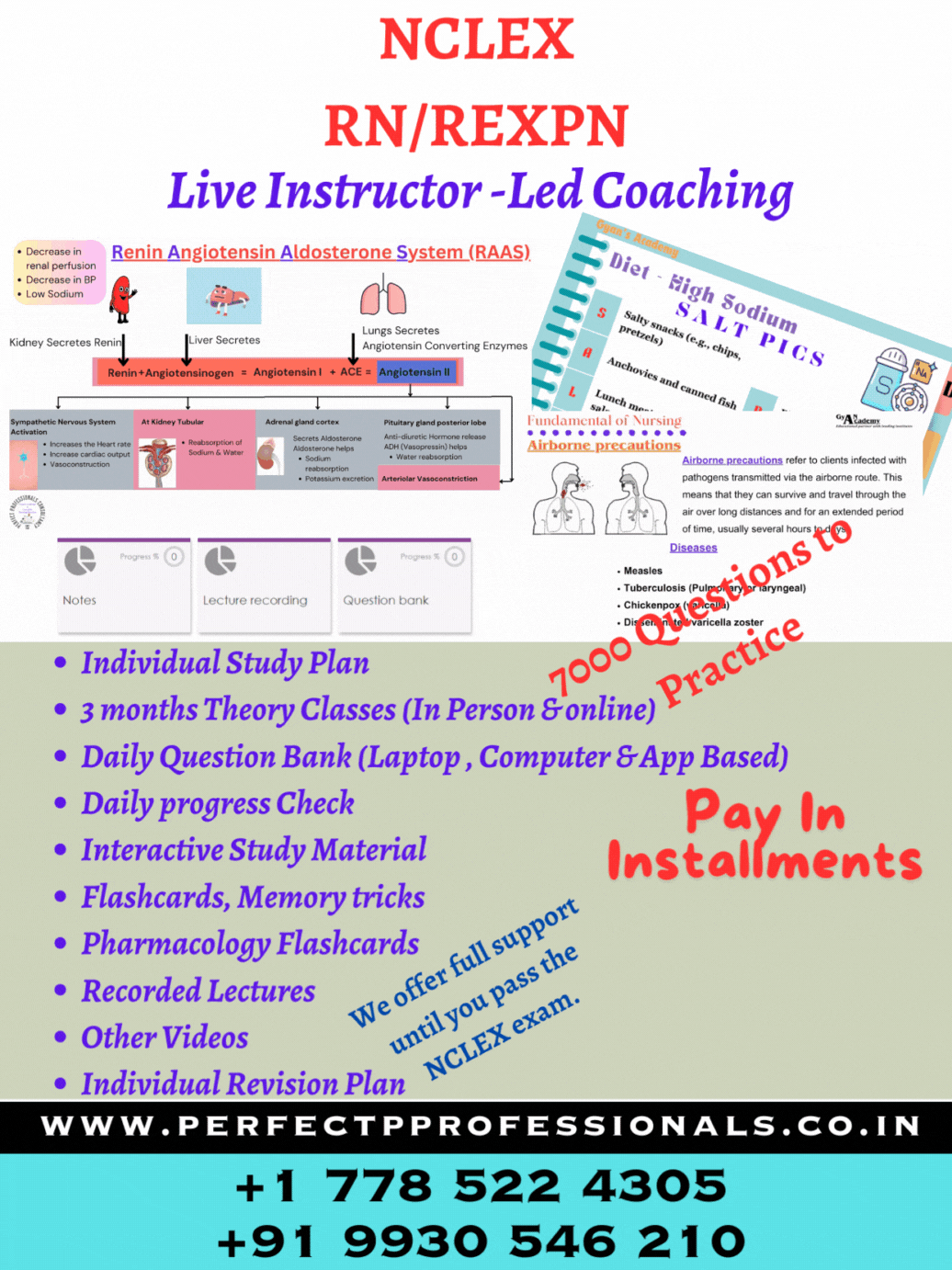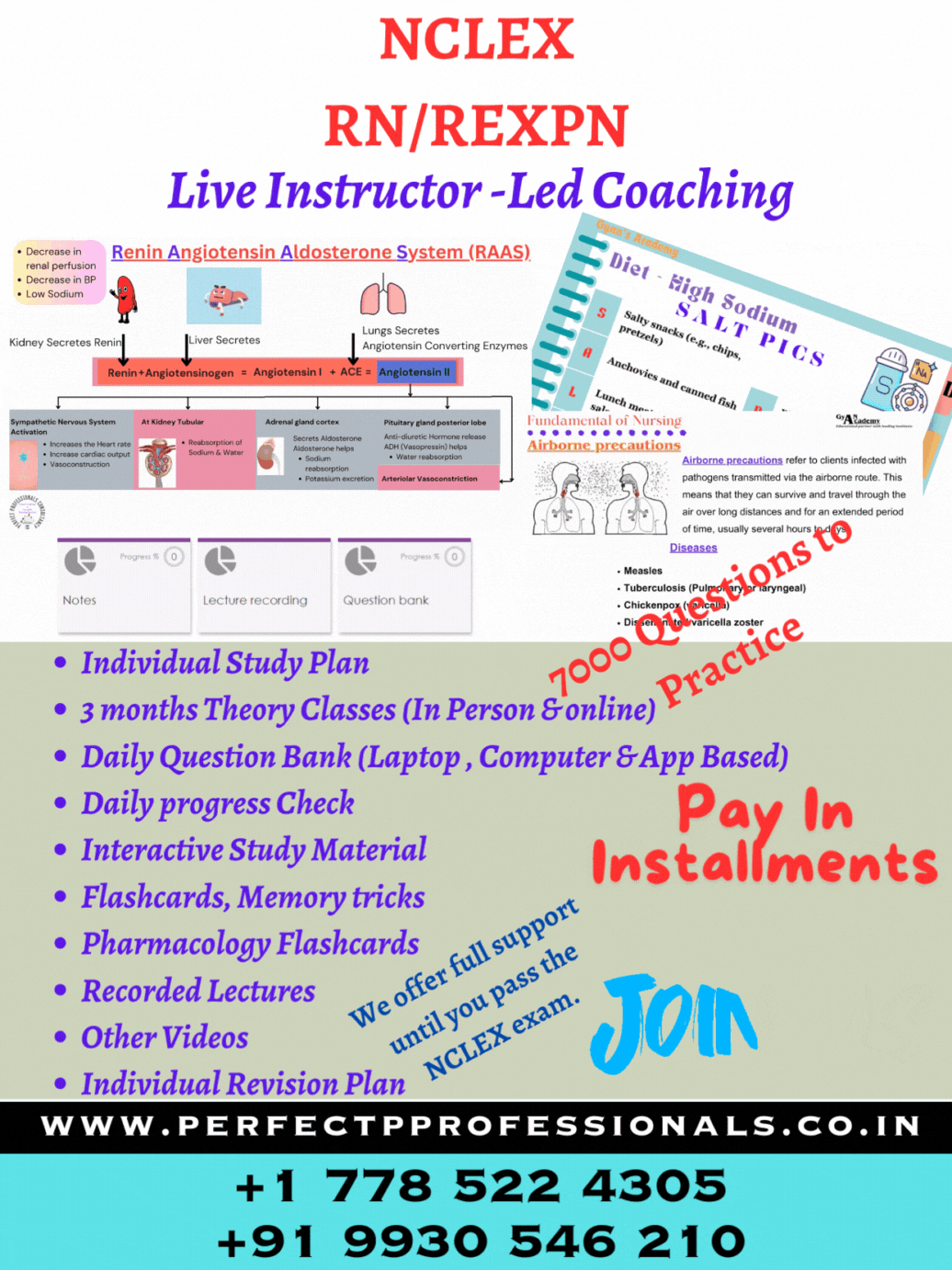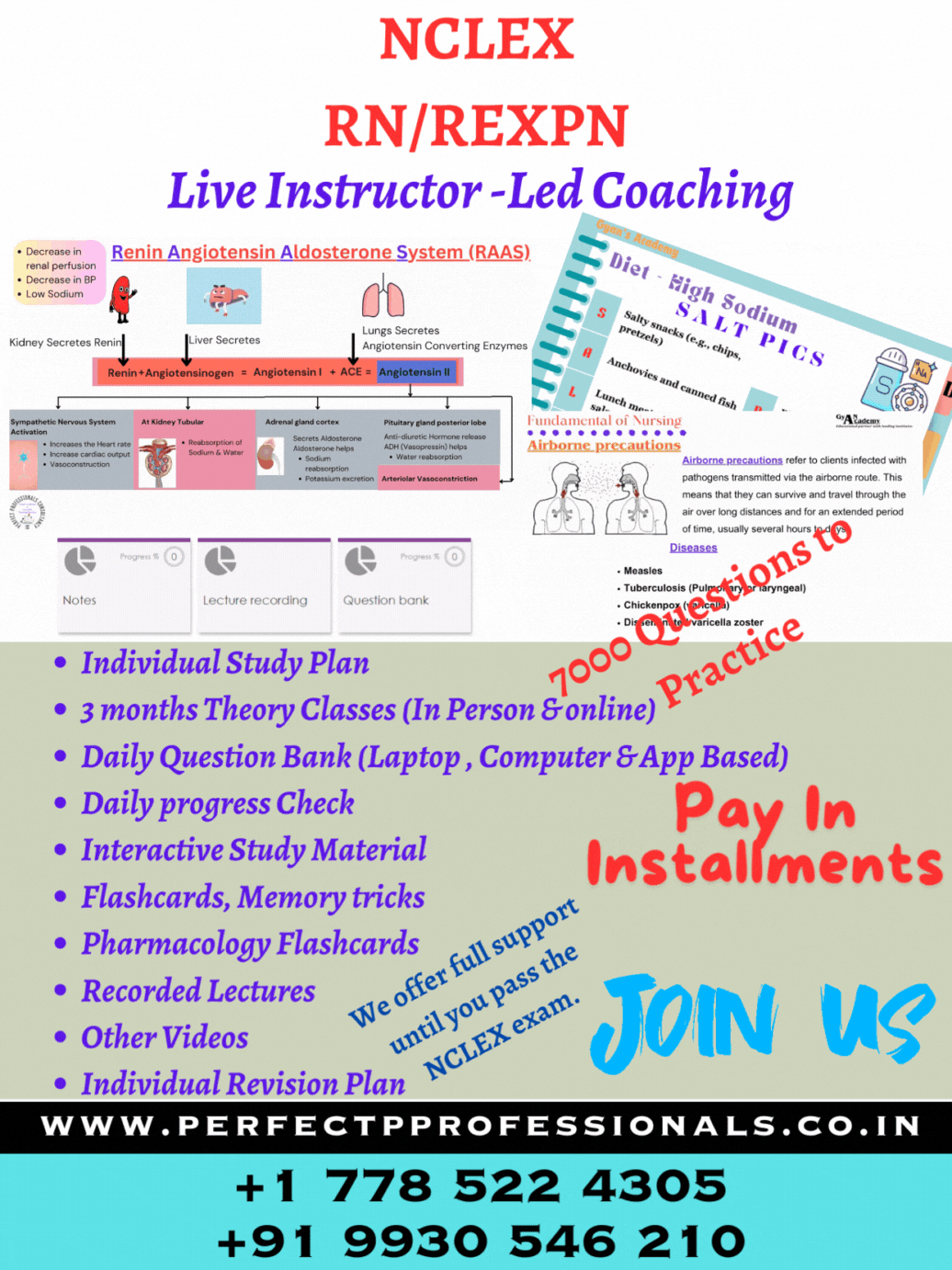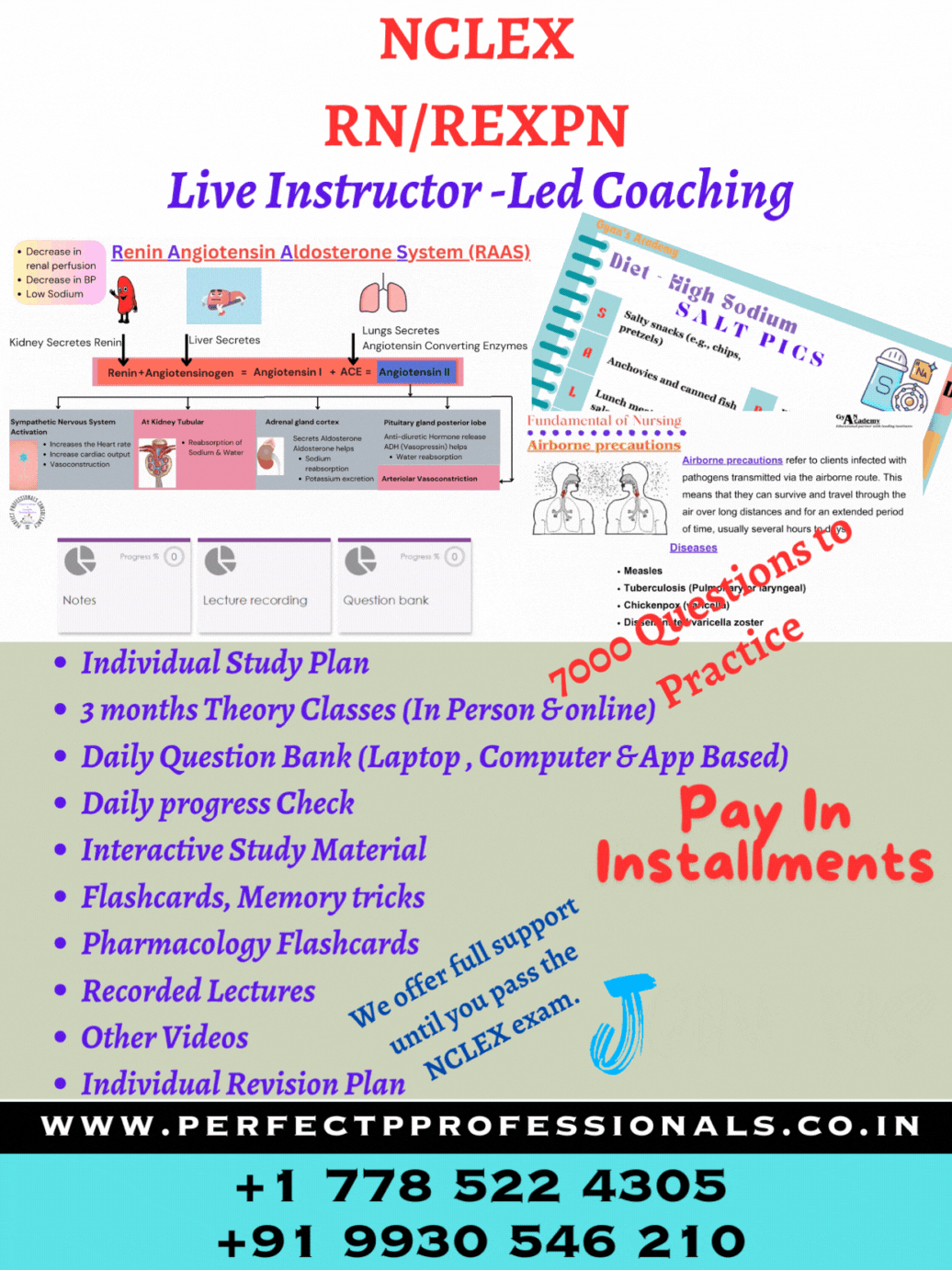
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Sie müssen keine zusätzlichen Schritte unternehmen,
um auf Ihrem Telefon, Tablet oder Computer zu spielen, da LeonCasino Ihre
Fortschritte, Favoriten und Boni an einem Ort speichert.
Sie können LeonCasino-Spiele auf Android, iOS und anderen Geräten spielen. Wenn in einem Code „keine
Einzahlung“ steht, müssen Sie keine Einzahlung tätigen, um die Spiele zu spielen. Bevor Sie beginnen, schauen Sie sich das Infosymbol an, um zu
sehen, welche Spiele weniger oder gar nicht zum Durchspielen zählen. Real-money slots count as 10% Ihres Fortschritts, während
Tischspiele als 0 % zählen. Um Freispiele zu erhalten, ist eine qualifizierte
Einzahlung von €20 oder mehr erforderlich.
Teilen Sie Ihre Meinung mit oder erhalten Sie Antworten auf Ihre Fragen. Der Spieler aus Deutschland
hatte die höchste Stufe des neuen Treueprogramms erreicht, aber den entsprechenden Bonus von 5.000 € nicht erhalten, da
die Punkte des vorherigen Programms die Teilnahmeberechtigung beeinträchtigten. Die Spielerin aus Curaçao
hatte 20 Euro eingezahlt und eine Stunde gespielt, bevor ihr Konto aufgrund eines Selbstausschlusses aus einem anderen Casino desselben Unternehmens für einen Monat gesperrt wurde.
Der Sicherheitsindex ist die wichtigste Kennzahl, die wir
verwenden, um die Vertrauenswürdigkeit, Fairness und Qualität
jedes einzelnen Online Casinos in unserer Datenbank zu beschreiben.
Durchsuchen Sie alle von Leon Casino angebotenen Boni,
einschließlich jener Bonusangebote, bei denen Sie keine Einzahlung vornehmen müssen, und durchstöbern Sie auch alle Willkommensboni,
die Sie bei Ihrer ersten Einzahlung erhalten werden.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/top-crypto-slots-2025-spiele-wichtige-features/
You also get automatic, free portfolio rebalancing if the asset values deviate by 5%.
So, what you get is the expertise honed over years of experience in the field.
Fidelity offers excellent customer support and access
to high-quality research. The company creates portfolios out of about 3400 no-transaction-fee
mutual funds operated by the Fidelity group.
To anyone concerned about their account security, I recommend checking out these resources,
including one from Roblox itself. If a hacker gains access to
your email, they can bypass both your password and 2FA.
Even with strong passwords, this vulnerability still leaves
accounts exposed. That said, the issue with email-based 2FA shows that it’s not
over yet.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/27_best-high-roller-bonus-casinos-2022_rewrite_1/
Crown Perth offers ample on-site parking, including multi-level facilities, accessible bays, and
valet parking. Enjoy valet parking, chauffeur services, and secure multi-level parking with EV charging.
The award-winning Crown Spa Perth offers a
serene oasis with indulgent treatments, La Prairie facials, aqua retreats, heated vitality pools, and tranquil massage suites.
Whether visiting for leisure or celebration, Crown Perth’s hotels offer personalized service, riverside
views, and VIP privileges like valet, express check-in, and spa access.
Both hotels are connected to the Crown complex, offering seamless access to
dining, gaming, and entertainment.
Central urban nest with pool gym pool free parking The Crown Metropol is a
first-class luxury hotel providing panoramic views of the city.
Featuring opulent suites, private infinity pools, high-end furnishings, and panoramic
views of the Swan River or city skyline, it’s the top choice for
celebrities and VIPs.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/treasure-casino-a-comprehensive-overview/
casino online paypal
References:
http://workompass.com/employer/10-best-android-casinos-for-us-players-reviewed-in-2025/
casino mit paypal einzahlung
References:
generaljob.gr
taya333 https://www.taya333.org
ph789 login https://www.ph789-login.com
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.