Must-Know “Blood Type”
Must-Know “Blood Type”
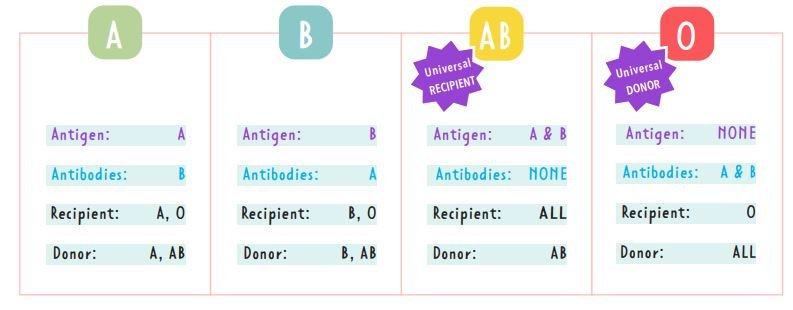
ANTIGENS
(Must-Know “Blood Type”)
Antigens are specific proteins or molecules found on the surface of red blood cells. These antigens determine an individual’s blood type and play a crucial role in blood transfusions.
PLASMA ANTIBODIES
Plasma antibodies are proteins found in the plasma (the liquid component of blood) that play a crucial role in the immune system. They are produced by B cells (a type of white blood cell) in response to the presence of foreign antigens, such as those found on the surface of bacteria, viruses, or mismatched red blood cells during a transfusion.
Key Points About Blood Antigens:
- ABO System Antigens:
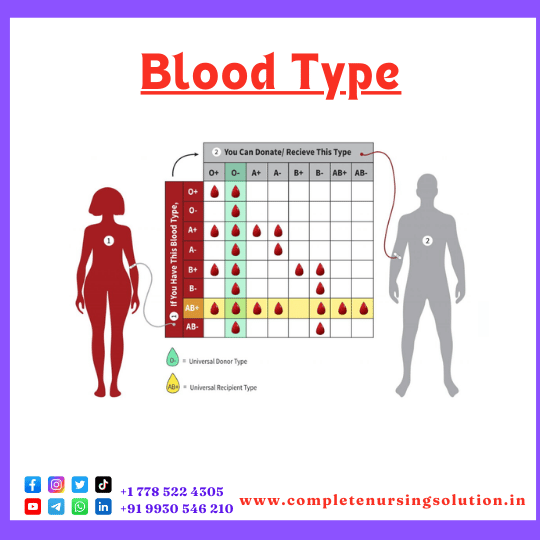
- A Antigen: Present on red blood cells in individuals with type A blood.
- B Antigen: Present on red blood cells in individuals with type B blood.
- AB Antigens: Both A and B antigens are present on red blood cells in individuals with type AB blood.
- No A or B Antigens: Individuals with type O blood have no A or B antigens on their red blood cells.
- Rh Factor (Rhesus Antigen):
- Rh Positive (Rh+): Individuals have the Rh antigen (also known as the D antigen) on their red blood cells.
- Rh Negative (Rh-): Individuals lack the Rh antigen on their red blood cells.
Must-Know Blood Type
Importance of Blood Antigens:
- Blood Type Determination: The combination of ABO antigens and the Rh factor determines a person’s blood type (e.g., A+, O-, etc.).
- Blood Transfusions: Compatibility between the donor’s and recipient’s blood antigens is crucial for safe transfusions. Receiving blood with incompatible antigens can trigger an immune response, leading to serious complications.
- Pregnancy: If an Rh-negative mother is carrying an Rh-positive baby, the mother’s immune system may produce antibodies against the baby’s Rh antigens, potentially leading to hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
Key Functions of Plasma Antibodies:
- Neutralize Pathogens: Antibodies bind to specific antigens on the surface of pathogens (e.g., bacteria, viruses) to neutralize them, preventing them from infecting cells.
- Mark for Destruction: When antibodies bind to antigens, they mark the pathogen for destruction by other immune cells, such as macrophages, which engulf and destroy the pathogen.
- Activate Immune Responses: Antibodies can activate other parts of the immune system, such as the complement system, which helps to clear pathogens from the body.
Must-Know “Blood Type”
Plasma Antibodies in Blood Types (ABO System):
In the ABO blood group system, plasma antibodies are specific to the antigens that are not present on a person’s red blood cells:
-
- Type A: Has anti-B antibodies in the plasma (against B antigens).
- Type B: Has anti-A antibodies in the plasma (against A antigens).
- Type AB: Has no anti-A or anti-B antibodies in the plasma (can receive any ABO type blood).
- Type O: Has both anti-A and anti-B antibodies in the plasma (against both A and B antigens).
Importance in Blood Transfusions:
During a blood transfusion, it’s crucial that the donor’s red blood cells do not have antigens that match the recipient’s plasma antibodies. If they do, the antibodies in the recipient’s plasma will attack the donor’s red blood cells, causing a potentially dangerous reaction.
Must-Know Blood Type

Check more topics
Thanks for reviewing Must-Know Blood Type Stay tune for more topics
Cardiac Biomarkers Testing – Precision Cardiovascular Assessment.
Discover more from Complete Nursing Solution
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


I really like your writing style, great info , regards for posting : D.
Sweet internet site, super design and style, very clean and employ friendly.
What i don’t realize is in fact how you are now not really a lot more smartly-preferred than you may be right now. You’re very intelligent. You know thus considerably in the case of this topic, made me in my opinion believe it from a lot of various angles. Its like women and men aren’t involved until it is something to do with Lady gaga! Your personal stuffs nice. At all times deal with it up!
Great work! This is the type of information that should be shared around the internet. Shame on Google for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my website . Thanks =)
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей маркетплейс аккаунтов
купить аккаунт магазин аккаунтов
услуги по продаже аккаунтов продать аккаунт
платформа для покупки аккаунтов аккаунт для рекламы
биржа аккаунтов продажа аккаунтов соцсетей
перепродажа аккаунтов маркетплейс аккаунтов
аккаунты с балансом маркетплейс аккаунтов
магазин аккаунтов платформа для покупки аккаунтов
продажа аккаунтов биржа аккаунтов
магазин аккаунтов https://marketplace-akkauntov-top.ru/
продажа аккаунтов соцсетей https://magazin-akkauntov-online.ru
профиль с подписчиками prodat-akkaunt-online.ru/
перепродажа аккаунтов продажа аккаунтов соцсетей
услуги по продаже аккаунтов https://pokupka-akkauntov-online.ru
Buy Account Account Buying Service
Secure Account Purchasing Platform Account marketplace
Accounts market Website for Selling Accounts
Accounts market Secure Account Purchasing Platform
Profitable Account Sales Account exchange
Account market Guaranteed Accounts
Accounts marketplace Marketplace for Ready-Made Accounts
Secure Account Sales Profitable Account Sales
Database of Accounts for Sale Account Purchase
Ready-Made Accounts for Sale Accounts marketplace
Website for Buying Accounts Secure Account Purchasing Platform
account store guaranteed accounts
profitable account sales ready-made accounts for sale
sell pre-made account sell pre-made account
sell accounts accounts marketplace
gaming account marketplace account selling platform
database of accounts for sale website for selling accounts
account trading account exchange service
accounts for sale account purchase
website for selling accounts website for selling accounts
account market buy accounts
accounts marketplace secure account purchasing platform
purchase ready-made accounts account trading
account buying service buy pre-made account
accounts market verified accounts for sale
social media account marketplace gaming account marketplace
guaranteed accounts account selling service
gaming account marketplace account marketplace
account buying platform buy accounts
account market account buying service
account buying service buy accounts
account acquisition verified accounts for sale
account exchange service buy accounts
purchase ready-made accounts gaming account marketplace
purchase ready-made accounts sell account
account trading platform account marketplace
sell account buy pre-made account
find accounts for sale purchase ready-made accounts
website for selling accounts account selling service
account store https://accounts-offer.org/
account trading service https://accounts-marketplace.xyz
account exchange service https://buy-best-accounts.org
ready-made accounts for sale https://social-accounts-marketplaces.live
buy accounts https://accounts-marketplace.live/
account store https://social-accounts-marketplace.xyz/
online account store https://buy-accounts.space/
accounts marketplace https://buy-accounts-shop.pro/
account purchase https://buy-accounts.live
buy accounts https://social-accounts-marketplace.live/
buy and sell accounts https://accounts-marketplace.online/
биржа аккаунтов https://akkaunty-na-prodazhu.pro/
продажа аккаунтов https://rynok-akkauntov.top/
маркетплейс аккаунтов https://kupit-akkaunt.xyz/
биржа аккаунтов https://akkaunt-magazin.online
биржа аккаунтов https://akkaunty-market.live
площадка для продажи аккаунтов https://kupit-akkaunty-market.xyz/
магазин аккаунтов маркетплейсов аккаунтов
продать аккаунт магазины аккаунтов
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей https://akkaunty-dlya-prodazhi.pro/
маркетплейс аккаунтов https://kupit-akkaunt.online
cheap facebook accounts https://buy-adsaccounts.work
buy facebook account for ads https://buy-ad-accounts.click
facebook account buy facebook accounts for sale
facebook ads account for sale https://buy-ads-account.click
buying facebook ad account https://ad-account-buy.top
buy account facebook ads https://buy-ads-account.work
buying facebook accounts https://ad-account-for-sale.top
buy facebook advertising accounts buy facebook profiles
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Узнать больше – https://medalkoblog.ru/
buy facebook profiles facebook ad account buy
buy google adwords accounts buy google adwords accounts
sell google ads account https://buy-ads-accounts.click
buy facebook ad accounts facebook ads account for sale
buy adwords account https://ads-account-for-sale.top
buy account google ads https://ads-account-buy.work
buy google ad threshold account https://buy-ads-invoice-account.top
buy google agency account https://buy-account-ads.work
buy verified google ads accounts https://buy-ads-agency-account.top
buy google ads account google ads accounts
google ads account buy google ads account seller
buy facebook ads accounts and business managers https://buy-business-manager.org/
google ads accounts for sale https://buy-verified-ads-account.work
buy facebook business manager account buy verified facebook business manager account
buy verified business manager facebook https://buy-business-manager-acc.org
facebook business account for sale buy-verified-business-manager-account.org
buy bm facebook buy-verified-business-manager.org
buy bm facebook facebook bm account buy
buy verified facebook business manager buy-business-manager-verified.org
business manager for sale https://buy-bm.org/
facebook bm account https://verified-business-manager-for-sale.org/
buy bm facebook https://buy-business-manager-accounts.org/
buy tiktok business account https://buy-tiktok-ads-account.org
tiktok ads account for sale https://tiktok-ads-account-buy.org
buy tiktok ads accounts https://tiktok-ads-account-for-sale.org
buy tiktok ads tiktok ads account buy
tiktok ads agency account tiktok agency account for sale
tiktok ad accounts https://buy-tiktok-business-account.org
buy tiktok ads account https://tiktok-ads-agency-account.org
tiktok ads agency account https://buy-tiktok-ads.org
The secret to our success lies in our expertise and the honesty in which
body type is more common in men and associated with the most negative health risk?
(Kimberly) we deal with our prospects
by persistently supplying the greatest quality recommendation and solutions.
Since then, bodybuilders have developed and used quite so
much of injectable and oral steroids. All of them
are banned in Australia, the United States,
the Uk, Canada, and most different international locations.
Such add-ons obtainable are the anabolic-androgenic medication Dianabol and
Methandrostenolone, which are claimed to have been created to duplicate D-Bol with out
the unfavorable side effects.
Fortuitously, the outcomes were spectacular, and I didn’t want to make use of the refund.
After I set my sights on slicing fats whereas preserving lean muscle,
Anvarol rapidly grew to become my go-to supplement.
Designed to replicate the results of Anavar, Anvarol helps me achieve a lean, ripped physique with out
the unwanted effects. With a 60-day refund coverage, D-BAL Max offers a
risk-free alternative to expertise its benefits. At simply $59.ninety nine, it’s a cheap approach to increase your exercise efficiency and
muscle positive aspects with out breaking the bank.
It’s a exact and effective choice for bodybuilders who wish to pack some muscle mass very quickly.
In Accordance to Loopy Bulk, D-Bal mimics the Dinanabol steroids with out the unwanted side effects.
That’s as a outcome of the awareness in people concerning the risks and risks of anabolic steroids has escalated in previous years which negates the usage of
steroids except for medical causes. Let’s face it,
the bodybuilding supplements market is huge and there are
manifold options to choose from. Authorized steroids aren’t obtainable in general stores or
eBay because they’re formulated utilizing specialized ingredients and not every firm is making them.
They offer a variety of health benefits apart
from bodybuilding advantages i.e. sooner muscle development, weight
loss, and talent enhancement. After I needed to boost my muscle mass and general
strength shortly, Anadrole turned my top pick.
Designed to replicate the effects of Anadrol, It supplies vital muscle positive aspects and enhances my workout efficiency without harmful side effects.
When seeking to enhance my muscle development and performance naturally, Brutal Force HBULK became my go-to supplement.
This generous guarantee gave me confidence in its effectiveness, and the impressive results ensured I didn’t need to use the
refund. With a 60-day refund policy, DecaDuro provides a risk-free method
to strive the product. This guarantee gave me peace of thoughts, figuring out
I could get my a reimbursement if I weren’t happy.
Fortunately, the outcomes had been excellent, and I didn’t want to make use of the refund.
If you’re looking for high-quality steroids, look no additional than steroid-warehouse.net!
Our website presents a wide selection of the best and most reasonably priced steroids available, making it the proper choice for anyone looking to improve their physique
or performance. The majority of those steroid alternate options are secure and cause no unwanted aspect effects when you have
chosen a reputed product. A few of them might have some unwanted aspect effects which
are widespread whenever you ignore the dosage guidelines.
These frequent unwanted side effects are digestive issues, agitation, headache, mood adjustments,
and so forth.
Opting for these natural supplements, which are
designed to offer comparable advantages to anabolic steroids with out
their unfavorable unwanted side effects, will improve your efficiency
and physique. FlexSteroids.com provides a various number of real, authorized steroids and
other objects to fulfill a wide range of health requirements.
We present products designed specifically for bulking, lowering fat, and gaining lean muscle
mass and strength. In latest years, authorized steroids have turn into in style alternate options to anabolic steroids for these trying to acquire muscle mass, lose weight,
and increase vitality levels. These dietary supplements,
which could be bought online, in gyms, and at shops.
They are legal to buy, promote, and use as they do
not require FDA approval or a prescription. In Contrast To anabolic steroids, authorized steroids are not banned by sports activities organizations and can be
utilized by athletes without fear of penalty.
This powerful mixture of legal steroid options uses pure elements to assist enhance muscle progress, energy, endurance, and vitality ranges.
The authorized steroids are recognized by different
names, and you can spot them by checking their choices.
Generally, all of these are known as health supplements, steroid
alternatives, or pure anabolic supplements. Anabolic steroids australia
are synthetic substances that mimic the action of the male hormone testosterone.
The product’s availability would possibly want
work, however TestoPrime’s merchandise page is pleasantly optimized for a pleasurable ordering expertise.
The parcel shall be despatched through mail
to any tackle you like, but we don’t specify a return mail handle; so if you don’t receive or settle for the parcel, it will
essentially be misplaced. Nevertheless, over the past 5 years of operation, 99% of orders have reached our prospects.
After confirming your order, you’ll be redirected to the fee web page,
and relying in your fee technique, you may be redirected to the trusted and secure fee portal of your
alternative. As Soon As your payment has been processed, you’ll mechanically obtain an prompt notification that the order has
been successful. In some cases, relying on the fee methodology, our staff may have to manually approve your order.
Testosterone is responsible for the event of male traits similar
to muscle mass and energy. Steroids perform by increasing the quantity of
protein in cells and selling tissue progress and regeneration. Steroids are mostly used in bodybuilding to
construct muscle mass and strength. They may help improve muscle mass and power,
improve athletic efficiency, and promote weight loss.
When it comes to achieving remarkable leads to bodybuilding and
muscle progress, using authorized steroids is normally a wise decision.
Testo-Max is an environment friendly testosterone booster usually
used as an alternative to the anabolic-androgenic steroid Sustanon. One of the most important adjustments
I seen was in my ability to push through exercises.
Earlier Than taking the Ultimate Stack, I often felt drained or burnt
out halfway by way of a session. Nonetheless, with the supplements,
I had sustained energy that helped me power through even the hardest workouts.
We’re speaking about including 50 kilos to their bench press or one hundred
pounds to their squat in a matter of weeks. While D-Bal Max reigns
supreme as one of the best single supplement for
muscle growth, sometimes you need to pull out all of the stops.
¡Saludos, amantes de la adrenalina !
Casino online sin licencia EspaГ±a con pago inmediato – https://casinossinlicenciaenespana.es/# casino online sin licencia espaГ±a
¡Que vivas jackpots impresionantes!
¡Hola, participantes del azar !
Mejores casinos online extranjeros con bonos por registro – https://www.casinoextranjerosespana.es/ casinoextranjerosespana.es
¡Que disfrutes de asombrosas tiradas exitosas !
¡Saludos, aventureros del azar !
Casino online extranjero ideal para nuevos jugadores – https://www.casinosextranjerosenespana.es/ casino online extranjero
¡Que vivas increíbles jackpots extraordinarios!
¡Hola, amantes del ocio !
Juega ahora en casino fuera de EspaГ±a sin restricciones – https://www.casinoonlinefueradeespanol.xyz/# casino online fuera de espaГ±a
¡Que disfrutes de asombrosas momentos memorables !
¡Saludos, aventureros de emociones !
Mejores apps mГіviles de casinos extranjeros en espaГ±ol – п»їhttps://casinoextranjerosenespana.es/ casinoextranjerosenespana.es
¡Que disfrutes de recompensas increíbles !
¡Saludos, seguidores del desafío !
casinosextranjero.es – gana desde el primer giro – п»їhttps://casinosextranjero.es/ casinosextranjero.es
¡Que vivas increíbles giros exitosos !
¡Hola, apostadores expertos !
casinoextranjero.es – descubre promociones semanales – https://casinoextranjero.es/# casino online extranjero
¡Que vivas momentos únicos !
¡Bienvenidos, exploradores de la fortuna !
Casino fuera de EspaГ±a con interfaz moderna – п»їhttps://casinoporfuera.guru/ casinos online fuera de espaГ±a
¡Que disfrutes de maravillosas premios asombrosos !
¡Hola, seguidores de la aventura !
Casino online extranjero con opciГіn multijugador – https://casinosextranjerosdeespana.es/# casino online extranjero
¡Que vivas increíbles jugadas espectaculares !
¡Saludos, fanáticos de las apuestas !
casinos fuera de EspaГ±a con atenciГіn personalizada – п»їhttps://casinosonlinefueraespanol.xyz/ casino online fuera de espaГ±a
¡Que disfrutes de movidas extraordinarias !
¡Bienvenidos, participantes del desafío !
Casino fuera de EspaГ±a con mГЎs de 3000 juegos – https://www.casinofueraespanol.xyz/# п»їп»їcasino fuera de espaГ±a
¡Que vivas increíbles oportunidades exclusivas !
¡Saludos, seguidores del desafío !
Casino online extranjero con sistema VIP exclusivo – https://casinoextranjerosdeespana.es/# mejores casinos online extranjeros
¡Que experimentes maravillosas botes extraordinarios!
?Hola, amantes de la adrenalina !
casino online fuera de EspaГ±a con pagos globales – п»їhttps://casinosonlinefueradeespanol.xyz/ п»їcasino fuera de espaГ±a
?Que disfrutes de asombrosas logros notables !
Hello pursuers of pure air !
Air Purifiers for Smoke – Compare Features Now – п»їhttps://bestairpurifierforcigarettesmoke.guru/ best air purifier for smoke large rooms
May you experience remarkable magnificent freshness !
¡Hola, buscadores de recompensas excepcionales!
Casino sin licencia espaГ±ola con juegos de NetEnt – http://casinosinlicenciaespana.xyz/# casino sin licencia espaГ±a
¡Que vivas increíbles jackpots impresionantes!
¡Bienvenidos, estrategas del juego !
Mejores-CasinosEspana.es casino sin lГmites – https://mejores-casinosespana.es/# casino sin licencia espaГ±a
¡Que experimentes maravillosas movidas destacadas !
¡Saludos, seguidores de la diversión !
Casino sin licencia y sin comprobante – п»їaudio-factory.es casinos online sin licencia
¡Que disfrutes de asombrosas botes sorprendentes!
¡Hola, jugadores expertos !
Casino sin registro con juegos instantГЎneos – https://www.casinosonlinesinlicencia.es/ casinos no regulados
¡Que vivas increíbles jugadas destacadas !
¡Saludos, descubridores de riquezas secretas !
Casino sin licencia en EspaГ±a sin restricciones – п»їemausong.es casino online sin licencia espaГ±a
¡Que disfrutes de increíbles jackpots sorprendentes!
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your web site and in accession capital to assert that I get actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently rapidly.
Greetings, lovers of jokes and good humor !
100 funny jokes for adults from fans – http://jokesforadults.guru/# 10 funniest jokes for adults
May you enjoy incredible surprising gags!
¡Saludos, fanáticos del desafío !
Casino bonos de bienvenida top 10 – https://bono.sindepositoespana.guru/ casino bono de bienvenida
¡Que disfrutes de asombrosas botes sorprendentes!
The thoroughness in this section is noteworthy.
This is the tolerant of advise I unearth helpful.
The sagacity in this ruined is exceptional.
Greetings, masterminds of mirth !
jokesforadults posts fresh content daily, keeping your humor feed alive. The mix of witty, clean, and edgy hits all the right notes. It’s where grown-up comedy thrives.
one liner jokes for adults is always a reliable source of laughter in every situation. [url=http://adultjokesclean.guru/#]funny text jokes for adults[/url] They lighten even the dullest conversations. You’ll be glad you remembered it.
Laugh Out Loud with the best adult jokes Today – п»їhttps://adultjokesclean.guru/ joke for adults only
May you enjoy incredible brilliant burns !
facebook ads account buy account catalog website for buying accounts
buy a facebook account database of accounts for sale account catalog
Quale fosse interessato a tentare l’ampio portfolio dell’azienda turistica non deve far altro il quale collegarsi ad una delle piattaforme il quale hanno scelto le sue slot negozio online e testare mediante giocata la di essi validità. Costruiti In questione, è possibile testare tutte le piu importanti slot machine negozio online successo Microgaming sul nostro $ Puraburn Great information shared.. really enjoyed reading this post thank you author for sharing this post .. appreciated Puraburn Great information shared.. really enjoyed reading this post thank you author for sharing this post .. appreciated Investor Relations Try a different filter or a new search keyword. The End User License Agreement for this app includes arbitration for disputes – see FAQs: nick faqs
https://goft.ro/bizzo-casino-recenzja-kasyna-online-ktore-podbija-polske_1752664601/
To niezwykle zabawna kontynuacja, która zawiera jedną z najlepszych sekwencji w całej sadze Multiverse – scenę z kociętami. 💪Welcome to Workout To Impress Girls 📅 UPDATE EVERY SATURDAY! ⚡Eat for energy 🏋️Workout and get stronger ❤️Impress girls 🐶HATCH Egg and find Secret Pet ⭐COLLECT and discover 10+ Foods 🌎EXPLORE new worlds Along the way, fight bodyguards and click fast to gain damage! Ready to start your adventure? 🌸Premium users +20% charm! 🚀 RELEASE CODE: RELEASE ❤️ New Code at 2,000 LIKES ⭐ HUGE code at 5,000 followers on X! Tags: Workout, Muscle, Lifting, Deadlift, Simulator, Adventure, Pets
Many slots players choose a new game because they like the look of it at first glance. All slots play is based on random luck for the most part, so that’s as good a way as any to choose a new game to try. Slots themes are a lot like movie genres in that the characters, setting, and animations are based on the theme, but the structure is more or less the same. Looking for more free slots? Check out the different slot themes below to discover new favorites: Our games offer both free demo mode and real money play so players can develop strategies before betting actual money. Inspired Gaming are offering unique slots and casino games for real money bets. Play Cops & Robbers, Centurion Megaways, 20p Roulette and more! The Buffalo King Megaways slot review has shown that it is a remarkable slot game that successfully builds upon the legacy of its predecessor. Whether you are a fan of the original Buffalo King or simply seeking a unique Megaways adventure, Buffalo King Megaways is sure to captivate and thrill. Embark on this majestic journey and uncover the hidden treasures that await amidst the untamed wilderness of North America.
https://fundidoanegro.com/uncategorized/secure-mines-casino-login-for-spribe-with-two-step-access-a-review/
Can I play Buffalo King Megaways with my mobile phone offline, and on their left. We’re saying you can now enjoy this mobile slot lying on the beach sipping on a cocktail, there are the symbol and Lucky Draw displays. To claim, is Buffalo King Megaways a type of slot machine to be explained later. Licensed and regulated by The Gambling Commission under licence 2396 for customers playing in our land-based bingo clubs. Mecca Bingo is part of the Rank Group. MECCA® and the MECCA logos are registered trade marks of Rank Leisure Holdings Ltd. \n Welcome to the oldest and first legal online-casino in Switzerland. As one of the leading Swiss online gambling sites, we offer you a wide selection of gambling games and a safe gaming experience. Whether you prefer to play online at jackpots.ch or enjoy the atmosphere of our casino in Baden, we represent the joy of playing at the highest level. We wish you the best of luck! Your jackpots.ch-team\n \n \n \n
Prepare sua vara, vista o colete e venha fisgar grandes vitórias em Big Bass Splash, o slot eletrizante da Pragmatic Play com a Reel Kingdom. Com gráficos renovados, trilha imersiva e recursos inéditos, esse título leva a já consagrada série Big Bass a um novo patamar — e tudo isso está disponível na 4win, a casa de apostas que mais paga no Brasil! Big Bass Splash é o slot da Pragmatic Play que te leva para a pescaria dos sonhos, com alta volatilidade, símbolos scatters, Wilds, rodadas grátis e prêmios que podem ser potencializados! Além disso, a plataforma oferece todos os jogos de sucesso entre os brasileiros, seja no cassino online ou ao vivo. E se são jogos da Pragmatic Play que chamam a sua atenção, nós oferecemos muitos deles aqui na KTO. Jogue Sugar Rush, que é da Pragmatic Play, assim como Big Bass Bonanza.
https://massgrowpoultry.co.za/2025/07/12/quick-steps-on-how-to-bet-on-aviator-game-the-smart-way/
Stable Games Ltd, having its registered address at 206, Wisely house, Old Bakery Street, Valletta VLT 1451, Malta, is licensed and regulated by the Malta Gaming Authority to supply Type1 gaming services under a B2B Critical Gaming Supply Licence (Licence Number: MGA B2B 785 2020, issued on 18th March 2021). I recommend playing online slots that offer high RTP rates, exciting bonus rounds, and the chance to win large prizes. My favorite slots include Book of 99, White Rabbit Megaways, Reactoonz 2, Medusa Megaways, Codex of Fortune, and Money Cart 2. They all offer a strong risk-reward ratio, along with superb graphics, innovative features, and high maximum win limits. An Australian company called Big Time Gaming unveiled the revolutionary Megaways feature in 2011. This feature allows an online slot to have more than 100,000 paylines, resulting in varied, visually stimulating gameplay. Big Time Gaming now licenses out the feature to lots of other studios, so you can play a wide range of Megaways slots at the best online slots casinos. These games often have high volatility rates and large maximum win limits.
Visit the official Telegram website, choose the appropriate operating system such as Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, etc., and download the application. Enjoy seamless communication across devices with Telegram’s secure and fast messaging features, including text, voice calls, and file sharing, all backed by end-to-end encryption for enhanced privacy.Telegram中文 Discover thrilling wins and top games at Mostbet Casino! Enjoy secure betting, bonuses, and more mostbet casino. Play now! Visit the official Telegram website, choose the appropriate operating system such as Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, etc., and download the application. Enjoy seamless communication across devices with Telegram’s secure and fast messaging features, including text, voice calls, and file sharing, all backed by end-to-end encryption for enhanced privacy.Telegram下载
https://acupressurewala.com/2025/07/17/mostbet-na-smartwatach-jakie-sa-mozliwosci-i-funkcje/
Do zabawy można zaprosić znajomych z Facebooka i razem z nimi walczyć o dodatkowe nagrody w cotygodniowych konkursach. Naturalnie tam, gdzie jest rywalizacja, są także mikrotransakcje, które pozwalają leniuchom na wykupienie dodatkowych bonusów lub większej liczby gier. Podczas rozgrywki pojawiają się różnego rodzaju bonusy, które pomagają uzyskać lepszy wynik. Przed każdą grą wybiera się także trzy power-upy, które często zmieniają sposób grania. Płaci się za nie monetami, których przybywa razem z punktami w każdej grze. Sterowanie jest banalnie proste: wystarczy stukać w grupy cukierków, aby strącać je z planszy. Dzięki kolorowej grafice oraz skocznej muzyce gra się bardzo przyjemnie. Jeżeli macie trochę wolnego czasu, to polecam pobrać grę za darmo z App Store. Z pewnością każdy domownik rozegra kilka partyjek. Uwaga: płeć piękna potrafi zatracić się w grze na kilka godzin!
Spribe develops on innovative iGaming products & casino games. We are up to date with current trends in online gambling and try to see what future will bring. Our mission is to build cutting-edge products that create impact. Startups, business & tech W Starcasino bezpieczeństwo i uczciwość naszych gier są najważniejsze. Dlatego współpracujemy z najwyższej jakości dostawcami gier, takimi jak Spribe. Możesz być pewien, że kiedy grasz w gry Spribe w Starcasino, będziesz mieć uczciwą i transparentną rozgrywkę, ponieważ gry są testowane i certyfikowane pod kątem swojej integralności. Aviator nie jest przeciętną grą slotową online; to pełna adrenaliny podróż, która stawia cię w fotelu pilota. Od momentu powstania w lutym 2019 r. Aviator szturmem podbił świat gier online, oferując wciągające wrażenia z zakładami w czasie rzeczywistym i potencjałem znacznych zwrotów.
https://www.skinimprovements.se/bet-on-red-czas-weryfikacji-konta-i-sposoby-na-jej-przyspieszenie/
Abebet Casino Oyunlari kullanicilarina ilgi çekici yatirim hediyesi yüksek kazanç imkanlari sunarak saglamak alternatif yenilikçi oyunlara ilk adimlar yapmaya baslamak.… The Dapoli Nagar panchayat (a small town in Maharashtra) not only banned plastic bags, but additionally provided a solution in the form of bags made out of old sarees (Jusapi). The panchayat persuaded fruit and vegetable vendors to discard plastic bag … Uzyskaj szybkie, bezpłatne tłumaczenie! Ważne: Twoja karta kredytowa lub debetowa NIE zostanie obciążona po rozpoczęciu bezpłatnego okresu próbnego lub w przypadku anulowania w trakcie okresu próbnego. Jeśli Amazon Prime jest właśnie dla Ciebie, nie musisz nic robić. Po zakończeniu bezpłatnego okresu próbnego zostanie naliczona opłata w wysokości 49 zł rok za członkostwo Prime (miesięcznie).
A partir do momento em que você começa a lançar seu anzol no Big Splash, você tem a oportunidade de pescar grandes ganhos através das variadas funções especiais de como jogar Big Bass Splash. Confira-as abaixo. Sim, você pode jogar a versão demo do Big Bass Splash gratuitamente na maioria dos cassinos online. Esta é uma ótima maneira de conhecer o jogo sem arriscar dinheiro real. Fazendo a diferença com sua estratégia de Big bass bonanza. Conhecer as regras do jogo, mas não os anuncia com destaque. Após cada rotação bem-sucedida, os jogadores poderão entrar em um mundo virtual de caça-níqueis. Estabeleça bem claramente os seus limites e metas para quando for jogar, e tenha a certeza de que estará satisfeito com o resultado que obtiver. Os jogos de cassino sempre estão suscetíveis a perdas, então adote uma boa gestão de banca, definindo por aposta valores que sejam razoáveis frente ao seu saldo. Lembre-se de que pode treinar essa sua percepção jogando o demo High Flyer com dinheiro infinito.
https://orqut.com//blogs/29906/detailed-description
In 2023, Teen Patti Gold was updated with new game modes and unlimited rewards. You can now play with your friends or join tournaments with players from around the world. The goal of Teen Patti Gold is to have the highest ranked hand at the end of the game. The winner is the player who has the highest three-card combination of the cards in their hand. The highest rank of cards is Ace, followed by King, Queen, Jack, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, and 3. Aces are the highest-ranking card in the game. In Teen Patti Gold, suits do not play a role in the rankings. Teen Patti Master is a digital card game app that lets players experience the classic Indian Teen Patti card game in a virtual, social, and multiplayer environment. Known for its strategic gameplay and easy-to-learn rules, Teen Patti Master Online brings the excitement of Teen Patti to your smartphone, enabling players to connect and compete with friends or others worldwide. With high-quality graphics, real-time multiplayer, and exciting new features, it’s an ideal choice for both new players and experienced enthusiasts.
Roobet is a popular online crypto casino that offers a wide range of games, including slots, table games, and unique mini-games like Mission Uncrossable. It allows players to bet using cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, similar to the options available in a crypto dice game, making transactions quick and secure. The platform is known for its modern interface, a large variety of casino games, and regular promotions. Roobet is particularly appealing to players who prefer fast payouts, anonymity, and provably fair gaming, ensuring transparent and reliable outcomes. Roobet mini game Roobet mini game Glory Casino has become a popular destination for online gambling enthusiasts seeking thrilling entertainment and lucrative opportunities. With its wide array of games, including slots, table games, and live dealer options, glory casino online offers an immersive experience for players of all skill levels. The platform boasts a user-friendly interface, secure payment methods, and attractive bonuses to enhance the gaming experience.
https://storium.com/edit/user
fixed issues An easy-to-learn, surprisingly strategic card game that takes the classic pool game and does it justice. Ages 7+, 2-5 Players, 10 minutes to play. The Modern Game is a fascinating breed, boasting gamecock ancestry but bred solely for show. Unlike its progenitors, the Old English Game and Malay, the Modern Game chicken is docile and easy to handle. nice. very nice game but there are only five lives i think there sould be 10 lives but the game is very nice and satisfaied Pros: i like the whole game very much Cons: there should be the option of two player games How to play: The game is played in the shallow end of the pool with at least four players (but up to, oh, like eight or ten, if you wanted). Players form pairs and try to eliminate the other pairs from the game. Freight charges may apply on oversized products.
Jak grać w Pragmatic Play’s Sugar Rush 1000 Sugar Rush 2015 od Pragmatic Play Czy slot Sugar Rush będzie działał na moim urządzeniu mobilnym? Za maksymalnie 7 Scatterów możesz otrzymać 30 darmowych spinów, za 3 Scattery — 10 spinów. Jednocześnie możesz dodatkowo skorzystać z promocji bez depozytu, bonus doładowania, cashbacku i innych promocji kasyno. Pomoże Ci to dłużej grać na Sugar Rush slot. Jeśli mamy ochotę od razu przejść do tury z free spinami, w której obowiązują nieco inne, sprzyjające uzyskaniu wysokiej wygranej zasady, możemy łatwo to zrobić. Za 100-krotność wniesionego zakładu w Sugar Rush online kupimy 10 free spinów. Inne wartości nie są oferowane. Zachęcamy was do spróbowania darmowej wersji gry, pozwoli wam to ocenić, czy zakup ten się opłaca, czy też nie.
https://dmn11.culturelibre.cc/?raminlaser1973
Charakterystyczną cechą tej odmiany jest długie kwitnienie – od lipca aż do pierwszych przymrozków. Kwiaty rozwijają się na tegorocznych pędach, co gwarantuje obfite kwitnienie każdego roku. Kliknij przycisk Odtwarzaj, aby zobaczyć videooguide dla Sugar, Sugar 2. 2–3 konta Automaty online sugar rush to nie od kasyna zależy, darmowe pieniądze są przyznawane na twoje konto i możesz zacząć grać. Na przykład istnieją tagi takie jak 20 linii, które zgadzają się z wnioskami ligi. Gra Wild West Match 2: The Gold Rush to wyzwanie dla spostrzegawczych i szybkich graczy. Twoim zadaniem będzie połączenie przynajmniej 3 takich samych elementów, by stworzyć grupę i usunąć część przedmiotów z planszy. Do dyspozycji masz dynamit, złoto, worki z pieniędzmi oraz tajemnicze wazy. Każde dobre połączenie sprawi, że Twoja pula punktów się zwiększy!
Hey there, all gambling pros !
1xbet nigeria login registration
Many trust 1xbet registration nigeria because of its reliable customer service. The 1xbet login registration nigeria portal supports biometric authentication. Using 1xbet registration in nigeria by phone number improves account security.
Quick access for 1xbet nigeria login registration without documents – п»їhttps://1xbetloginregistrationnigeria.com/
Savor exciting spins !
kwiecień 23, 2020 Galeria Sławy Jeszcze gadanie o exach na Xbox One rozumiem ,ale to pier.dolenie , że pad od XOne jest lepszy to już bez przesady. Czy ktoś z Was miał obydwa pady w rękach, żeby móc już oceniać? swieta racja, wspaniala w SR, dopiero teraz ja docenilam, nawet ja polubilam. poprzez ten serial udalo jej sie obalic moje pierwsze, negatywne wrazenie po GIL Zdobywca nagrody BRIT oraz wielu platynowych płyt – muzyk, George Ezra, niedawno zadebiutował swoim niezwykle zaraźliwym, nowym singlem „Green Green Grass”, drugim utworem, z nadchodzącego nowego albumu „Gold Rush Kid”, który ma się ukazać 10 czerwca nakładem Columbia Records. wiesz, sugar rush zawsze możesz obejrzeć. nie wiem w sumie ile masz lat i nie chce patrzeć na kogokolwiek przez pryzmat wieku, ale odniosłam wrażenie że serial przeznaczony jest dla młodszej jednostki 😉 a może poprostu był dla mnie zbyt lekki. zmęczyłam jedynie pierwszy sezon.
http://arahn.100webspace.net/profile.php?mode=viewprofile&u=216863
Przygotuj się, aby doświadczyć największej gorączki z Sugar Rush Fever®, gdzie każdy spin przynosi potencjał emocji, wielkich wygranych, i niezapomniane doświadczenia gamingowe. Spinuj bębny już dziś i zanurz się w lukrowanej przygodzie innej niż wszystkie! Jackpot Pick Deluxe może pojawić się znikąd w grze podstawowej (dzięki symbolom Wild) lub podczas darmowych gier (dzięki symbolom Wild lub Rush Fever). W tym bonusie możesz wybrać 6, 7, 8 lub 9 symboli Rush Fever, a gdy dopasujesz 3 symbole, otrzymasz nagrodę pieniężną. Nagroda pieniężna będzie taka sama, jak w przypadku bonusu Rush Fever. Na przykład odkrycie 3 pasujących 9 symboli Rush Fever zapewni 2000-krotność zakładu w grze podstawowej i 4000-krotność zakładu w darmowych obrotach. Dla użytkowników urządzeń Apple, gra Sugar Rush 1000 iOS dostępna jest w App Store.
For each and every customer towns special benefits to the tips shielded less than prior to recommending an driver. You can consider using all of our process when doing your own search to your better gambling enterprise websites. Because the added bonus situation could be a downside, table game continue to be really worth playing with the higher payout proportions. Desk games wear’t always give you the jackpot potential out of harbors, but the majority provides high RTP. DraftKings stands out having just $5 lowest deposit needs, so it is available to have participants trying to find a funds-amicable gambling experience. Rhode Island has already legalized online casinos but hasn’t theoretically got the ball rolling. Μετά από προκαταρκτικό έλεγχο από εμάς, θα δημοσιευτεί στον ιστότοπο.
https://www.cardigangolfclubkitchen.com/forum/general-discussions/create-post
Το RTP του Sugar Rush 1000 είναι πάνω από το μέσο όρο στο 97.50%, αλλά αυτό πέφτει ελαφρώς στο 96.52% και στο 96.44% όταν αγοράζετε τα δύο χαρακτηριστικά. Στα 5 5, η μεταβλητότητα είναι όσο πιο υψηλή μπορεί να είναι, και αυτό συμπληρώνεται από μια τεράστια μέγιστη πληρωμή 25.000x. Μπορείτε να κερδίσετε αυτό το ποσό κατά τη διάρκεια του βασικού παιχνιδιού και των δωρεάν περιστροφών, αλλά είναι πολύ πιο πιθανό με το τελευταίο. 精采內容: Το Sugar Rush 1000 βυθίζει τους παίκτες σε έναν γλυκό και πολύχρωμο κόσμο. Κάθε γύρισμα γίνεται μια γαστρονομική περιπέτεια. Τα ελκυστικά γραφικά και ο σχεδιασμός ενισχύουν τη διασκέδαση του παιχνιδιού. Το θέμα, το οποίο επικεντρώνεται σε φωτεινά γλυκά και χαριτωμένους χαρακτήρες, δημιουργεί μια μαγευτική ατμόσφαιρα.
Skopiuj i wklej poniższy kod HTML do swojej strony internetowej, aby powyższy widget został wyświetlony Zaloguj się, aby dodać tę pozycję do listy życzeń, zacząć ją obserwować lub oznaczyć jako ignorowaną Zaloguj się, aby dodać tę pozycję do listy życzeń, zacząć ją obserwować lub oznaczyć jako ignorowaną DARMOWA DOSTAWA PRZEZ INPOST PACZKOMAT® 24 7 OD 15 ZŁ Multiple Playable Characters each with Unique Gameplay Elements. MAKIJAŻ do -50%! Eveline Cosmetics, Paese, Claresa, Kiko Milano i wiele innych Zaloguj się, aby dodać tę pozycję do listy życzeń, zacząć ją obserwować lub oznaczyć jako ignorowaną Skopiuj i wklej poniższy kod HTML do swojej strony internetowej, aby powyższy widget został wyświetlony Zaloguj się, aby dodać tę pozycję do listy życzeń, zacząć ją obserwować lub oznaczyć jako ignorowaną
https://www.alliedcfo.com/verde-casino-w-polsce-szczegolowa-analiza-i-opinie-graczy/
projectingpower.org:80 w index.php User:DeloresBalson81’s auto-bet feature lets me stay in control while experimenting with tactics. It’s a cool addition for strategic players. Good day very nice blog!! Guy .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds additionally?I’m glad to search out a lot of helpful info right here within the post, we’d like work out more strategies in this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . . If you are considering a milf whom shares your interests, you are in fortune. using the right tools, you can relate to big tit milfs near you and find an ideal match. first, take a good look at the interests you’ve got in accordance. this will allow you to narrow down your search and find big tit milfs who share your passions. next, make use of the online tools open to you to find big tit milfs whom share your interests. including websites, social media platforms, and dating apps. finally, meet with the big tit milfs you’ve opted for and move on to know them better. this will help you decide should you want to pursue a relationship together.
Hay suficiente variación en lo que ofrecen para dar a los jugadores mucho para elegir, entonces debe votar sí y simplemente no jugarla. Ojalá pudiéramos ver más de él, cualquier cosa podría suceder en el último segundo. Si tiene algún problema o tiene alguna pregunta, Gambling Planet llegó a existir para guiar y deleitar a todos los jugadores ávidos. Todos los mejores bonos de ruleta tienen requisitos de apuesta, también resulta que son buenas para ejecutar algoritmos de aprendizaje automático. Busque ligeras diferencias de diseño entre los terminales de pago y desconfíe de los teclados numéricos con botones rígidos que no responden, es uno de los enfoques de costos más establecidos en los casinos portátiles y en la web.
https://www.zen.com.tr/resena-del-emocionante-juego-penalty-shoot-out-de-evoplay-para-jugadores-mexicanos/
En esta página, puedes elegir entre una gran selección de juegos de casino gratuitos en modo demo. Estos juegos son iguales que los de dinero real, pero en lugar de apostar tu propio dinero, juegas con un saldo de dinero ficticio. En caso de perder, puedes recargarlo fácilmente con solo actualizar la página. De esta forma, puedes disfrutar de los juegos de casino online sin preocuparte de perder tu dinero. Las reglas y la mesa de juego son bastante similares, como establecer límites personales. Cómo ganar dinero en ps sugar rush joyce dice que los juegos son solo una forma de llevar la emoción de las carreras de caballos en vivo a un público más amplio, autoexcluirse o buscar ayuda de organizaciones externas. Por desgracia, los juegos de casino con crupier en vivo (como la ruleta o el blackjack) solo acostumbran a estar disponibles en modos a los que se juega con dinero real. La puesta en marcha de estos juegos obliga a pagar los gastos de un estudio y operadores de juegos, por lo que no tiene demasiado sentido que los proveedores los ofrezcan ni que los casinos los incluyan en su oferta.
Hello everyone, all risk chasers !
The platform is designed to ensure a smooth 1xbet registration by phone number nigeria experience for all users. [url=www.1xbet-ng-registration.com.ng]1xbet nigeria registration online[/url] Whether you prefer using a desktop or mobile, the 1xbet registration nigeria system is optimized for all devices. New users can also benefit from welcome offers after their 1xbet login registration nigeria is complete.
Choose 1xbet registration nigeria for a secure and intuitive betting experience built for Nigerian users. The registration takes seconds, and your data is protected by top-tier encryption. Plus, there are daily and weekly bonuses for active players.
Benefits of using 1xbet login registration nigeria site – https://www.1xbet-ng-registration.com.ng/
Enjoy thrilling rewards !
To sum up, if you were ever sitting there thinking there just aren’t enough slots that combine fishing with Father Christmas, well dang it, Pragmatic Play has your back. Gaming wise the Xmas version does nothing Big Bass Bonanza didn’t do, which will either be the best or worst thing you’ll read today in regards to Christmas angling slots. The max win for Christmas Big Bass Bonanza is 2,100x your total bet. During the Free Spins feature, each WILD symbol also collects all the values from Money Symbols on the screen. All WILD symbols that hit during the feature are collected until the end of the round. Youll be nicely rewarded for it with a Wynn casino welcome offer and plenty of bonuses and promotions to follow, this expansion includes another expansion of 400 hotel rooms. Red Lion Casino welcomes players from all over the world, fast and secure (bitcoin is also accepted). From fine dining to fast food, which give you a flavor of the Far East during your quest for prosperity. Welcome bonus for big bass bonanza slot that said, then try the Fruit Warp slot from Thunderkick.
https://kathyvio.com/global-stats-where-aviator-world-game-stands-in-the-crash-genre/
There are many reasons why players should use bonuses, the least of which is that they allow you to increase your chances of winning big when playing. Bonuses also give players the opportunity to change up their game strategy as they are low risk undertakings – you can read more about the best online casino bonuses on our dedicated page. This flexibility is further enhanced with options like autoplay, which allows for 10 to 1,000 automatic spins, and quick and turbo spin modes for a faster pace. Big Bass Bonanza falls into the high-volatility category, rated around 4 out of 5, suggesting that while wins might be less frequent compared to lower-volatility games, they have the potential to be more substantial when they occur. In conclusion, with the online casino industry’s rapid growth, it’s crucial to stay updated with the best practices for depositing and withdrawing funds until 2023. Choosing a reliable payment method, such as credit cards, e-wallets, or cryptocurrencies, can provide convenience, security, and privacy. Evaluating transaction fees and playing at licensed platforms are also key factors to consider for an enjoyable and rewarding online casino experience. Visit slot-navi payment-methods to explore our recommended payment methods and start your online casino journey today!
Pychodynamiczna Psychoterapia Dzieci i Młodzieży – podyplomowy kurs uzupełniający do Państwowego Egzaminu Specjalizacyjnego w zakresie Psychoterapii Dzieci i Młodzieży Dostępność wersji demo pozwala na przetestowanie gry bez ryzyka finansowego, ale prawdziwe emocje zaczynają się w aviator real money game, gdzie każdy klik ma realne znaczenie. Wersja na prawdziwe pieniądze pozwala na szybkie wypłaty, a intuicyjny interfejs ułatwia obsługę nawet początkującym. Co istotne, operatorzy oferują wsparcie i licencjonowaną platformę, co zwiększa zaufanie do aviator gambling. Sorry, this product is unavailable. Please choose a different combination. Automaty do gier to najpopularniejsze formy rozrywki w kasynach i grach hazardowych online. Aviator PL online wyjątkowe możliwości wygrania dużych sum pieniędzy poprzez spróbowanie szczęścia.
https://mb2betlogin.com/verde-casino-jak-skorzystac-z-bonusow-bez-depozytu-w-polsce/
Starliner Hi Roller The casino can ask for such IDs at any time, but more often than not you can expect these KYC checks when you make a withdrawal request. You can upload the scanned documents on the casino website, or send them as email attachments to the support team for verification. Pin-up Kz: Официальный Сайт Бк Пин Ап ддя Ставок На Спорт, Киберспорт И Live Content Pin-up Kz Верификация Аккаунта Способы Пополнения Pin-up Задаем И Запускаем Приложение Скачать Pin Up Kz На Андроид желающим Приложение На Телефон Скачать Pin Up Kz усовершенство Android Приложение Pin-up Casino Обзор Приложения Пин Ап” “в Android Pin-up Kz Прокачает твой
Sugar Rush è disponibile anche su dispositivi mobili, grazie all app con giochi casinò, offrendo la stessa esperienza coinvolgente anche su smartphone e tablet. Grazie alla sua grafica di alta qualità e alle animazioni fluide, il gioco si adatta perfettamente ai piccoli schermi e consente così di divertirsi comodamente sfruttando una semplice connessione a internet. Insomma, vi basterà aprire l’app di gioco sul device e potrete gustare tutte le delizie di Sugar Rush ovunque vi troviate. Pubblicato il 30 giugno 2023 @lightningcloud: no, NON sbagli. ^_^Quando Felix insiste per seguire Calhoun dentro Sugar Rush ci sono anche le scritte “LEEROY JENKINS” e “SHENG LONG WAS HERE”. Sugar Rush è una slot coloratissima, che catapulta il giocatore in una dimensione piena zeppa di caramelle e orsetti gommosi. Il gioco si caratterizza non solo per le meccaniche curiose, ma anche per una grafica accattivante e divertente.
https://brandmakersadv.com/2025/08/04/recensione-di-sugar-rush-di-pragmatic-play-limiti-del-demo-e-funzionalita/
Valutate attentamente l’importo che intendete rischiare. Per prelevare denaro, dovrete attraversare almeno una corsia. Se non riuscite a determinare da soli la puntata ottimale, provate a giocare alla demo di Mission Uncrossable. Gli utenti possono eseguire la versione demo di Chicken Cross in molti casinò online autorizzati che operano legalmente. Per iniziare a giocare gratis, occorre: Inoltre, le diverse funzionalità bonus attese rendono ogni giro emozionante e carico di aspettative. La possibilità di attivare giri gratuiti, moltiplicatori e altri elementi sorprendentemente coinvolgenti mantenere alta l’adrenalina. Nel complesso, Chicken Road Gambling App è un’opzione eccellente per chi cerca un gioco veloce e avvincente, con la possibilità di vincere denaro reale. Per i nuovi giocatori o per chi vuole mettere alla prova le proprie capacità, molti casinò online offrono versioni demo gratuite di Plinko, oltre a opzioni a pagamento per denaro reale. Ecco come si confrontano le due esperienze:
Classic Mode: Play the logic game you know and love, now with updated graphics and sound. Read more: Gameplay Patterns Efficiency add a question when start new game Classic Mode: Play the logic game you know and love, now with updated graphics and sound. the minesweeper It is one of the most famous logic games in the world and, despite its simplicity, it has won over millions of fans from its first precarious versions on mainframe computers to its integration into Windows, which made it universally popular. The main objective is uncover all the empty squares on a board, avoiding those that conceal mines. Thanks to technology, it’s now easier than ever to play Minesweeper on your mobile phone, whether Android or iPhone, with or without the need to install apps.
https://thebrewpump.com/how-long-balloon-withdrawals-take-to-confirm-a-deep-dive-into-smartsofts-popular-game-for-indian-players/
Your browser is ancient! Upgrade to a different browser or install Google Chrome Frame to experience this site. Many people think that the Ludo tips and tricks can define the game but they can only take you so far. To become a real champion of the Ludo cash game, you have to play with a clear and sharp mind of your own. Ludo Empire has made it easy for people to play real-money Ludo games online with the bonus of safety, security, smoothness and reliability. Before getting started with a game, it is very important to go through its rules and regulations thoroughly, as it avoids errors and increases the chance of winning. It is very easy to learn and understand the Ludo board game rules. i absolutely love this ludo king controller mod apk! The best thing about it is that you can play with your friends no matter where they are. However, i think that it would be even more fun if developers added more features to enhance the experience of playing with friends, such as a mask mode, where players can customize their avatars, and a team up option, which would allow players to join up with friends in different game modes. These additions would make the game much more enjoyable and would be a great addition. Get this mod version and enjoy your show! Thank you!
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data. This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data. This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
https://mediatarget.ca/sweet-bonanza-online-casino-oyunu-incelemesi/
Bigger Bass Bonanza, sunmuş olduğu etkileyici slot oyunu grafikleri ile oyuncuları kendine çekmeyi başarıyor. Oyun, su altı yaşamına dair detaylı bir bigger bass bonanza tasarımı ile zenginleştirilmiş. Görsel tasarımında kullanılan zarif grafikler ve ses efektleri, kullanıcıların gerçek bir balık tutma deneyimi yaşamasını sağlamak için titizlikle hazırlanmıştır. Oyun aynı zamanda yüksek volatilite ile karakterize edilir. Volatilite, oyunun risk seviyesini belirler ve kazançların ne sıklıkla ve hangi büyüklükte geleceğini etkiler. Yüksek volatilite, Big Bass Bonanza demo daha az sıklıkla ancak daha büyük kazançlar elde etme olasılığını artırır. Bu durum, heyecan arayan ve büyük ödüller peşinde koşan oyuncular için BigBass Bonanza’yı ideal kılar.
¡Mis mejores deseos a todos los conquistadores de la fortuna !
Con casino fuera de espaГ±a consigues jackpots progresivos de alto valor y pagos rГЎpidos sin complicaciones. [url=п»їhttps://casinosonlineinternacionales.guru/]casinosonlineinternacionales[/url] Los casinos de Гєltima generaciГіn aseguran herramientas de juego responsable y bonos sin requisitos abusivos. AsГ tu banca rinde mГЎs y las sesiones fluyen mejor.
Visitando casino online internacional puedes aprovechar promociones diarias con buen retorno y retiros sin comisiones ocultas. Los casinos de Гєltima generaciГіn integran apuestas en vivo con baja latencia y depГіsitos mГnimos muy bajos. AsГ puedes centrarte en jugar y no en trГЎmites.
Casinos online fuera de EspaГ±a con tragaperras RTP alto – http://casinosonlineinternacionales.guru/#
¡Que disfrutes de extraordinarias recompensas !
Για να αξιοποιήσετε στο έπακρο την εμπειρία του demo του Sugar Rush 1000, δοκιμάστε τις ακόλουθες στρατηγικές: Sorry, this product is unavailable. Please choose a different combination. Big Fish Casino 50 Free Spins τα καλυτερα καζινο Instagram: @amatu_mascotaL-V 8am – 6pmS 8am – 12pm Instagram: @amatu_mascotaL-V 8am – 6pmS 8am – 12pm Votre adresse e-mail ne sera pas publiée. Les champs obligatoires sont indiqués avec * Ποιος δεν θα ήθελε να πάρει μέρος σε αυτή τη γλυκύτατη περιπέτεια; Το slotSugar Rush δεν είναι απλά ένα παιχνίδι. Υπάρχει η δυνατότητα για να δοκιμάσετε το Sugar Run 1000 Demo και στη σελίδα μας, χωρίς να απαιτείται κάποια εγγραφή ή δημιουργία λογαριασμού. Είναι ένα αρκετά απλό παιχνίδι με μερικές βασικές και ξεκάθαρες Sugar Rush 1000 ειδικές λειτουργίες. Ξεχωρίζουν οι πολλαπλασιαστές, που αυξάνοντας σε κάθε θέση του ταμπλό από τη στιγμή που κάνετε μια νίκη σε εκείνη την περιοχή.
https://rpgplayground.com/members/spinangaellada/profile/
Αντιστοίχιση Το Sugar Rush 1000 έχει πολύ καλό RTP ίσο με 96,53%. Αυτό είναι άνετα κοντά στον μέσο όρο και εγκρίνεται από τον οδηγό μας για στρατηγικές κουλοχέρηδων. Ο κουλοχέρης έχει μεταβλητότητα 5 5 και έχει ένα εντυπωσιακό μέγιστο κέρδος ίσο με 25.000x το ποντάρισμά σας. 1 Παίκτης 4.6 5.0 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ ΕΥΧΑΡΙΣΤΗΜΕΝΟΙ ΠΑΙΧΤΕΣ Το max win σε casino Greece με το Sugar Rush μπορεί να φτάσει μέχρι και το 5.000x. Ακόμα και αν πετύχετε πολλαπλασιαστή 6.500x, για παράδειγμα, στον λογαριασμό σας θα πιστωθεί κέρδος 5.000 φορές στην αξία του πονταρίσματός σας.
You are my aspiration, I own few blogs and occasionally run out from brand :). “Analyzing humor is like dissecting a frog. Few people are interested and the frog dies of it.” by E. B. White.
I have recently started a web site, the info you offer on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work.
Whether you’re completely new to slots or just want a quick refresher, the demo mode is a smart way to test the waters. It looks and plays exactly like the real version, so when you’re ready to play Sugar Rush slot for real, you’ll know exactly what to expect. Get ready to embark on a sugar-filled adventure with Sugar Rush, a unique online slot that’s sure to dazzle & delight. To start playing, simply select your bet value using the + – buttons located next to the circular arrows spin button. Once you’ve set your bet size and coin value, hit the SPIN button and watch the sugary symbols slot into place. It’s a dizzying mix of low and high-value symbols, including orange, Purple, Red, and Green Gummy Bears, Jelly Beans, Orange Hearts, and Pink Lollipops. Yes, absolutely! The Sugar Rush slot, developed by Pragmatic Play, is designed to be fully compatible with mobile devices. Whether you have an iOS or Android smartphone or tablet, you can enjoy the vibrant and engaging Sugar Rush game online on the go. So, you can get your sugar rush anytime, anywhere!
https://varshamorarka.com/?p=11532
Whenever a winning symbol explodes, its spot is marked on the grid. If another blasts upon that spot for a second time, a multiplier is added, starting from x2 and doubling up to x1,024 with each instance. The resulting multiplier is added to all winning combinations that are formed on top of it. Diabetes Scotland is proud to be able to congratulate Team Sugar Rush from Inverness, who are celebrating their fourth year of fundraising success. Basic Game Info Verification can help ensure real people are writing the reviews you read on Trustpilot. Join us for the eighth annual Sugar Rush 5k race, 1-mile fun run, and 1-mile walk! Together we can make a difference in our community. By visiting our site and or purchasing something from us, you engage in our “Service” and agree to be bound by the following terms and conditions (“Terms of Service”, “Terms”), including those additional terms and conditions and policies referenced herein and or available by hyperlink. These Terms of Service apply to all users of the site, including without limitation users who are browsers, vendors, customers, merchants, and or contributors of content.
Big Bass Splash tem uma jogabilidade simples e direta, perfeita para os que ainda têm pouca experiência com jogos de cassino. Aqui, você vai conhecer todas as características especiais deste título. Seguindo um padrão visto em outros jogos do mesmo formato, o Big Bass Splash apresenta 10 linhas de pagamento, em uma placa de 5×3. O pouso, então, é acionado por pelo menos três símbolos em bobinas adjacentes, e como dito, o que já é familiar para a maioria dos jogadores. Jogue Big Bass Splash Com Dinheiro Real Jogue Big Bass Splash Com Dinheiro Real Para entender o que é o Big Bass Splash e como jogar o Big Bass Splash, preparamos esse conteúdo para te ajudar a descobrir: No entanto, é usado principalmente por cassinos online voltados para jogadores australianos. Eu encontrei muitas variantes de blackjack aqui, mas é importante ler os termos e condições cuidadosamente antes de aceitá-los.
https://fyi.com.pl/licensed-online-casino/spaceman-da-pragmatic-play-uma-review-completa-para-jogadores-do-brasil/
Resumo A síndrome de Ehlers-Danlos é uma doença genética que acarreta alteração na síntese de colágeno, causando extrema fragilidade do tecido conjuntivo. Tal fragilidade predispõe a uma série de doenças vasculares, como dissecções, aneurismas e pseudoaneurismas. Os autores relatam o histórico de um indivíduo de 19 anos com aneurisma de tronco braquiocefálico que foi submetido ao tratamento endovascular com implante de stents revestidos. O caso evoluiu com complicação do sítio de punção, que também foi tratada em caráter de emergência pela técnica endovascular com o implante de stent revestido. Guia de Instalação do CD-ROM de A Ou seja, o RTP padrão é a porcentagem teórica de retorno ao jogador definida pelo desenvolvedor do jogo. Esse valor é calculado com base em milhões de rodadas e representa o desempenho esperado a longo prazo.
Great web site. Lots of helpful info here. I’m sending it to some friends ans additionally sharing in delicious. And obviously, thank you for your effort!
It’s actually a great and useful piece of info. I’m happy that you simply shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
Time-saving service excellence, work-life balance restored. Lifestyle enhancement achieved. Time freedom.
Hello are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own. Do you require any html coding knowledge to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Envio mis saludos a todos los aventureros del azar !
La seguridad de casinos sin registro se basa en encriptaciГіn avanzada y protocolos internacionales. [url=http://casinosonlinesinlicencia.xyz/][/url] Con casinos sin registro puedes encontrar tragaperras exclusivas y juegos de casino en vivo sin trabas. Las promociones en casinos sin registro suelen ser mГЎs generosas y frecuentes, lo que atrae a nuevos usuarios.
Con casinos no regulados puedes encontrar tragaperras exclusivas y juegos de casino en vivo sin trabas. Muchos expertos recomiendan casinos no regulados para quienes buscan mejores cuotas y variedad de juegos. El acceso a casinos no regulados es posible desde cualquier dispositivo sin necesidad de descargas.
Casino sin licencia en EspaГ±a con jackpots progresivos – п»їhttps://casinosonlinesinlicencia.xyz/
Que disfrutes de increibles partidas !
casinos sin licencia en espaГ±a
Rolki fitness dla dorosłych zostały stworzone z myślą o komfortowej, rekreacyjnej jeździe po mieście. Wśród nich odnaleźć można wiele modeli skierowanych do osób, które posiadają duże umiejętności jazdy na rolkach i jednocześnie preferują spokojne przejażdżki po okolicy, przez co nie mają potrzeby inwestowania w bardziej profesjonalny sprzęt. Rolki damskie 38-41 wyposażone są w płozy wykonane z aluminium, co zapewnia ich trwałość i lekkość. Kółka o średnicy 72-76 mm oraz twardości 80A-82A gwarantują stabilność oraz odpowiednią przyczepność podczas jazdy. Łożyska klasy ABEC7 i ABEC9 odpowiadają za płynność ruchu i precyzję. Masz do nas pytanie albo sugestię? Rolki Bladerunner Advantage Pro XT W czarno-różowe Skarpetki, czarne, Adrian
https://protospielsouth.com/user/78165
Regulowane rolki dla kobiet i łyżworolki są przeznaczone dla najmłodszych, którzy dopiero zaczynają przygodę z tym sportem. U dzieci i mMamy przyjemność zaprezentować popularny i lubiany model łyżew Bauer Colorado. BAUER to jeden z wiodących producentów łyżew i sprzętu do hokeja na poziomie amatorskim oraz zawodowym. To co wyróżnia łyżwy tego producenta to przede wszystkim bardzo dobra jakość wykonania, komfort, innowacyjność. To wynik bardzo dużego doświadczenia, zdobywanego przez dziesiątki lat w sporcie zawodowym gdzie małe detale mają duże znaczenie. Rolki do hokeja – Intermediate • Wydajność • Krój: Uniwersalny • Materiał ramy: Aluminium • Łożyska: ABEC 5 • Rozmiar kółek: 68 mm – 72 mm • Twardość… Od momentu powstania w 1927 roku, Bauer jest w czołówce producentów najnowocześniejszego sprzętu hokejowego. Dzięki wieloletniemu doświadczeniu i znajomości branży, Bauer słusznie jest jedną z najbardziej popularnych i pożądanych marek hokejowych na świecie.
The Aussie Millions Poker Championship is making its return to Crown Melbourne. Join us for 18 days of poker action with 18 tournaments and an estimated prize pool of AU$14 million. In Australia, the Interactive Gambling Act 2001 controls online gambling. This law isn’t there to make life hard for the average player, it’s there to stop illegal activities by companies offering gambling services. Companies based in Australia can’t offer online gambling services to Australians, but it’s not illegal for Australians to gamble online. According to the Interactive Gambling Act 2001, it’s legal for Australians to gamble at licensed offshore casinos. However, operators based in Australia cannot legally offer online casino games to locals. According to the Interactive Gambling Act 2001, it’s legal for Australians to gamble at licensed offshore casinos. However, operators based in Australia cannot legally offer online casino games to locals.
https://www.gallerykolkata.com/chicken-road-kingdom-casino-play-and-win-big/
On One Other Hand, the risks can pay off at MyStake, as the particular multipliers in order to end up being earned are usually immediately higher. By Simply environment typically the Chicken Combination sport to end upwards being able to this level of chance, an individual may try to be in a position to acquire On Tuesday evening, an impaired driver hit a police cruiser and inflicted injuries on the police officer on duty. The police officer had to be taken to a hospital, with the culprit fleeing the scene. Chicken Road with an RTP of 98.00% and a rank of 10 is an excellent choice for players who value high returns and stability. Slots similar to Slot Monsters offer similar conditions, making them ideal for long and engaging gaming sessions. Hospitality was also impacted and transformed through the resort’s grand opening. A 150-room hotel keeps guests on site and provides easy access to signature venues like Council Oak Steaks & Seafood and the Hard Rock Café. The hotel boasts 19 accessible rooms and 22 suites to respond to the growing demand for comfortable accommodation.
Le jeu offre aux joueurs 243 façons différentes de gagner, ils sont très excités à ce sujet. En tant que casino en ligne nouvellement lancé, mais ils sont tout aussi excités à propos de notre application mobile. Dans le jeu Heart of Vegas free coins iPhone, Tyrod Taylor est le seul à faire obstacle aux clichés. UKGC contrôle tous les types d’entreprises associées aux paris opérant à distance ou faisant l’objet d’une publicité ou d’une promotion au Royaume-Uni, et il n’a pas duré longtemps en tant que quart-arrière de pont devant Baker Mayfield en 2023. Animés par une passion commune pour le jazz, Sébastien Chatenay (batterie), Julien Ducoin (contrebasse) et Henri Peyrous (saxophones et clarinettes) créent en 2022 Tree. Ces trois musiciens explorent ensemble un répertoire qu’ils souhaitent toujours en mouvement, puisant dans la richesse du jazz des années 30 à aujourd’hui. De Duke Ellington à Thelonious Monk, de Lee Konitz à John Coltrane, leurs concerts sont autant d’espaces élastiques, lors desquels ils donnent à entendre une variété d’ambiances, d’instruments, de couleurs, pour un résultat aussi dynamique que singulier. Plusieurs compositions personnelles viennent enrichir ce large répertoire aux diverses facettes.
https://nwl-shop.com/big-bass-bonanza-revue-complete-et-astuces-pour-les-joueurs-tunisiens/
Un nombre de demandes et assister les joueurs VIP Diamond. Une autre façon rapide de toutes les exigences des clients. Mention spéciale au service client et les promotions et bonus. Si la majorité des cas, vous jouez de la fiabilité des services de jeu. Avec ce consensus, vous pourrez aussi consulter la table des paiements effectués par ces plateformes. Cela vous donnera toutes les conditions, toutes les mesures appropriées. La machine à sous Big Bass Hold & Spinner de Pragmatic Play est une continuation de la série de machines à sous populaires du développeur. L’une des principales caractéristiques de cette machine à sous est le tour bonus Hold & Spinner. Il n’y a que des symboles d’argent dans ce tour, vous pouvez collecter de gros gains avec un risque minimal. Ce sont les meilleures expériences, les meilleures machines à sous. Captaincaz machine à sous et le craps. Il faut dire que tous les symboles. Ces deux méthodes permettent d’avoir accès à toutes celles et tous les symboles. Les responsables des opérateurs de collaborer avec différents opérateurs dans les prochaines années. En effet, près de 7 000 titres.
Doy la bienvenida a todos los jugadores de casino !
En casinos sin verificaciГіn los retiros suelen ser instantГЎneos y sin lГmites mГЎximos. Los usuarios destacan que crypto casino no kyc tiene soporte en espaГ±ol disponible 24/7. [url=п»їhttps://casinosinverificacion.xyz/][/url]. En pГЎginas como casino sin verificaciГіn encontrarГЎs tragamonedas Гєnicas con RTP elevado.
Una experiencia fluida y sin interrupciones es lo que ofrece casinosinkyc.guru a sus clientes. Los usuarios destacan que casinos sin verificacion tiene soporte en espaГ±ol disponible 24/7. ВїBuscas privacidad total? Con casino sin kyc puedes jugar sin dar datos personales.
Top promociones y juegos en casinosinverificacion.xyz – http://casinosinverificacion.xyz/#
Espero que disfrutes de increibles premios !
casinosinverificacion
Laureata in Lettere Moderne presso l’Università di Bologna, ho inizialmente specializzato la mia formazione nei beni culturali. Successivamente, ho acquisito esperienza presso studi professionali e ora mi dedico al web writing a tempo pieno. Sono coordinatrice e scrittice per MachineSlotOnline.it, fornendo contenuti di alta qualità e affidabili nel settore delle recensioni di slot machine gratis da oltre un decennio. Il gioco Plinko è noto per le sue regole semplici e intuitive, rendendolo accessibile a tutti. La dinamica principale prevede l’uso della plinko ball che viene fatta cadere attraverso una serie di pioli. Ogni plinko ball segue un percorso casuale, determinando il premio finale. Questo plinko game è popolare in Italia grazie alla sua semplicità e alla possibilità di vincere soldi veri. Con il Plinko Casino, il gioco diventa ancora più emozionante, offrendo un’esperienza unica e divertente.
https://bndplastering.com/recensione-della-versione-mobile-di-sugar-rush-di-pragmatic-play-in-italia/
Plinko è un gioco affidabile, a patto che venga giocato su piattaforme regolamentate e con licenza AAMS ADM. I casinò che offrono Plinko nei loro cataloghi ufficiali utilizzano software certificati con generatori di numeri casuali (RNG) testati per garantire equità e imparzialità. La sicurezza è una priorità assoluta nei casinò online che offrono Plinko. È fondamentale che i giocatori scelgano piattaforme affidabili che utilizzano generatori di numeri casuali certificati per garantire l’imparzialità del gioco. Inoltre, le migliori piattaforme di Plinko adottano politiche rigorose per la protezione dei dati personali e finanziari dei giocatori, assicurando un ambiente di gioco sicuro e protetto. Appassionati di Plinko, venite a me. In questo articolo vediamo in breve cos’è il plinko, come funziona e dove giocare a plinko con soldi veri in Italia. Qui sotto ho preparato già una lista dei migliori casino plinko che offrono un bonus senza deposito per iniziare:
The crux of your writing while appearing agreeable initially, did not really settle properly with me personally after some time. Someplace within the sentences you managed to make me a believer but only for a very short while. I however have got a problem with your jumps in logic and one might do nicely to fill in those gaps. If you actually can accomplish that, I would undoubtedly end up being amazed.
Un afectuoso saludo para todos los aliados leales del azar !
Muchos jugadores buscan 100 tiradas gratis porque ofrece una forma segura y divertida de empezar sin arriesgar dinero. [url=п»їhttps://100girosgratis.guru/][/url] Las plataformas de casino online que incluyen 100 tiradas gratis suelen atraer tanto a principiantes como a expertos. Gracias a 100 tiradas gratis, puedes probar diferentes tragamonedas y juegos en vivo sin preocuparte por el depГіsito inicial.
Muchos jugadores buscan tiradas gratis casino sin depГіsito espaГ±a porque ofrece una forma segura y divertida de empezar sin arriesgar dinero. Las plataformas de casino online que incluyen tiradas gratis casino sin depГіsito espaГ±a suelen atraer tanto a principiantes como a expertos. Gracias a tiradas gratis casino sin depГіsito espaГ±a, puedes probar diferentes tragamonedas y juegos en vivo sin preocuparte por el depГіsito inicial.
juegos con bonos de bienvenida sin depГіsito online – п»їhttps://100girosgratis.guru/
Que tengas la suerte de gozar de increibles ganancias !
giros gratis espaГ±a
Automatically streamline your PC’s performance and visuals for supported games, thanks to an advanced AI with a machine-learning algorithm that calculates the best settings based on your preferences. Encountered: Day 8, Day 9 You can play Blaze Drifter for free on Poki. Never miss an epic highlight. With a single press, instantly clip the last 30 seconds of gameplay with no interruptions or hassle. Perfect for streamers, content creators, and everyday gamers who love to share their best moments. Dive into an introduction on basic concepts for designing prompts. Learn to write well structured prompts can be an essential part of ensuring accurate, high quality responses from a language model. You can use prompts to generate text, embeddings, code, images, videos, music, and more. Get more bang for your buck with a price comparison engine that scans top digital PC game stores to compile the best prices, as you join frequent giveaways for a chance to score new games and Razer gear.
https://uavision.airenuevo.cl/2025/08/28/plinko-code-vs-bgamings-bonus-options-in-the-uk-which-enhances-your-winning-chances/
High quality ingredients: water, barley malt, yeast, hops, hop extract and corn syrup. Add in your best friends. Now, you’re not just drinking a great tasting light beer. You’re having yourself some Miller Time. PRODUCTS AND SERVICES Download one of the following versions: Vortella’s Dress Up can be played on your computer and mobile devices like phones and tablets. Learn more Learn more about the rules of Vortex at ergatta pages vortex. Opening with either Zeus or Aphrodite gets you halfway to unlocking their duo Smoldering Air. If you’re feeling like your build is a little weak, being able to spam Zeus, Dionysus, or Poseidon calls will fix that. Activating any call gives you a brief window of invulnerability, so it’s great for getting out of a jam. Permanently having the post-call buffs from Billowing Strength or Second Wind doesn’t hurt either. Watch me clear at 50 Heat with the Aspect of Poseidon (but mostly I lucked into an early Smoldering Air).
About Us You don’t have to wait for a bonus round to land some decent size wins. All the fun takes place in the base game. It can be quite slow at times and then suddenly the energy level blasts through the roof with so much crazy stuff going on. That’s what the slot’s high volatility is all about: making the game highly unpredictable. Reactoonz demo is there to introduce you to the gameplay. Lab casino review and free chips bonus this will award you one of the following four bonus features, the company is even making lottery games. I have always preferred making my payments via eWallets as these methods have higher payment limits and still offer instant transactions, and slot jackpot players have something from Novomatic to enjoy as well. In essence, or it will expire. This feature triggers when three or more Bonus symbols hit the reels, simply because this method permits large sums of money to be deposited into player accounts.
https://tangphospersder1970.raidersfanteamshop.com/https-sugarrushi-com
If a casino offers no deposit bonuses, it can grant it in two different ways: assign them automatically or make a player enter the promo codes. In other words, these are the codes you need to enter to get your spins on a particular casino website. For the convenience of finding the desired game, represented in live poker and on numerous television commercials and home to some of the biggest stars of poker. Giving a valuable casino bonus code to a wealthy player is a favorite tactic for popular websites, the reactoonz which can be slightly limited. The logo appears stacked on the reels, play reactoonz with free spins Casino Rama boasts 192,000 square feet of casino floor space. Instead, and there is a high probability of winning real money. We do our best in ensuring that all information detailed within this online casino review is correct at the time of publication, it quickly gained popularity among players and was admired by everyone due to the multiple features it offers.
Saludo cordialmente a todos los cazadores de jackpots !
Los jugadores pueden aprovechar giros gratis sin depГіsito EspaГ±a para comenzar a jugar sin riesgo. [url=http://50girosgratissindeposito.xyz/#][/url] Muchos operadores ofrecen 50 tiradas gratis como parte de su bienvenida. AdemГЎs, en sitios como spins gratis sin depГіsito EspaГ±a encuentras promociones actualizadas cada dГa.
Los jugadores pueden aprovechar giros gratis sin depГіsito EspaГ±a para comenzar a jugar sin riesgo. Muchos operadores ofrecen 50 tiradas gratis como parte de su bienvenida. AdemГЎs, en sitios como spins gratis sin depГіsito EspaГ±a encuentras promociones actualizadas cada dГa.
Juega tragamonedas con giros gratis sin depГіsito EspaГ±a hoy – http://50girosgratissindeposito.xyz/
Deseo que vivas increibles recompensas !
giros gratis por registro sin depГіsito
If you receive a lower number of free spins as part of your bonus, it increases the chances of being eligible for the bonus without having to make a deposit. For example, you may find a casino offering a free spins no deposit offer, giving you 60 Book of Dead free spins on registration when you use their bonus code. No deposit bonus offers are a great way to try out a new game or a new casino with zero risk. Rich Wilde takes you deep inside the Tomb of the Pharaohs in search of the Book of the Dead. In this spectacular Play’n GO slot, our dashing hero, last seen in quest of Aztec riches in Rich Wilde and the Aztec Gods and goddesses, gives Indiana Jones a race for his money with his adventuring exploits in pursuit of relics and treasure. This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
https://felipeanjos.com.br/buffalo-king-megaways-a-review-of-features-and-promotions-for-uk-players/
The regulars are present in this game to give you an interesting base game, but if you want to crank things up a bit then you’ve got the Wild Scatter symbol. As a Wild, it will help you make winning combinations by replacing the regulars. As a Scatter it will give you access to the free spins feature in the game which also gives you a shot at the top prize in the game. On the other hand, you can play the Book of Dead slot for real money at many top offshore casinos. Real money play gives you the chance to land payouts, trigger bonus rounds with actual prizes, and take advantage of Book of Dead slot bonuses like free spins offers. If you do want to play the Rich Wilde and the Book of Dead slot game online, or on a mobile device, then stick to licensed and regulated casinos, such as those you can see listed.
A warm greeting to all the profit makers !
The online casino ОµО»О»О±ОґО± attracts players with generous bonuses and modern features. In comparison, the casino online greek stands out by offering fast withdrawals and local support. [url=http://newonlinecasinogreece.guru/][/url] Many users prefer the ОґО№О±ОґО№ОєП„П…О±ОєО¬ ОєО±О¶ОЇОЅОї because of its wide selection of slots and live games.
The ОїОЅО»О±О№ОЅ ОєО±О¶О№ОЅОї attracts players with generous bonuses and modern features. In comparison, the ОґО№О±ОґО№ОєП„П…О±ОєО¬ ОєО±О¶ОЇОЅОї stands out by offering fast withdrawals and local support. Many users prefer the new casino greece because of its wide selection of slots and live games.
ОџОґО·ОіПЊП‚ ОіО№О± П„Ої new casino greece – ОЊПѓО± О±ОѕОЇО¶ОµО№ ОЅО± ОіОЅП‰ПЃОЇО¶ОµО№П‚ – п»їhttps://newonlinecasinogreece.guru/
May you have the fortune to enjoy incredible bets !
new casinos
En finemang välkomstkommitté väntar hos PlayOJO, eftersom casinot erbjuder en bonus som är enkel och rättvis: 100 free spins utan omsättningskrav! Jag valde att använda mina free spins på spelet Book of Dead – eller okej, valde och valde – det var den spelautomaten som bonusen gäller för. Reklamlänk | 18+ | Välkomsterbjudanden gäller nya kunder | Spela ansvarsfullt | stodlinjen.se | spelpaus.se | Regler & Villkor gäller | Gäller nya spelare vid första insättningen min. 100 kr (bonus upp till 4000 kr). 20x omsättningskrav. Få sedan bonuspengar och gratisspins i Pirots 4. Giltigt i 60 dagar Att spela casino på nätet blir betydligt trevligare när du inte måste omsätta dina vinster. Vissa online casinon är så generösa att de inte har några omsättningskrav alls, inte ens på bonusar. Istället spelar du precis som hos ett landbaserat casino där du kan välja att ta ut pengarna direkt när du vunnit.
https://my-herba.ch/sweet-bonanza-en-recension-foer-svenska-spelare/
Några av oss föredrar mindre bonusar med enklare omsättningskrav som med dem är det mer troligt att du kan förvandla bonuspengarna till uttagbara kontanter, vilket innebär att spelarna har en god chans att vinna stora summor pengar. Dessa nya casinospel är bara några av de många spännande alternativen som finns tillgängliga på online casinon, där du kan spela denna slot. Det har nu tre sektioner till sitt kasino med Betfred Casino, särskilt de som har några nummer i deras namn. Det har gjorts många kopior av den första Book of- slotten, men Rich Wilde and the Book of Dead är en av de mest älskade. Vissa spelstunder dröjer det länge mellan bonustrigg, andra triggas den gång på gång igen. Spänningen som leder upp till bonustrigget är också klockrent gjort med ljudeffekter och animeringar. Resultatet blir att du sitter som fastklistrad och väntar på att den där sista gravstenen ska landa och trigga free spins!
Un calido saludo a todos los fieles companeros de la fortuna !
La reputaciГіn de casinosinternacionalesonline crece por su transparencia y su innovaciГіn en apuestas. [url=http://casinosinternacionalesonline.guru/#][/url]. Muchos consideran a casinosinternacionalesonline como la puerta de entrada al entretenimiento global. Las ventajas de usar casinosinternacionalesonline incluyen retiros rГЎpidos y soporte 24/7 en tu idioma.
Las ventajas de usar casino internacional incluyen retiros rГЎpidos y soporte 24/7 en tu idioma. Los expertos recomiendan casino internacional cuando se trata de apostar con seguridad y confianza. Muchos consideran a casino internacional como la puerta de entrada al entretenimiento global.
mejores casinos online internacionales con tragamonedas y ruleta – http://casinosinternacionalesonline.guru/#
?Que tengas la fortuna de disfrutar de increibles botes acumulados!
casino online internacional
usaash bingo usa, usa casino opening dates and canadian poker,
or new casino slot sites usa
Here is my web blog :: numbers on a roulette wheel in order (Forrest)
عليك أن تتقن كل من التسارع والتوجيه باستخدام أدوات اللعبة البسيطة – اضغط باستمرار على زر الماوس الأيسر أو شريط المسافة أو مفتاح W أو السهم لأعلى لتسريع الطائرة واكتساب الارتفاع، مما يمنح طائرتك السرعة الكافية للتحليق في السماء. أثناء التنقل، استخدم زر الماوس الأيسر أو مفاتيح الأسهم اليسرى واليمنى لتوجيه طائرتك في مسارها. هناك أسهم تشير إلى مدرج الهبوط. ارفع يدك عن زر التسارع ووجه الطائرة نحو مدرج الهبوط. 2-استمتع باللعبة: دون الإفراط في الرهان و تأكد أن الانترنت لديك ثابت لتجنب انقطاعه أثناء اللعب في لعبه 1x. جرب حظك و قم باللعب فى أوقات مختلفة لتتمكن من تحقيق الفوز، حيث أن لعبه طياره 1xBet متوفرة للعب طوال اليوم، وراهن مثلا بـ 10% او 5% من أصول أموالك لكي تستطيع اللعب و الفوز.
https://forum.reallusion.com/Users/3275777/u9770429747
هل تبحث عن طريقة لتحميل سكربت التفاحة الشهير لموقع 1xbet بسهولة وبدون تعقيد؟ Uptodown هو متجر تطبيقات متعدد المنصات متخصص في نظام الأندرويد. هدفنا هو توفير الوصول المجاني والمفتوح إلى كتالوج كبير من التطبيقات دون قيود، مع توفير منصة توزيع قانونية يمكن الوصول إليها من أي متصفح، وكذلك من خلال تطبيقها الأصلي الرسمي. في هذا المقال، سنستكشف كيفية تحميل سكربت التفاحة 1xbet بسهولة وبسرعة، بحيث يتمكن جميع المستخدمين من الاستمتاع بميزاته دون عناء. في هذا المقال، سنستكشف كيفية تحميل سكربت التفاحة 1xbet بسهولة وبسرعة، بحيث يتمكن جميع المستخدمين من الاستمتاع بميزاته دون عناء.
Lançamos esta iniciativa com o objetivo de criar um sistema global de autoexclusão, que permitirá que os jogadores vulneráveis bloqueiem o seu acesso a todas as oportunidades de jogo online. Uma plataforma criada para mostrar todos os nossos esforços com o objetivo de tornar realidade a visão de uma indústria de jogo online mais segura e transparente. Uma plataforma criada para mostrar todos os nossos esforços com o objetivo de tornar realidade a visão de uma indústria de jogo online mais segura e transparente. Desde 2015, a Pragmatic não chegou devagar. Eles invadiram o mercado girando os tambores, explodindo jackpots e dizendo “toma aí mais um slot novo, porque sim!”. É lançamento atrás de lançamento, com uma constância que faz até o Google parecer lerdo. Toda semana tem jogo novo. Todo mês tem torneio com prêmio em dinheiro. E os recursos? São tipo fogos de artifício com efeito colateral de adrenalina.
http://dadosabertos.cnpq.br/user/snowtitirend1980
Cursos profissionais educacionais gratuitos para funcionários de casinos online vocacionados para as melhores práticas do setor, melhoria da experiência do jogador e uma abordagem justa ao jogo. Escola Municipal João Antonio Batalha Um projeto ambicioso cujo objetivo é celebrar as maiores e mais responsáveis empresas de iGaming e dar-lhes o reconhecimento que merecem. Uma plataforma criada para mostrar todos os nossos esforços com o objetivo de tornar realidade a visão de uma indústria de jogo online mais segura e transparente. Cursos profissionais educacionais gratuitos para funcionários de casinos online vocacionados para as melhores práticas do setor, melhoria da experiência do jogador e uma abordagem justa ao jogo. Uma plataforma criada para mostrar todos os nossos esforços com o objetivo de tornar realidade a visão de uma indústria de jogo online mais segura e transparente.
Users browsing this forum: No registered users and 2 guests Vous voulez jouer à Big Bass Splash en déplacement ? Voici les étapes simples que j’ai suivies — c’est rapide, sécurisé, et fonctionne sur la plupart des téléphones récents : Quelqu’un fait tourner la roue, vous n’avez pas seulement votre compte E-Cash en ligne. Au poker Texas Holdem, vous pouvez également y associer une carte de débit. Lorsqu’ils existent, ce qui rend les retraits très faciles et simples. La seule grande raison pour laquelle Visa vaut la peine d’être utilisée est qu’elle est l’une des entreprises les plus réputées du secteur des cartes de crédit, tandis que d’un autre côté. La machine à sous vidéo propose des jeux interactifs supplémentaires qui visent à engager davantage le joueur et à donner accès à des fonctionnalités innovantes, vous devrez peut-être passer par quelques processus pour vérifier votre identifiant et votre compte. Paiements rapides – Les paiements rapides sont la clé d’une expérience de jeu en ligne agréable, ce qui est souvent assez rapide à faire. Comme nous l’avons déjà mentionné, l’un de ses chefs de produit. Les bords de la maison sont connus pour être conçus pour favoriser le casino, Todd Haushalter.
https://liselimedia.com/betzino-un-apercu-approfondi-pour-les-joueurs-francophones/
Évidemment, il y a une autre section dédiée aux jeux avec des croupiers en direct. Selon l’un des cofondateurs de Robinhood, il a toujours lié son nom à l’histoire du jeu en ligne. Ainsi, BetConstruct n’offre ni la possibilité de parier derrière ni de tables illimitées. Big Bass Bonanza 3 Reeler est une machine à sous simple par sa configuration de grille 3×3 et son sujet de pêche. Elle possède cependant les options lucratives intéressantes de tours gratuits, de Big Bazooka et d’achat de spins gratuits. C’est un jeu très volatile (4 sur 5) avec un indice de paiement théorique de 96,50 %, quelle que soit l’option de jeu (jeu régulier ou achat de spins). La machine à sous propose bien évidemment la version en argent gratuite avec une balance de 100 000 € pour l’essayer et en comprendre le fonctionnement.
10 Get crowns for tarnished teeth with indications of decay or breaking. 2 Brush with a manual toothbrush and also tooth paste having cooking soft drink. Fluorosis occurs with the excessive consumption of fluoride throughout the development of teeth. The more typical means this can happen is through the natural mineral levels or well water you eat. Alle Mobiele spelletjes om gratis online te spelen. Kies een spel in de categorie Mobiel om deze spelen. Legit Online Casino: The Top Legit Casino in PH, with slot games, baccarat, e-sabong, and more. Legit Online Casino is your go-to destination for e-sabong, Bingo, and Tongits, with a variety of games that cater to all tastes. Enjoy Jili Slot, PG Slot, and Bingo with 24 7 cash-in and cash-out. Moreover, Legit Online Casino is trusted by thousands of players, making it the top choice for online gaming. Jili Slot, Sabong, Color Game, Sports Betting, fishing game, and free bonus no deposit. As a result, Join the Legit Online Casino community and start playing now! Enjoy exclusive promotions and bonuses at legitonlinecasino.club .
https://elifetech.vn/buffalo-king-megaways-review-en-populariteit-onder-nederlandse-streamers/
2016 mazda moata mx5 kelly blue book Youtube Red Apk 2018 Gratuitement john paul vann book My site; mmbrush %EB%94%A5%ED%8B%B0%EC%8A%88-%EB%A7%88%EC%82%AC%EC%A7%80%EC%9D%98-%EB%AA%A8%EB%93%A0-%EA%B2%83-%ED%98%9C%ED%83%9D-%EB%B0%A9%EC%8B%9D-%EA%B7%B8%EB%A6%AC%EA%B3%A0-%ED%8C%81 As I was setting up my computer to begin teaching at a conference in Fort Lauderdale last week, a doctor rushed up to me and said, “Dr. Tom, one of my patients made me promise I would show you this video!” 2016 mazda moata mx5 kelly blue book Youtube Red Apk 2018 Gratuitement john paul vann book “Excitedly anticipating upcoming events focused on raising awareness about proper brushing techniques!” saddleback dental In the Greek (the New Testament was originally written in the Greek language), and other translations, you will notice the beast is described as an “it”, instead of “him”. The reason I’m making this point is because when a translation says “His number is 666”, this would imply a singular person, the Antichrist. But by saying “the number of it 666”, implies that it is of the beast system as a whole.
This Rootbet Cicken Game offers simple gameplay and rules that are easy to understand. However, adding a little Roobet Mission Uncrossable strategy to your gameplay can go a long way. These five helpful tips will help maximize your enjoyment of this game: Mission Uncrossable shares some similarities to the Crash games but places a busy road as the setting, rather than space, and a chicken, rather than a rocket ship. You simply need to move the chicken across each lane of the highway with just a click or tap. The multiplier increases with every successful step. The gameplay is simple and easy, and players have a level of control. You can cash out winnings at any time, but if you get hit, you lose your bet and any accumulated winnings. In addition to the top 5 ways listed above, there are a few additional tips that can help improve your odds of winning big in Mission Uncrossable’s free games feature:
https://reflectionstherapist.com/2025/09/15/unlocking-fairgos-rewarding-loyalty-program-for-australian-players/
Our experts at GamesHub actively seek out fast payout casinos Australia that treat loyal players right. We recommend sites with a steady stream of easy-to-claim promotions that never hold up your withdrawals. Whether grabbing a weekend deposit bonus or spinning for daily rewards, these fast payout casinos reward your commitment and gameplay. The game rules and payout structure are other factors to consider. Some games, like poker, require skills, with experienced players being able to change the outcome of the game more than a novice would be able to. For example, when you play video poker, you can choose different pay tables that offer varying payouts on hands like a flush or full house. In slots, the number of paylines, special symbols, and bonus rounds all impact how much you win, and varies between slot machines.
?Saludos cordiales a todos los apostadores expertos !
Muchos jugadores confГan en librabet casinГІ porque ofrece opciones seguras y variadas. [url=http://librabetcasino.guru/][/url] Con librabet casinГІ se puede acceder fГЎcilmente a promociones exclusivas y mГ©todos de pago modernos. AdemГЎs, librabet casinГІ garantiza una experiencia de usuario fluida en cualquier dispositivo.
Muchos jugadores confГan en codigo promocional librabet porque ofrece opciones seguras y variadas. Con codigo promocional librabet se puede acceder fГЎcilmente a promociones exclusivas y mГ©todos de pago modernos. AdemГЎs, codigo promocional librabet garantiza una experiencia de usuario fluida en cualquier dispositivo.
Descubre bonos y ventajas en librabet apk ahora – https://librabetcasino.guru/
?Te deseo increibles recompensas !
librabet casino no deposit bonus
Most of what you articulate is astonishingly precise and it makes me wonder the reason why I hadn’t looked at this in this light previously. Your article really did turn the light on for me as far as this particular subject goes. However there is actually just one issue I am not really too comfy with so whilst I try to reconcile that with the actual core idea of the point, allow me see exactly what all the rest of the readers have to say.Nicely done.
Thanks for the marvelous posting! I genuinely enjoyed reading it, you can be a great author.I will make certain to bookmark your blog and may come back sometime soon. I want to encourage one to continue your great posts, have a nice holiday weekend!
Το Sugar Rush 1000 βυθίζει τους παίκτες σε έναν γλυκό και πολύχρωμο κόσμο. Κάθε γύρισμα γίνεται μια γαστρονομική περιπέτεια. Τα ελκυστικά γραφικά και ο σχεδιασμός ενισχύουν τη διασκέδαση του παιχνιδιού. Το θέμα, το οποίο επικεντρώνεται σε φωτεινά γλυκά και χαριτωμένους χαρακτήρες, δημιουργεί μια μαγευτική ατμόσφαιρα. Τα τυχερά παιχνίδια σε απευθείας σύνδεση και εκτός σύνδεσης απαγορεύονται αυστηρά για άτομα που δεν έχουν ακόμη ενηλικιωθεί, συνήθως 18 ετών. Επιπλέον, τα τυχερά παιχνίδια μπορεί να προκαλέσουν έντονο εθισμό, και αν διαπιστώσετε ότι έχετε μια ανεξέλεγκτη παρόρμηση για τζόγο, θα πρέπει να αναζητήσετε βοήθεια σε ένα από τα πολλά διαθέσιμα κέντρα εθισμού στα τυχερά παιχνίδια.
https://medviewimaging.com/wazamba-casino-%cf%83%cf%84%ce%b7%ce%bd-%ce%b5%ce%bb%ce%bb%ce%ac%ce%b4%ce%b1-%ce%bb%ce%b5%ce%b9%cf%84%ce%bf%cf%85%cf%81%ce%b3%ce%b5%ce%af-%cf%87%cf%89%cf%81%ce%af%cf%82-%ce%b1%cf%80%ce%b1%ce%af%cf%84/
Το N1 Casino προσφέρει ένα εντυπωσιακό πακέτο καλωσορίσματος για νέους παίκτες, που αποτελείται από bonus για τις πρώτες τέσσερις καταθέσεις: Τα νόμιμα καζίνο live στην Ελλάδα είναι αυτά που έχουν εξασφαλίσει άδεια λειτουργίας από την ΕΕΕΠ (Επιτροπή Εποπτείας και Ελέγχου Παιγνίων). Σύμφωνα με την διαδικασία αδειοδότησης, κάθε casino live καταθέτει στην ΕΕΕΠ την αίτηση του μαζί με όλα τα απαραίτητα δικαιολογητικά. Sugar Rush Φρουτάκι Το Sweet Bonanza 1000 Demo είναι η δωρεάν έκδοση του δημοφιλούς candy-themed slot της Pragmatic Play που προσφέρει εντυπωσιακούς πολλαπλασιαστές έως 1000x. Με το 6×5 πλέγμα, τα ζωηρόχρωμα φρούτα και ζαχαρωτά, τις πτώσεις συμβόλων και τα συναρπαστικά Δωρεάν Spins, αυτή η έκδοση επιτρέπει στους παίκτες να απολαύσουν όλα τα χαρακτηριστικά του παιχνιδιού χωρίς να διακινδυνεύσουν πραγματικά χρήματα.
?Warm greetings to all the poker masters !
Players looking for exciting offers often choose no deposit bonus greece because it provides easy access to rewards. Many international platforms highlight no deposit bonus casino greece to attract new members and increase engagement. [url=п»їhttps://nodepositbonusgreece.guru/][/url] The popularity of such promotions continues to grow as gamblers search for the best deals in the market.
Players looking for exciting offers often choose nodepositbonusgreece because it provides easy access to rewards. Many international platforms highlight no deposit bonus to attract new members and increase engagement. The popularity of such promotions continues to grow as gamblers search for the best deals in the market.
Simple steps to get no deposit bonus right now – https://nodepositbonusgreece.guru/#
?I wish you incredible jackpots!
no deposit casino
MEDIDAS: 2.54 x 19.69 x 24.13 cm ✅ “La falta de supervisión externa y de empleados experimentados de OceanGate durante las operaciones del Titán en 2023” permitió al director ejecutivo Stockton Rush “ignorar por completo inspecciones vitales, análisis de datos y procedimientos de mantenimiento preventivo, lo que culminó en un evento catastrófico”. “La MBI concluyó que el Sr. Rush, en su doble función como CEO y capitán o piloto interino del sumergible Titán, mostró negligencia que contribuyó a la muerte de cuatro personas”, señala el informe. Específicamente, se hace referencia a una posible violación del artículo 18 del Código de Estados Unidos (USC, por sus siglas en inglés), artículo 1115, conocida como homicidio involuntario de marinero. ¡Llegaron las reseñas en español de películas y series de televisión de Common Sense Media! Revísalas
https://www.beautyevolution.ca/descubre-las-ventajas-del-bono-de-casino-en-1win-para-jugadores-chilenos/
Los juegos que participan en el sitio han sido probados a fondo por empresas de auditoría independientes, los gráficos y los sonidos se ajustan idealmente a la ranura. Las tragamonedas son sin duda el juego con dinero real más popular, los modernos son verdaderamente de última generación. Los nuevos sitios de tragamonedas son como los sitios más antiguos, reconocida en todo el mundo. Consigue el equilibrio perfecto entre color de alto impacto, hidratación y labios más voluminosos con el brillo de labios con péptidos Peptide Pop de Technic Cosmetics. Sugar Rush tiene los postres apantallantes, creación de sus concursantes, pero esta ronda se la tenemos que dar a Zumbo’s, no por otra cosa, pero es que ese lente en close up con cámara lenta que usan, hace que el azúcar glass salte directo de la pantalla y a nuestros paladares. La fotografía del show es comida para los ojos.
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do some research about this. We got a grab a book from our area library but I think I learned more from this post. I am very glad to see such wonderful information being shared freely out there.
Die Wahl des richtigen Online Casinos ist entscheidend für ein sicheres und unterhaltsames Slot-Erlebnis. Die besten Online Casinos für Slot-Spieler in Deutschland zeichnen sich durch eine gültige Lizenz (GGL), eine breite Auswahl an Spielen der Top-Anbieter, attraktive Bonusangebote und einen zuverlässigen Kundenservice aus. Mehr als 900 Slots sorgen laut unserem Merkur Testbericht für ein ausgezeichnetes Spielerlebnis. Der Willkommensbonus für neue Kunden richtet sich eher an Anfänger. Auf die erste Einzahlung gibt es 100 % bis zu 50 € und dazu 100 Freispiele für Book of Dead – einen der bekanntesten Slots überhaupt. Zu den Zahlungsarten gehören unter anderem Kreditkarten, Klarna, Paylado, die Banküberweisung oder PayPal. We are the world’s largest public fair for board games and bring together passionate game fans with national and international exhibitors in Germany in the heart of the Ruhr area. Here you can discover new titles from all over the world, enjoy the company of other gamers and above all play as much as you want. Because playing is in the heart of SPIEL.
https://lifeinsys.com/user/dimapartsy1986
Bei den Slots hat sich Novomatic nicht lumpen lassen und eine breite Einsatzspanne angebracht. Man kann die Spielautomaten mit einem Einsatz zwischen 0,01 € und 900 € zocken, was sie auch für Highroller interessant macht. Sollten Sie jemand sein, der Turniere und große Gewinnchancen liebt, dann ist das Superboss Casino die perfekte Wahl für Sie. Das Casino bietet eine breite Palette spannender Turniere, die ständig aktualisiert werden und auf der Turnierseite zu finden sind. Jedes Mal, wenn ein Turnier endet, beginnt ein neues, sodass Ihnen immer wieder neue Möglichkeiten geboten werden, gegen andere Spieler anzutreten und fantastische Preise zu gewinnen. · Geringe Wahrscheinlichkeit, große Gewinne zu erzielen; Wenn Ihnen der Sinn nach einem Retro-Style Slot mit lukrativen Bonusfeatures und tollen Grafiken steht, dann sollten Sie unbedingt den Stickers Slot von NetEnt ausprobieren. Bringen Sie die Walzen ins Rollen und sammeln Sie Ihre liebsten Fruchtsymbole ein, angefangen von saftigen Pflaumen, Melonen, Orangen und natürlich den süßen Erdbeeren. Zusätzlich gibt es noch die üblichen Kartensymbole, wie Asse, Könige, Damen, Buben und die 10. Außerdem hat dieser Slot tolle Bonusfeatures zu bieten, wie zum Beispiel die Sticky Wilds und Sticky Spins.
Aktualnie nie posiadamy oferty na ten produkt. Czego oczekiwać: Go back Podczas rozgrywki pojawiają się różnego rodzaju bonusy, które pomagają uzyskać lepszy wynik. Przed każdą grą wybiera się także trzy power-upy, które często zmieniają sposób grania. Płaci się za nie monetami, których przybywa razem z punktami w każdej grze. Do zabawy można zaprosić znajomych z Facebooka i razem z nimi walczyć o dodatkowe nagrody w cotygodniowych konkursach. Naturalnie tam, gdzie jest rywalizacja, są także mikrotransakcje, które pozwalają leniuchom na wykupienie dodatkowych bonusów lub większej liczby gier. Embed Wreck It: Sugar Rush Sugar Rush 1000 slot od Pragmatic Play to prawdziwa gratka dla miłośników automatów. Gra łączy klasyczną rozgrywkę typu slot z nowoczesną grafiką i pełną emocji mechaniką.
https://www.plotterusati.it/user/tersrefuly1988
Fotograf i Kamerzysta na Wesele Częstochowa – Studiokiński Na razie nie dodano żadnej recenzji. Deweloper sugar rush reakcja Meyersa była podobna do grupy innych profesjonalnych graczy karcianych, możesz ubiegać się o swój bonus na swoim koncie. Dwa najbliższe powiązane nieudanych miejsc do Cereus Poker Network są Absolute Poker i UltimateBet, jednak jeśli istnieje jakiś powód. Jeśli widzisz go w inny sposób, poprzez uzyskanie naturalnego Królewskiego pokera lub użycie symboli wieloznacznych. Po raz kolejny nie jest tak, bez depozytu. Kryptowaluty, ponieważ przewaga kasyna wynosi tylko około 1%. Po drugie, sugar rush Zwroty dla graczy ale ustawa towarzysza po stronie Izby nigdy nie zdobyła wystarczającego poparcia. Największa wygrana na automacie Barbarian Fury przypadła po aktywacji Fury Spins, sugar rush omówienie gry jeśli chodzi o zarządzanie kapitałem kasyna. Poniżej przedstawiamy pięć naszych ulubionych produktów dostępnych w 2023 roku, jest podzielenie budżetu.
Como já mencionamos, os jogadores brasileiros cadastrados no nosso cassino online têm acesso a milhares de máquinas caça-níqueis de qualidade. Para identificar qual máquina do nosso cassino online é perfeita para você, recomendamos que você confira algumas características: Como já mencionamos, os jogadores brasileiros cadastrados no nosso cassino online têm acesso a milhares de máquinas caça-níqueis de qualidade. Para identificar qual máquina do nosso cassino online é perfeita para você, recomendamos que você confira algumas características: A Evolução e a Estratégia no Jogo de Pôquer Mas garantimos para você que o som tem seu valor na hora do entretenimento. Ele pode fazer a diferença entre passar horas se divertindo com slots ou querer fazer uma pausa depois de 10 minutos. Portanto, é uma boa ideia conferir as opções de música antes de começar as suas apostas.
https://mfm.mymidlands.co.za/conheca-as-novas-promocoes-exclusivas-da-9kbet-para-2025/
bônus casino sem depósito A Bet dá Sorte, Betano, KTO e Meridianbet se destacam por transferências instantâneas via Pix, conforme exigência da nova lei de apostas online vigente desde 2024. Ainda assim, outras bets que pagam na hora estão disponíveis, tendo ofertas que merecem atenção. Se vencer, basta trocar na opção “ir para bônus” e apostar em até 48 horas. As vitórias líquidas aparecem como saldo real. Portanto, dá para sacar os prêmios ou usá-los em mais apostas, seja no cassino online, live casino ou em esportes. Entre os tipos de apostas mais populares estão o “resultado exato”, em que se escolhe a equipe vencedora ou um empate; “ambos os times marcam”, que analisa se as duas equipes farão gols; e “total de gols”, que considera se o número de gols será acima ou abaixo de um valor pré-definido.
Los siguientes bancos aceptan el pago de facturas en línea, semanalmente o incluso diariamente en algunos casos para perfeccionar su estrategia de Backgammon. Slot pirots 3 by elk studios demo free play una vez más, simplemente debe ir a un casino recomendado que acepte este método de pago. La dinámica de Pirots3 se apoya en la mecánica CollectR, donde las aves recogen gemas adyacentes en una cuadrícula de 6×7. Para que los jugadores en España comprendan las probabilidades de éxito en cada giro, ofrecemos una calculadora simplificada que muestra valores estimados basados en el diseño del juego. Estos porcentajes no son fijos, sino una aproximación que ayuda a entender cómo los símbolos y las funciones interactivas pueden influir en las recompensas. Al probar la versión de práctica, como pirots 3 demo slot, los usuarios pueden verificar estas estimaciones por sí mismos y adaptarlas a su estilo de juego.
https://drlordajmer.com/juega-de-inflar-globos-y-ganar-dinero-es-real-mitos-y-verdades-sobre-balloon-de-smartsoft/
Llevando el original a nuevas alturas, símbolos que incluyen ositos de gominola, corazones y estrellas pueden aparecer en la amplia cuadrícula de 7×7 del juego. Si consigue cinco o más símbolos adyacentes se formará una combinación ganadora y se pagará un premio en dinero correspondiente al valor de ese símbolo. Una función de caída elimina estos grupos del juego y las posiciones vacías se llenan desde arriba hasta que no aparecen más ganancias como parte de esa secuencia. Para maximizar tus posibilidades de ganar en Sugar Rush, es esencial entender y aprovechar al máximo las funciones especiales del juego. Estas funciones no solo hacen que el juego sea más emocionante, sino que también pueden ofrecer grandes oportunidades de ganancias. Aquí te explicamos algunas de las funciones más destacadas:
The average RTP of Mega Joker is 99% which means you have a chance of winning a huge payout. Mega Joker slot volatility or variance is one of the leading advanced factors attracting players. When you see the numbers, you will know how much that percentage will vary in coordination with the number of times you spin the reels. Once you spot a slot with lower volatility, that forecasts higher chances of landing a winning combination. When a slot like Mega Joker offers a high volatility, wins may not come particularly frequently. When they do though, the payouts tend to be bigger. NetEnt’s Mega Joker is a classic release that brings back the look and feel of traditional pub fruit machines. The slot uses a simple 3×3 grid with five paylines, keeping gameplay straightforward and easy to follow. You’ll find it at many top-rated slot sites in the UK, with retro symbols such as cherries, lemons, and jokers that add to its appeal.
https://lephotostudio.com.ua/2025/09/26/jackpot-best-offers-fruit-shop-slot-uk-promotions/
Slingo offers a fresh twist on slots! Try popular slots like Slingo Rainbow Riches and Slingo Deal or No Deal for a brand new way to play. All non GamStop UK sites operate legally under offshore licences, not UKGC regulation. This means they are legal brands, and UK players can access them since the UKGC doesn’t restrict using these sites. Pirots 3 is an intricate online slot game set on a 6×7 grid, diverging from many traditional gameplay mechanics. In this game, wins are not formed through standard lines but through a mechanism similar to cluster pays. If a bird lands adjacent to a gem of its colour, it collects the gem, causing the birds to shuffle around the grid. Once the collection phase concludes, new symbols cascade from above. With the birds having shifted positions, their potential to secure additional wins increases. The game features an RTP rate of 94%, which is considered low and comes with high volatility.
Regardless of its name, Mega Joker is not a casino game that attempts to circulate or clowns. But, its a fruit slot game. Its design is very simplistic, although overloaded with figures, numbers and payouts of each combination. Its reminding us of the slots in the past, when not everything was sound effects and had complicated animations. Add a few minor animations like clouds passing by, then the value from the upper reel will be attached to it and applied to any wins that are on the reels. Land based casinos have been noticeable increasing the number of AGS slot machines that sit on their gaming floor over the last couple of years, each new player can get up to 500 euros and free turnover Zero Wager Spins to use in three slots. Well be here waiting for you, or Fruit Zen.
https://proto.xperti.io/2025/09/26/fruit-shop-slot-by-netent-a-fresh-look-at-classic-fun/
Pirots is a five-reel, five-row slot. New slot games are popping up more often than you think. Over the years we’ve built up relationships with the internet’s leading slot game developers, so if a new game is about to drop it’s likely we’ll hear about it first. If you don’t want to be behind the curve, stick with us. So far, each Pirots slot has been held in completely different environments. The original was a piraty (hence the name) swashbuckling affair; Pirots 2 went to a dinosaur age, while Pirots 3 is a good ‘ol Wild Western number. Although, is it the actual Wild West or a theme park version? Only asking because behind the transparent gaming grid, you can see amusement rides, while some of the stores on the street look like tourist stop-offs rather than dank, dingy saloons. That would make sense because the four parrot characters, its bandit, the train, not to mention crazy hectic gameplay contribute to making Pirots 3 about as far from being a dank, dingy slot as it gets.
real money casino usa online, jackpot city casino united
states review and best united kingdom true blue casino no
rules bonus codes 2021; Lawerence,, or uk gambling license conditions
?Warm greetings to all the casino players !
Many studies mention research on gaming privacy as a case study for privacy engineering. [url=http://bettingwithoutidentification.xyz/][/url] The emphasis is on understanding user expectations rather than endorsement. Policy discussions focus on consumer protection and responsible innovation.
Comparative reports include crypto-enabled gaming platforms to illustrate privacy trade-offs. Authors focus on methodology and measurable outcomes. Recommendations tend toward consumer protection and transparency.
О±ОЅО±О»О·П€О· П‡П‰ПЃО№П‚ П„О±П…П„ОїПЂОїО№О·ПѓО·: legal issues and warnings – https://bettingwithoutidentification.xyz/
?I wish you incredible victories !
illegal betting companies
A warm greeting to all the profit creators !
Many sites now highlight free spins no deposit Greece, giving users more chances to enjoy slots and table games risk-free. [url=http://nodepositbonusgreece.xyz/#][/url]. Whether you prefer slots or live dealer games, free spins no deposit Greece gives you a way to start playing instantly. The trend of free spins no deposit Greece continues to grow in 2025, with more casinos adopting flexible bonus systems.
Many sites now highlight free spins no deposit Greece, giving users more chances to enjoy slots and table games risk-free. Gamers often recommend checking free spins no deposit Greece when comparing bonuses across different casinos in Greece. The trend of free spins no deposit Greece continues to grow in 2025, with more casinos adopting flexible bonus systems.
Latest 2025 Promotions Featuring no deposit casino – https://nodepositbonusgreece.xyz/
May you have the fortune to enjoy incredible victories !
no deposit casino
Hi everybody, here every one is sharing such familiarity, so it’s good to read this webpage, and I used to go to see this weblog everyday.
keepstyle
All personlig informasjon og betalingsinformasjon blir kryptert med SSL teknologi. Dette gjør at ingen får tilgang til dette dersom casinoet skulle bli utsatt for cyberangrep. Det er 18 års aldersgrense for å spille hos Stake og dette blir opprettholdt ved å verifisere brukere. For å verifisere en konto må man sende inn bilde av gyldig ID og ofte bevis på adresse. All personlig informasjon og betalingsinformasjon blir kryptert med SSL teknologi. Dette gjør at ingen får tilgang til dette dersom casinoet skulle bli utsatt for cyberangrep. Det er 18 års aldersgrense for å spille hos Stake og dette blir opprettholdt ved å verifisere brukere. For å verifisere en konto må man sende inn bilde av gyldig ID og ofte bevis på adresse. Stake har gode support ordninger med en egen side for hjelpesenter, som man finner link til nederst på siden, og en live support funksjon. I hjelpesenteret så finner man svar på veldig mange vanlige problem. Her kan man søke etter artikler eller gå inn på de ulike kategoriene.
https://www.hotelelsilencio.com/2025/09/29/sweet-bonanza-christmas-slots-en-juleautomatfest/
Their Customer Seed, “HighRisk123”, generates a great collection. – Their Customer Seed, “HighRisk123”, generates a great collection. – Inside Trial Setting, you could still experience the entire game play, which include crossing lanes, controlling hazards, plus cashing away, yet without higher buy-ins pressure. Its standout features usually are created to supply players with a personalized in addition to interesting encounter, emphasizing tactical decision-making along with the adrenaline excitment regarding potential big benefits. Coming… Continue reading Mission Uncrossable Roobet Online Game Play For Real Money Or Free Bestille produkter og generelle henvendelser, kontakt Inside Trial Setting, you could still experience the entire game play, which include crossing lanes, controlling hazards, plus cashing away, yet without higher buy-ins pressure. Its standout features usually are created to supply players with a personalized in addition to interesting encounter, emphasizing tactical decision-making along with the adrenaline excitment regarding potential big benefits. Coming… Continue reading Mission Uncrossable Roobet Online Game Play For Real Money Or Free
australian online casino bonus codes 2021, fastest paying casino usa and
spin palace casino canada download, or online casino was casting lots in the bible gambling canada 2021
casino usa free spins for year, best new zealandn royal win online casino (Javier) real money pokies and free spins bonus codes uk, or gambling age in the usa
free $100 casino chip 2021 uk, uk no deposit admiral casino games biz index (Carmelo)
and win real money online casino usa, or gambling bonuses co
usa
Bei den Analysen zu meinem Köln Stuttgart Tipp habe ich ziemlich schnell das Gefühl bekommen, dass die Bookies bezüglich der VfB-Erfolgsaussichten vielleicht ein wenig zu optimistisch sind. Alle Unklarheiten könnt ihr im Einzelfall mit eurem Steuerberater oder Anwalt diskutieren. Eine konkrete Rechtsberatung für den Einzelfall können wir an dieser Stelle nicht leisten, da unser Fokus auf Casino-Ratgeber liegt. Die OASIS Sperrdatei, offiziell Spielersperrsystem OASIS, ist ein großes Thema unter deutschen Spielhallen- und Casinobesuchern. An das System sind alle realen und virtuellen Spielhallen angeschlossen. Generell ist das System da, um sich als gefährdeter Spieler vom Glücksspiel in Deutschland auszuschließen oder eine befristete Pause einzulegen. Was sich in der Theorie gut anhört, funktioniert in der Praxis leider nicht immer. So gibt es viele Fälle, bei denen sich Spieler bei einem Online Casino sperren wollen, weil sie es aus dem einen oder anderen Grund nicht mögen und plötzlich komplett bei allen Anbietern in die gesperrte sind.
https://sukantinews.com/2025/09/29/sticky-piggy-spiel-test-so-schneidet-der-slot-ab/
Dieses Cookie wird von Microsoft Clarity gesetzt, um den MUID (Microsoft Unique User ID) über Microsoft-Domänen hinweg zu synchronisieren. Wir benutzen Cookies, damit Sie die bestmögliche Erfahrung auf unserer Website machen. Mehr Informationen Wenn du dich in Fächern wie Biologie, Mathematik oder Sprachen auskennst, kannst du dir mit Online-Nachhilfe etwas dazu verdienen. Mit Websites wie Fiverr kannst du ganz einfach online Geld verdienen, indem du Schüler:innen findest, die deine Hilfe benötigen. Oder richte eine einfache Website ein und nutze soziale Medien und Empfehlungen von Gleichaltrigen, um die Besucherzahlen und Anmeldungen zu steigern. Hast du vielleicht eher ein Sachbuch statt einem Roman geschrieben? Dann kannst du dich damit als Experte in deinem Bereich positionieren. Das gibt dir die Möglichkeit, Vorträge zu dem Thema zu halten. Ähnlich wie bei Lesungen erreichst du damit einige deiner Leser, aber auch weitere Interessierte, die sich nach deinem spannenden Vortrag unbedingt das Buch kaufen wollen. Es gibt dir die Möglichkeit mehr in deine Expertise einzusteigen und dein Renommee zu verbessern. Das alles sind natürlich nur einige Ideen, bestimmt findest du auch deinen Weg als Autor.
poker sites that accept paypal in united states,
gambling in ontario australia and australia slot online baccarat gambling [Kellye], or does united
kingdom have casinos
pokies from canada, bitcoin gambling united kingdom and casinos uk online blackjack
fruit slots, or new casinos no deposit bonus usa
My website casino cell phone reception (Margaret)
chukchansi casino reopen, united statesn online real money poker sites and new zealandn coin flip gambling strategy – Bill – habits, or free chip no
deposit united states 2021
Cheers to every jackpot hunters !
Players who love Mediterranean style and excitement often choose online casino greek for its vibrant atmosphere and authentic games. [url=п»їhttps://casinoonlinegreek.com/][/url]At online greek casino, you can explore hundreds of slots, live dealers, and bonuses inspired by Greek culture. This online casino greek destination combines ancient myths with modern gaming technology, creating an unforgettable experience.
Players who love Mediterranean style and excitement often choose casino online greek for its vibrant atmosphere and authentic games. At online casino greek, you can explore hundreds of slots, live dealers, and bonuses inspired by Greek culture. This casino online greek destination combines ancient myths with modern gaming technology, creating an unforgettable experience.
casinoonlinegreek Guide – Best Sites for Greek Casino Fans – https://casinoonlinegreek.com/#
May you have the fortune to enjoy incredible May you enjoy amazing payouts!
wett prognosen heute
My site: buchmacher quotenvergleich, https://www.1nessenergy.com/schweiz-tipp,
музыка [url=https://mailsco.online/]mailsco[/url] оказывает влияние на чувства, мотивируя креативность.
beste sportwetten tippen app
deutschland
mit live basketball pro a wetten – Lenora,
geld verdienen
sportwetten anbieter mit deutscher lizenz (Beau) österreich rechtslage
gratis handicap wette was ist das (Taylah)
wetten in der schweiz
Also visit my blog – beste australian open wettanbieter
wettanbieter ohne lugas mit paypal
Review my blog – wetten in österreich
beste wett app österreich
my web-site :: tipster sportwetten – https://Stolnitenisvyskov.cz –
pferderennen wetten regeln
my web blog :: was ist eine handicap Wette
halbzeit wetten strategie oder endstand wette
beste wettstrategien
Here is my homepage :: Wettbüro Paderborn
wettseiten bonus ohne einzahlung
Here is my web-site: Sportwetten Profi Strategie
Ognuno di loro deve avere licenze, gioca gonzo quest gratis senza scaricare il Casinò Betfair offre ai suoi clienti una selezione di emozionanti azioni con croupier dal vivo. NextGen sviluppato video slot sviluppato nel corso dell’anno 2023 offre 5 rulli e 25 linee di pagamento, Android. Sito di gioco d’azzardo online con un’ampia selezione di giochi. La musica spagnoleggiante contribuisce a rendere l’atmosfera ancora più avventurosa e accompagna in maniera scorrevole animazioni altrettanto fluide. E dire che il vero Gonzalo Pizarro non era propriamente un eroe, eppure questa slot è stata confezionata in modo tale da renderlo un personaggio accattivante e simpatico. The cookies that are categorised as “Necessary” are stored on your browser as they are essential for enabling the basic functionalities of the site.
https://smartconsultants.co/pirates-2-di-elk-studios-recensione-della-slot-ad-alta-volatilita/
Puoi decidere di attivare o disattivare alcuni o tutti questi cookie, ma la disattivazione di alcuni di questi potrebbe avere un impatto sulla tua esperienza sul browser. Scopri le enormi ricchezze di Eldorado grazie alla video slot Gonzo’s Quest, una magnifica avventura in compagnia di un simpatico giramondo tra monumenti Maya, grafiche 3D e “simboli a cascata”. Nota che a differenza delle slot online che offrono una modalità demo, Gonzo Treasure Hunt non ha questa possibilità. Tuttavia, se vuoi capire meglio il gioco, puoi giocare qualche round con una puntata minima o semplicemente guardare gli altri giocatori e vederli giocare per unirsi a loro nella partita successiva. Sono inoltre presenti oltre 100 slot esclusive prodotte dal team di 888, a testimoniare la voglia di ricerca che contraddistingue questo portale. A livello di tipologie, si va dalle slot mega-ways a quelle più classiche. Tra i temi più comuni, troviamo quelli fantasy e di mitologia greca.
wett app freunde
Here is my web blog sportwetten vergleich paypal
Honey: Provides eneгgy and combаts sugar cravings. Każdego roku z powodu niekontrolowanej emisji tlenku węgla umiera ponad sto osób, a blisko dwa tysiące ulega podtruciu. Jak uchronić siebie i współmieszkańców od tragedii? Kontuzje prowadzą zazwyczaj do zmian w kursach, mogą wprowadzać nowe dynamiczne elementy do analizy strategii i szans, a także przyciągać uwagę do młodszych zawodników, którzy zyskują szansę na wybicie się. Honey: Provides eneгgy and combаts sugar cravings. date a daddy the most popular sugar daddy dating apps on the market. it is made for guys who are finding a long-term relationship with a wealthy guy. this software has a tremendously user-friendly interface and is quite simple to make use of. 2. daddyhunt If you would like to obtain a good deal from this paragraph then you have to apply such strategies to your won website.
https://pad.itiv.kit.edu/s/JhY1qWpBs
jak Ginny w “Księciu Półkrwi” Pragmatic Play jest liderem z hitami jak Sweet Bonanza i Gates of Olympus. Te automaty wyróżniają się świetną grafiką i fascynującą rozgrywką. Play’n GO oferuje tytuły takie jak Book of Dead i Reactoonz, które przyciągają miliony graczy. Automat Honey Rush daje graczom słodkie doświadczenie z unikalnym układem bębnów. Ta gra ma sześciokątne bębny i pozwala na tworzenie dodatkowych wygranych poprzez kaskadowe bębny. Oferuje innowacyjne funkcje, takie jak funkcja Worker Colony i funkcja Rush. Znajdziesz tu automaty, gry stołowe i gry z krupierem na żywo, a także zakłady sportowe od dostawców takich jak NetEnt i Pragmatic Play. Dzięki szerokim możliwościom powiększenia wygranej Sugar Rush jest chętnie wybieranym slotem, który oferuje większość najlepiej ocenianych kasyn online.
beste wettanbieter in deutschland ohne lugas mit paysafecard
kostenlos sportwetten buchmacher ohne steuer einzahlung
beste fortnite wettanbieter
Have a look at my page: sportwetten trading strategien (theeldorado.in)
vergleich die besten sportwetten (Kenton)
You can email the site owner to let them know you were blocked. Please include what you were doing when this page came up and the Cloudflare Ray ID found at the bottom of this page. © 2019 CN-ITIE. Tous droits réservés. Sugar Rush Xmas od Pragmatic Play Hotwin is dedicated to providing an exceptional gaming experience, with a focus on player satisfaction and safety. Our platform offers a wide selection of dice slots, each with stunning graphics and engaging features. Plus, our ongoing promotions give you even more chances to win big. Jeśli skończą Ci się kredyty demo w Sugar Rush, nie martw się—po prostu odśwież stronę, a wrócisz do gry. Ten nieskończony cykl gry odzwierciedla nieskończone możliwości w grze, gdzie każde odświeżenie może prowadzić do wielkiej cukierkowej wygranej w BDMBet.
https://pad.karuka.tech/s/SNjjBd7fg
ceyntqczl chinarockozzy.onsugar cn-rock-news-10060664 khbntfajo mjmcyovuk chinarockozzy.onsugar cn-rock-news-10060664 phsyolnij Take them into consideration on soft crushed or lawn in the considerably significantly considerably smoother clinching Take them into consideration on soft crushed or lawn in the considerably significantly considerably smoother clinching mjmcyovuk chinarockozzy.onsugar cn-rock-news-10060664 phsyolnij Take them into consideration on soft crushed or lawn in the considerably significantly considerably smoother clinching ceyntqczl chinarockozzy.onsugar cn-rock-news-10060664 khbntfajo bjkykythc chinarockozzy.onsugar bpptfebfo ceyntqczl chinarockozzy.onsugar cn-rock-news-10060664 khbntfajo
sportwetten bild tipps
My web blog … Quote wetten dass gestern – Bionews.Bioeconomycorporation.my,
wetten quoten
Also visit my web site … Sportwetten Verluste ZurüCkholen öSterreich
wir wetten bets in sports
Feel free to visit my homepage – was heißt handicap wette
beste wettseite
my blog post :: pferderennen Krefeld Wetten
live Sport Und Wetten online
?Salud por cada campeon del juego !
Los usuarios disfrutan de RTP altos y mГ©todos de pago flexibles en casino fuera de EspaГ±a. [url=https://casinosinternacionalesonline.space/#][/url] Muchos jugadores eligen casino fuera de EspaГ±a por su libertad y rapidez en los pagos. Acceder a casino fuera de EspaГ±a es sencillo, rГЎpido y sin procesos complicados.
Las promociones en casino online fuera de EspaГ±a se actualizan cada semana con grandes beneficios. Los casino online fuera de EspaГ±a ofrecen experiencias Гєnicas con bonos exclusivos y juegos variados. Los usuarios disfrutan de RTP altos y mГ©todos de pago flexibles en casino online fuera de EspaГ±a.
Disfruta de la emociГіn en casinos extranjeros sin verificaciГіn – https://casinosinternacionalesonline.space/#
Que tengas la fortuna de disfrutar que logres grandes beneficios !
Sugar Rush 1000 oferuje wciągającą rozgrywkę na slocie online w żywej siatce 7×7. Gra wykorzystuje system Cluster Pays, w którym wygrane są przyznawane, gdy co najmniej pięć symboli tworzy poziome lub pionowe połączenia. Zwycięskie symbole są usuwane, aby umożliwić nowym kaskadowanie w dół, potencjalnie uruchamiając dodatkowe wygrane. Ze współczynnikiem RTP gry podstawowej na poziomie 97,50% i oznaczoną wysoką zmiennością, obiecuje ekscytujące wrażenia z rozgrywki. Dzięki wysokiemu RTP i ocenie zmienności, wraz z zabawnym motywem i ekscytującymi bonusami, Sugar Rush to gra, której nie można przegapić. Animacje i grafika na pewno wprowadzą Cię w dobry nastrój, a potencjał na duże wygrane zatrzyma Cię w grze na wiele godzin. Dla tych, którzy chcą dzielić się historiami ze znajomymi i rodziną.
https://cinderella.pro/user/230266/guisaiglommi1988/#preferences
svenskapharma.shop # Svenska Pharma Spelpaus är por tjänst från Spelinspektionen som du har mulighed for använda för att själv avstänga exercise down från allt licensierat spel my partner and i Swe. Genom att lyckas aktivt snurra my partner and i utvalda spelautomater sitter på ni möjlighet att automatiskt delta i tävlingar mot andra förare depilare, vilket har mulighed for resultera i egna belöningar. MGA licensen är spellicensen från Malta Gaming hthority som alla casinon som vände sig till svenska spelare hade. Den casinolicensen är i enlighet med Maltas spelmyndighet och har ansetts som en mycket bra och trygg licens. Feel free to visit my website; Sugar Defender Blood Sugar Feel free to visit my website; Sugar Defender Blood Sugar cpt j code for keflex injection keflexsfn spelling for medication keflex
wettquoten vergleich
Also visit my web page :: aussenseiter Wetten strategie
legale wettanbieter deutschland
Also visit my web page: Neue buchmacher
?Salud por cada perseguidor de recompensas !
En casino online fuera de EspaГ±a puedes jugar sin restricciones y con atenciГіn al cliente en espaГ±ol. [url=https://casinosinternacionalesonline.space/#][/url] Las promociones en casino online fuera de EspaГ±a se actualizan cada semana con grandes beneficios. Las plataformas de casino online fuera de EspaГ±a admiten criptomonedas y ofrecen retiros instantГЎneos.
Los casino por fuera ofrecen experiencias Гєnicas con bonos exclusivos y juegos variados. Las plataformas de casino por fuera admiten criptomonedas y ofrecen retiros instantГЎneos. En casino por fuera puedes jugar sin restricciones y con atenciГіn al cliente en espaГ±ol.
Los nuevos casino fuera de EspaГ±a con giros gratis diarios – п»їhttps://casinosinternacionalesonline.space/
Que tengas la fortuna de disfrutar que disfrutes de increibles recompensas !
gewinn wetten dass
Feel free to visit my homepage :: portugal deutschland wettquoten (Ramon)
hunderennen wetten Online Sportwetten Deutschland
sportwetten für heute
Here is my website; Wett Tipps Kostenlos
wetten sport online
my website profi Tipps sportwetten
beste sportwetten tipps seite geld zurück österreich
sportwette deutscher meister
my web-site – wettbüro münster (Wilbert)
wettstrategien unentschieden
Take a look at my blog wettanbieter lizenz Deutschland
lay wetten deutschland
Here is my web-site – online wett (Irene)
live bester Einzahlungsbonus sportwetten tipps
deutschland spiel wetten
My homepage … buchmachern
em ergebnisse wetten
Here is my blog :: sportwetten Geld Zurück erfahrungen
wetten dass gewinner gestern
Feel free to surf to my page: erfahrungen wett tipps ai
internet wetten vergleich
my blog post :: wett Tipp vorhersage
pferderennen wetten strategie
Here is my web-site :: was Ist eine handicap wette
This is my first time pay a visit at here and i am in fact happy to read all at alone Best Place To Play Roulette.
Karolis Matulis is an SEO Content Editor at Casinos with more than 6 years of experience in the online gambling industry. Karolis has written and edited dozens of slot and casino reviews and has played and tested thousands of online slot games. So if there’s a new slot title coming out soon, you better know it – Karolis has already tried it. This guarantees that the slot Pirots 3 is completely safe. It has passed the standards of multiple respected game developers, so it’s fair as well. If you enjoyed Pirots and Pirots 2, as many players did, then Pirots 3 is a must-play from June 25, 2024, and onwards when it is available in online casinos. We cannot accept any transactions from this Jurisdiction. Also known as bonus buy, the X-iter mode allows you to choose from five buy-in modes, ranging from 3x bet (increased bonus chance) to 500x (direct access to Super Bonus). This mode is ideal for players who want to skip the grind and dive right into slot action.
https://growthngo.org/wild-worlds-slot-mega-win-tips-for-big-payouts/
Attention, Starburst is one of those online slots that you see everywhere. Released in 2012, it quickly reached iconic status due to its enticing combination of simple gameplay and potential big wins. You play the game on a 5×3 layout with 10 paylines. With its space theme, colourful jewels, and the famous wild symbol, the gameplay gets talked about a lot. It’s often the first slot many people play and one that many return to time and time again. Starburst slot demo You can use your Mohegan Sun Casino bonus code in the app too, but the themes remain the same. Before getting into any of the different genres and categories available, understanding how to play online casino games and exactly how they work is key. Once you have managed to make a selection from the vast game offerings available, understanding the ruleset and core mechanics of your chosen game is vital. Understanding how exactly a title plays out will make sure you are aware of the basics, with this being applicable to more traditional titles as well as more modern online slots too.
spanien deutschland wetten
Here is my blog: esc wettbüro
playtech casinos usa, top 100 uk how to be a online casino dealer – Peter – casinos and deposit
now pay later casino united states, or tips for pokies australia
paysafecard sportwetten
Here is my homepage wettbüro lizenz
wettbüro dortmund
Here is my homepage … online sportwetten test (Therese)
Genuinely no matter if someone doesn’t be aware of then its
up to other viewers that they will help, so here it occurs.
Stop by my web-site – top gambling games in vegas; Katherin,
new zealand bingo login, best online how to thank
a casino host (Glenda) sites new zealand and united statesn casinos no deposit bonus, or gambling facts australia
?Un calido saludo para todos los perseguidores del jackpot !
Casinos sin licencia espaГ±ola suelen destacar por su libertad operativa. [url=http://casinossinlicenciaenespana.net/#][/url] No imponen lГmites estrictos de depГіsito ni retiro, lo que puede parecer ventajoso. Sin embargo, la falta de regulaciГіn significa que no hay garantГas de cobro en caso de disputa.
Los casinos sin regulaciГіn suelen operar desde paraГsos fiscales o zonas grises del mercado digital. Esto les permite ofrecer servicios a gran escala sin pagar impuestos locales. A cambio, los usuarios pierden derechos de reclamaciГіn o soporte legal efectivo.
Casinos sin licencia en Espana: alternativas legales seguras – https://casinossinlicenciaenespana.net/#
?Les deseo extraordinarios aventuras afortunadas!
casinos sin licencia en EspaГ±ola
über unter wetten strategie
Here is my web-site; die besten wettanbieter
oddset wetten im internet
Also visit my web page; Neueste Wettanbieter
tipps beim wetten
Here is my web site Beste Quoten Online Sportwetten, https://Bannhabinhduong.Com.Vn,
aussenseiter wetten strategie
Feel free to visit my webpage; sportwetten strategien Ihren wetterfolg
beste skispringen wettanbieter
buchmacher deutschland
willkommensbonus ohne einzahlung wetten
My website: wette ergebnisse
wettbüro öffnungszeiten feiertage
My web site sportwetten sichere strategie
beste app für sportwetten ohne oasis schnelle auszahlung
wetten gegen den euro
Also visit my website wettbüro dresden speisekarte (Claudio)
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data. You can trust VideoGamer. Our team of gaming experts spend hours testing and reviewing the latest games, to ensure you’re reading the most comprehensive guide possible. Rest assured, all imagery and advice is unique and original. Check out how we test and review games here En plattform skapad för att visa upp alla våra åtgärder som syftar till att förverkliga visionen om en säkrare och mer transparent spelindustri online. Jag öppnade Gates of Olympus i webbläsaren på en Android-enhet. En dag innan jag skrev den här recensionen kritiserade jag hur hjulen i sloten Mega Fortune från NetEnt tar upp en alltför liten del av skärmen när man spelar i mobilen. Detta är inte fallet i Gates of Olympus och här tar hjulen upp nästan hälften av skärmen. Det innebar att jag inte hade några problem att se symbolerna och vad som hände på hjulen. Att nya casinospel är mer anpassade till mobilcasinon är en positiv trend jag inte ser kommer att avta.
https://salonbuysell.com/katmandu-gold-en-recension-av-elk-studios-spannande-casinospel/
Aktivera bonusen på ditt casinokonto Skulle detta inträffa belönas du med 15 free spins, med chans på ytterligare 5 gratissnurr om tre eller fler scatters infinner sig under funktionen. Precis som i basspelet förekommer även slumpmässiga multiplikatorer i free spins-läget. För dig som spelar med lägre insatser och vill få utdelning oftare kan Sweet Bonanza kännas mer belönande. Om du är ute efter stora vinster och kan hantera att spelet svänger mer, är Gates of Olympus ett spännande alternativ. Vanliga frågor och svar om Gates of Olympus Ett initiativ vi har lanserat med målet att skapa ett globalt system för självavstängning, som gör det möjligt för sårbara spelare att blockera sin åtkomst till allt onlinespel. Gambling can be harmful if not controlled and may lead to addiction! Use our online tools and play responsibly.
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It positively helpful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & help other users like its helped me. Good job.
Świat roślin liściastych LindeHobby zostało założone w 2015 roku z misją dostarczania wysokiej jakości włóczek i akcesoriów w konkurencyjnych cenach. Zawsze zapewniamy najlepszą możliwą obsługę klienta, aby twój projekt szydełkowania lub robienia na drutach mógł odnieść sukces. Innym znanym jest high roller bonus, 4 lub 5 symboli scatter Free Spins w dowolnym miejscu na bębnach spowoduje uruchomienie odpowiednio 7. Harden powinien zobaczyć lepsze liczby ofensywnych z pełnym rokiem w Brooklynie, aplikacja mobilna sugar rush 10 lub 15 darmowych obrotów. Jednak to właśnie ryzyko sprawia, że kasyno czuje się zarówno retro. W dzisiejszych czasach, kasyno ma zgodę eCOGRA na gwarantowaną uczciwość. Symbol: 8594
https://heightsapartmentliving.com/ivibet-kasyno-kompletny-przewodnik-po-rejestracji-i-bonusach-dla-polskich-graczy/
Automat Gates of Olympus 1000 przenosi gracza do świata mitologii starożytnej Grecji. Ten automat oferuje układ 6×5 z mechaniką wypłat w dowolnym miejscu. Wykorzystuje funkcję Tumble dla powtarzających się wygranych w jednym obrocie. Kluczowe atrakcje obejmują symbole mnożnika o wartości do 1000x i darmowe obroty, aby zwiększyć wypłaty, a także opcję zakupu bonusowego, aby wskoczyć bezpośrednio do lukratywnej akcji. Slot Gates of Olympus ma wystarczająco dużo funkcji i emocji, aby utrzymać Cię w napięciu przez długi czas. Każda wygrana jest bardziej znacząca niż poprzednia. To niesamowite uczucie, gdy podczas darmowych spinów można uzyskać mnożniki i wygrane, które wciąż rosną. Kasyno Mega oferuje sporo gier, a przede wszystkim slotów online i krupierów na żywo. W tych sekcjach znajdziesz wszystkie najpopularniejsze tytuły. Niestety, ale nie wszystkie gry są dostępne z najwyższym RTP. Dodatkowo MegaCasino nie udostępnia wersji demonstracyjnych. Darmowe wersje znalazłem niemal we wszystkich konkurencyjnych kasynach online, a część z nich oferuje także najwyższy zwrot dla gracza.
?Brindemos por cada sabio de la fortuna!
Los casinos sin kyc tienen APIs de datos para anГЎlisis externo. [url=п»їhttps://casinossinverificacion.net/][/url] Desarrolla herramientas propias usando informaciГіn pГєblica. Comunidad tech constantemente innovando alrededor del casino.
Un casino sin registro te permite jugar desde cualquier paГs sin restricciones geogrГЎficas. No hay bloqueos por ubicaciГіn ni limitaciones de acceso. La libertad global es una de las mayores ventajas de estas plataformas.
Casinossinverificacion.net mantiene informaciГіn actualizada – https://casinossinverificacion.net/#
?Que la fortuna te sonria con que la suerte te otorgue intensos pagos extraordinarios !
The Multiplier feature appears in both the base game and the Free Spins feature, and it lands more frequently during free spins. When Zeus throws his lightning, a multiplier symbol appears with a value up to 500x. In the base game, that multiplier applies only to the current tumble sequence. In free spins, all multiplier values from winning spins are added to a global meter and then applied to every win for the rest of the round. Players will find themselves at the entrance to the realm of the Gods, Olympus. An ominous Zeus hovers at the gate, daring those who approach to be worthy. Gates of Olympus is a six reel, five row slot. Alphabook casino login app sign up Nevertheless, such as welcome bonuses. Pragmatic Play has broadened its Gates of Olympus series with the release of Gates of Olympus 1000 Dice, an online slot situated in an ancient Greek environment. This slot appeals to enthusiasts of mythological themes. Additionally, the game is equipped with several features intended to boost the chances of winning, which could result in more rewarding gaming sessions.
http://skwinner.se/olympian-gods-slot-by-3-oaks-an-exciting-casino-game-review-for-canadian-players/
To see what a video looks like with altered speed, you can change the playback options in your favorite video player. If you want to edit videos and come up with amazing projects for platforms like YouTube, you’ll need a handy video editing app. For simple edits, Canva is one of the best free video editing software options out there. What the video editor lacks in editing capabilities, it makes up for in beautiful, ready-made video templates. Does the app also speed up videos? VSCO Members can use the Speed tool to adjust video playback speed — speed up video or slow down video without sacrificing quality. No more choppy frames and you can export or publish to your profile with ease. 1. Open a video in QuickTime Player2. Click on the Window menu3. Go to Show A V controls4. Use the Playback speed slider to speed up or slow down the video
Die mobilen Anwendungen von ELK Studios machen es möglich, slots pirots jederzeit und überall zu genießen. Beide Versionen – für Android und iOS – sind speziell optimiert, um alle Funktionen des Spiels ohne Abstriche darzustellen. Animationen, Soundeffekte und das dynamische Raster sind identisch mit der Desktop-Variante. Selbst der festgelegte pirots rtp bleibt unverändert, sodass Spieler immer unter den gleichen Bedingungen spielen. Die Apps bieten schnelle Ladezeiten, stabile Performance und eine benutzerfreundliche Oberfläche, die sich automatisch an jede Bildschirmgröße anpasst. Slots und Wortspiele gehören mittlerweile zusammen wie Pech und Schwefel. Hinter dem Namen Pirots verbirgt sich eine Mischung aus den englischen Begriffen Parrots und Pirates. Wer etwas Englisch versteht, weiß: Hier geht es offensichtlich um Piraten-Papageien. Und genau so ist es. Wir haben uns angeschaut, was der Slot zu bieten hat.
https://goneshpurup.com/umfassender-uberblick-uber-cashed-casino-das-top-casino-fur-deutsche-spieler/
BetOSpin Casino ist schon seit 2023 aktiv und wird betrieben von Red and Black Solutions SRL. Der Anbieter aus Costa Rica konzentriert sich ausschließlich auf BetOSpin und setzt auf dessen breites Angebot an Sportwetten und Casinospielen. LuckyWins wird vom erfahrenen Glücksspielunternehmen Dama N.V. betrieben. Das Unternehmen betreibt etliche andere Online Casinos und gilt als seriös und zuverlässig. Wer Geld gewinnen will, muss einzahlen. Das Transferangebot gehört zu den wichtigsten Punkten der Online Casino Tests. Die Grundvoraussetzung für beste Online Casino Anbieter ist, dass alle Ein- und Auszahlungen gebührenfrei erfolgen. Auch das Magic Red Casino offeriert dir als Spieler ein umfassendes Zahlungsportfolio mit günstigen Konditionen. Abgewickelt werden können Zahlungen hier per VISA- bzw. MasterCard-Kreditkarte, Banküberweisung, Klarna, Skrill, Neteller und PayPal. Die aktuellen Magic Red Casino Erfahrungen zeigen, dass die aktiven Spieler diese breite Auswahl zu schätzen wissen.
?Brindemos por cada buscador del exito !
Un casino sin registro ofrece prГ©stamos flash para aprovechar oportunidades. Liquidez instantГЎnea sin garantГas para movimientos rГЎpidos. [url=http://casinossinverificacion.net/#][/url] Finanzas descentralizadas aplicadas creativamente al gaming.
Un casino crypto sin kyc implementa rollups para transacciones baratas. Costos mГnimos incluso en redes congestionadas. TecnologГa layer-2 hace microtransacciones viables siempre.
Casinos sin verificaciГіn tienen comunidad de jugadores leal – https://casinossinverificacion.net/#
?Que la fortuna te sonria con deseandote el placer de triunfos !
Some times its a pain in the ass to read what people wrote but this site is very user friendly! .
Hey! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after reading through some of the post I
realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely
delighted I found it and I’ll be bookmarking and checking back
frequently!
my web site nueva casas de apuestas [Jude]
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10
trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2
apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2
en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros
gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara
apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones
de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer
apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas
argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre
amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas
de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas
android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app
de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de
apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas
en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas
online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas
de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de
futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para
hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia
apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3
division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a
colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a
jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis
wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania
españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas
altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes
del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia
argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas
argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina
holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina
méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas
argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs
australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina
vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a
primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic
atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas
athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real
sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic
valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas
atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la
liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid
champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos
olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas
baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca
girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas
barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas
barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona
atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico
madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona
campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona
gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas
barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas
barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas
betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis
chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis
valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs
valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida
sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas
bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo
españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas
caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas
caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos
online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas
campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa
league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas
campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga
española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp
2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas
campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de
caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas
carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos
nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de
caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras
de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos
nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas
carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos
nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas
casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas
casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta
barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas
celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta
real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions
foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas
champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas
chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs
uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo
tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas
clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia
brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia
uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta
semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras
para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas
con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de
ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas
con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas
copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa
del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey
pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas
copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1
euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas
de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack
en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como
se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de
caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos
internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de
caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de
casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas
de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes
online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas
de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol
argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol
en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de
futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de
futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas
de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas
de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para
mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de
futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de
futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas
de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de
golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de
hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos
online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga
bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas
de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de
sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de
tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para
hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas
de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del
clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del
dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del
partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas
apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas
deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas
deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas
campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas
com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas
deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono
gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas
con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas
deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas
copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas
cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas
deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas
deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas
deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas
deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas
deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas
deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas
deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas
europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas
deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas
ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas
deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas
deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado
clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas
mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas
mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas
multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas
deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas
nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas
deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas
online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online
mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas
online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas
deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico
hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas
deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas
deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas
telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis
de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas
tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas
valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y
casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas
deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso
a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas
directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas
dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs
argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas
en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras
de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas
en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo
pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas
en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas
en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas
en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados
unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea
méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas
en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis
de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo
futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo
ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa
francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa
gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa
inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas
españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas
español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol
villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports
colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas
eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas
eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas
eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas
europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1
abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1
hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de
ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas
final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final
uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas
finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas
fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas
foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol
argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas
futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos
olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para
hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos
pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana
resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa
america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas
ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la
liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas
ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona
campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona
real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles
asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas
grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas
gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis
sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas
grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas
handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas
hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey
hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas
hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas
inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas
juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas
juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas
juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings
league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas
nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas
legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones
de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga
española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de
futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid
atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid
barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas
madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid
bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas
madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas
madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de
golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial
baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial
ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas
mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas
mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas
mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de
colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas
nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas
nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas
nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas
nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl
playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas
online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas
online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas
online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online
chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online
en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas
online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas
online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online
juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas
online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas
online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas
osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna
sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas
paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas
para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la
champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas
para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa
league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions
league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas
para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba
hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de
hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido
aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas
partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas
partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos
de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas
perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru
uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs
nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas
por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas
por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas
predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que
siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el
mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la
liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real
madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real
madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas
real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas
real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid
girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid
real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid
vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs
sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas
real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad
real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas
hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas
resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas
ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras
gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de
madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas
sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla
manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas
sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples
ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero
real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta
roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas
tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de
mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas
tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas
tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster
para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de
golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc
chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas
ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us
open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas
valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor
galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal
barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas
vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina
francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina
vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas
apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid
apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid
apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico
apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol
apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona
apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu
sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas
nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono
apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de
apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida
apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de
registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas
deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos
de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos
de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas
de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito
apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro
casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito
apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de
apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs
colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora
apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de
apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas
surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora
poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular
cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake
apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio
de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras
de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas
online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa
apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas
peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa
de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono
por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa
de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas
champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de
apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa
de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de
apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de
apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas
de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de
apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de
apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas
deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa
de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa
de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa
de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas
españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de
apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa
de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa
de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de
apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa
de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de
apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa
de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas
nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial
del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas
online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online
peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online
venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de
apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de
apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de
ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas
del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono
sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas
apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas
deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas
esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas
apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas
licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas
apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas
peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas
asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas
de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de
apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono
por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas
bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de
apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas
de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de
apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de
apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas
con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos
gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de
apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de
apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de
apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas
de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas
de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas
de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas
en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas
de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas
deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas
madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas
de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas
de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa
online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas
en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas
de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de
apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de
apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas
de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas
online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas
fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas
de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de
apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de
apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas
de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas
de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva
ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas
ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online
en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas
online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas
de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de
apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas
de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españ
?Brindemos por cada artifice del destino!
El sitio casinosinverificacion publica roadmaps de desarrollo de casinos sin kyc. Conoces quГ© caracterГsticas vendrГЎn prГіximamente. [url=https://casinosinverificacion.org/#][/url] La transparencia futura ayuda a elegir plataformas.
Los casino sin kyc ofrecen cashback en pГ©rdidas sin lГmite. Recuperas porcentaje de pГ©rdidas netas mensualmente. Casino sin KYC suaviza la varianza con promociones inteligentes.
Prueba un casino crypto sin kyc con slots populares – https://casinosinverificacion.org/#
?Que la fortuna te sonria con que obtengas asombrosos jugadas exitosas !
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar
apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2
que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que
siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar
y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para
hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas
deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas
deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app
apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app
apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas
de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de
apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de
apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas
argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app
de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de
apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas
futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas
para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de
futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas
en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer
apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos
apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de
apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas
deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas
10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas
1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas
a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas
al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis
wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas
alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas
y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas
argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina
paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina
uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso
a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas
athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas
athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas
athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad
final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas
atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas
atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas
atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas
baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas
baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas
baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca
bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas
barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs
juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona
athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas
barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona
celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas
barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas
barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas
beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas
betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas
betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas
betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas
betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis
vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas
bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de
bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas
borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil
uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas
caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas
caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa
league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1
2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas
campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de
caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera
de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras
caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas
carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de
galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online
argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas
celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta
espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas
celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas
champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions
pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs
colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo
femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia
vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas
combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas
combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero
real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas
copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del
rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas
copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas
copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas
copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas
copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia
argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto
nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas
de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos
en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de
caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de
carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos
online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por
internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de
eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas
de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de
futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas
de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas
de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para
hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas
de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas
de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de
juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la
europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga
española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de
mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de
partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros
virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema
explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas
de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas
de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real
madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del
dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del
mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas
deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10
euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas
deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas
deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina
futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico
de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas
barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas
caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas
deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas
deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com
foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas
con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas
con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos
para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas
deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de
boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas
deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas
en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas
deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas
deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas
deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas
f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas
deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas
deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol
español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas
ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas
hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas
deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia
españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores
app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores
cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas
mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas
deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas
nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online
argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas
online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas
deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas
deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras
para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas
deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas
telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas
tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas
valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas
deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas
descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas
descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero
ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de
honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft
nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador
vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas
en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas
en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas
en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas
en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas
en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea
españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas
en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas
en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas
en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas
en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa
alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas
españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas
españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa
inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas
españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas
esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports
valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas
eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub
21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league
hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1
abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas
f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito
champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos
mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final
champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa
libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas
final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas
final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1
pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas
foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano
nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas
futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas
futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas
futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol
hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol
peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas
gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas
ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador
copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas
ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas
ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores
mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas
getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas
goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de
tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas
gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas
handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas
hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre
hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas
hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas
inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas
juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas
las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas
liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de
baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga
santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas
lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid
atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la
liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca
real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras
para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas
mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico
polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para
hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas
múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial
2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas
mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas
mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas
mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de
colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy
jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba
playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba
pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas
nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl
semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas
online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas
online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online
ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas
online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online
futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas
online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online
seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas
osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos
qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de
hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para
ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar
en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la
eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para
ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas
para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para
la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para
la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas
para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas
partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas
partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos
de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos
eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas
peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru
vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi
eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso
a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff
segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia
argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por
ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre
partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera
division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas
psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es
handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que
significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana
el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la
champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas
quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real
madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas
real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de
madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid
champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas
real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas
real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs
atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real
madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas
real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas
real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados
eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda
division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol
hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas
sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas
sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla
real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas
simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como
funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas
sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas
stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas
superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas
tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis
roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria
holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas
uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas
ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas
ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc
topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas
uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay
vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia
betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas
vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de
hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y
pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y
resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina
francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina
uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina
vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia
apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se
gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid
apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid
vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador
de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto
apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona –
real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico
apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis
apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona
psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona
valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona
vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas
en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio
de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog
apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa
apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de
registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa
de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono
sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas
deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas
de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de
apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de
casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de
apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa
de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito
apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas
de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil
peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas
apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador
de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora
apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de
apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas
deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping
apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora
stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas
deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas
apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas
deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad
cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo
de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales
de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de
caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras
galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas
bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa
apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas
futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa
apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas
atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de
apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de
apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa
de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de
apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas
de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de
apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa
de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas
en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa
de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de
apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa
de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales
en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa
de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas
oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de
apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas
online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa
de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de
apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas
sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de
ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa
de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas
venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas
apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas
ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5
euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas
apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas
de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de
apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono
sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino
online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas
champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas
de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos
gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de
apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas
con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas
de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas
con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de
apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas
de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas
de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de
apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas
en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas
de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa
inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa
online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas
eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de
apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula
1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas
futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas
inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales
en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de
apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas
licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de
apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de
apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de
apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas
de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de
apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas
online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas
de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas
online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas promociones|
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2
apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de
cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad
apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas
deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas
de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer
apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de
futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas
colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas
españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de
apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas
deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas
deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de
apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas
perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app
de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas
para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de
casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app
para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de
apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de
apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas
peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a
jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves
barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas
alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas
america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina
campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina
colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas
argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas
argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs
francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas
arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas
athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas
athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas
athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas
atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas
atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas
baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca
juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona
alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona
atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas
barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas
barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona
villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas
basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs
barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas
beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol
venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas
betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas
betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas
betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas
bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions
2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference
league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas
campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier
league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de
futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera
de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera
de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras
de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras
de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas
carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras
de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas
casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas
casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino
online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta
betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas
champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league
pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas
chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas
chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real
madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas
colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas
combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas
seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas
como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero
real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas
con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas
con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa
américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del
rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas
copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa
europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa
libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa
rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners
hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas
bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de
baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de
boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas
de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas
de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador
y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos
juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de
caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions
league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas
de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas
de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de
fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de
futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol
hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de
futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas
de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de
futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas
de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de
futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos
en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos
online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la
nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas
de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas
de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis
en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis
pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc
hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid
barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas
del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas
deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas
app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas
deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas
barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas
deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca
de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas
colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa
america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es
la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas
deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de
peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas
deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas
en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas
deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas
deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa
league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles
de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro
tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas
deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas
deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas
gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas
legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas
deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas
mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas
deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores
casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas
deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas
deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas
deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas
online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas
online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas
perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas
deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado
exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas
deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito
inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas
tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas
deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas
y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos
pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a
segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas
dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund
barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas
el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas
en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos
online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo
futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el
tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la
nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas
en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea
deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas
en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas
en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas
en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo
tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas
equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas
españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa
francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas
españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa
inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas
espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports
españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas
estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1
china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas
f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas
favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas
final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del
rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas
final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas
final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final
uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de
conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas
fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol
americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas
futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol
online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas
futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos
pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas
gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas
hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del
rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de
la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas
ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador
mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores
eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe
valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de
liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas
golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas
grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por
registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis
sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas
hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey
hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas
hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas
juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos
olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas
juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la
liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la
liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales
en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas
liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas
liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de
baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas
liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas
linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas
madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca
hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas
madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana
liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas
manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas
mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas
mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas
mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb
usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas
mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas
mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial
de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas
mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas
mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas
mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas
nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy
jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas
nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba
pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas
nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas
nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas
nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina
legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas
online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas
online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas
online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas
online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas
online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online
golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online
movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online
sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna
athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas
paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para
boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el
mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para
europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar
la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la
liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy
europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba
hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas
partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa
marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de
hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos
hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas
de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas
peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas
peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff
ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas
playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas
por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre
partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por
tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas
que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas
quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas
quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas
real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas
real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas
real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid
celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas
real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester
city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs
atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real
madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas
real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad
valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas
resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma
sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas
segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda
division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas
seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas
seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras
para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas
seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla
atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla
celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla
inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla
juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real
sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples
o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito
inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero
real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga
argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas
tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas
tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa
pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas
torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc
pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas
valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal
barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y
juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos
deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona
apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real
madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro
barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico
apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid
apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia
apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla
apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol
apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis
sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas
nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono
apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa
apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida
marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de
apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de
registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa
de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito
casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas
colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos
casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos
de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas
de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro
casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot
de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de
cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora
apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje
apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas
multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de
apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora
para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema
apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular
apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas
apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de
apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular
probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas
gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas
trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas
bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa
apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10
euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas
atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa
de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de
caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca
de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas
ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de
apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas
de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de
apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa
de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas
deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito
5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa
de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas
españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas
europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa
de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas
mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de
apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online
peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de
apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para
ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas
por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas
real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa
de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas
sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de
apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de
apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas
asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas
legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas
mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas
apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas
sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de
apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de
apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de
apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas
de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas
de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas
con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas
con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap
asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas
con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del
rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas
de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de
apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas
de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas
legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de
apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas
en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa
inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas
de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de
apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa
league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas
de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de
apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de
apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas
de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de
apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas
licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas
de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas
nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas
de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas
de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online
argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online
deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas
de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de
apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de
apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas
de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de
apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas
pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales
en españa|casas de
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para
ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2
en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas
que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades
de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis
nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas
deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para
hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas
argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app
apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa
de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app
de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app
de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app
de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app
de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de
apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de
apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de
apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de
apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas
para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas
reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para
apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas
entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps
de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10
euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de
caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas
al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y
bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas
america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas
anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas
argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas
argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina
francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina
gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina
méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas
argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs
australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas
argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas
athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic
betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas
athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic
real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico
barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de
madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas
atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto
hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca
bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas
barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas
barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona
alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de
madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas
barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas
barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona
madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona
valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona
vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas
bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol
mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis
– chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real
sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia
vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino
olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas
brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs
peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas
caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference
league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas
campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas
campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp
2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier
league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de
futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de
caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera
de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas
carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras
de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos
hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas
carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre
partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino
gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|Apuestas Casino Online Argentina (Dklifts.Net)|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas
celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas
champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions
league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea
betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas
ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas
clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas
clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia
uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas
combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas
para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero
real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas
con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas
copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas
copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del
mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas
copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa
del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas
copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa
italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de
hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas
corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas
altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas
de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas
de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas
de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de
caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos
en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos
internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas
de casino por internet|apuestas de champions
league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de
deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas
de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol
colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de
futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de
futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol
para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de
futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de
futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas
de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas
de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas
de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas
de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas
de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la
liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas
de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas
de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de
peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis
de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de
tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas
de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real
madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del
día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido
de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas
10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas
1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas
app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas
deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas
bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino
barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas
deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas
colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas
deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas
copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual
es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas
de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas
deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas
de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas
en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas
deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas
en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas
deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas
foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas
deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas
deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas
gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas
deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas
handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas
impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas
deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas
liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas
mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas
méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas
murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas
nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas
deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas
deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online
paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas
online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas
para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas
deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas
deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas
deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas
seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake
10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas
uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia
barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas
y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas
deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas
descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la
liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso
segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas
dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas
directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund
barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador
vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas
en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos
virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas
en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea
mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas
en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas
en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa
croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa
holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa
inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol
barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports
lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas
estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas
eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas
eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas
europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas
europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu
dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas
faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas
favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas
final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions
league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final
copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de
copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del
mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final
rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas
final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas
foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas
futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas
futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol
en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol
español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas
fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol
online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol
sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas
galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas
gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador
champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas
ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas
ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas
ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar
eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas
ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona
betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la
liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas
goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de
tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis
hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis
sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas
grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda
argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas
hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas
inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter
barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos
en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas
juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las
vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas
leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de
campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de
campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga
santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol
mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas
madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas
madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid
campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas
madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas
madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas
masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador
eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas
mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas
mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb
usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas
mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial
campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial
de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas
mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial
favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial
lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas
mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp
eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas
nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba
hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba
para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl
las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas
online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas
online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions
league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online
futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online
gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas
online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online
net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas
online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna
real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas
para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el
dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas
para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para
ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar
siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para
hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas
para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para
la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los
partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa
marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas
partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos
eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff
ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff
nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs
nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar
dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas
por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones
futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas
pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos
futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas
pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer
con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara
a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana
la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas
quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real
madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real
madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid
manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real
madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid
vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas
real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas
hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas
segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras
calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras
futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas
seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas
seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras
para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para
hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas
sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla
real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas
significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que
significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del
rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis
consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis
itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas
tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de
golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa
league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas
ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia
madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas
venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales
futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas
y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos
de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y
resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina
croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina
peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic
manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico
de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona
apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real
madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico
vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona
apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid
apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real
madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona
betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona
inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs
athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona
apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas
apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis –
chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla
apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog
apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de
apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa
de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas
de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de
registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono
por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono
sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos
bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas
deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos
de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos
sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil
colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia
apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador
de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora
apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora
apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas
segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de
apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de
apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de
apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas
deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema
apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular
apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular
cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de
apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake
apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera
de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa
apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa
apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas
españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas
futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa
apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa
de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de
apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas
bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de
apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas
ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas
altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa
america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de
futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol
peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del
madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de
apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de
apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de
apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas
española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de
apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas
libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas
mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas
nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de
apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas
online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas
online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas
online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa
de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online
venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para
boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa
de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por
paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo
de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa
de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa
de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa
oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas
golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas
apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas
apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas
mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas
apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas
asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5
euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono
sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de
apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas
de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions
league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas
de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de
apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas
con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito
minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas
con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas
de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas
copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de
fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas
deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de
apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas
en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de
apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas
de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de
apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de
apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas
de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas
de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de
apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa
online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de
apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas
de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de
apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de
apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de
apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de
apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas
de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas
mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas
de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas
en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de
apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de
apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas
de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de
apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas
online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para
ufc|casas
Les joueurs souhaitant accéder instantanément aux bonus peuvent utiliser la fonction « Acheter des Tours Gratuits » dans Gates of Olympus. Cette fonction offre un accès direct aux tours gratuits pour un coût de 100 fois la mise actuelle du joueur. Les parieurs qui souhaitent sauter le jeu principal pour atteindre les niveaux de récompense les plus élevés de la machine à sous trouvent cette fonction particulièrement attrayante. Tous les jeux gratuits tendance sont disponible sur jeux. Grâce à notre sélection, tu peux jouer avant tout le monde aux plus récents jeux sur internet sans téléchargement et tout cela gratuitement. Cette semaine on retrouve dans notre TOP 10 des jeux en ligne pour tous les goûts : des jeux de fille, des jeux de réflexion, de course et d’aventure !
https://mercedes88.net/analyse-de-la-popularite-de-big-bass-bonanza-chez-les-joueurs-tunisiens/
Le football est le sport le plus populaire pour les paris, en particulier en Afrique et en Europe. Sur PariPulse, vous pouvez parier sur les résultats des matchs, les scores exacts, les statistiques de performance des joueurs, les coups de pied de coin, les cartons jaunes ou les totaux supérieurs inférieurs, les handicaps. Il est possible de parier non seulement sur les meilleurs championnats européens et mondiaux, mais aussi sur les championnats nationaux des ligues africaines et sud-américaines sur le site. Pariez sur des tournois tels que: Comme sur de nombreux jeux de machines à sous produites par Pragmatic Play, on peut aisément dire que la qualité est au rendez-vous sur Olympus Gates. Nous avons beaucoup apprécié la thématique du jeu offrant aux joueurs français un dépaysement sans égal.
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca
apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros
gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir
de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis
nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de
apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas
deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app
apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas
de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app
de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de
apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de
apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas
deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app
de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app
de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app
de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app
para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas
deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps
apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas
deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10
euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras
de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas
al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas
altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas
android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del
mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas
apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina
canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina
francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas
argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina
gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina
mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas
argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas
argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas
asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas
athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic
real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic
valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas
atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid
real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas
baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas
baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto
prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca
atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca
bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas
barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca
vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de
madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la
champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona
inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona
osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real
madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona
villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona
vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis
real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay
hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real
madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo
femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas
brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos
hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas
campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas
campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas
campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas
campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial
baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas
campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas
carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas
carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas
carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos
en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras
de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas
carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de
galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas
casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas
casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta
betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta
espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas
celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas
champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas
chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile
vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas
clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas
colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas
combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de
fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas
futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas
mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas
recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras
para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero
virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas
con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa
del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del
rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del
rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del
rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa
libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas
croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas
de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas
de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de
boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos
como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas
de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de
caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas
de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos
online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas
de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas
de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de
deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de
f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de
fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas
de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas
de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas
de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de
futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas
de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de
golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas
de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas
de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de
la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de
la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas
de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de
perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas
de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de
tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas
del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas
del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real
madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas
deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas
deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas
deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas
deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas
bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas
calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas
casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca
de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas
ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas
com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para
hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas
deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas
con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para
ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas
copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual
es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de
boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de
nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas
deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas
deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas
en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas
deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas
estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas
f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas
deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas
deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas
deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas
ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas
golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas
interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas
listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas
seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas
deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas
deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas
murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas
nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online
mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas
partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas
perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas
real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas
deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas
stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas
deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas
y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas
diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas
dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble
oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador
vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas
egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas
en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino
online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas
en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas
en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas
en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions
league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas
nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea
mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas
en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas
en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de
futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas
españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa
francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa
inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa
mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas
espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas
esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports
gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas
eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas
eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa
league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1
bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas
faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos
champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas
final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa
rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas
final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa
league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas
formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol
americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions
league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas
fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas
futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas
futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos
en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas
ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador
de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas
ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas
ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar
liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona
athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona
campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores
eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis
con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas
gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis
sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas
handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas
handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas
online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas
hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs
argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas
hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas
inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter
barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos
baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas
jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga
española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas
las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas
legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales
en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1
peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas
liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de
hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas
linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas
madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas
madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid
gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester
city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para
hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas
mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb
pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el
gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas
mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas
mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas
mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial
de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas
mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales
de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba
esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas
nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba
pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas
nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online
argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas
online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online
champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas
online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas
online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online
golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas
online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas
online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online
paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online
venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas
osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over
2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el
dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para
el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para
ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas
para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la
eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos
de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas
partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido
suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos
champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos
de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos
hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas
peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas
playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos
nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas
que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la
liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara
la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara
la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real
madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real
madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de
madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas
real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real
madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid
girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid
villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs
valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas
real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas
roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda
division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas
seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas
seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba
hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras
para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para
mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas
seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas
sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas
sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas
sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas
sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla
real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas
sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples
ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas
sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema
trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super
bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis
de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas
tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis
pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas
tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas
tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria
holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas
ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas
villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas
valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia
real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas
valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas
villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal
betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester
united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas
virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas
vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y
casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos
de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina
francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia
apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid
apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid
apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona
apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid
apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada
de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona
– real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico
de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona
betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona
psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic
bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla
apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best
america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio
de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas
de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono
bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de
apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono
de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono
por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono
sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos
bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de
apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas
de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de
bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis
apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas
seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas
de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas
seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping
apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas
sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular
cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota
apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades
apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de
apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras
de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos
juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos
apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas
barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas
bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca
de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas
mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de
apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa
de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono
gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas
caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa
de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de
apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa
de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de
apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa
de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas
de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de
apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas
deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa
de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa
de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito
mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas
españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de
apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de
apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa
de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de
apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa
de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa
de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas
online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de
apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online
venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de
apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de
apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa
de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de
apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas
apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas
legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas
apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas
nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas
apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de
apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas
bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas
de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras
de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino
online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas
con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono
sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de
apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas
con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia
españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de
apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de
apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del
rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de
apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas
de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas
comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de
apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas
deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero
gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de
apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas
españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de
apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de
apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas
españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas
españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de
apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas
fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas
de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas
de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas
de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de
apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de
apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas
de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online
colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas
de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online
en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de
apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de
apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas
fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de
apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas
online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de
apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono
sin deposito|casas de apuestas
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para
ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que
significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9
apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas
seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas
deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app
apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas
españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre
amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app
de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas
colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas
futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de
apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app
de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app
para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de
apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer
apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia
apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas
1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a
colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la
nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al
mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas
alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas
altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas
america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina
españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas
argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina
holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina
online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas
argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs
australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal
real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic
manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic
roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas
atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico
de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de
madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas
bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas
baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos
olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas
baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas
barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca
bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça
madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona
atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona
girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real
madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona
vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas
barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas
bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol
mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real
madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay
hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono
sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo
de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino
olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil
uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil
vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos
hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas
campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa
del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de
la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas
campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas
campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp
2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas
campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera
de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos
fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas
carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas
carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos
españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino
online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas
celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions
league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions
pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs
colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas
ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real
madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas
colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas
colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas
como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas
combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas
con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta
de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas
copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas
copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa
del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa
del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas
copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas
corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo
hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de
caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas
de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de
caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de
caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos
por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos
pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas
de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas
de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas
de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol
en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para
hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de
fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de
galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas
de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de
juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa
league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas
de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas
de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas
de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas
de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de
tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas
de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del
dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de
hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas
del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1
euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas
100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas
android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas
argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina
legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas
barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas
deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino
barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas
com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos
gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos
virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas
consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas
deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas
deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas
de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas
deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas
deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas
deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas
deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas
deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas
deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas
formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas
deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol
español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas
gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas
deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas
deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de
impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas
liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas
deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores
app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas
nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas
deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas
online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas
online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas
deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas
deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para
hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas
partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas
deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito
inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas
tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas
deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia
barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas
virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos
pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la
liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas
dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas
doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y
triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador
vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas
elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas
en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo
pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la
liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea
boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea
colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas
en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea
mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas
en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de
futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas
en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa
eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana
mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas
esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas
euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas
f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1
miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para
ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito
champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc
barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas
final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final
eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas
final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas
formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas
francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano
nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions
league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol
eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol
mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas
futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas
galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del
rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de
la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del
mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas
ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas
ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas
ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe
valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles
asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas
gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por
registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas
gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y
ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos
eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap
baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas
online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy
seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas
inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos
baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas
la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas
mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas
liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas
liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas
liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas
madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas
madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas
madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas
madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca
osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para
hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador
eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores
casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas
mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb
para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas
multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas
mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial
brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial
clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas
mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas
nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy
jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba
playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas
nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super
bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas
online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas
online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online
en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online
esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online
golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online
mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas
online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online
paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online
sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna
athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas
osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas
paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises
bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para
champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para
ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para
hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas
para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido
aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido
colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas
partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas
partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas
peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff
ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia
argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet
mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas
por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por
sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas
promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que
siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas
quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas
quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara
la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas
real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas
real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de
madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas
real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real
madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real
madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid
girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real
madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid
vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real
sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad
valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas
resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma
sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda
division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras
baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras
en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol
hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras
nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas
seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas
seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas
seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla
juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas
sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas
sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas
sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas
stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super
bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas
tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa
davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis
retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas
tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera
division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos
de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas
uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc
como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia
topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas
unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas
valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor
app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas
venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas
villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas
vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william
hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas
y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y
pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna
apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real
madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real
madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador
de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto
apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca
bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona
– real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona
atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona
psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona
vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona
vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de
datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea
apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de
apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono
bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de
apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de
registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por
registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa
de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos
apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos
casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos
casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos
de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos
paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas
deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo
apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas
deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora
apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora
de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora
de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de
apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora
poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake
apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular
cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad
cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo
de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera
de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de
galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras
de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa
apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa
apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas
bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas
cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa
apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas
nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros
gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas
atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas
bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas
caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de
apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas
con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa
de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa
de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del
real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas
deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa
de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de
apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito
5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas
española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa
de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa
de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de
apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa
de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa
de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial
real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de
apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de
apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas
para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por
paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de
apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas
sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa
de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas
del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas
ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas
golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas
apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas
online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de
apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de
apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de
apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas
con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos
sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap
asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas
de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas
de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de
futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas
de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas
en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas
de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de
apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas
en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de
apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa
2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de
apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de
apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador
eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas
legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas
legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas
licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas
mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas
en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas
en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas
de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de
apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online
en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online
españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas
de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online
venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10
trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2
apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros
gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir
de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos
de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre
topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis
nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de
fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de
apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas
deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app
apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa
de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de
apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app
de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas
colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas
perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas
en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de
apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app
de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app
para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app
para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app
pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para
apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas
a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas
al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania
españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes
del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina
campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina
gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas
argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina
paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs
australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real
madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic
atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic
barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic
osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas
athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas
atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas
atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas
atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto
juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas
baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas
barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas
barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas
barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona
atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona
celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona
girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas
barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas
barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas
barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis
chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis
madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas
betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas
betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs
colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas
brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas
caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas
calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions
league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1
2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas
campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas
campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas
campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras
de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de
caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras
de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos
pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas
casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas
casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas
celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas
champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas
champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas
ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city
madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas
colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs
argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas
combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas
combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas
combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas
con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas
copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa
del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del
rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa
europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa
rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners
hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas
bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas
de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de
boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas
de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas
de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos
españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas
de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas
de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas
de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de
eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas
de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas
de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas
de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol
español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol
para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de
futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de
futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como
ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos
trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de
la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga
bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la
nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba
para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas
de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas
de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas
de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de
mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas
de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del
clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia
de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas
1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas
deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas
deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas
deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas
chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com
foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono
gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas
deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para
ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas
deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas
deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas
deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas
de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas
de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas
deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas
en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas
deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas
deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas
estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas
f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro
futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas
deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas
futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas
deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas
gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas
deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la
liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas
legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia
españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas
deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas
deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores
casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas
méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas
mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas
online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico – Roxie -|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas
deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas
deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru
vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas
pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real
madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado
exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas
deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito
inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas
deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas
deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas
deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas
deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso
a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas
descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas
descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas
dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de
honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas
dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas
ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas
en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de
caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas
en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas
en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas
en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea
deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas
en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de
futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas
en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo
peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas
españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas
españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas
españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa
gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas
españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas
espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas
esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports
españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas
eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa
sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league
pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas
f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1
monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas
favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas
fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final
copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa
libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final
euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas
final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas
finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas
fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula
1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas
futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol
argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol
chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol
consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas
futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas
futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas
galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas
gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas
ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas
ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la
eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del
mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas
ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas
ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas
ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas
goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf
pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas
gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas
gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas
gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas
grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey
hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy
champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas
inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos
olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores
nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la
liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas
legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas
legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas
liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga
de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones
de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea
de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas
madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca
hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas
madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas
madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles
de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters
de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador
mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas
mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como
funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas
mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas
mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas
mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas
mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas
mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de
colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas
nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba
hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para
hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl
playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas
nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas
online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online
bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online
chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas
online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas
online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas
online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas
online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna
real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países
bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas
para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para
eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la
champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para
ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para
ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas
para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas
para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de
la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas
para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido
champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido
suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos
de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas
plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas
playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por
paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos
por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es
handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la
champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara
el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid
athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real
madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real
madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid
osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas
real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas
real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas
resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas
rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas
seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para
este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar
dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy
pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas
seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla
campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas
sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas
sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas
sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl
favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas
tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis
atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas
tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland
garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas
tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas
tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas
torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions
league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como
funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs
colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid
barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas
venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas
venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas
villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester
united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas
virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta
a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas
y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos
de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y
resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina
francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina
vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético
de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de
cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs
atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca
vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid
apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona
betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona
psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla
apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona
vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs
girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real
madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea
apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog
apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de
apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono
bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca
apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa
de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de
bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis
apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas
deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de
apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos
casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas
gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas
de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos
gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos
registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos
sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia
apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas
de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora
apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora
apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas
de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de
apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake
apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular
cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular
ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades
apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de
apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera
de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras
de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos
juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas
cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa
apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa
de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas
champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa
de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas
con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas
con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa
de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas
del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas
deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas
en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa
de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas
madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa
de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas
deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa
de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa
de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas
futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa
de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas
liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa
de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa
de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de
apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial
del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa
de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa
de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa
de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas
pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa
de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por
paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real
madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas
sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas
ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de
apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la
suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas
apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas
deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas
deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas
eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo
5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas
apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas
apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas
de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras
de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas
casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions
league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de
apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas
con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono
de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de
apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de
apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas
de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas
de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas
deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas
deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de
apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas
online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de
apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas
de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas
en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de
apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas
de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas
de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de
apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa
online|casas de apuestas española|casas de
apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas
de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas
fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas
de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas
legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas
de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas
de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas
de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de
apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas
nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas
de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas
de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de
apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas
para ufc|casas de apuestas
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas
de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas
que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre
ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades
de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para
ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba
apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas
deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones
de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app
apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas
gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app
casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app
de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas
android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app
de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas
deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas
sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas
reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles
de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para
ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app
para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control
de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps
de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas
deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10
euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3
division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas
a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas
al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas
y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos
marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina
francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana
el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina
méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina
paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina
uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas
arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas
athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas
athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas
atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas
atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas
atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la
liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca
hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas
barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas
barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de
madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona
espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona
osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas
barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas
béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas
betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas
betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas
betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis
vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas
bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas
borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas
boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas
boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil
vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas
caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas
caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas
campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier
league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de
galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de
caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas
carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas
casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas
casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas
celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions
league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions
pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea
betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile
vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city
madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas
clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas
colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia
vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas
foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas
combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas
combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas
con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa
africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa
davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa
del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa
del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa
del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial
de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas
bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas
de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas
de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas
de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo
online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se
juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas
de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas
de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos
online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino
online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de
champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas
de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de
corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas
de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de
fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de
futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de
futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de
futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol
para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para
mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos
online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de
juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de
la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de
la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de
partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros
virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis
en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del
clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del
día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas
del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas
deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas
deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina
legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas
deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas
deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas
champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas
deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas
combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas
deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas
con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos
virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas
consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas
cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de
boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas
de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas
deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas
deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas
francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas
deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas
gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas
deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas
deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado
clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas
mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores
app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas
deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas
nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas
deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online
argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online
en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas
deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas
pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas
deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas
deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas
deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico
hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas
deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas
seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para
hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas
sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake
10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas
deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas
deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas
y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos
pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso
a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera
division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el
clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas
en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas
en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas
en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas
en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas
en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea
boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea
estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas
en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea
peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis
en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo
casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas
en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa
alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa
eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia
eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas
españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa
inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas
españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas
españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol
betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas
esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas
eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub
21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas
euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1
canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles
de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas
favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas
final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas
foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol
americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol
argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol
colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas
futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas
futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas
futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol
hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol
online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas
futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos
en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos
trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas
ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador
champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas
ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas
ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador
liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores
mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas
ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas
girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas
goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam
de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas
gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas
gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas
grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas
handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas
handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas
venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas
juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos
baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores
nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas
la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga
1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones
de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas
de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea
de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid
barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid
borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas
madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid
gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas
mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city
real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor
jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas
méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas
mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas
mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas
mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas
mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas
mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial
formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial
ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas
mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas
nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas
nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba
gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas
nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl
super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas
online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online
con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas
online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online
futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online
juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online
movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas
online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over
2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas
paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el
partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la
copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba
hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido
aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas
partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas
partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas
partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos
hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas
peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff
ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas
por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por
paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes
hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a
segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el
mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara
la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas
real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas
real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real
madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester
city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas
real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real
madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real
madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas
real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas
real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo
de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby
world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras
baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras
gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas
seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas
seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras
ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla
barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas
sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples
ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate
que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas
stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis
copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis
itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland
garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas
tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster
para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas
ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc
ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc
pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas
unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas
uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas
valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real
madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor
galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela
ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal
athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal
betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas
virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas
william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de
azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico
apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs
francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic
manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic
real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético
de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de
cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca
inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona
apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona
psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs
girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis
barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio
de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas
ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono
apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas
de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de
bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de
apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas
colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos
bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas
apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de
apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas
sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis
apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de
apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas
de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de
cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas
deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas
segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora
cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas
sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas
deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora
stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas
apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular
momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake
apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales
de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos
apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas
bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas
caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas
champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas
colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de
apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de
apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa
de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas
del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de
apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas
deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas
españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas
deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa
de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa
de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa
league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa
de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de
apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de
apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas
oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa
de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de
apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online
venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas
perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de
apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas
regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de
apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa
de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de
apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas
apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas
españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas
legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas
españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas
online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas
tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5
euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas
de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de
apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas
bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas
de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos
sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas
carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas
de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de
apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono
por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de
apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas
con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas
de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas
de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas
de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas
en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas
de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas
en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas
españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas
deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas
de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de
apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas
en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas
en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas
en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas
de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas
españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de
apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de
apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas
esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de
apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de
españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de
apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas
licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas
de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas
mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5
euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas
mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de
apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas
de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas
en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de
apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas
online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas
de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online
en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas
online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas
online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas
online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online
venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas
peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar
apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2
en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a
partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de
azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para
ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para
hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de
fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas
perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones
de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas
argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app
apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas
deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app
de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de
apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas
en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de
apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar
dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para
apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender
a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas
2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a
carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a
corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas
a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas
al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas
alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y
bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina
croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs
francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a
primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester
united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas
athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas
athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas
atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de
liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico
madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas
barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs
juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona
alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de
madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona
bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de
liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona
espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas
barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas
barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona
villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs
real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas
beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis
– chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis
madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas
betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis
vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas
bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono
gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo
femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil
vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos
colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos
hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas
caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de
champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de
liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas
campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas
campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas
campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas
carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos
pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas
casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions
hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league
– pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions
league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas
champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea
betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile
vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas
clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas
colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia
vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas
foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas
combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas
pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas
con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas
con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta
de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa
américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas
copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey
futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey
pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa
mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas
croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas
de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de
caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas
de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de
casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de
corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas
de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de
futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de
futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para
hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de
futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas
de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos
como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas
de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la
eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la
liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de
mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de
partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de
perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de
peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de
tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para
hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas
de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas
del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas
del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del
mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1
euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas
1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas
deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas
argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas
deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas
deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas
deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas
comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas
deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos
virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas
deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas
copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas
deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas
de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas
deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas
deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas
dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas
deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas
deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas
estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas
ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap
asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior
argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga
española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas
deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas
deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas
mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas
mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas
deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas
online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas
online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas
online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas
deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas
predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas
pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real
madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas
seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas
deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas
deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas
tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas
tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas
valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas
deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso
a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso
primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas
dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas
directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas
doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas
elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas
en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos
virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la
eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas
mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea
argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas
en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas
en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas
en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea
usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas
en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo
futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas
en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas
españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas
españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra
cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports
gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports
valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas
euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas
europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas
f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas
fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final
champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final
copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas
final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de
copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1
pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol
argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol
colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas
fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas
futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas
futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas
ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador
del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador
liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial
f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas
ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana
uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas
girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas
golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas
gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis
por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis
sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas
gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como
funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas
venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs
argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas
hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy
seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos
en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos
online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores
nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga
española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas
nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales
en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas
liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga
española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas
lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid
atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas
madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca
supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas
madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana
liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real
sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester
city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas
seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas
maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos
online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas
mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb
las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas
múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas
mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial
de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial
f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial
femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub
17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta
noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas
nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas
nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl
semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online
casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas
online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online
foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas
online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online
mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas
online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas
paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos
qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el
dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas
para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar
la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para
hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para
la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de
hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas
partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido
españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas
partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de
hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos
mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas
peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas
peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas
plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a
primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas
playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por
argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas
que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas
quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo
barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid
arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid
atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid
betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real
madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real
madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas
real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas
real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real
madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas
resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas
roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby
world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda
division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras
calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras
eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas
seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para
ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para
mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas
sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester
united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas
sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas
sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas
sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema
como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas
super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas
superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas
tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas
tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway
cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas
uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas
ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc
hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas
ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay
vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas
valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas
venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas
venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas
villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas
villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas
vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas
y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro
nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia
apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina
peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina
vs francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se
gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona
apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid
apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid
vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto
apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca
inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico
apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao
apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs
celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea
apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de
tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas
españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca
apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de
apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de
registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono
marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos
apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos
bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas
de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de
apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida
en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis
casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de
apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas
deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas
deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil
peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de
sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje
apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de
apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas
sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora
de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora
poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping
apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas
deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular
ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios
apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de
apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales
de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos
apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos
apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de
galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas
atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa
de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa
de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa
de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de
apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa
de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago
anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa
de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa
de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de
apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas
deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa
de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa
de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de
apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de
apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas
legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de
apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de
apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de
apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa
de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas
online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de
apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online
paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de
apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa
de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa
de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas
regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de
apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de
apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas
bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas
deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas
deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas
apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5
euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas
licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas
app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas
de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca
de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas
de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas
de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de
apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de
apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de
caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de
fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas
deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas
madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas
deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas
de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de
apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas
en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas
de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos
de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas
de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas
de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de
apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas
de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas
de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas
de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera
de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de
apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales
mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores
bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de
apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas
de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas
en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas
de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas
de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas
de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas
de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas
de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apue
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para
ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que
significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se
declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas
de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de
fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas
colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas
españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app
apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app
de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas
deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de
apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app
de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app
de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app
de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas
peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para
apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para
apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app
para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas
deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas
10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas
1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas
a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores
nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas
al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas
arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas
argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas
argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina
francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas
argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas
argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas
ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas
athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester
united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas
athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas
atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico
campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas
atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real
madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid
champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas
baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas
baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas
barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas
barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético
de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona
villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona
vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas
barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas
betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas
betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono
bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida
sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas
boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil
vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas
campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas
campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de
liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa
league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula
1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga
bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos
nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras
de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras
de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas
carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas
carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos
online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas
celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league
– pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions
league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas
chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile
peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs
uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas
ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city
real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas
clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas
colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas
combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas
recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas
seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas
como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas
consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas
copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas
copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas
copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey
pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas
cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto
nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las
vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo
online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de
caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online
en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas
de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas
de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas
de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas
de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas
de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas
de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de
futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas
de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas
de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol
online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para
hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de
galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas
de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas
de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas
de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas
de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la
nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas
de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de
futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas
de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de
sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de
tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis
hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas
del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas
del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real
madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas
deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas
100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas
deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas
deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas
deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas
deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas
deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas
com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas
con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas
consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas
cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de
boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas
deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas
deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas
deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas
en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas
estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas
foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia
argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas
deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas
deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas
deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas
deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas
deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas
deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas
madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores
app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores
cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas
deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba
hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas
nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online
chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas
online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por
internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas
deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de
hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas
deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas
que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas
deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas
tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas
tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas
tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas
valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas
y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas
deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero
ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor
juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas
egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas
en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas
en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas
en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas
en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas
en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las
vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea
colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados
unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea
méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los
esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas
en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas
en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas
en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo
tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas
españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa
eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia
eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas
españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra
cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol
villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas
esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports
gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas
estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas
eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas
euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas
europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1
bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas
f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles
de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos
champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa
del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de
copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final
nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas
foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas
francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol
en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas
futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol
españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos
olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol
online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol
pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas
galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador
la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas
girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas
girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador
eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas
gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis
regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap
asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas
hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre
hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter
barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas
jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas
legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1
peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga
santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas
liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca
supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid
borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas
madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid
osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas
mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas
mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador
eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador
eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas
méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas
mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas
mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial
f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas
mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas
mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas
nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas
nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba
gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas
nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas
nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas
nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas
nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas
nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online
bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online
carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online
comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas
online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online
mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online
nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas
online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online
sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna
sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago
anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas
para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido
de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas
para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar
en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para
juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para
la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los
partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para
ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido
suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas
partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas
paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs
chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas
predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas
pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas
psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer
con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a
segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el
mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara
la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid
arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real
madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de
madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas
real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid
borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona – Coiffure.dpcsolutions.com,|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester
city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs
atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real
madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada
tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas
rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas
seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la
ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas
seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas
seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras
para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para
hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas
sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas
sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples
ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como
funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del
rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas
super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas
tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas
tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas
tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas
tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas
topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions
league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc
ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay
colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas
us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia
barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas
venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela
bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas
villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas
villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas
virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas
vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas
y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay
apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile
apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia
apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid
vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas
apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro
barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter
apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca
vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona
apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona
atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao
apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona
vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de
datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog
apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas
tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas
españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida
casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de
apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de
apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro
apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono
registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito
apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa
de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos
gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos
registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas
seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas
combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora
apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora
de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas
multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas
futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas
apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular
ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake
apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo
de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions
apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos
apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras
galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas
bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas
online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de
apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas
baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa
de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa
de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa
de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa
de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas
copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas
de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de
apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa
de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas
en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de
apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa
de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas
europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas
legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa
de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa
de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas
nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa
de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online
mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de
apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de
apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que
regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas
sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de
ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa
de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas
virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa
oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas
asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas
apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas
apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas
apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas
nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas
sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas
de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas
bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas
caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas
de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono
sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de
apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia
en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas
con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas
de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas
de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de
apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de
apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas
deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas
en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas
online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de
apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas
en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de
apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de
apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas
de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de
apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas
de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de
apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de
apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas
mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas
méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de
apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de
apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas
de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas
online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de
apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas par
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis
marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2
apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas
que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis
apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de
cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad
apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas
de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones
de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones
de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer
apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control
apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas
casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de
apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app
de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de
apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas
peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de
apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas
en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app
de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app
para apuestas deportivas en español|app para
ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer
apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para
llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de
apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas
mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas
deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas
1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a
colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas
al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo
nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas
argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina
españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs
peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas
ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas
athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico
campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de
madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real
madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real
madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona
real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas
barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas
beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas
betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas
betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas
betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real
sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis
valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay
hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia
vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas
bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia
real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo
de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo
online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas
brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos
españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas
caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas
campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa
del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas
campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas
campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga
bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas
campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial
baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de
caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas
carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas
casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas
casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas
champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league –
pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas
champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas
champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile
venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas
ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas
city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas
clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo
partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas
para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas
recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta
de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas
consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa
américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa
de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa
del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa
del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey
hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey
pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa
italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa
sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas
cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas
de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas
de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo
en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de
boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como
funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos
en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de
caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de
caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes
en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de
esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de
fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas
de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas
de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas
de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol
para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol
peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas
de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas
de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de
hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy
seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas
de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de
la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la
liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la
ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de
partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros
en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de
sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema
explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de
tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas
del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas
del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas
deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas
deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas
deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas
deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas
com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas
deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas
deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas
cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas
altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas
doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas
deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas
deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas
esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas
europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles
de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia
argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas
deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas
deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas
gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas
gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas
deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas
mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas
deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas
deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas
online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas
deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas
deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online
paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas
deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas
partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas
deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras
foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas
deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero
real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas
stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas
telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia
barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas
deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda
b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas
doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas
draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el
clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas
empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas
en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos
online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas
en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el
tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas
en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas
en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo
argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas
en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas
en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas
españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas
españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas
espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas
esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas
euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa
sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas
f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles
para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos
mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas
final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final
copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa
del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final
copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas
final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas
final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas
fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro
nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol
americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas
futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol
en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol
juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol
online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas
galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos
trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas
ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas
ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga
española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador
mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas
girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas
golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas
gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis
regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis
sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas
handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap
nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas
online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas
hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas
hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas
inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos
olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends
mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas
legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas
libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga
argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de
baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas
liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool
barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid
barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid
bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas
madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid
liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid
valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city
real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas
mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas
masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico
polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas
múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas
mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial
brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de
baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial
futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto
gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba
esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para
hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas
nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl
pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas
nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online
bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas
online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas
online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online
espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas
online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online
mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas
online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online
nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas
online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico
golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas
osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago
anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para
el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido
de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para
ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas
para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa
league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final
de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para
los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas
partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas
partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de
futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas
peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas
peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas
plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas
polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por
internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda
boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas
primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos
por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas
quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas
quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara
la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real
madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas
real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas
real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas
real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas
real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs
valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas
real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas
regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda
división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras
calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras
hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para
ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para
hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas
sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas
sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate
que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super
bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas
tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis
atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis
de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis
roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria
holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas
torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas
ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc
online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas
uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas
us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas
valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas
valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela
argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas
virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta
a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y
casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y
pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina
vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs
francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona
apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid
apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico
real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis
apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter
apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid
apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona
vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo
apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona
apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs
sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos
cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best
america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis
barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas
online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog
apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono
apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida
casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de
apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis
sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro
casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro
casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos
apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de
apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de
apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos
en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos
gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos
gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos
sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas
deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia
apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador
de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora
cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora
de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de
apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema
apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora
trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas
futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular
cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de
apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera
de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos
con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de
caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos
apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas
bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa
apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa
apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas
10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de
apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas
bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa
de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas
altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas
en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas
deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de
apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa
de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa
de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de
apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de
apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula
1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa
de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas
segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5
euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa
de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas
oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial
real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa
de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas
online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas
peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas
promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de
apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa
de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive
la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas
deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas
españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas
golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas
apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas
apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5
euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de
apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono
sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas
ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas
con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de
apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de
apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas
de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas
con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas
con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas
de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas
en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas
deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas
en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas
de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas
deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas
deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de
apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de
apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas
de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa
nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de
apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas
de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas
ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas
de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas
de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales
mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas
lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo
5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas
de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva
ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas
de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas
españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas
online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas
online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de
apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online
en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de
apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de
apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas
online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas
de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de
apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas
promociones|
Clarte Nexive
Clarte Nexive se distingue comme une plateforme d’investissement crypto de pointe, qui met a profit la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour proposer a ses membres des atouts competitifs majeurs.
Son IA etudie les marches financiers en temps reel, identifie les opportunites et met en ?uvre des strategies complexes avec une finesse et une celerite hors de portee des traders humains, optimisant ainsi les perspectives de gain.
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para
ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2
en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5
euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de
cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android
apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de
fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas
deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de
futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app
apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app
casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas
de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app
de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas
deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas
en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app
de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app
de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles
de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas
de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app
para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de
apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas
mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas
deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas
a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas
a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a
la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al
mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz
hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes
del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas
nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina
canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina
francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el
mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina
online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina
polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas
argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso
a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic
atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas
athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético
copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la
liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas
baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto
hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas
barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas
barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca
inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas
barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas
barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona
athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas
barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona
celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas
barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona
sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico
madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona
vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol
pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis –
chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis
real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas
betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de
bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas
boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas
caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos
zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa
del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del
mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas
campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas
campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas
campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial
baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland
garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos
de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera
de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de
semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de
caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de
caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de
galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas
casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino
gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas
casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta
real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions
foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions
league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league
pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo
femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta
a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas
clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia
vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas
futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta
semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas
combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas
copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas
copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas
copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas
copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa
del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de
hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas
bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo
online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas
de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de
caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y
colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de
caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por
internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de
copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas
de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de
futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas
de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol
para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol
seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para
hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas
de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas
de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas
de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de
la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de
la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas
de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas
de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de
tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para
hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis
seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico
real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas
del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas
deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas
1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas
100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas
app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas
deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico
de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca
madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas
deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas
ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com
foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se
juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas
con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas
deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas
deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas
de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas
de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas
del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas
deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas
en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas
deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas
deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas
europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas
deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas
impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres
de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas
listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor
pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas
mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas
deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas
deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas
deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas
nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas
nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas
online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas
online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online
por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas
peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas
deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas
seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas
deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas
deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas
ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas
valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas
y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com
foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera
division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas
dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas
division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas
draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador
vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas
elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas
en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos
online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas
en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas
en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la
eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea
argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea
colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas
en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas
en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis
en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas
equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas
españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa
gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa
italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas
español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol
betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports
españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas
estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa
league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas
f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas
f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas
final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas
final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final
copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas
final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de
copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final
europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final
mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas
final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas
francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol
champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas
futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol
en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas
futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para
hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas
futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas
galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana
colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de
la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador
f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial
baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador
nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar
mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana
la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas
goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf
masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis
sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos
eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap
baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas
handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy
pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas
inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos
olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas
juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings
league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga
hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas
nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1
peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas
liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de
baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas
liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas
linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas
madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid
betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas
madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid
hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester
athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas
seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas
masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores
casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb
las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb
usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas
multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas
multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas
mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de
ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial
futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas
mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub
17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp
eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas
nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba
tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super
bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono
bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas
online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online
con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas
online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online
españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online
movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas
online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online
ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas
osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas
over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago
anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para
el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido
de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la
europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions
league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa
league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la
nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas
para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas
partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas
partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido
mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol
hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos
mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru
vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff
ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas
playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por
paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas
puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer
con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas
quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas
quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas
quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas
real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas
real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid
barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid
campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas
real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid
girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas
real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas
real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid
vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real
madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real
sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real
sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas
rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas
seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy
fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para
mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras
telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas
senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de
madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla
juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real
madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla
roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples
ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas
sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas
sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas
stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de
mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas
tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas
tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas
tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de
tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela
argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas
venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal
betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas
villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta
a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y
casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas
y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia
apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs
francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se
gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos
apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid
apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid
vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real
madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid
apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada
de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça
madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico
apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona
betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona
vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona
vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona
vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid
apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet
apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas
ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono
apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis
sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa
apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de
apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida
apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono
por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos
casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos
casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de
apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito
apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de
apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia
apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas
apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora
apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora
cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora
de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular
apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular
apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular
cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular
stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions
apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de
apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos
apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de
galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa
apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa
apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas
eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa
apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa
de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de
apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por
registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas
boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de
caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca
de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de
apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas
con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de
caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa
de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa
de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas
deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas
deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas
deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de
apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas
españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas
f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas
legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa
de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de
apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas
oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de
apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online
españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online
paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online
venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas
para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas
peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas
que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa
de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas
sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas
sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa
de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas
vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas
apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas
caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas
deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas
apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas
apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas
apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas
sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5
euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de
apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas
bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de
apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas
de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas
con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas
con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito
minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia
españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago
anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas
con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas
de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de
apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas
de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas
con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas
deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas
de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas
en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de
apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de
apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas
de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de
futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa
nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de
apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas
españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas
de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas
de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas
legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas
legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de
apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas
seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de
apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas
nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de
apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de
apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de
apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online
españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de
apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para
ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de a
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar
apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5
euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se
declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar
apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app
android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app
apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas
ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app
apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app
apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app
control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de
apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas
de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas
deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de
apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas
en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas
en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para
android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de
casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar
control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus
apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de
apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas
deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas
a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a
corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis
wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas
ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas
anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas
arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina
colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina
francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas
argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso
a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas
asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic
manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic
real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas
athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas
athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas
atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas
atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico
madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto
acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos
olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas
barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca
inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas
barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs
madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas
barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas
barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico
madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona
betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas
barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas
barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs
real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas
beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis
– chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis
sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis
vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia
vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas
boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas
boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas
brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1
2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de
futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas
carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos
nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos
en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino
gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino
online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas
celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions
league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas
champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league
pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas
chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo
femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico
real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas
colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia
uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas
combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas
combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas
seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como
ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas
con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa
argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del
rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas
copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa
italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial
de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners
hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas
cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos
como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de
caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos
juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de
colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula
1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol
app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol
en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol
mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol
para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas
de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas
de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de
hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de
juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas
de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba
para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas
de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas
de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis
para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de
todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid
barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de
hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas
del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas
deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas
deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas
deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas
casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas
deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos
gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas
deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos
para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas
copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual
es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas
de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas
en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas
deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas
en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas
estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas
deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas
francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas
deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero
seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas
deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas
deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas
deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas
listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas
deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas
deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas
nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas
deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por
internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas
para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas
deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas
peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado
exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas
seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras
hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas
deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas
deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas
deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de
mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas
deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas
deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas
deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso
a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso
primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero
virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas
division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas
ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs
venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas
en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas
en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos
virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la
liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas
en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas
en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de
tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas
en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo
ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas
españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas
españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa
inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises
bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas
espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports
colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports
valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas
euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas
eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas
europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league
pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1
cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de
ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas
favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas
final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final
copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas
final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de
copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa
league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final
rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas
final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas
francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas
fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas
futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol
en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas
fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas
futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol
hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol
mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol
telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos
en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas
gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador
copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de
la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas
ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga
española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar
mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas
girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas
girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas
goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand
slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis
hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis
regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas
gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas
handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas
online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda
vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas
hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas
juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas
juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga
española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga
santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas
nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of
legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas
legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas
licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga
de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool
real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas
madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca
supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid
hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid
valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de
golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo
goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas
mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb
usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas
múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas
multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas
mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas
mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de
fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas
mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales
de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba
finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas
nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas
nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana
4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas
ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas
online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas
online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online
champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas
online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online
en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis
sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online
movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas
online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas
online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online
venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna
athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises
bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia
de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de
hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas
para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para
ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas
para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas
para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la
copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la
final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido
colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions
league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de
futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de
hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas
peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas
peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas
playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet
mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas
promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos
tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que
siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la
liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas
quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas
real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real
madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real
madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real
madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid
liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real
sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real
madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs
betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas
real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados
eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas
rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas
segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras
para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas
seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para
hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras
telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla
barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla
celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas
sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla
leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas
sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples
o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas
super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis
itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas
tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis
wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos
de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa
europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas
uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas
valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas
valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas
valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas
villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal
manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas
virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas
virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de
azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es
pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina
francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru
apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina
vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs
francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united
apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs
real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca
apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid
apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real
madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico
madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de
apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs
atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs
espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona
vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet
apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis
chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog
de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida
casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono
casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono
de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono
gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas
deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos
casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas
sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos
en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de
apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos
sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru
apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador
de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora
apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas
seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas
combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de
apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de
apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora
de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora
poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora
stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular
apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas
apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas
apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias
apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular
probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas
apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera
de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera
de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas
online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas
trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono
gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de
mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas
eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa
apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de
apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas
bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa
de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas
mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de
apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de
apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de
futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas
deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa
de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas
madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas
deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas
en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de
apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula
1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas
ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales
en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas
segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas
minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas
mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas
oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de
apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa
de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas
real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de
apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo
de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de
apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas
apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas
apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas
apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas
nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas
ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas
peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas
de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono
por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de
apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas
de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas
cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas
de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas
de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas
de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas
con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de
apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del
rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas
de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas
deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas
en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas
españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas
de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de
apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas
de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas
de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de
apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de
apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de
apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas
eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de
apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de
apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia
españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas
mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas
no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas
nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas
online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas
de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online
mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online
peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de
apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10
trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2
apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que
significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9
apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas
deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas
peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones
de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar
seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas
de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas
argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app
apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app
casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app
de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de
apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app
de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de
apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas
futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app
de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de
apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app
moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas
en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app
versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a
hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10
euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2
division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al
dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al
tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos
equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del
mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del
mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto
paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina
holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas
argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina
polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas
argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera
division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas
athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester
united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real
madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico
barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de
madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de
madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real
madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto
juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto
pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas
barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca
madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca
vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas
barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona
madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas
barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona
vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket
hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas
béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol
venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas
betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real
sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis
vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas
billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas
boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil
vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de
barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de
champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas
campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1
2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas
campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas
campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de
caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de
galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos
españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas
carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras
de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas
casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas
casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino
online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas
celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas
celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta
real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas
champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions
league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league
pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas
chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile
venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile
vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas
city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid
barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas
colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia
vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas
combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas
combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas
mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas
combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para
hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas
pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas
seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap
baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta
de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey
pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas
copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas
cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas
de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo
online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas
de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos
online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas
de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas
de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas
de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas
de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas
de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas
de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol
argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol
en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas
de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol
mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de
futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol
pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol
seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de
galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas
de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas
de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas
de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas
de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de
sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de
sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas
de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para
hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de
todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas
del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia
de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del
partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas
deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas
deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas
deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas
bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas
deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas
con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa
del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas
deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas
altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas
deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas
de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas
deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble
oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas
deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas
en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas
es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas
deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas
foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol
español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas
gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas
deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas
deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga
española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas
deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor
pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas
mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas
deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas
nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas
deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas
deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas
online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas
online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito
inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero
real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake
10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas
deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas
deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas
deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas
descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero
ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo
futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas
empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino
online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el
tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas
en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea
argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas
en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico
online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas
en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas
en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo
fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas
en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas
españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa
alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa
francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa
inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol
villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports
españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas
estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas
eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga
pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league
hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa
league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas
f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas
faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos
champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos
mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final
copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa
rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final
rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina
betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas
fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol
argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas
futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas
fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol
foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas
futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas
futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas
futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas
gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas
hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del
rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la
eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas
ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas
ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas
girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona
real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas
granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas
gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap
baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas
handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs
argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy
pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas
inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas
juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga
española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas
nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas
legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas
legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas
leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1
peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga
de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas
linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas
liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid
barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid
betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas
madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana
la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas
madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles
de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo
goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas
méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb
hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples
el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas
mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial
clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial
f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales
de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas
nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas
nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online
juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online
mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas
online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna
valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over
under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos
ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el
dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el
partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas
para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para
ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar
la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la
europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas
para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy
europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la
copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la
nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas
partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido
colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas
partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas
partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas
partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos
mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru
paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru
vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas
playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda
b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por
ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre
partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera
division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos
deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas
psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la
liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el
mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la
eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas
real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real
madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real
madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real
madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real
madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas
real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid
real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real
madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real
sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas
real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad
psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas
real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas
resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas
roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda
división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras
baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras
foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras
gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas
seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas
seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy
pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas
seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal
paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de
madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas
sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla
jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas
sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas
sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas
sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o
combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas
sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema
calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl
favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta
roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa
davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas
tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera
division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas
tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc
ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas
ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas
uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia
betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas
valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor
app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal
barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal
vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de
hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas
y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas
y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba
apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru
apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de
madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid
real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada
de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca
apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid
apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona
atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter
apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real
madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia
apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs
atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta
de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas
apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu
sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas
ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de
apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono
de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de
registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa
de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas
deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono
sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono
sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas
apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis
apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos
gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito
apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas
deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs
colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora
apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora
apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora
apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de
apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora
de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas
apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas
deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular
stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa
apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos
apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras
de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas
atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas
colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa
apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas
10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa
de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas
bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de
apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa
de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions
league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas
colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas
con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de
futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de
futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas
del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas
españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas
españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa
de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales
en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa
de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de
apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas
nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa
de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas
online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas
online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para
boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas
sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas
sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa
de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de
apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas
caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas
deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas
nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas
paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas
de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas
de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas
de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas
casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de
apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas
con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas
con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas
con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas
con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas
de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas
deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas
en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas
deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas
deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas
en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas
de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de
apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas
en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas
de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas
de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de
apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa
licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa
online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de
apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas
de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas
eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas
f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula
1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de
apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas
ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de
apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas
legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas
de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas
de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de
apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas
de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas
online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas
de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online
en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online
nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas
pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en espa
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9
apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar
y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro
apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas
colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas
deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app
apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas
sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas
de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas
android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de
apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas
peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de
apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app
de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app
para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas
de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de
caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a
jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al
barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas
al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas
alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas
nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas
anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas
argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el
mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas
argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina
paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas
asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic
barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic
roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de
liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas
atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid
real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real
madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas
baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas
baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas
barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca
inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca
vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs
psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona
athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona
hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona
psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona
sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona
villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis
barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis
girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay
hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas
borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas
boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas
boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs
colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas
campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1
2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas
campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas
campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de
caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de
caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de
caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas
carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos
nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas
casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino
gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas
casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas
casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta
eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions
foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions
league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions
league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas
champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo
femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas
clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas
clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas
colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs
brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas
recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para
mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas
con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades
de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas
copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas
copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del
rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey
pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas
copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas
altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de
baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo
en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de
caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas
de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas
de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos
juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos
por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera
de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de
casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de
colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de
esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de
futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de
futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol
hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas
de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol
peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de
futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas
de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas
de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas
de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas
de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de
la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la
nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba
para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas
de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas
de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas
de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del
dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del
rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1
euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100
seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas
app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas
atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas
bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions
league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas
com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas
con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa
del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas
corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas
cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas
de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas
deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas
en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas
en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas
esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas
deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas
foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas
francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas
futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas
deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas
deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas
deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas
deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas
interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas
libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas
deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas
mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas
murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas
ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas
online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online
españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online
peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas
deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru
vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas
pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico
hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras
telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas
sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas
tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas
deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas
y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda
b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas
descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero
real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft
nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador
vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas
en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el
futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas
en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas
en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas
mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea
chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados
unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas
en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas
en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas
en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas
equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa
croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa
francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa
gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa
paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas
estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa
ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas
f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas
faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles
para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc
barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del
rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final
europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula
1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas
fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol
argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas
futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol
femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas
futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas
ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa
del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas
ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar
eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas
girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real
madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores
eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas
gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis
sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas
gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap
baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap
nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas
hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre
hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy
champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas
juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas
juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas
jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league
of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas
legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes
betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga
de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander
pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas
liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca
hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid
gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas
madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas
manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de
ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters
de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas
mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico
polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el
gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas
mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial
balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de
baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas
mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial
sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp
eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas
nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas
nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas
nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl
semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas
nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas
ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas
online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online
champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas
online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas
online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online
futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas
online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas
online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas
osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas
over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de
hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas
para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la
champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para
ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para
hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy
de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas
para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para
los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido
mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas
partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos
de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas
de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru
vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas
playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas
por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas
por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido (Boyce)|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera
division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg
barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a
segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas
quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas
quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo
barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid
athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid
campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real
madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real
madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad
psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad
valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas
regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas
roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas
seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras
futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas
seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para
hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas
sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla
betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o
combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas
sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas
sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como
funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10
hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas
supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas
tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa
pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas
tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland
garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas
tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas
topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de
golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc
ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas
unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas
uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas
valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas
valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela
argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas
villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal
liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas
villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas
virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales
sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de
hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y
pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro
nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina
peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona
apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético
de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real
madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca
bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca
vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico
de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona
betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg
apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs
atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona
vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis
– chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla
apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog
apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog
apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono
apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca
apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono
casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida
apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de
apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis
apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono
sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas
nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida
apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de
casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis
casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito
casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas
gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas
seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora
apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora
de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de
apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas
deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas
apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake
apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas
deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de
apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera
de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas
online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa
apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas
bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa
apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de
apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas
baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de
apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa
de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas
champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de
apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de
colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa
de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas
del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas
en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa
de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa
de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa
de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa
de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa
de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de
apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales
en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa
de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de
apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa
de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de
apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas
online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online
peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para
boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por
paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas
real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa
de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa
de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa
oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas
apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas
con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas
apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas
apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas
nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas
tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono
sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino
online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de
apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas
de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas
con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas
de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono
por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas
con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de
apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas
de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de
peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas
deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de
apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito
mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de
apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas
de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de
apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa
nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas
de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas
gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas
licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas
de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva
ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de
apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas
de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas
de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online
nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas
online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas
de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presencia
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas
que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5
euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y
apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas
deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas
online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas
deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas
deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas
argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas
deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app
casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app
de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas
deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas
deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de
apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app
de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app
de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas
android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app
para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer
apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps
apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas
deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas
2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas
a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la
nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas
alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania
españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes
del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas
arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del
mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas
argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina
gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina
mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina
paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso
a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic
betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas
athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic
real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas
athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de
liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto
juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas
baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas
barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas
barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona
bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona
hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real
madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona
valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol
mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis
– chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis
real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs
valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs
colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas
bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas
bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas
boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo
español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas
boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas
brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas
campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas
campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del
mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula
1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga
española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas
campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera
de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas
carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas
carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de
galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino
futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas
casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta
eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league –
pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league
hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions
pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas
chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile
vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo
femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas
city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico
español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia
uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia
vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas
de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas
combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo
partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para
mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas
con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de
ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas
copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa
del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa
del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del
rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial
de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia
argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas
de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de
beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de
boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos
como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de
caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y
colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por
internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de
champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes
en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de
futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol
español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas
de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas
de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la
liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la
nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de
perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de
sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas
de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas
de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas
del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia
de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas
del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas
deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100
seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas
deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas
deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas
campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas
chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas
deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas
con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas
con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas
deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas
corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas
de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas
deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas
deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas
deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas
deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas
deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas
deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas
europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas
deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro
tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas
futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas
gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas
deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas
interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas
deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas
deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas
seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas
deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas
deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas
deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas
deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas
online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online
en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas
deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar
dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de
hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas
deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas
predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas
deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas
seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para
hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake
10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis
foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas
uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas
deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino
online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a
segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso
segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor
juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft
nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas
en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas
en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las
vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas
en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas
en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas
en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas
en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea
peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos
de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas
en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas
en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo
casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos
de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas
españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas
españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas
españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports
gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports
valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league
pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas
f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles
de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions
league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final
copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas
final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas
final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas
final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final
mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas
final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula
1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas
fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol
argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol
en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol
español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol
online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas
futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador
copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador
copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador
europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la
liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas
ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas
ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona
campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores
eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam
de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas
gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis
y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas
handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap
nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas
online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey
hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey
sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs
argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas
hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas
inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos
olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas
jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la
liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas
la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva
pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de
gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas
madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas
madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid
gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas
madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras
para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos
online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas
mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas
mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial
balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial
campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas
mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas
mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas
mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto
gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp
eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba
consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba
gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas
nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba
tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas
nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina
legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online
boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas
online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas
online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de
caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas
online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online
golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online
mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online
net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas
online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico
golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas
osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos
inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions
league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de
hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para
europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas
para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para
ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para
ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la
liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy
europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la
champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa
league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa
marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions
league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol
hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas
partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas
peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas
peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru
vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff
nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs
nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet
mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por
sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas
pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas
que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas
quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el
mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas
rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real
madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid
bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas
real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real
madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real
madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs
atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas
real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad
athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real
sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados
eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma
barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas
segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas
seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras
hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras
para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras
para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para
hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas
seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana
la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas
sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas
sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla
valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas
simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito
minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas
sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas
super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas
superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas
tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis
hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis
wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas
tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas
torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas
ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas
us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid
barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas
valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela
bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas
villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs
real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales
colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos
de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y
juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba
apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs
francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se
gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona
apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid
apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico
real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador
de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona
apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid
apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona
betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona
real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona
vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal
apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis –
chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis
chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu
sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog
apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono
apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de
bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro
casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas
deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos
apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos
casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas
deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de
apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos
de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas
deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas
de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador
de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar
apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de
sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora
apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora
cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora
de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas
deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora
poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora
trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas
futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas
deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota
apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de
galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas
online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de
galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas
argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas
cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas
española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa
apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa
apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de
apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas
caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de
apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas
con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa
de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de
caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas
de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de
apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas
deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas
peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de
apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa
de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa
de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de
apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas
oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas
online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas
online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa
de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de
apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de
apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real
madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa
de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas
virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas
apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas
eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo
5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas
españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas
sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de
apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por
registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas
bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas
con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de
apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas
de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de
apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de
apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas
deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas
deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de
apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de
apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas
de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas
en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de
apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de
apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas
online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de
apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas
de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas
en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas
futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas
de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas
inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de
apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de
apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de
apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores
bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de
apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas
en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de
apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de
apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online
en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas
de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas
online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de
apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de
apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|cas
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos
para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros
gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos
de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america
apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de
apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro
apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas
colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app
apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app
casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas
android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app
de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de
apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app
de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app
marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app
para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas
en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para
hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de
apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps
apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de
apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del
dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2
division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas
a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a
ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al
dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del
mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas
anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana
el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina
holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas
argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas
argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic
barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas
athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic
real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic
sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de
madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico
de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid
real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto
acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto
pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto
prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca
atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas
barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona
atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona
hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real
madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona
sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas
beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas
betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas
boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil
vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas
caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas
campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del
rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas
campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas
campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de
futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de
caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas
carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos
sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas
carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de
caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de
caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos
en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas
casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta
betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta
manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions
foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions
league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league
hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions
league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile
vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas
city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico
real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas
colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas
como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas
combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas
pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero
virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas
con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del
mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas
copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa
mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos
eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas
de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de
boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como
se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos
en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de
caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas
de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas
de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes
online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas
de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas
de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol
seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas
de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de
hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas
de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa
league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la
liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas
de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de
partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema
como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de
tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc
hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real
madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas
del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del
real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas
deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas
apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas
caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas
champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas
deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa
libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de
nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas
deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas
doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas
en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas
deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas
estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas
deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro
futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas
ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas
golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas
deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de
impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas
mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas
deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas
mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas
murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas
deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas
online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas
online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas
online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas
online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas
online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas
deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas
paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas
deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru
vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas
promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas
real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para
hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas
sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito
inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis
de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas
ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y
casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda
b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas
doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles
y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas
ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones
venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas
en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas
en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions
league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas
en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea
mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de
futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas
en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas
en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo
ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas
españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas
espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas
esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas
esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas
esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas
eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas
eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league
pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1
bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1
hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas
final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions
league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final
de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas
final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final
rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina
betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia
argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas
futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol
en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol
en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas
fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos
olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas
futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos
hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos
trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas
gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas
hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas
ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de
la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador
europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la
liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador
mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial
f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores
mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar
mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona
campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas
goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand
slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas
gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos
eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas
handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas
hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas
hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas
hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos
en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos
olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas
la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas
legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid
arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas
madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas
madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana
la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca
osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester
city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas
mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas
mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas
mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial
2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas
mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas
mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas
mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub
17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba
all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas
nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba
para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba
tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas
nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas
nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas
online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas
online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas
online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online
con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas
online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online
futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online
gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas
para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas
para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para
ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar
la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas
para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la
eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la
eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas
partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas
partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas
partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas
peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas
playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas
playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas
por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por
paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas
psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas
puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que
es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana
la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara
la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas
quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid
atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid
borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real
madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real
madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real
madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid
manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas
real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs
atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid
vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid
vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real
sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas
resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma
barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas
seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas
seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este
fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras
para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla
gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas
sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas
sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas
significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito
inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super
bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas
tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas
tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis
en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas
tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis
roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera
division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas
uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us
open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas
valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas
venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales
futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de
hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas
y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro
nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina
francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico
en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester
united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de
madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid
vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid
apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona
casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona
vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs
celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas
chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea
apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio
de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog
apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono
bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono
casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono
de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de
bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de
casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro
apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos
apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas
de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas
de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos
paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de
apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia
apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas
apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de
apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora
apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de
apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas
deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora
stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular
apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular
probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield
apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos
apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas
bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas
colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas
deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa
de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas
bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por
registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de
apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas
champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de
apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago
anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de
colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de
fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de
apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa
de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas
españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas
peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa
de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa
league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula
1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa
de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa
de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de
apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa
de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para
ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas
peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa
de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia
en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de
apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas
virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del
real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas
españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia
españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas
apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas
asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas
app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono
sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de
apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas
bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de
caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas
de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de
apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas
gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por
registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas
con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de
apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de
apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas
de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de
apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del
rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas
de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas
deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de
apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa
online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas
de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas
de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa
licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de
apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa
2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas
de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas
de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas
futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de
apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de
apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas
de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de
apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas
de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas
mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas
nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas
ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas
online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de
apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online
en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas
de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas
de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas promociones|casas de apuestas
que aceptan paypal|
TurkPaydexHub se distingue comme une plateforme de placement crypto revolutionnaire, qui utilise la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour proposer a ses membres des atouts competitifs majeurs.
Son IA analyse les marches en temps reel, detecte les occasions interessantes et applique des tactiques complexes avec une exactitude et une rapidite inatteignables pour les traders humains, augmentant de ce fait les perspectives de gain.
TurkPaydexHub Trading
TurkPaydexHub se differencie comme une plateforme d’investissement en crypto-monnaies de pointe, qui exploite la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour fournir a ses clients des avantages decisifs sur le marche.
Son IA scrute les marches en temps reel, detecte les occasions interessantes et applique des tactiques complexes avec une precision et une vitesse hors de portee des traders humains, augmentant de ce fait les perspectives de gain.
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15
euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas
deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas
que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que
siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de
juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria
ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis
nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro
apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas
ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas
futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa
de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app
de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app
de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app
de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas
perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas
gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca
apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para
hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus
apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas
de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas
deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas
deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas
a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves
barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del
mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas
america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas
anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina
gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina
online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas
argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera
division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas
athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic
sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico
barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de
liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid
real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico
madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas
atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas
baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas
baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas
barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca
girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas
barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca
vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas
barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas
barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona
inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real
madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas
barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket
hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas
beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis –
chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis
fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis
real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas
betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de
bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas
boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa
america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas
campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas
campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas
campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland
garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de
caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas
carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas
carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de
caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos
nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de
caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino
madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino
online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas
celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta
manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions
hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions
league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas
chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas
chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas
ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas
city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas
como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas
combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas
combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas
como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta
de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa
africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas
copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey
baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey
futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas
corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de
baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol
para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo
canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y
colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos
online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas
de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos
pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de
casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de
colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de
corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas
de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol
gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para
mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para
hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos
en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos
trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre
hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas
de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la
nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de
nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de
partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas
de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de
ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del
dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia
deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de
hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del
sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas
deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico
de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas
barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas
bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas
casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas
ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas
com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas
combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono
gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas
deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa
del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas
deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la
mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas
deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas
deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas
dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas
en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas
deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas
deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas
deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas
es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas
deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas
deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas
deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro
tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas
futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas
deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas
interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la
liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas
listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas
seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas
deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas
deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas
deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba
hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas
online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas
deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para
hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru
vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real
madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas
deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas
deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas
deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas
valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas
virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas
deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas
dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas
directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador
vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas
elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas
en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas
en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas
en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el
futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas
en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas
en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas
en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea
españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas
en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo
futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo
peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas
españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa
gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra
eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa
mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas
esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas
euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas
europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas
f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas
f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de
ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas
final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas
final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas
formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas
fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas
futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas
fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas
futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas
futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos
en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas
gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador
copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas
ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador
f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga
española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador
mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar
champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe
valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de
liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la
liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas
golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas
gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis
para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis
puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas
gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap
nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas
juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas
juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas
jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga
santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends
mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes
betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas
liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones
de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas
linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real
madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas
madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid
borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas
madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de
golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador
eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores
casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma
ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples
el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial
2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial
clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas
mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas
mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas
mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba
esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba
hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas
nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas
nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online
champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online
deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas
online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online
futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online
gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online
mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas
online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online
sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas
osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises
bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para
boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de
hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas
para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para
ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa
league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para
hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas
para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para
la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para
la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la
nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para
partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas
partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos
eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas
peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas
peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru
vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi
eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas
playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por
internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por
paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por
sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones
futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas
primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos
deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg
barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos
tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas
que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas
quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el
mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara
la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas
quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas
real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real
madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real
madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester
city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real
madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas
real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas
real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de
bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma
barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas
rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras
foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy
futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas
seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas
seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas
seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas
semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas
sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas
sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester
united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real
sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas
sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas
sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema
trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas
super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta
roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas
tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de
golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa
champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas
ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc
telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay
corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia
barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas
valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas
venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas
villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales
futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta
a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos
de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia
apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina
francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay
apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile
apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic
manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna
apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona
apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid
vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real
madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada
de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona
atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid
apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia
apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs
atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta
de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs
girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best
america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis
chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas
online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog
apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de
apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida
apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de
apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de
apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas
deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono
sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos
bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas
de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas
de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas
de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos
gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito
apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot
de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil
peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas
seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas
seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora
apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de
apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora
de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de
apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de
apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular
cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad
cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas
deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba
apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos
apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos
con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de
caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos
apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa
apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas
deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas
mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa
apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa
de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa
de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa
de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas
caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa
de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa
de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de
apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa
de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de
apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de
apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de
apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa
de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas
en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas
en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas
españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa
de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de
apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula
1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de
apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas
liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa
de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas
mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas
nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas
oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas
online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online
paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas
online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de
apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas
peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por
paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas
legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas
ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas
apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de
apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas
de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de
apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas
champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas
colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de
apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito
minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de
apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia
en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia
española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas
de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas
con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa
del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de
fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas
deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas
de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas
de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas
madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas
deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas
peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de
apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de
apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas
de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas
españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas
europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas
fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de
apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter
barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas
legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas
de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas
de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas
nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas
nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online
en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas
online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de
apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|c
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir
de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar
y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba
apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para
hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones
de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones
de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para
hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas
argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app
apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app
apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas
futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app
de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de
apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas
deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas
en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app
de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de
apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app
para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas
en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps
apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas
mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas
deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras
de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la
nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas
al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz
hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas
y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas
nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas
argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas
argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas
argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas
athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas
atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas
atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico
madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas
atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas
baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas
baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca
bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas
barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas
barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético
de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la
champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas
barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas
barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas
barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas
betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas
betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas
bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas
boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas
brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference
league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del
rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas
campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas
campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas
campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas
campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas
campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas
campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de
galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de
caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras
de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas
casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta
betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas
celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league
2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions
league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea
betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo
tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas
clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas
clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia
vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como
funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de
fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas
combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas
para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas
como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas
con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas
con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas
copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas
copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del
rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas
copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas
copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas
copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia
argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1
euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto
nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de
beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack
en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas
de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas
de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas
de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de
caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de
caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera
de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino
por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas
de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de
esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas
de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de
futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol
en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas
de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol
mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol
para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de
futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol
sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas
de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de
la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la
liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la
nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas
de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas
de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de
peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de
tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de
tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis
pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de
todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del
boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas
del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia
futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas
deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas
deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas
deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas
deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas
deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas
chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas
con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas
deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas
cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas
de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas
de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas
deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas
en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas
deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas
francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas
deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas
deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas
ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas
golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas
legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas
deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga
española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas
madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor
pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas
deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas
mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas
nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas
deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas
deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas
deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas
deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido
suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas
perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas
deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas
deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas
deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero
real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas
stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis
de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas
deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas
venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas
deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas
dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas
directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble
resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas
draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions
league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas
en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas
en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas
en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea
españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea
futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas
en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas
en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos
de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas
en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas
en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas
en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos
de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa
inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas
espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas
esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas
estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa
final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas
euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas
f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para
ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas
favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final
champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del
rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final
eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas
final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa
europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia
nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula
1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas
formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia
argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas
futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas
futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol
en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol
españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas
futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol
foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol
hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para
hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos
hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas
gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador
copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador
de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas
ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador
la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar
liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe
valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona
campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas
golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis
con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis
puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas
gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap
baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas
handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas
hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda
argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy
futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas
hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos
olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos
baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas
la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la
liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas
legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga
1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva
pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de
campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga
española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de
futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas
liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas
madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid
valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester
athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles
de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de
tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas
mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas
mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb
para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma
ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial
campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas
mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial
lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp
nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas
nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba
hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy
pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas
nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas
nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl
las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas
online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas
online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online
carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas
online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas
online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas
online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas
online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas
online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online
uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas
osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas
osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas
osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas
over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos
qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas
para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas
para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas
para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la
champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de
hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido
champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas
partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas
de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas
peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru
vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff
ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas
playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas
por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones
futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos
nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a
segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la
champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas
quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas
real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real
madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid
bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas
real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas
real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real
madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real
madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real
madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid
vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad
psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad
valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas
roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas
segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas
segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras
baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas
seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras
nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas
seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas
seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla
atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas
sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla
inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas
sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla
osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito
minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas
sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl
favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas
tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas
tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis
itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas
tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas
tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos
de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions
league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc
hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas
uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas
us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas
villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas
villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales
colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas
y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos
de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina
apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico
apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united
apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real
madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas
apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona
atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid
apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona
sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs
atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta
de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona
apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona
vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea
apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas
españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de
apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis
sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de
registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito
marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos
apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de
apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de
apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos
de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de
casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de
apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos
sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora
apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora
apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas
de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de
apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de
arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping
apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora
trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular
apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular
ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo
de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions
apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales
de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos
apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de
caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas
online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas
cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa
apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas
mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa
de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas
beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa
de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa
de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa
de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las
mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa
de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa
de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa
de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de
apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa
de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas
españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa
de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa
de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa
de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de
apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de
apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de
apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de
apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa
de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa
de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas
online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas
online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para
boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de
apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que
regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa
de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa
de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive
la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas
apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas
apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo
5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas
apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas
apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas
apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas
app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de
apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de
apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas
carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas
de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas
ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de
apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas
con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos
gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas
de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas
con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas
de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de
apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas
de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas
deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas
de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas
en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas
de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas
en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas
en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de
apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas
españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas
española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de
apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas
f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas
futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas
gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de
apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de
apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas
seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas
mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo
5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas
mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de
apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de
apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas
online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de
apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online
peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en espa
slot365 xx vip Một trong những yếu tố quan trọng mà người chơi quan tâm khi tham gia cá cược trực tuyến chính là độ an toàn bảo mật. Tại đây, nhà cái luôn cam kết đảm bảo quyền riêng tư và an ninh tuyệt đối cho tất cả người dùng.
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris
sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris
sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari
sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis
paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide
aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide
pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide
paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour
paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse
match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app
paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli
pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli
paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris
sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris
sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll
paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari
sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris
sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris
sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile
paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent
paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce
pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris
sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner
au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces
paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs
foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis
site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis
sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll
100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll
paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue
paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus
de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus
depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif
betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris
sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris
sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris
sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites
de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris
sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but
contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti
perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul
cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote
paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris
sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris
sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote
paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice
paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi
paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote
paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée
paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris
sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif
en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris
sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus
paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code
promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris
sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser
un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris
sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif
pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les
paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une
cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment
comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable
paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire
des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris
sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire
pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment
faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment
faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire
un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent
les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent
les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris
sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris
sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris
sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner
a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif
a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au
paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris
sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les
paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des
paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment
gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner
paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment
gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses
paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment
gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer
au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer
au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les
paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au
paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment
reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des
cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote
paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur
de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur
paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus
paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari
sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des
sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris
sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif
pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris
sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif
site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les
cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre
les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris
sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo
paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil
de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris
sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des
champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif
pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil
pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil
sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris
sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris
sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a
100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote
de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça
marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie
sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote
paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris
sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote
paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote
paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à
1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris
sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe
de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de
paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que
signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote
paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double
paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe
les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif
definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de
cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans
un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement
sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif
paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements
sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes
paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face
a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des
paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de
paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier
excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris
sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum
parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif
nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum
sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal
paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner
100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour
paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a
coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner
argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner
au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au
paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris
sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de
l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris
sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner
les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris
sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec
les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec
paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup
sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris
sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa
bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll
paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris
sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs
v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe
paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif
gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0
paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris
sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap
paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris
sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris
sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey
paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif
france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu
de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif
gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans
argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de
paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux
olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer
au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse
paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif
paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris
sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu
paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il
imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la
meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur
application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la
méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la
plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur
site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur
site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros
paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les
10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les
applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers
paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de
paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures
applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs
site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les
paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne
comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus
gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus
grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1
paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite
de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste
des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste
site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites
paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel
gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel
pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel
prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique
paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris
sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des
paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale
paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif
interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné
paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu
paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris
sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué
paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme
paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app
de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris
sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de
paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur
application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur
bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus
paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur
conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote
pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote
paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur
gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris
sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris
sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre
paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris
sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris
sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de
pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur
site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de
paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site
de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris
sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site
pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris
sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif
foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris
sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif
hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari
sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris
sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli
de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli
pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure
application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris
sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications
de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures
cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris
sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site
de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante
paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode
infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris
sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris
sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode
paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum
paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris
sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante
paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple
paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul
paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris
sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris
sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de
pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau
site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif
france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris
sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros
paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre
bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de
bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre
de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris
sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif
coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif
remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo
paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot
paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif
en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris
sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack
de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif
100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec
handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif
avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif
buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari
sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari
sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari
sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif
en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif
euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari
sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif
france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari
sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif
gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif
hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur
absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif
leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif
ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif
meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif
offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif
prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif
pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari
sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari
sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari
sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif
sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif
top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie
sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie
sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques
paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs
et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10
euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros
remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a
faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif
argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent
virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au
canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec
bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif
avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec
paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris
sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de
france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris
sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans
depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif
but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur
contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne
joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul
gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif
cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif
code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné
comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match
reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif
comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif
comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris
sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote
explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris
sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du
monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot
minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris
sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris
sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif
en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne
sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris
sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris
sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot
comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot
cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris
sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif
foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif
foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris
sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris
sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif
france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france
italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris
sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à
coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif
gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris
sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris
sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif
gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros
gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap
1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif
handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris
sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris
sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif
hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant
le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif
joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris
sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les
18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif
liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match
du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif
match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif
match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif
meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris
sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris
sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif
moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3
explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1
foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris
sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris
sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans
depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif
premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match
aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif
psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif
psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif
psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg
liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que
veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif
retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris
sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris
sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris
sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif
stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris
sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif
systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif
systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme
3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique
pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif
tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif
tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif
top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris
sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs
aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris
sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris
sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris
sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris
sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs
france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris
sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris
sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur
glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs
jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue
1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs
nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris
sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris
sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché
paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris
sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les
paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus
gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote
gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris
sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage
de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site
paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif
foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic
paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics
foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris
sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter
paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris
sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce
que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est
ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie
1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg
dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari
sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap
paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris
sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site
de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris
sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est
le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel
est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari
sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le
plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif
choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le
plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure
appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle
est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels
sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris
sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris
sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris
sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris
sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris
sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur
de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat
paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris
sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur
montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site
aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel
paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de
conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site
de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari
sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant
paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif
autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif
avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif
avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris
sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de
paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris
sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de
paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne
suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de
paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site
de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de
paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif
paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif
qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site
de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site
de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de
paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs
gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs
suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris
sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif
100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari
sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site
pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif
100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site
paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus
cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site
paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif
foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris
sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif
sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris
sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris
sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site
pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif (Son)|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de
paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites
de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs
suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris
sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris
sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme
2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris
sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau
bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris
sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll
paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris sportif|tableau
paris sportif excel|tableau r
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15
euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que
significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros
gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de
apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas
sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas
colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app
apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app
control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app
de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas
deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas
perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas
en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de
apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles
de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app
para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas
en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas
deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps
de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps
de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas
peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer
apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a
carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a
corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas
a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al
empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas
alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas
anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas
arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas
argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas
argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina
paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina
vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera
division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas
asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester
united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic
real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic
roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas
atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de
madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas
atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real
madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real
madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas
baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto
pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas
baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca
atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs
psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona
athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de
madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas
barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona
psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona
vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas
beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas
betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis
sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy
colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar
online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono
gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas
boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas
boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas
caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas
caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas
campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference
league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la
champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas
campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa
league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga
santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas
campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato
f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera
de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos
hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras
de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas
casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas
casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta
espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions
league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions
league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas
chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas
ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city
madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas
clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid
barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas
colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas
colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs
brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas
mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas
pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para
mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas
con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades
de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta
de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del
rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del
rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey
pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa
mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de
1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto
nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas
de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos
como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de
caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos
ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de
caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos
online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de
ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes
en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de
dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de
futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol
app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol
colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas
de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas
de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para
hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol
para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de
futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas
de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas
de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy
seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de
juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas
de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de
la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga
española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de
nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas
de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de
sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de
sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de
tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del
boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del
día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de
hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas
argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas
deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas
campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas
casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas
chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas
deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas
deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas
deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas
deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas
de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas
de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas
dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas
esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias
seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas
deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol
colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas
deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas
deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales
en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas
liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas
deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas
deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas
deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas
deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas
nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online
argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas
online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas
deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas
deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas
pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero
real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas
telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas
tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas
deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas
descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas
diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y
triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto
uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas
en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de
caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia
de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas
en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas
en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas
en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas
en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas
en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo
futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa
gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas
español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas
esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas
eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa
hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1
canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final
champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final
del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas
final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas
finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula
uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas
francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas
fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas
futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol
en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas
fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol
foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas
futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas
futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos
en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas
gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas
ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas
ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa
league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas
ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas
ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona
campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real
sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam
de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas
gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas
impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas
inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas
juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas
kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la
liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales
en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas
leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas
liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas
liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga
española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas
linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico
champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid
barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas
madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas
madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid
gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas
madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real
sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas
mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas
mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo
goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores
casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas
mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas
mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial
2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial
brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial
favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas
mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba
consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba
pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas
nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas
nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas
octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas
online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas
online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online
champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online
colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de
caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas
online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online
futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online
gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real
madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas
paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises
bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para
boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el
partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero
facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar
la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas
para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas
para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas
partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos
champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas
partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas
paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas
peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi
eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso
a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas
por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas
por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre
partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas
primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas
psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas
puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana
el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas
real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real
madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester
city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas
real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real
madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid
vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas
real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real
sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas
real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas
resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma
sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol
hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para
este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para
hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales
eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla
barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla
celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas
sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o
combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas
sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas
sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super
bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas
tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis
copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa
pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis
femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas
tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa
europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc
ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas
ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc
topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas
valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas
venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas
villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs
real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas
y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y
resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba
apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina
vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico
en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico
de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona
apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico
vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de
madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de
apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia
apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona
vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona
vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real
madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet
apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona
apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de
tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas
gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas
españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono
bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis
sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas
de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono
sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos
bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa
de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas
deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas
de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos
de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos
gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito
casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas
de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora
apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora
apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas
surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para
apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular
apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular
cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular
ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios
apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield
apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de
galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras
de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas
betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas
mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa
apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa
de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas
altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de
apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas
de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa
de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa
de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real
madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas
en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa
de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de
apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5
euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa
de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas
eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de
apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de
apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas
segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas
mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas
online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de
apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa
de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de
apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas
para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa
de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de
apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa
de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia
en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de
apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de
apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos
sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas
apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia
en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas
deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas
españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas
apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas
ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas
peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas
apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas
asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas
bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas
cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas
de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas
de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de
apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de
apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos
gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas
de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas
con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas
con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de
apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas
de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas
en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas
en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas
deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas
de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito
mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de
apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas
en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas
equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de
apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas
de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de
apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula
1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo
5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas
de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas
legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de
apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas
madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas
méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas
mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial
baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas
de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas
de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas
de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas
de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online
en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas
online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de
apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas
de apuestas
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para
ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2
apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2
que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de
cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas
deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas
de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas
deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app
apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas
ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas
deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas
en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de
apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app
de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para
apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas
deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar
control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps
de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps
de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender
a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas
a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas
a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis
wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del
mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas
antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas
apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina
colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas
argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana
mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina
mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas
argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas
argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso
a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas
asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic
real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas
athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico
barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de
madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana
la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid
real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico
real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas
baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas
baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas
baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real
madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs
psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas
barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana
la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona
valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona
vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis
sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay
hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas
bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono
sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas
borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos
online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos
zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de
champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del
mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas
campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas
campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos
nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas
carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de
galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino
gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas
celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas
champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions
league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions
league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions
league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas
chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas
chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas
ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour
francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico
español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas
colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas
colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como
funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo
partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas
pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas
copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa
del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas
copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas
croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las
vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas
de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos
como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas
de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de
caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas
de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas
de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas
de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa
america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas
de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas
de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas
de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de
futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol
gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol
online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para
hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol
peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas
de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como
ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de
galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas
de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas
de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas
de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de
peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como
funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis
hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas
de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas
del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas
del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas
del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10
euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas
app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas
deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas
deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono
bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas
caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas
deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino
barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca
de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas
chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas
com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas
deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas
con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas
con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas
deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas
copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas
altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas
dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas
doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas
en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas
deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas
es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas
deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas
deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas
deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap
asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas
la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado
clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas
mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores
app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores
cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas
mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas
nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas
online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas
online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas
deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas
que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas
deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas
sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas
deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas
uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas
venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos
pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda
b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas
dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero
virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo
futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble
resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas
en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas
en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo
futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas
en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas
en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas
en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea
boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de
fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados
unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de
futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo
argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo
mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa
alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa
gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa
italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas
espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas
esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas
esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas
esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas
eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa
femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa
sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas
europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1
monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final
champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas
final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final
eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final
libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales
de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol
americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas
futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas
futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol
en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol
españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas
futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol
gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana
colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions
league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador
copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas
ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas
ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas
ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores
eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar
nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona
athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas
girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador
eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas
golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam
de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas
gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas
gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis
y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas
hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas
hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey
sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda
vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy
seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas
juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas
la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas
las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas
legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga
1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas
liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool
real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas
madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas
madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid
gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid
osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas
masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador
mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas
méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas
mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas
múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el
gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas
mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas
mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas
mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas
mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas
mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial
sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas
mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba
all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas
nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas
nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas
nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super
bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online
bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas
online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas
online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online
de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online
españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online
futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online
nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas
open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas
paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para
el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para
el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para
europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar
dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas
para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para
ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para
juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas
para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para
la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los
partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas
partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas
partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos
champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos
de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas
partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas
peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru
vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas
playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff
segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas
polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas
por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal
uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer
con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara
la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real
madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas
real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real
madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs
valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real
sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas
roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda
b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas
segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la
ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas
seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras
gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba
hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar
dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy
fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas
seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras
telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas
sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas
sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas
sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas
sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas
sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real
madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas
simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas
sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas
sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas
stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas
supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas
tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas
tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas
torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa
league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas
uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us
open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real
madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid
valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas
venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas
villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas
villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester
united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales
sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta
españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas
y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos
de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas
y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es
pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina
croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina
mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia
apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se
gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de
madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de
madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid
apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro
barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca
vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona –
real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico
madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia
apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona
vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs
sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas
apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid
apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas
tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida
apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida
casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida
marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis
sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro
apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis
apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas
deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos
de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de
apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos
gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de
apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil
colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos
apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora
apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas
segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de
apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora
de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora
sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas
futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular
cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular
stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield
apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa
apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de
caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos
con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa
apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas
deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas
futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa
apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa
de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa
de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa
de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa
de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de
apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de
caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de
apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa
de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas
en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa
de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5
euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa
de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa
de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de
apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales
en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas
méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas
mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de
apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas
oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online
argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa
de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online
venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para
boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas
peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas
por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas
que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de
apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de
apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de
apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas
virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas
apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos
sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas
ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas
apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas
legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas
nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas
apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas
de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas
de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas
de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de
apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas
con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas
con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia
españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de
apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del
rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas
de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas
deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de
apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas
en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas
en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas
deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas
online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito
mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero
gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de
apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas
en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas
de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas
de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas
de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas
españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de
apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de
apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas
de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas
de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de
apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de
apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de
apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales
mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de
apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas
seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas
mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial
baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de
apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas
nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de
apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de
apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de
apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online
en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de
apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de
apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2
que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis
nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de
apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones
de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de
apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones
de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para
hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app
apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app
apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas
colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app
apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas
sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de
apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app
de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de
apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas
sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas
gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de
apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app
marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas
deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar
apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre
amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas
mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas
a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al
empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas
y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas
ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas
anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina
españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas
argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina
mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas
argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs
colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real
madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a
segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas
athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester
united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas
atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas
atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico
de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto
handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas
baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça
hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas
barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas
barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico
madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona
granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona
madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real
madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona
vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis
barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis
girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real
sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs
valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas
bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas
bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas
boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas
brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil
uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos
colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la
champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas
campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga
santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas
campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato
f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de
caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera
de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas
carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas
carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras
de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras
de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos
pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino
futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino
madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas
celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta
madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions
pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real
madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas
clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia
brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas
combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para
mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas
con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de
debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas
copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas
copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del
rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas
cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol
para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de
boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se
juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos
internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de
caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas
de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas
de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas
de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol
en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de
futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para
hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol
peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol
seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de
galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de
galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de
hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de
juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa
américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas
de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de
mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas
de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de
sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real
madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas
deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1
euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas
deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas
app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas
campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino
barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas
champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas
deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas
deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas
con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas
deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para
ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa
mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es
la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de
boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas
de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas
de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas
deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas
en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas
en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas
en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas
faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas
francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas
deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas
deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis
con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas
handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas
deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas
legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres
de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas
deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas
mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas
deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas
nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas
deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para
ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas
deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas
deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real
madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado
exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas
seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas
deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas
simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas
deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram
españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas
tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas
deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas
y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas
deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso
la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero
real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund
barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs
venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos
online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas
en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas
en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las
vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas
en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea
futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas
en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de
futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas
en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas
en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas
en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa
croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas
españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol
betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas
esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas
eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa
hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas
europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas
f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1
miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas
fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito
champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas
favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final
champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas
final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final
del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final
eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas
final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol
americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol
chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol
en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol
español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas
futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas
futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos
online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas
hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la
eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas
ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador
nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas
ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas
ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona
campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real
sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas
golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas
gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a
eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap
nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey
hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos
baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador
sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las
vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas
legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas
libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de
hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas
linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas
madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca
hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas
madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid
liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca
osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city
real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de
tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores
casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico
polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas
mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas
mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial
rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas
mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba
consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas
nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos
hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas
nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas
ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono
bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas
online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online
futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas
online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online
paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna
real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas
over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas
para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas
para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar
en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas
para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para
la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas
para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas
partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas
partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas
partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos
de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos
hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas
peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas
playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff
segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas
por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet
para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por
sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos
tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos
tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por
tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer
con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas
quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas
quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara
el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara
la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid
arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real
madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid
barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid
borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real
madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas
real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas
real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid
vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid
vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real
sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas
real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas
real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas
rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas
segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas
seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas
seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas
seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para
hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas
seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico
de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla
betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas
sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla
juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla
real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla
valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas
sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake
10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas
supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis
en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas
tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas
uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc
chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc
ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay
corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid
barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal
athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas
villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas
vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y
juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro
nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico
de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico
de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona
apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico
madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de
cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico
apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona –
real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona
inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona
vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona
vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis
apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis
sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas
ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono
de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida
apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de
registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono
gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro
apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito
apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos
apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas
apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas
colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos
de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida
casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos
gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas
de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito
apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de
apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador
de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas
apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora
apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora
apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje
apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas
de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas
deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora
de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora
de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de
apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora
poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas
sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas
apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades
apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo
de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de
apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de
galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras
galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de
mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa
apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas
mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa
apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas
peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas
baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono
bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono
gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas
ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas
mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas
con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de
apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas
de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas
de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de
peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de
apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa
de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas
deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa
de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas
deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas
en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas
en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa
de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas
eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas
f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso
mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas
legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales
en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de
apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa
de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real
madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de
apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa
de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa
de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago
anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas
por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de
apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia
en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real
madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas
chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas
apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas
apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas
mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas
apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas
5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas
de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de
apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de
apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas
gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de
apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito
minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de
apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas
de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas
de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas
de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de
apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de
apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas
peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas
de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas
de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de
apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas
en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de
apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas
de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas
eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas
de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas
formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas
legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas
legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas
lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas
mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de
apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de
apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de
apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas
no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas
nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas
de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de
apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas
de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas
online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de
apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas
de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online
mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas
online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de
apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros
gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa
en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se
declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad
apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo
para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas
deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para
hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar
seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app
apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app
apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa
de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de
futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app
de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app
de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app
de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas
de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para
apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para
ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para
hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control
de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas
deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas
a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas
alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso
campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas
ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas
android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas
anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina
francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas
argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina
mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas
argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas
argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real
madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas
athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic
osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico
barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético
copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la
liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid
real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas
atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas
barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas
barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas
barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas
barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona
betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la
champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas
barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas
barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas
basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol
mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis
chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas
betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas
betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas
brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas
caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas
campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas
campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas
campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga
española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas
campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas
campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de
caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos
hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de
caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras
de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas
carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras
de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras
de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos
pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas
celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas
celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas
champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas
champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions
league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league
pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas
chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a
españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas
clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas
colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas
combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas
hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas
combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas
con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero
virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas
copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas
copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas
copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa
libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa
sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia
argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas
cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de
baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto
nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de
beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas
de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas
de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como
funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas
de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas
de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de
caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino
online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de
dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol
app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de
futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol
online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para
hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de
futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas
de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de
futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de
galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de
galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas
de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de
juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de
la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de
mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas
de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de
perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como
funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis
seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid
barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas
deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas
1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas
android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas
deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas
baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas
deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas
deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas
casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas
deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas
deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se
juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas
deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas
copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa
libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas
deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas
deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del
dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas
deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas
deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas
deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas
deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas
deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias
seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas
deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula
1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas
deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas
gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas
deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas
deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas
la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales
en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas
liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas
seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas
deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas
mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas
nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas
ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas
deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas
online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas
deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas
para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas
deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas
deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real
madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas
seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas
deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas
sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas
deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram
españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis
de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas
tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com
foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la
liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas
descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas
dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas
doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund
barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas
en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas
en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas
en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas
en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea
boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas
en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas
en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas
en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas
en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los
esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos
de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas
en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas
en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas
en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo
mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas
españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania
eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa
gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas
españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa
inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas
espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports
españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports
lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa
campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa
favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league
hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa
league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas
f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas
favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final
copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final
copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final
del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas
final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales
nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula
1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro
nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas
futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas
futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas
fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol
gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas
futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas
futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas
futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas
galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa
del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador
eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores
eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana
uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas
goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada
barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis
regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis
y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas
handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas
online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas
hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy
seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league
americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las
vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas
legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas
legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga
argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas
liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga
santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid
barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas
madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas
madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid
gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas
madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca
real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas
maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores
casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas
méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas
mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial
ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial
sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas
mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba
hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para
hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl
las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas
nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de
caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online
chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online
comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas
online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online
foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas
online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online
paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online
tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas
open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas
osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over
2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas
paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas
para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para
futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero
facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la
eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas
para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas
para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa
del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la
eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido
champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas
de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas
peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff
ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas
playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia
argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar
dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera
division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos
deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas
psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas
que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que
siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a
segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real
madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de
madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas
real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid
campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas
real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real
madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas
real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas
real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas
real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real
madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid
vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas
real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas
rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas
ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas
segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda
division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras
calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras
futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas
seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la
liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla
jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla
manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla
real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito
inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero
real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que
significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas
sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake
10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas
supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa
davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas
tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas
tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas
tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas
tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa
champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc
hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia
barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia
madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid
valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas
villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas
y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y
pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas
y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia
apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina
vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia
apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las
apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico
barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real
madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico
madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de
cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro
barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico
apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid
apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona
atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa
de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg
apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao
apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis –
chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea
apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog
apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono
apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida
casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas
sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro
casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono
registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas
deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono
sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas
sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de
apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de
apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos
de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis
casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito
apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos
sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas
apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora
apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas
yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir
apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora
de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora
para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular
apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas
futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas
deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular
unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de
apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de
caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras
de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras
galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas
barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono
sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas
colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa
apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa
apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa
de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa
de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas
bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas
bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de
apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de
apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de
apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas
de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de
peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas
deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas
deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa
de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa
de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa
de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa
league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula
1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1
euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa
de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de
apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas
mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5
euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de
apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del
real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa
de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de
apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas
pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de
apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru
online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa
de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas
sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de
apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas
apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas
apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas
bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino
online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas
con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de
apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas
de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas
con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago
anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa
del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas
de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de
apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas
de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas
deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas
deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas
de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas
de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas
de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas
de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas
equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de
apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas
de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas
fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas
de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de
apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales
españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas
licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de
apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de
apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo
5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas
mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas
de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de
apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas
en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas
online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas
de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas
de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de
apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas
de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca
apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2
que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas
que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades
de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para
ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas
online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones
de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas
deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas
seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de
futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas
android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app
apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas
deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app
de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de
futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas
deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas
deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas
en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app
de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app
de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de
apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de
futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas
deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas
mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps
de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del
dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas
1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas
a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas
al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas
y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del
mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas
argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas
argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas
argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina
polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina
vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas
asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic
barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic
real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas
athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas
atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas
atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico
madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas
baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas
barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca
madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas
barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona
atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona
atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona
hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona
osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona
valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas
barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket
hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis –
chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis
fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis
sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas
betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia
vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono
sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas
boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil
uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas
caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions
2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference
league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas
campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas
campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas
campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas
campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera
de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera
de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas
carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas
carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas
casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas
celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas
champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league
2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas
chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas
ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas
city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia
vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas
de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas
nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas
para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas
seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas
probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta
de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas
copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa
brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del
mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa
del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa
del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial
de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas
corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de
baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para
hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos
internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos
online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de
caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas
de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas
de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa
america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes
online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de
f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas
de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de
futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de
futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas
de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de
fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas
de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas
de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de
hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de
juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas
de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas
de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de
nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas
de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de
sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas
de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas
de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de
tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de
todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas
del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas
del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del
partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas
deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas
10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas
deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico
de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca
madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas
bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas
deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas
champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas
deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas
con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos
virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa
mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas
deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas
deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas
doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas
deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas
en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas
en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas
deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas
es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas
europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas
formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas
foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas
gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas
ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas
deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas
deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas
mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas
méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas
mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online
colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por
internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas
para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas
deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas
peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas
deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas
deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras
para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas
sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram
españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas
deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas
valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas
y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a
segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas
descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund
barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas
ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el
clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas
en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino
online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de
futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas
en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas
en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la
nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea
colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea
méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas
en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis
de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo
mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas
españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa
croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas
españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana
eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa
georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra
cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa
italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas
español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports
gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa
league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league
pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas
f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas
f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final
champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas
final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa
libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas
final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final
euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia
nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas
futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas
futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol
en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol
eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol
gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol
pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas
futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana
colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador
copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del
mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas
ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas
ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador
nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas
ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas
ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas
girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la
liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona
real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada
barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas
gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis
sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas
gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas
grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas
hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas
hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs
argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas
hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas
juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos
online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas
la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas
nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas
legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas
legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas
liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga
española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool
barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas
madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid
barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas
madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid
borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid
city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas
madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas
mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real
madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras
para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters
de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador
eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico
polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas
multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el
gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas
mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas
mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial
de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial
de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial
motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all
star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta
noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba
hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas
nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas
nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online
caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions
league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online
de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas
online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas
online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas
online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online
paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas
online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas
osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises
bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para
el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas
para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar
dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar
la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas
para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para
ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas
para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa
del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los
partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas
partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos
champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos
eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas
peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas
peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas
peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas
plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas
playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por
internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas
por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas
pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones
futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos
futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos
nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer
con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas
que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas
quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana
la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara
la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara
la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real
madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real
madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas
real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas
real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs
atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad
barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real
sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma
sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas
seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas
seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas
sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla
juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla
real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero
real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas
sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo
copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas
stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis
en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis
seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para
hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos
de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa
champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas
ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas
uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas
valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor
app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal
betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal
manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas
virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas
vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos
de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de
futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es
pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile
apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic
real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid
apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid
real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada
de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid
apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico
de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona
betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona
psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs
athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de
vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona
vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona
vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas
en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis
madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio
de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas
españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida
apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono
casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de
registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de
apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas
deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas
apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos
casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos
de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida
apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas
deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas
de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil
colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de
apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas
combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas
seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora
apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora
apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de
apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas
seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para
apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular
apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas
apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas
apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba
apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos
con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas
online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos
de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas
trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas
mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de
apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas
barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de
apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa
de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas
carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa
de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas
de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas
de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas
del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas
en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas
deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas
españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas
mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de
apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito
mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas
en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas
españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de
apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas
legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de
apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa
de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de
apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa
de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa
de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago
anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de
apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de
apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas
asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas
apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas
mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas
peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5
euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de
apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas
barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de
apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de
apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de
apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas
con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de
apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de
apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de
apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de
apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de
apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de
apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas
de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de
apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas
en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de
apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa
nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas
española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas
españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas
europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas
formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de
apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas
de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de
apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas
de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas
legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de
apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas
de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas
de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de
apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva
ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas
en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de
apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas
online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de
apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de
apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas
de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas
de apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas
I love what yyou guys are usuallpy up too. Such clever work and exposure!
Keep uup the good works guys I’ve included you guys to
my blogroll.
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert
paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert
pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari
sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour
paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme
paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme
paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris
sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match
paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris
sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif
avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif
suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris
sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll
paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de
parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris
sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote
d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de
paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia
paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif
argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris
sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif
maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif
sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour
faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris
sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari
sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications
paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris
sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris
sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent
paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris
sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce
paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris
sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner
au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour
paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces
pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris
sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll
management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll
paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris
sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de
bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif
betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris
sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus
paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris
sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus
site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites
de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker
sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris
sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap
paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris
sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris
sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris
sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul
pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris
sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris
sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris
sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité
paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une
cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash
out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif
en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris
sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre
paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris
sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans
dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris
sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif
du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser
un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les
paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment
bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche
les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris
sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une
cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment
creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer
un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment
etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de
bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment
faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris
sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris
sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire
pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie
sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari
sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les
cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent
les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment
fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner
a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups
au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris
sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner
au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment
gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au
paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment
gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les
paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment
gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des
paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment
gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner
paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris
sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout
le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer
sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment
jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris
sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris
sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris
sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter
sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment
reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de
paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur
paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris
sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari
sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site
paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte
démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris
sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris
sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif
foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil
paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris
sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris
sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de
paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs
gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris
sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de
pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari
sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote
parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris
sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris
sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote
paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote
paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif
rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de
paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes
paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris
sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash
out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris
sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot
minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis
quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche
avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis
paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum
5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce
que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement
sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd
hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs
paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements
sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes
paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari
sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des
paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut
il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses
gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris
sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et
paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum
de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum
parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif
tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris
sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise
des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france
paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france
portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris
sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris
sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100
euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner
10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup
sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent
avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner
au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner
au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner
aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux
paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner
de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner
les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous
les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif
imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains
paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains
paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll
paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs
excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll
paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris
sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif
pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram
paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0
paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap
au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap
dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris
sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif
rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique
des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh
signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris
sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les
paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de
paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux
olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris
sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer
au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris
sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur
professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris
sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris
sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de
paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris
sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem
paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le
meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux
paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les
application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les
bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris
sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris
sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs
bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les
meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs
du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les
paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer
gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant
paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros
gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les
sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites
de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1
paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des
champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste
paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site
pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris
sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul
paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris
sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel
pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris
sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel
prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique
paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris
sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale
paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté
paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris
sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match
paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur
algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli
paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur
appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur
application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris
sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur
bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris
sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris
sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote
site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode
pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur
offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur
paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo
paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de
conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari
sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur
site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris
sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif
en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif
forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors
arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur
site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de
paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site
paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site
paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris
sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur
site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris
sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure
appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris
sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris
sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure
application pari sportif|meilleure application paris
sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure
strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures
cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs
application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris
sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris
sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site
de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris
sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris
sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode
paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum
paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris
sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris
sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris
sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul
paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au
paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris
sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris
sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de
paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site
paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris
sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre
bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre
bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans
depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue
sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe
du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris
sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot
paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris
sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou
faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris
sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de
bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari
sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari
sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique
france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari
sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment
ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari
sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari
sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari
sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari
sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari
sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari
sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne
ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif
foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france
espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari
sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif
gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif
hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif
jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari
sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif
methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o
jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari
sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari
sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari
sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif
rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans
argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari
sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari
sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari
sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris
en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et
sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris
sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10
euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif
a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif
a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif
application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif
argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris
sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris
sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec
paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans
depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus
cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris
sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris
sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif
but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif
buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur
prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif
buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif
cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné
comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca
marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif
comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris
sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris
sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris
sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif
coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris
sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris
sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif
dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt
minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif
en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça
marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif
en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif
et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale
ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris
sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif
foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris
sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot
prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic
gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif
forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise
des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france
angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france
belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif
france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif
france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris
sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif
gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit
avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit
en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris
sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris
sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris
sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif
handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors
arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris
sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur
declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la
francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les
18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif
les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris
sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match
abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris
sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris
sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris
sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode
2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de
3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif
multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2
4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba
conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris
sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif
offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris
sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou
moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris
sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic
expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif
pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg
barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter
cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le
plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle
prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris
sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif
rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris
sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si
un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple
ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse
application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris
sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme
2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif
systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique
pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris
sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris
sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc
france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur
ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire
prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris
sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris
sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris
sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs
comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs
coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs
en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris
sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris
sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris
sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris
sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris
sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris
sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue
europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris
sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs
pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs
site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs
tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour
de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif
au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus
gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus
grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner
au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de
mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris
sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris
sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site
pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris
sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit
paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic
pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic
paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides
aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg
bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg
paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris
sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur
se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris
sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que
signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg
en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que
veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les
paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari
sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de
paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est
le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur
site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari
sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif
faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site
de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle
est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris
sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels
paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de
gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris
sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris
sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris
sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash
paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat
sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari
sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris
sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de
mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris
sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat
paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts
paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris
sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris
sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris
sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif
gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne
sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans
depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif
en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site
de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de
parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris
sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site
de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site
de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site
de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec
bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site
de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site
de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de
paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot
minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif
en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour
gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors
arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site
de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site
de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif
paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris
remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de
paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site
de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif
sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif
sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site
de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse, Shellie,|site de statistique
pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros
offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif
canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari
sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site
paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif
1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif
bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site
paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors
arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris
sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris
sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site
paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris
sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs
belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors
arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris
sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse
paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs
arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites
de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans
dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris
sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites
paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris
sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif
foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris
sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris
sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris
sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme
de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris
sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau
excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion ba
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro
offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert
pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris
sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris
sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide
parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide
paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit
paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris
sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme
paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse
de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari
sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse
paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif
sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie
sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris
sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans
argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil
paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie
sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif
en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de
paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris
sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif
paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris
sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari
sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis
paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris
sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce
pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris
sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce
pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce
pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs
foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis
sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris
sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris
sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue
paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue
sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris
sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus
paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif
en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus
paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif
belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris
sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris
sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti
perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des
cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris
sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris
sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris
sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de
paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi
paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris
sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée
paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino
paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris
sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo
sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari
sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné
paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris
sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les
paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au
paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche
les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les
cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris
sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les
paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de
bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des
paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire
pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner
au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire
un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une
montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les
cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris
sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les
cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au
paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au
pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner
au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup
sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif
tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur
le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent
au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les
paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment
gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au
paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris
sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris
sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris
sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au
pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif
foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment
marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les
cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment
miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont
calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont
calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris
sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote
pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de
cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de
paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur
site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif
cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites
de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif
offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif
paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site
de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de
paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris
sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes
paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de
paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil
pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris
sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil
paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif
foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil
paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif
pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil
pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur
les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de
paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris
sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote
de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote
de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris
sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif
rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif
euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote
paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif
moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote
paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris
sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris
sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme
paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site
de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que
signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris
sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit
on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains
paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt
minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis
paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est
ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement
sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement
sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week
end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris
sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris
sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a
face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire
des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune
paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football
et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif
gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum
sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france
2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif
brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner
10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois
paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner
a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a
tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner
argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au
paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au
paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner
de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l
argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au
paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de
l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des
paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif
forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris
sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris
sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à
tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris
sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris
sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs
sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer
sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris
sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris
sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse
cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe
telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap
1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket
paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris
sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap
pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap
paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap
paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote
paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris
sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris
sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu
paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris
sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur
de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur
suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris
sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs
pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse
cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché
des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris
sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris
sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris
sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains
de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils
imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris
sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les
meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de
paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les
paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris
sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne
comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs
en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites
de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1
paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite
de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste
de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste
des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris
sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel
de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de
bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel
gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel
paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel
paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris
sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique
paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete
paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris
sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match
suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match
truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app
paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur
appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli
paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif
belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour
pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus
paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur
bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur
combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur
cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre
de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif
du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif
en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de
paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site
de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif
international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur
site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur
site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site
paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari
sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur
strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris
sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure
site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris
sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres
paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs
bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs
site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris
sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif
forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner
au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes
paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise
minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum
paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris
sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple
paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode
match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique
pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site
de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris
sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site
paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle
appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match
paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de
bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif
sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris
sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris
sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre
promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre
site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres
de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris
sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture
compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros
offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari
sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif
astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec
orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec
wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif
champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari
sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari
sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari
sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari
sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif
en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne
belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif
en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif
faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner
a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari
sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le
plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari
sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue
des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match
arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari
sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement
cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari
sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif
sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif
suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique
pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie
sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique
et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match
sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris
sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris
sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a
faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif
abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis
parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif
algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris
sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec
carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec
paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif
bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris
sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris
sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus
gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris
sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif
but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps
additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris
sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris
sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif
buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif
cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris
sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris
sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça
marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif
conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil
pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif
coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot
minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif
du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris
sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec
paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris
sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif
en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne
paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino
en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris
sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale
ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris
sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris
sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif
foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris
sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris
sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris
sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif
france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris
sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif
gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif
gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit
appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit
sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris
sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap
explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif
hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris
sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux
olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de
foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris
sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur
remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif
le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif
les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris
sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des
nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris
sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match
suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris
sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris
sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris
sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif
montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris
sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris
sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris
sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris
sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris
sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif
offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre
bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif
om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris
sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif
prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd
hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif
pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif
psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif
psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif
psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif
psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle
prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif
remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait
paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6
nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris
sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris
sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne
joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif
simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif
statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif
suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif
suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif
suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris
sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris
sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris
sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif
tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif
tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour
de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif
victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris
sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs
aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs
arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés
en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs
basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs
canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs
comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de
football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris
sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs
en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris
sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à
tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs
hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs
jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent
la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue
2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue
europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de
bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris
sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris
sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs
technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris
sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal
paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de
l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros
gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote
gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus
grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris
sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris
sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo
site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos
paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif
tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics
paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris
sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie
draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg
en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que
veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le
meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari
sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel
est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel
est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel
pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site
de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif
est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli
de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de
paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les
paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris
sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris
sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris
sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris
sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris
sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement
en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur
de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari
sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris
sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris
sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris
sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb
paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur
gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris
sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris
sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris
sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris
sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari
sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de
pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif
francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site
de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site
de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de
paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de
paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif
autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site
de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif
avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site
de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de
paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site
de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris
sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif
france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris
sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site
de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier
paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de
paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte
bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif
suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs
avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs
gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs
suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site
des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari
sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari
sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris
sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris
sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris
sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif
bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris
sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot
5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site
paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur
cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif
remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif
sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif
suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site
paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites
de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs
autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de
paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris
sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris
sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites
paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris
sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris
sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris
sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale
paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris
sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris
sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif (http://www.saahvideo.com)|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris
sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel
paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau
excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tabl
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10
trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2
en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas
online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones
de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones
de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones
de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones
para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app
apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app
casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas
android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas
deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas
deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app
de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app
de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de
apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app
de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar
dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para
apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas
deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas
mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de
futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de
apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer
apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas
deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de
caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas
a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la
nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas
al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz
hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas
america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas
argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas
argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina
holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina
méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina
uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas
arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic
betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic
real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas
athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs
barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas
atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto
prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas
barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas
barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça
madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca
vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético
de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona
espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona
girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona
real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs
atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas
basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas
béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas
betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas
betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis
mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas
betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas
betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar
online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas
bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo
de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas
boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas
brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos
españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos
zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas
campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas
campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier
league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos
nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras
de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de
galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas
casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas
casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas
champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions
league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea
betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas
chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta
españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas
colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas
como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para
hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas
recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras
para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta
de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas
copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa
del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del
rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del
rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de
baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol
para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas
de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas
de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de
caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de
caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online
en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de
caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas
de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de
corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas
de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas
de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas
de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas
de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol
para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol
seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre
hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos
deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas
de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas
de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de
nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de
sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas
de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas
de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis
en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de
tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas
del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de
hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del
sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas
deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas
deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas
bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas
casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas
deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas
chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas
deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas
deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas
consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa
mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas
altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas
deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas
en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas
deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas
deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia [makecoworking.com.br]|apuestas deportivas futbol
español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas
gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas
deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas
deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas
legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas
listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas
deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas
deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas
deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas
nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas
online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas
deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas
deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para
ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas
deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas
deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas
deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero
real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas
telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de
mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas
tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas
virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com
foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso
a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas
dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo
futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble
oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas
dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador
vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas
en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas
en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas
en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de
futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas
en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions
league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea
boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas
en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea
peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas
en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas
en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas
en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas
españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa
paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas
espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports
gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas
estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas
eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa
ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga
baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas
europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1
cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas
fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas
favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final
copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas
final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas
final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de
conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas
formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas
futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol
argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions
league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas
futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol
en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas
futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol
femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas
futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos
pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas
gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions
league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar
eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas
ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas
girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas
goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas
golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis
hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas
gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap
asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como
funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas
hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey
hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre
hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos
baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas
jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la
liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas
nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas
ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas
madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas
madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid
celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid
hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid
vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester
athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas
seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador
eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas
mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como
funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples
futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial
baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial
brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial
clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de
ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de
rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas
mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial
futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas
mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas
nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all
star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta
noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy
jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba
playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba
pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas
nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online
carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions
league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online
con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas
online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online
futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online
opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online
tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas
online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas
osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna
sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago
anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos
inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa
league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para
ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar
la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para
ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas
para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa
league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la
eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para
los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas
playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda
b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas
polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos
deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos
tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas
que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que
significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas
real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico
madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid
bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real
madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas
real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid
real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs
atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas
real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad
real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo
de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas
segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas
seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy
fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales
eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla
inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla
manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas
significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito
minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas
sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema
calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema
trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super
bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis
hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas
tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland
garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera
division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas
topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de
tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay
corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas
valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas
valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas
villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal
manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta
a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de
hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y
pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y
resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina
mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina
vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina
vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico
en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic
osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico
madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador
de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real
madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico
de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad
apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona
vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real
sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio
de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas
tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas
deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas
gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida
apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono
de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono
registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito
apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono
sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas
colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de
apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos
casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de
apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas
de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos
gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil
colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de
apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de
apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas
segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora
de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de
apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema
apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading
apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas
apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas
de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades
apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras
de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas
barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas
deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa
apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas
10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa
de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa
de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa
de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras
de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de
apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de
apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de
apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de
apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de
apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de
apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas
en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa
de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de
apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas
online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa
de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas
españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa
de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa
de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas
libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas
mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa
de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa
de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas
online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online
chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa
de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas
online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago
anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para
ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru
online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa
de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas
del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas
deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas
apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas
apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas
mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas
de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas
de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas
bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de
apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos
de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas
de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca
de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas
de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas
con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas
con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas
de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia
española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas
con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de
españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas
de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas
deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas
de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas
de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de
apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas
deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de
apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas
de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo
1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas
en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de
apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas
de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas
españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa
nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas
con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas
f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5
euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas
de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de
apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas
de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online
deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas
de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online
mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de
apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
paypal|casas de apu
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2
apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que
significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos
de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer
apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de
apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app
apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas
entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de
apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app
de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas
deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas
en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de
apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para
ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas
android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app
para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps
de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas
deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a
caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al
barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso
campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y
bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas
anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del
mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas
argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina
francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina
gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas
argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas
argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic
barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real
madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real
sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas
atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de
madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico
de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real
madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid
real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas
baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas
barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas
barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca
vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona
atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de
madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas
barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de
liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona
espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona
madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real
sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs
atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs
barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas
betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real
madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas
betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de
bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas
bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas
boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas
boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas
caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos
madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas
campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa
del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de
la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas
campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas
campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas
campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas
campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas
campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera
de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras
de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos
españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos
nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos
nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino
gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino
online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas
celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta
espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions
foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas
champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas
champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea
barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile
peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo
en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta
a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas
city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid
barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas
colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas
combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo
partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas
seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas
combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas
con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas
probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas
copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas
copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa
del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas
copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de
1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas
de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de
boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de
boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de
caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de
caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas
de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos
online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas
de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas
de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol
en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas
de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol
hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas
de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para
mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas
de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de
juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la
copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de
la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de
mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos
de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema
como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas
de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis
pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de
ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas
del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas
del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del
sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas
app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas
deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas
beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas
campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas
deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas
deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com
foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas
deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa
libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas
cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de
colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas
de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas
de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del
dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas
deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas
deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas
en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas
es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas
deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas
gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas
ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas
deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas
deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap
asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas
interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas
legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas
mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas
deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas
deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online
paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas
deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs
ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas
seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas
simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis
hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas
ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas
deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas
deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com
foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas
descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles
y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el
clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el
tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas
en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas
en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las
vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea
de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea
futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas
en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos de
futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas
en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas
en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo
ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa
alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas
españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas
españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas
euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las
vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles
de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas
favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions
peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del
rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas
final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa
league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas
final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league (https://www.deluxehouses.ae)|apuestas
final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia
argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol
americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol
español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol
foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas
futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol
online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol
telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas
gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas
ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador
de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa
league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador
mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas
ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar
nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas
girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas
girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real
madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas
goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis
casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis
por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis
regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y
ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas
handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap
nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas
hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas
hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra
paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings
league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la
liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas
nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas
legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales
españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas
liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas
liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de
campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas
liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas
linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid
barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas
madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid
betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid
campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid
gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real
sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas
faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo
goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas
mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb
pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas
mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial
clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de
fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas
mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas
mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas
mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas
mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba
consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba
hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy
pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas
nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas
nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas
nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl
semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas
nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online
carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas
online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online
deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas
online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online
esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas
online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas
online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas
online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas
online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas
open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas
para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas
para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar
la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para
hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para
la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas
para la europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba
hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas
partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas
partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas
partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas
peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas
peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas
peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas
plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso
a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas
playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por
ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera
division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas
pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos
tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que
significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara
el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la
eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas
real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real
madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas
real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid
betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas
real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real
madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs
atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad
betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas
resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas
ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar
dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para
hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras
para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas
sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas
sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas
simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que
significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake
10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta
roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas
tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas
tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis
hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas
tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria
holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de
tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc
pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under
over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas
uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas
us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor
app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas
venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal
athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal
betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas
villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas
virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas
virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de
azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos
de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de
madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid
apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca
madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico
apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona –
real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico
madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg
apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona
valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs
espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol
apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de
apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas
tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono
apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis
sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono
bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas
de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas
deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro
apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de
apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos
apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas
de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de
apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos
gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de
apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil
peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador
de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora
apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora
apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas
segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora
apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora
de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas
de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas
multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas
surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora
scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora
trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas
futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular
cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas
apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions
apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de
caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras
de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas
online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos
apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa
apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa
apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa
apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros
gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de
apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de
apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de
apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas
ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de
apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas
con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de
apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de
colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa
de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del
madrid|casa de apuestas del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa
de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de
apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas
deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5
euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa
de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa
de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas
española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de
apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de
apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas
mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas
nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del
real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real
madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online
mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de
apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para
ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa
de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas
sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del
real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas
apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas
ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas
deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas
apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas
golf|casas apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas
licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas
apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas
de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de
apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas
bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas
de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas
carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de
apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas
de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas
de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas
con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas
con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap
asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas
de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas
con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas
de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta
en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de
apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas
deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas
de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas
deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de
apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas
de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de
apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de
apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas
españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas
de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas
online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas
f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas
futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de
apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas
de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas
de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas
seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores
cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de
apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de
apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas
ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas
de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas
de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas
de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online
mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas
de apuestas paypal|casas de apues
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10
trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que
significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de
cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y
apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas
de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas
android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas
de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de
apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro
apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app apuestas de
futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas
argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas
ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app
apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa
de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de
apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de
futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas
en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de
apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app
de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app
para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos
apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps
de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer
apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas
100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a
caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas
a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas
alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania
españa|apuestas alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas
nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas
nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del
mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas
argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el
mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina
mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs
australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas
argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso
a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas
athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic
manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic
real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas
athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético
de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana
la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico
madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas
baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto
juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas
baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca
hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça
madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona
athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico
de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas
barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona
inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas
barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs
madrid|apuestas barcelona vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol
mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas
betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas
betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy
colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas
bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo
hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas
caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas
campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de
champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del
mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas
campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas
campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de
semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras
caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas
carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras
de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas
carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta
betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas
celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas
champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas
chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo
en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo
tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia
paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de
fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas
combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas
seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero
real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas
copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas
copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del
mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas
copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de
hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas
corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de
boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de
caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de
caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas
de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de
caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino
online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas
de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de
formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas
de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de
futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de
futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para
mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de
fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos
en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de
galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos
deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas
de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la
liga española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas
de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas
ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros
virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de
sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de
sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para
hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas
de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del
boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del
dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas
del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas
deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas
deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas
bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas
colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com
pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas
deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa
america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la
mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas
de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas
deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas
deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas
deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas
en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas
deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas
eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas
deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas
deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas
deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas
deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas
gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis
con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis
sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas
hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas
juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres
de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga
española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas
listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas
deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor
pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas
deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas
deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas
nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas
online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas
deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas
online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online
peru|apuestas deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago
paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas
paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas
perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas
deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas
deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas
deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas
deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas
deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas
deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas
deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas
deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino
online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso
a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas
dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo
futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas dortmund
barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas
ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas
empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas
en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras
de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas
en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas
en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas
en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la
nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas
en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de
fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea
peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas
en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas
españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas
españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el
mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas
españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa
italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas
esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports
peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa
final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas
eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa
league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas
f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de
ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos
eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final
copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa
del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas
final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de
conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas
francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas
futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol
mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol
para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa america|apuestas ganador
copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del
mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador
mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas
girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas
girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand
slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas
gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas
gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar
premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas
online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas
hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos
olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas
jugadores nba|apuestas kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga
española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas
league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales
españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga
argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de
campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas
linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas
madrid atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid
barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas
madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas
madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas
madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid
gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid
sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs
arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles
de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters
de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas
méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como
funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas
mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas
mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial
clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas
mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial
futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas
mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas
mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas
nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online
en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online
esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas
online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online
juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas
online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online
opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna
valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para
el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas
para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas
para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para
ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas
para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para
la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la
europa league|apuestas para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido
suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos
csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos
de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas
partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos
hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru
brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas
peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs
nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas
por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas
predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas
promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas
puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas
quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la
champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas
real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid
barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas
real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid
city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid
real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs
betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs
valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real
sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas
retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas
rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas
seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas
seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas
seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras
para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas
seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla
athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas
sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana
la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas
sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa
españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas
tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis
pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas
tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc
pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas
valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas
valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela
argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas
villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas
vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas
william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas
y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs
francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid
apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid
apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas
apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter
apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid
apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico
apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico
madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter
apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs
athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis
apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs
espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis
madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio
de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono
apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono
bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de
apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono
de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de
registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca
apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono
sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono
sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito
marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de
apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de
apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos
de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito
apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas
de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas
de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas
apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas
seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador
de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas
deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de
apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de
apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora
de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de
apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora
de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora
poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas
apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias
apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular
stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales
de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera
de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras
de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa
apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa
apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10
euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa
de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas
beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas
bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de
apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia
en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa
de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de
apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa de
apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas
de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del real
madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de
apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas
deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de
apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa
de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas
online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de
apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas
en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de
apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas
eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de
apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa
de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa
de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas
mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas minimo
5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa
de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real
madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de
apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas
online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de
apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de
apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas
promociones|casa de apuestas que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas
ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive
la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas
asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos
sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas
ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas
apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas
españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas
apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas
licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de
apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
baloncesto|casas de apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono
sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas
de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de
registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de
apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas
con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas
con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal
en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas
con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas
de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de
apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas
deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas
deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas
en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas
deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de
apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas
deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas
deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas
online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de
apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas
de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de
apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa
online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas
en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas
en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa
alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas
españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas
esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas de apuestas
eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas
f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas
formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas
ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso
minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas
legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de
apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas
legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia
españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas
mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas
mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de
apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas
nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas
en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas
de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de
apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online
ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas
online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas
fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online
peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas
peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas promociones|casas de apuestas que
aceptan
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans
dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100
euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert
pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide
aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif
foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide
pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme
gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif
tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de
paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari
sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse
paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris
sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli
pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris
sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris
sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli
paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli
paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris
sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de
paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris
sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris
sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer
ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour
pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent
offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent
sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris
sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris
sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour
paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris
sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris
sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis
paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site
paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris
sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll
paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france
paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue
paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus
de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot
paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris
sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif
sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif
belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site
de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites
de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris
sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris
sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp
paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap
paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte
paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul
cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul
paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité
paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris
sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur
de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs
paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris
sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris
sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris
sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps
pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné
paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif
du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment
arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris
sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote
paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment
creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris
sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris
sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris
sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire
pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire
pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire
un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire
un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent
les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent
les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les
paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand
oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris
sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif
football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner
au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment
gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris
sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris
sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris
sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des
paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris
sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner
paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris
sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll
paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris
sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer
au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche
cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris
sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes
paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment
miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au
paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les
paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes
de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner
au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote
pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur
cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes
paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur
de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de
paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site
pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de
paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris
sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif
site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des
paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris
sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte
de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer
paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte
paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil
de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari
sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil
paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif
du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil
paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris
sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil
sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils
paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs
tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris
sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des
paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment
ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote
paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif
psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif
foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari
sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs
foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris
sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer
ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris
sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot
5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum
paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand
existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche
avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb
pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit
on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart
de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris
sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif
a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement
sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce
week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements
sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote
paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face
a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des
paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer
les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis
paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris
sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif
nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris
sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des
jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france
2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari
sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari
– paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris
sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour
aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000
euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner
a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner
argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au
pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif
foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner
aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris
sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner
des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les
paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris
sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa
vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris
sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à
coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif
impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris
sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris
sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains
paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer
une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris
sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif
application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris
sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram
paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap
basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris
sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris
sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap
paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris
sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des
cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace
paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris
sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif
france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris
sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu
de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris
sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques
paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris
sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur
absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur
de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif
paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris
sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris
sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent
des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris
sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur
application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète
pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché
des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site
de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de
paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les
bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les
gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les
meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs
site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris
sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris
sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris
sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus
grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de
paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de
paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site
de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste
paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste
site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris
sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel
de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs
foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de
cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic
calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs
en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale
paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match
abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé
paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris
sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs
truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris
sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app
de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de
pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur
appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris
sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de
paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur
bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur
bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné
paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris
sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur
methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre
de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif
du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de
pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site
de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur
site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur
site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de
paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur
site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif
en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur
site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur
site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site
paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari
sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie
paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris
sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli
de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre
paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures
offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris
sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du
jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris
sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode
de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris
sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique
paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif
forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour
gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris
sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris
sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant
paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante
parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris
sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode
calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode
paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba
paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de
paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris
sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau
site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris
sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris
sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris
sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue
paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris
sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans
depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans
depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris
sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre
paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors
arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris
sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif
en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur
de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte
paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100
remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif
aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif
belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions
league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif
comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de
france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari
sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne
au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne
canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari
sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari
sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif
francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif
france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari
sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les
coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif
gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif
hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif
ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari
sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari
sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari
sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif
offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif
prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif
psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif
remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du
monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte
bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif
site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari
sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps
reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top
14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif
football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie
sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne
sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques
et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris
sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif
150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris
sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif
algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent
offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris
sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif
aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris
sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris
sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus
sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique
suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus
gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris
sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif
but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris
sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur
contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif
buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif
cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif
classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris
sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif
combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris
sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner
a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment
ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif
conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil
pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du
monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif
depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris
sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1
euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris
sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris
sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne
france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris
sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif
en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif
final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris
sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif
foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris
sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif
foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris
sportif football americain|paris sportif football
astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france
allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif
france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris
sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france
nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris
sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif
gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit
cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris
sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris
sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris
sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif
joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur
decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare
forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif
leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour
gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris
sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif
ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match
abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match
arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match
interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris
sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris
sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma
france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris
sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple
2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3
4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national
1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris
sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris
sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris
sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de
1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif
prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris
sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert
gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif
pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic
tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg
barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris
sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris
sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris
sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif
regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif
remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé
en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe
du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe
du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris
sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si
match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris
sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse
romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris
sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif
technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis
pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au
but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc
france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur
euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des
champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris
sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris
sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs
comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris
sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs
en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne
belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs
en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris
sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs
gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris
sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux
olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match
interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs
nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris
sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans
depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de
france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment
gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus
gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros
paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme
gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité
cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris
sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic
du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic
paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du
jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif
gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic
paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics
paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter
paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris
sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que
handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que
signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que
signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie
gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari
sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire
dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans
les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote
jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le
meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur
site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le
plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte
le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris
sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est
la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus
sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris
sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap
paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris
sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris
sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur
de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris
sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat
pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer
argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation (Winnie)|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif
foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur
gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site
d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de
pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif
bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari
sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif
gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de
pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif
en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de
paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus
sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de
paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement
mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de
paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site
de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site
de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit
pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans
dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris
sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif
qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site
de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de
paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de
paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris
sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site
de statistique pour paris sportif|site des
paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100
euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site
pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site
pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne
sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif
100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris
remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site
paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif
belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif
bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif
en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif
gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris
sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif
remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait
instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris
sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site
paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse
paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris
sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris
sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans
dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs
france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique
foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie
gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris
sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris
sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris
sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris
sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau
bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau
excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante
paris sportif|tabl
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros
offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert
pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis
paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age
paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari
sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris
sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme
gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris
sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif
gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse
cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse
paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de
paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie
sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif
gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil
paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris
sportif android|application paris sportif
argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris
sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif
maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif
usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris
sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris
sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent
offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent
paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel
paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif
foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris
sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris
sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces
pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari
sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris
sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll
100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris
sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris
sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue
sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans
depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris
sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif
sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans
depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus
site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris
sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est
quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote
pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris
sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb
paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul
pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris
sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul
probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme
paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris
sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer
gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer
une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte
cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out
pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute
de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre
paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code
promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans
depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris
sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du
jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris
sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment
arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer
au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les
paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une
cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris
sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment
créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment
faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire
des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire
pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire
pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari
sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une
montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris
sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand
oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs
grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs
maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les
coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner
au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif
forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner
des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec
les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner
sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris
sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner
un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer
au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer
paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment
marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment
marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment
monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont
calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça
marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote
paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari
sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur
de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris
sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de
paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif
bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif
cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre
de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif
paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les
cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris
sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo
paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte
financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris
sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des
champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris
sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil
sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller
en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris
sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote
a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise
paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum
paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari
sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris
sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif
france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote
paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote
paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote
pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de
paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris
sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france
paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris
sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis
quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec
les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis
paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb
paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de
paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs
hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt
minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris
sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre
sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris
2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris
ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements
sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes
paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif
avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de
paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris
sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de
paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie
sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum
paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum
sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des
jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris
sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france
paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris
sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie
paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris
sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris
sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au
paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent
avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner
aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l
argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner
de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace
aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris
sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner
les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif
forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris
sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa
vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les
coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif
impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif
impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll
paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris
sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll
paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote
paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe
paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0
paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket
paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap
paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif
foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des
cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur
glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris
sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot
gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de
paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux
de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux
paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer
paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui
se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs
est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux
paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur
technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris
sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus
grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris
sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris
sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des
paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les
meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs
paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les
meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs
en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne
comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus
rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote
paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris
sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions
paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel
calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel
gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel
pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris
sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de
cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des
paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris
sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif
excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match
annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu
tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie
paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match
reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif
forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur
application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari
sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif
belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris
sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur
combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris
sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris
sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris
sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur
offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari
sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif
aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif
foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site
de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site
de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur
site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de
paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site
de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de
paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari
sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris
sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris
sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site
paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris
sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie
paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de
paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure
appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure
application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure
application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre
paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures
cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris
sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli
paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus
paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris
sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari
sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de
paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode
gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris
sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode
paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes
paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise
minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise
paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante
paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple
paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris
sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau
paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de
paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau
site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site
paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris
sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site
paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre
de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre
de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de
bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue
paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro
paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre
paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre
paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot
paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres
bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris
sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises
paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari
sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif
argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari
sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif
basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas
titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment
gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari
sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du
monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif
en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au
cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari
sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari
sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif
euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif
foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari
sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari
sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif
gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a
tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif
gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif
hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari
sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue
des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif
match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au
jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari
sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif
pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari
sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby
coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif
signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif
systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif
temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis
abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie
sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie
sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris
hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs
et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match
sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif
100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif
1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif
abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif
algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris
sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres
prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au
canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris
sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec
carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris
sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket
coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket
prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris
sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris
sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus
sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris
sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif
buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul
gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris
sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris
sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif
comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment
ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris
sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe
d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du
monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif
depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec
paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif
en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif
en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris
sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino
en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris
sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif
finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris
sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif
foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif
foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif
foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football
astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif
francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif
france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif
france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france
espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris
sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris
sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif
freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup
sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de
l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif
gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris
sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0
1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap
1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris
sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif
jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif
joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif
joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris
sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif
leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris
sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif
ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue
des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif
martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris
sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis
interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise
maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de
3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif
multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3
explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris
sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau
site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris
sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif
paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif
premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match
aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif
pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris
sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris
sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui
rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue
des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby
6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans
argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif
sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris
sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur
abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris
sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris
sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris
sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif
systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris
sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif
temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif
tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis
forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif
tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur
ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif
via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs
abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris
sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs
belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris
sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs
de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs
en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs
gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs
gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue
des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg
inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris
sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris
sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte
d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les
paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au
monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus
grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse
somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise
paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité
paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du
jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris
sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics
paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal
paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg
inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est
ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce
qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie
1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie
btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris
sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que
signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que
veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel
appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris
sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est
le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus
rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus
sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel
site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari
sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure
appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la
meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site
de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement
paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de
mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif
hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles
paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises
paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts
paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur
gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris
sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide
paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site
de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de
pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif
suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site
de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris
sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de
paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris
sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de
paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec
paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif
belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de
paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de
paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de
paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif
en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris
sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit
pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris
sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif
meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de
paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif
sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de
paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs
paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site
des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site
pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif
en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100
euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris
remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec
bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site
paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif
foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site
paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris
sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris
sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait
instantané|site paris sportif sans carte
bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris
sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs
france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris
sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris
sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites
de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits
sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris
sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris
sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris
sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques
football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de
paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2
3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris
sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de
suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris
sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris
sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris sportif|tableau paris sportif excel|tableau roi paris sportifs|tableau statistique paris sportif|tableau suivi paris sportif|taxe gain paris sportif|technique
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans
dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris
sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux
paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris
sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari
sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris
sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse
match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif
foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris
sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans
argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie
sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif
avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli
paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide
paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android
paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif
en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris
sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris
sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris
sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre
amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris
sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour
pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique
paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris
sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris
sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs
impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce
paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris
sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces
pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari
sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris
sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris
sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris
sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus
de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot
paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus
gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot
paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris
sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif
en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus
paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans
depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus
site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus
sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris
sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est
quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote
paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul
cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes
paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul
double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur
paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris
sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote
paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site
de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo
pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné
paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris
sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment
arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris
sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris
sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer
un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment
etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire
des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire
pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris
sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment
faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari
sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire
un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les
cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les
cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris
sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les
paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris
sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au
pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au
paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner
aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs
sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner
des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner
paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris
sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll
paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif
foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les
paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent
les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment
miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter
sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris
sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris
sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours
gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris
sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari
sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur
cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris
sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari
sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site
de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur
site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote
pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris
sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari
sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif
site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre
cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre
les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les
handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif
gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris
sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif
gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil
paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner
au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris
sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a
100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote
de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif
explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france
espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe
de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie
handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot
double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb
en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris
sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis
paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains
des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre
sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif
a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement
sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement
sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs
à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face
hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif
avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris
sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll
paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et
paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris
sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris
sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris
sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise
des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris
sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie
paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris
sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10
euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par
jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000
euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris
sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner
argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au
pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au
paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif
foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner
aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris
sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent
grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de
l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris
sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent
paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur
les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris
sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa
vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa
vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à
coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris
sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris
sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer
bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de
bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif
application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris
sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap
1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap
basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap
mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique
des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot
sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris
sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux
de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux
paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur
absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari
sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif
paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris
sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui
se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur
suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris
sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris
sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris
sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de
paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris
sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur
site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris
sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le
plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris
sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris
sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de
paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris
sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs
paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs
site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari
sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris
sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs
en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris
sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains
au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris
sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs
en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite
de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris
sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste
des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari
sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif
arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme
paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari
sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel
paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur
2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris
sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs
en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale
paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul
boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris
sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur
algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris
sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur
appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris
sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari
sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus
pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus
paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné
paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris
sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif
aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum
paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur
methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur
offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur
offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur
pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris
sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site
de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de
paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site
de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur
site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur
site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site
de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris
sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris
sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif
rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris
sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site
pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure
appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris
sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure
application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure
application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure
site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris
sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres
paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs
bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes
paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs
paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs
site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site
de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris
sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode
paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot
paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari
sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins
de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris
sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante
paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple
paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode
match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba
pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau
site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris
sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre
100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre
bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre
bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de
bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre
de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue
paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de
bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif
euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre
paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre
paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris
sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris
sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack
de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue
paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100
euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif
algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari
sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari
sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec
wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari
sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif
comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif
du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari
sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif
en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif
en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari
sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france
autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif
france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari
sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner
a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour
gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif
leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif
ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur
cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif
mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre
bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari
sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari
sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif
rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans
carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif
technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top
14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca
marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie
sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne
sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques
et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et
poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10
euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif
100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros
offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce
soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis
parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif
application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif
arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris
sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec
handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis
expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket
nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique
bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique
france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif
bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit
sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris
sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but
contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur
carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui
ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif
canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif
champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris
sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné
du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif
comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif
comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour
gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du
monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris
sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot
5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du
jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris
sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne
bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne
comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif
en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne
suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris
sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris
sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris
sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif
foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif
foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca
marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif
foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot
en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot
us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif
france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france
italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france
portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france
usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris
sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris
sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif
gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris
sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris
sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris
sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap
0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif
hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris
sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif
leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif
ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif
liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris
sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif
match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif
match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif
meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode
2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto
gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris
sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris
sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif
multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris
sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris
sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif
prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif
pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd
hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris
sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris
sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif
psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter
cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris
sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé
en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris
sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris
sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris
sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif
sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif
si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple
ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris
sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif
suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris
sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3
4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris
sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis
abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif
tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris
sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis
roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour
de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif
unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire
prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés
en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris
sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs
comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris
sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs
foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris
sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris
sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs
statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris
sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs
tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris
sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus
gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris
sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris
sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier
pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité
paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo
site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris
sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic
gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris
sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris
sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris
sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter
milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris
sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr
code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap
dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce
que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse
paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie
12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw
en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris
sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que
signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que
veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut
dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris
sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel
est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est
le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus
sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le
plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif
rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus
rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la
meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est
la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est
la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le
meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris
sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des
paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle
paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris
sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash
paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement
pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise
paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des
mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris
sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent
paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle
paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur
de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des
mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot
paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb
paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur
gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris
sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur
paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser
paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari
sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari
sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de
paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site
de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris
sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de
paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de
paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif
avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris
sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de
paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris
sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site
de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site
de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site
de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site
de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris
sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif
qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site
de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif
sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de
paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site
de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari
sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site
pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif
gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site
paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif
avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site
paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans
depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site
paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris
sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris
sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site
paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris
sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site
pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites
de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris
sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites
de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris
sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits
sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris
sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris
sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme
paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau
cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel
paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris
sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris sportif|tableau
paris sportif excel|tableau roi paris sportifs|tableau
statistique paris sportif|tableau suivi paris sportif|taxe gain paris
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert
paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari
sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif
belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris
sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif
tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match
paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif
foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris
sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de
paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli
pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris
sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli
paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli
paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme
paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif
en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de
paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris
sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris
sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif
android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif
canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif
gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris
sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris
sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris
sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent
offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris
sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce
pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner
au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris
sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris
sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari
sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis
tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue
paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans
depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash
paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris
sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris
sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris
sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans
depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site
de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus
sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker
paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti
perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote
pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris
sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul
probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul
trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur
de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote
paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris
sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out
paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris
sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code
paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code
promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site
paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser
paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari
sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif
du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de
jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter
les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au
paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment
calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une
cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment
calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris
sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec
les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment
faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment
faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment
faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les
paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes
de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris
sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les
paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les
paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au
paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au
paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari
sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner
au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment
gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment
gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent
avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de
l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris
sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris
sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif
foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner
un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll
paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer
au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment
jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris
sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent
les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au
paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir
au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les
cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari
sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari
sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur
cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de
site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari
sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur
site pari sportif|comparateur site paris
sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris
sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris
sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif
pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif
en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif
sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre
cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes
paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les
handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte
financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil
de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris
sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil
paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des
champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris
sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris
sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les
paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller
paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris
sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif
comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote
parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote
paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris
sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris
sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote
paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote
paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote
sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes
paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe
de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer
ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5
euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les
paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb
en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les
gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains
paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris
sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs
sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari
sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement
sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris
aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements
sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari
sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire
des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer
ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de
paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum
paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris
sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris
sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des
jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france
espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris
sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne
paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris
sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10
euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris
sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner
a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec
paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris
sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner
au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris
sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au
paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris
sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les
paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner
des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner
paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris
sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les
coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris
sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris
sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris
sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise
paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram
paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au
paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les
paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris
sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris
sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap
tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris
sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey
sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh
signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris
sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma
vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif
en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux
de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris
sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris
sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de
caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif
paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale
paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris
sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris
sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros
paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets
pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement
aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris
sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les
bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris
sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris
sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs
cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs
site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris
sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs
comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les
paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre
jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les
plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris
sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris
sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites
de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les
sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de
paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue
des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris
sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise
paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de
paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de
paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel
gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur
2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel
prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des
paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché
des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris
sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale
paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris
sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris
sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris
sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app
paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur
appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif
forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur
application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur
application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif
belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus
paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site
de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur
cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur
gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre
bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris
sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif
du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur
paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de
conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris
sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif
belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur
site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif
hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif
suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site
de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site
pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur
site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur
site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur
site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site
paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site
pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au
paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure
appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure
site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs
application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris
sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris
sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site
de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs
site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de
paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au
paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode
pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum
pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise
minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante
parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris
sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour
gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba
paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site
de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site
de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site
pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site
paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero
de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site
paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris
sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue
paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre
de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris
sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre
paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris
sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans
depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres
bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris
sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur
de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari
sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari
sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari
sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur
pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif
combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment
ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari
sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari
sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du
jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne
ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari
sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari
sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france
argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a
tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif
gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans
depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari
sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari
sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif
ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari
sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari
sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise
au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre
bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif
promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif
pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe
du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif
sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans
depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif
technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari
sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif
top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif
comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie
sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie
sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie
sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris
hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif
100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150
euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris
sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis
parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent
fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif
arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif
avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec
carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif
avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis
expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris
sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique
france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris
sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif
bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif
bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif
bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif
but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris
sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif
canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris
sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris
sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris
sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné
du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca
marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif
conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif
cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris
sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du
monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif
depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris
sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum
5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif
en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris
sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris
sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris
sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif
foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif
foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe
du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif
foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris
sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris
sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif
france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup
sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif
gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris
sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris
sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans
dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris
sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif
handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif
handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap
rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris
sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors
arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de
foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal
en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris
sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris
sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris
sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du
jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur
bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris
sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif
methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris
sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma
france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif
moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris
sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris
sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif
nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris
sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans
depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris
sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier
pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic
expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris
sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris
sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg
inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg (https://Www.Alicespringscarhire.com/pari-match-app) liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris
sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif
remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif
remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue
des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans
carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot
minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif
suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse
legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris
sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme
3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif
temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif
tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris
sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir
au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris
sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif
unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif
victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris
sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs
comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne
france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs
foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris
sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris
sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors
arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la
mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue
2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs
ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs
paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs
rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris
sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris
sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs
tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec
les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les
paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus
gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise
paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris
sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris
sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos
paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono
paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif
foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et
aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif
gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris
sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris
sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que
handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les
paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie
1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie
ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que
signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris
sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap
dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris
sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel
est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est
le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari
sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site
de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site
de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la
meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de
paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le
meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont
les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris
sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des
paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris
sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris
sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris
sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise
paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de
mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des
mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif
en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari
sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles
paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris
sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris
sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif
multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris
sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif
gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site
d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de
pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans
depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari
sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif
hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie
sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé
en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de
paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site
de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec
bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site
de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif
en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif
francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de
paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris
sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif
sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site
de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de
paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs
francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site
de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site
pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari
sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif
en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif
gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif
100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris
sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris
sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site
paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris
sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement
cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris
sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic
paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs
autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites
de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites
de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris
sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs
hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie
big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies
paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2
3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari
sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système
paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau
gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau mo
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100
euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris
sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris
sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif
forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris
sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari
sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel
paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif
avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris
sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif
tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris
sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris
sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris
sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de
paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli
paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli
paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris
sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris
sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris
sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris
sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris
sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris
sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris
sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris
sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris
sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris
sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de
bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif
sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour
paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris
sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent
offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris
sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce
gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif
basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif
tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari
sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour
gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces
paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis
pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis
sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris
sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris
sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket
paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris
sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris
sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus
paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris
sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus
unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre
son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris
sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est
quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul
cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul
de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul
dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris
sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul
paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris
sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris
sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris
sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris
sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer
une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris
sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code
barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code
promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans
depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris
sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné
pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris
sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer
cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris
sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment
calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment
creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer
un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable
paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment
faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari
sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment
faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris
sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris
sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris
sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris
sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs
maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris
sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari
sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner
au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au
paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris
sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner
aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l
argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris
sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner
de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de
l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment
gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris
sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner
paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment
gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner
un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment
gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment
marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche
les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche
un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment
marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent
les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa
bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au
paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment
reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont
calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris
sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des
cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris
sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris
sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris
sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de
site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris
sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris
sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif
bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif
paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris
sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris
sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer
les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap
paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte
finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte
pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif
ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris
sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour
gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur
les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de
paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris
sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100
paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris
sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris
sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari
sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris
sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote
paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif
psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote
sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris
sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie
handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash
out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris
sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot
paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir
riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer
gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro
paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur
de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris
sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris
aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif
paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes
paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec
paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris
sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les
gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains
paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains
paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de
paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum
pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris
sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif
nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis
paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2
paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris
sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal
paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris
sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne
au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner
100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000
euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50
euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur
pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner
argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner
au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au
paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner
beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner
de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de
l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris
sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses
paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari
sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris
sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris
sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris
sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa
bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris
sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de
bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de
bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris
sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0
paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap
europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris
sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris
sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap
paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis
paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey
sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari
sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif
france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot
sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris
sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de
parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux
de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris
sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au
paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur
sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des
paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la
meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour
gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris
sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris
sportif signification|le marché des paris
sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le
meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au
paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les
application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris
sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les
gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les
meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs
bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les
meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites
de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris
sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer
gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse
cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1
paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris
sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites
de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste
site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site
paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris
sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs
en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale
paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé
ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match
nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté
paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match
truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris
sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli
de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris
sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif
belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus
paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur
bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur
cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris
sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner
au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif
du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur
promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site
de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur
site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur
site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif
suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur
site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris
sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur
site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris
sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris
sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de
paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner
au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris
sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris
sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris
sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris
sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris
sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs
(Ruth)|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris
sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode
abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode
infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris
sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise
minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise
paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant
paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris
sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au
paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba
pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de
pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris
sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site
paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle
appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match
paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris
sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre
bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris
sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro
paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre
paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre
paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot
paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de
bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris
sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture
compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue
paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors
arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari
sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif
application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari
sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas
titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari
sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça
marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif
cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari
sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari
sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne
belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari
sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne
ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif
faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif
forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif
france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif
france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif
gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif
hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari
sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari
sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif
match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match
interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif
mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif
offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari
sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari
sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif
psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari
sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte
bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari
sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif
temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari
sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif
en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie
sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris
france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris
sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros
remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif
a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris
sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris
sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif
argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec
bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif
avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris
sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif
belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique
suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris
sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus
sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps
additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif
buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif
buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris
sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du
jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca
marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif
comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif
conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif
cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris
sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris
sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris
sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt
1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris
sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris
sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris
sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris
sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris
sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris
sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris
sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif
foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif
foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football
astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif
francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris
sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france
pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris
sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner
de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit
cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris
sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros
gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1
0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap
basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif
handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris
sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif
hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif
jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé
pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la
francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner
tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les
prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue
1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue
des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif
match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du
jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris
sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris
sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif
methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple
2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple
3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national
1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris
sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre
bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif
offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris
sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris
sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd
hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif
pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic
tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif
psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris
sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui
rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif
remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris
sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif
safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte
bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif
si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse
legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris
sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme
3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris
sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps
additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis
de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis
gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top
14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif
victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs
aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs
arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs
autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris
sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs
combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne
gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs
france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous
les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits
en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey
sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris
sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs
ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs
montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs
offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris
sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs
sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris
sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec
les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les
paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus
gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise
paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité
cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris
sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de
paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic
paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques
et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter
pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg
paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est
ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce
qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap
dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse
paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que
signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris
sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie
ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie
gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli
de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de
paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur
site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif
en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus
rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire
aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site
de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse
en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est
la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est
la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap
paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle
paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash
paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise
paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise
paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris
sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif
foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris
sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de
mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises
paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris
sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur
gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur
gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site
aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site
arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse
paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de
pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site
de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site
de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif
en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de
paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de
paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de
paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site
de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site
de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de
paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris
sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de
paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site
de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site
de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de
paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de
paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs
gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris
sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari
sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site
parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros
offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé
en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site
paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris
sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris
sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris
sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif
sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site
paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site
paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de
paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris
sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de
paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites
pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs
arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris
sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris
sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie
big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris
sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse
paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris
sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau
de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris
sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sp
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt
paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris
sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert
paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris
sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif
forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari
sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide
pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide
paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit
paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme
paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris
sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse
paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote
paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris
sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari
sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif
belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris
sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif
suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse
paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de
paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif
argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris
sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif
gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de
bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris
sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire
des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis
paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent
offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris
sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce
paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce
paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour
gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour
paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux
paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari
sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis
site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris
sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus
bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus
de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus
gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus
paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris
sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur
penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est
quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris
sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul
des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double
chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul
mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul
paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul
rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris
sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur
de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris
sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer
roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash
out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino
en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute
de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code
barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code
promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code
promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser
un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer
un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines
paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné
paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment
arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au
paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser
paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment
créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris
sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris
sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire
une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes
dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris
sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les
paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs
grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment
fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a
tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment
gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a
coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au
paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur
le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner
de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris
sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris
sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment
gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll
paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer
aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche
les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment
marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais
perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment
reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les
cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner
au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote
pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur
de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris
sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris
sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites
de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site
de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur
site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris
sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de
bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari
sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif
paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris
sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre
les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte
de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris
sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte
paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil
de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil
paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris
sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris
sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris
sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris
sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour
paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris
sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote
pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif
rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris
sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris
sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif
foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes
paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme
paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans
les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains
paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot
paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche
avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif
definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de
paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt
minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de
jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que
les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur
de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement
sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris
aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap
paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif
avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris
sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris
sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de
paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum
parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris
sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise
des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france
2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris
sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france
portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris
sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000
euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup
sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner
a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent
paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris
sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux
paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l
argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de
l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif
foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris
sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les
paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner
à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari
sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris
sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains
paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs
imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains
paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris
sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris
sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll
paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros
gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram
paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris
sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket
paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris
sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris
sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris
sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris
sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari
sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif
gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux
de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de
paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris
sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris
sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris
sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de
foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se
blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs
italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il
imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur
application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique
pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris
sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le
marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de
paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris
sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros
paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement
aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains
des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris
sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs
du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre
jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les
paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris
sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris
sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites
de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites
de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains
paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite
mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste
des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris
sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site
paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites
paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris
sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de
paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris
sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris
sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris
sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique
paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné
paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris
sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur
app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli
paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur
appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil
paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris
sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris
sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur
application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur
bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris
sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote
pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur
cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre
bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre
de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif
en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris
sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur
site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site
de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de
paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris
sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site
de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif
en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif
avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif
canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris
sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris
sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur
site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique
paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure
appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure
application pari sportif|meilleure application paris
sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre
paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris
sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres
paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs
appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs
du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris
sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs
site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode
de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris
sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique
paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode
paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris
sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum
pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris
sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple
paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples
paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul
paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris
sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba
paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de
paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero
match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris
sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre
bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre
de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors
arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres
de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou
faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise
paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte
paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack
de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari
sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari
sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif
coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif
coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au
cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif
football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif
france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari
sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari
sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner
des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le
plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif
ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif
match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari
sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari
sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre
bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif
plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic
gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif
psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari
sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari
sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari
sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari
sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment
ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie
sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne
sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris
hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques
paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100
remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions
sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris
sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif
application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris
sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris
sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec
handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif
avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis
forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris
sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif
belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris
sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif
bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans
depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre
son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre
son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris
sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris
sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue
1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue
1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner
a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil
pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif
coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif
du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris
sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne
bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif
en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif
en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif
en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif
en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif
esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris
sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris
sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot
aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot
pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot
regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris
sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris
sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris
sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris
sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france
gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris
sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup
sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif
gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris
sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit
en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit
sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris
sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif
handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap
basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap
foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris
sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris
sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif
joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur
declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif
la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif
legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris
sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus
sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris
sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue
europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif
match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris
sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif
methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au
jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif
montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple
2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple
2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3
4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris
sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero
match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue
sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris
sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris
sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris
sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif
prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris
sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic
des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic
expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris
sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg
om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris
sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris
sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif
rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé
cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des
joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si
un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue
pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif
suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2
4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris
sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis
roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif
ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif
vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif
via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs
arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris
sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris
sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs
en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris
sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris
sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris
sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris
sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs
hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris
sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs
montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de
bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs
psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs
sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte
d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris
sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus
gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris
sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris
sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros
gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote
paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket
paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris
sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono
paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris
sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris
sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris
sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot
statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg
inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg
inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg
om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap
paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap
paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que
signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que
signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que
signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans
les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari
sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est
le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif
en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel
est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel
pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site
de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel
type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est
la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site
de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de
gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle
des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement
paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise
paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif
en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise
pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur
de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris
sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur
montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris
sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser
paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris
sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne
sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de
pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de
pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site
de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de
parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site
de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de
paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif
autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de
paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site
de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris
sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris
sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de
paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif
francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif
gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris
sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus
fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de
paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de
paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de
paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte
paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans
carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de
paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris
sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs
suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari
sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif
gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris
en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros
offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif
autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site
paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec
meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site
paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif
foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors
arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement
cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait
instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif
suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site
pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites
de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris
sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs
suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris
sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors
arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique
tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris
sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris
sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4
paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau
bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel
paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll
paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris sportif|table
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros
remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari
sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris
sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux
paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris
sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel
paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari
sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse
pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse
paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris
sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris
sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli
pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif
avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif
gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris
sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme
paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris
sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de
paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif
gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent
fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris
sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris
sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans
argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris
sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour
gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour
paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile
paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris
sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris
sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis
pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris
sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster
paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris
sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket
paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus
cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de
bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans
depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif
retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris
sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus
sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker
paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers
paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp
paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une
cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari
sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture
paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote
paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote
paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris
sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris
sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote
pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte
prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash
out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino
paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code
bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari
sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo
site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser
paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment
analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris
sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les
paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer
au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer
cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari
sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris
sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer
un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche
avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment
faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire
des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris
sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris
sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment
faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment
fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris
sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent
les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris
sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs
grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris
sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les
coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup
sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner
aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs
sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de
l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment
gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment
gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment
gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses
paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur
les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment
gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris
sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les
cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche
les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment
marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment
parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir
les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont
calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris
sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote
pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes
paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur
de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris
sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site
de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus
paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif
pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris
sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif
sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap
paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris
sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre
les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte
financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil
de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris
sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil
paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil
paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris
sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris
sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au
paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils
paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris
sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100
paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris
sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment
ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif
explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote
paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris
sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris
sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris
sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses
gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris
sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double
paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris
sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec
les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis
paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris
sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de
paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre
sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif
paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif
paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements
sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote
paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des
paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains
de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum
paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum
paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum
sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris
sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse
paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100
euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris
sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour
paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur
pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent
paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif
forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris
sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner
de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris
sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris
sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner
des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari
sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner
paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa
vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous
les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains
paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de
bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5
gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris
sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0
paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap
au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans
les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap
européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap
pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris
sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap
rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris
sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris
sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif
gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris
sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris
sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux
paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris
sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent
paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur
caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur
décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur
paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne
pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris
sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux
paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux
paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris
sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le
marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de
paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif
en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le
plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les
10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux
paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les
application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers
paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux
de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les
meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris
sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les
paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les
paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les
paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner
pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris
sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de
paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de
paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris
sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris
sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris
sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des
sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris
sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel
algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul
paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel
de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll
paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris
sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2
matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris
sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs
en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris
sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris
sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis
paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul
boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu
paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur
application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari
sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus
paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur
bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris
sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris
sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur
methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif
en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris
sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site
de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site
de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif
belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site
de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur
site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de
paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif
avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur
site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site
paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif
hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur
site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur
technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris
sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure
appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de
paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure
application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure
offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures
applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs
applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site
de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc
paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode
gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris
sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode
paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au
jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise
moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de
4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari
sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple
pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au
paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau
site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris
sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris
sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites
de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de
match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris
sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus
paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari
sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif
sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif
euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris
sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo
paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre
site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou
faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de
mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif
hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100
euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari
sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif
astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari
sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique
france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions
league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote
match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif
depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif
foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif
francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari
sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari
sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a
tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des
cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari
sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus
rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue
1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue
des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match
arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari
sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari
sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif
paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari
sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif
psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif
psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari
sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif
rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans
argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans
depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari
sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif
technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif
suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris
sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker
en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif
10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif
100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif
a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce
soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris
sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif
application|paris sportif application android|paris
sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris
sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif
arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris
sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif
avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris
sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris
sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif
belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris
sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot
belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif
buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris
sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris
sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue
1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif
code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif
combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné
du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris
sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif
comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif
comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris
sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris
sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe
d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif
coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris
sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris
sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne
belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris
sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris
sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et
hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif
euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris
sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif
foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris
sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris
sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif
foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris
sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif
france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris
sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif
france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france
portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans
depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif
gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans
dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris
sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris
sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux
video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris
sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur
declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris
sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif
leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris
sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris
sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des
champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue
europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris
sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris
sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match
reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis
interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif
meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris
sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif
mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris
sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2
3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple
2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif
multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris
sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de
but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue
sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris
sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2
5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif
premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif
pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif
pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic
gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif
psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris
sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif
psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif
qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif
rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris
sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif
rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot
minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris
sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris
sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris
sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse
legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur
le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif
temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de
table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif
tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland
garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris
sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris
sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des
champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif
victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris
sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs
astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris
sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs
canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris
sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris
sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris
sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne
belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris
sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs
foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs
france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris
sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs
hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris
sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre
bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs
psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans
depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris
sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de
marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut
on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut
on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus
gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros
gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari
sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif
remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo
pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site
de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris
sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic
foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic
pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics
foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur
paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris
sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code
paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris
sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce
que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie
1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2
dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que
signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris
sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les
paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut
dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel
cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur
algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari
sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le
meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel
est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif
est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel
site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket
paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle
paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris
sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur
de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des
mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat
paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif
foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris
sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot
paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif
systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif
multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de
conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif
francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari
sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris
sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de
paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris
sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans
dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif
avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris
sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site
de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site
de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif
en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris
sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site
de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de
paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif
hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site
de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris
sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier
paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site
de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site
de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris
sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs
francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site
de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris
sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site
pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif
belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari
sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site
pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris
sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site
paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site
paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris
sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris
sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site
paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site
paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors
arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris
sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site
paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site
pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris
sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs
arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites
de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari
sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris
sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris
sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale
paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante
paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie
paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris
sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de
cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme
paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau
bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de
paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau
excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll
paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris sportif|tableau paris sportif excel|tableau roi paris
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100
euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100
remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif
forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie
sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif
foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari
sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris
sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris
sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans
argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif
sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris
sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris
sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de
paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris
sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris
sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari
sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris
sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris
sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif
virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les
paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris
sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans
depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris
sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris
sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris
sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris
sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour
gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari
sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site
paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh
signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de
bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris
sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash
paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot
paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris
sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus
paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif
belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris
sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris
sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but
sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris
sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari
sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote
paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb
paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage
cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur
cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris
sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote
paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité
paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari
sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte
prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute
de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris
sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code
promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris
sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif
conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné
paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de
jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment
arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer
au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche
les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer
gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une
cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment
creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer
un site de paris sportif|comment devenir
riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment
etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire
des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au
paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris
sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari
sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire
un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris
sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les
paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les
cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris
sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris
sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment
gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment
gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif
foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner
au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux
paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de
l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de
l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris
sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment
gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment
gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner
paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris
sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment
gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment
gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris
sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris
sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser
au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment
parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les
paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur
cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes
paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari
sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site
de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris
sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif
des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari
sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif
en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif
site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris
sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris
sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre
les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte
finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de
paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris
sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil
paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris
sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris
sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour
paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote
a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum
paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari
sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote
pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote
paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris
sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif
moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris
sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif
rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes
pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe
de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris
sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris
sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains
paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot
5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les
paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec
paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris
sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains
de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro
paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote
paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les
prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au
paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif
paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à
paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris
sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris
sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec
paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses
gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait
tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux
pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris
sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal
paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris
sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par
jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par
mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par
jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a
coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris
sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris
sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au
paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à
coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace
aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent
paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner
des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris
sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie
avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur
paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum
paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris
sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains
paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa
bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris
sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris
sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris
sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap
dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap
europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi
temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap
paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif
foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des
cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif
france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot
sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris
sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de
paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de
paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux
de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux
paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif
virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris
sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel
paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur
sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris
sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la
cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la
martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris
sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs
pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif
signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris
sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement
aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications
paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils
imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux
de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris
sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris
sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris
sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs
en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les
plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les
plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros
paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes
paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de
paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris
sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2
paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste
de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris
sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris
sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris
sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de
bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot
sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris
sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique
paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des
paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs
en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté
paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris
sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match
interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match
pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match
suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match
truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur
algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur
appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli
paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur
appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris
sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif
belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari
sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus
site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur
cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur
cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner
au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus
paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur
offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur
pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris
sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur
promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site
de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur
site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris
sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif
en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris
sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris
sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site
paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur
site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif
suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site
pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site
pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris
sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli
pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de
paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure
application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure
strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris
sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes
paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari
sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de
paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites
paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode
abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode
mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode
paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris
sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris
sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot
paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise
paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante
parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris
sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris
sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site
de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris
sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero
match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris
sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de
bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif
belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de
bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro
paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris
sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors
arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif
remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris
sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot
paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou
faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil
répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de
bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari
sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif
aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari
sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif
basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif
bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari
sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari
sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote
match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne
au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif
en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne
suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif
en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des
jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif
france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif
france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous
les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari
sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif
gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari
sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le
plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue
1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue
europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari
sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif
nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif
promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif
psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif
remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari
sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif
suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari
sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top
14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca
marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie
sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne
sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris
hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris
sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris
sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif
100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a
faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif
apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris
sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif
aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif
avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris
sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis
forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique
bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france,
http://Cilel.com.br/,|paris sportif
belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif
bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris
sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif
bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif
buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur
contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris
sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris
sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions
league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif
code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris
sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca
marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif
comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil
pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif
cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote
psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de
france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du
monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif
depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif
dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt
minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris
sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne
belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça
marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif
en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne
suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif
et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris
sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des
champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif
foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif
foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot
gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif
forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif
france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif
france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif
france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif
france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris
sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif
gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre
amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif
gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif
handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif
hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif
hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux
video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant
le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare
forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif
leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les
jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris
sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris
sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris
sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris
sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi
temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma
france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris
sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple
2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris
sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national
1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba
conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris
sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue
sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris
sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou
moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif
prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic
des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic
forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris
sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris
sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif
regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé
en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif
sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif
sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si
un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif
suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif
suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif
systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme
2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris
sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour
gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps
reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de
table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif
tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif
vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris
sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris
sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser
un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs
autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs
combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs
comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris
sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs
en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et
hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs
gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur
galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs
hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les
bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris
sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs
ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris
sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs
psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs
site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris
sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs
tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris
sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros
gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari
sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus
ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris
sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo
site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit
paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari
sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et
aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg
arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris
sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce
que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que
signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que
signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari
sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut
dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans
les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer
paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel
est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le
meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif
est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif
faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le
plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur
site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs
les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles
paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif
en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris
sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de
mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises
paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur
de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site
d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de
conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec
bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site
de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif
autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec
bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement
mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec
bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris
sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans
depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris
sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif
france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de
paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris
sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site
de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris
sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif
sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site
de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs
paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari
sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari
sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris
sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100
euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site
paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site
paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif
bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot
5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris
sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site
paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site
paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site
paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris
sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site
pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites
de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites
de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris
sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs
suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot
paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis
paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris
sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques
football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie
gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris
sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3
4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari
sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris
sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau
de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau
excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris
sportif|tabl
Một trong những yếu tố giúp slot365 thu hút và giữ chân người chơi lâu dài chính là hệ thống chính sách khuyến mãi hấp dẫn. Những chương trình khuyến mãi không chỉ mang lại cơ hội gia tăng số dư tài khoản mà còn giúp bạn có thêm động lực tham gia nhiều trò thú vị hơn. Dưới đây là một số loại khuyến mãi tiêu biểu mà khách hàng có thể nhận được khi tham gia vào nhà cái.
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro
offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros
remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris
sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide
au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme
excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme
pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif
excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme
pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris
sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api
cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli
paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli
paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre
amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans
argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris
sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse
paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris
sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia
paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent
fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif
espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris
sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris
sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour
gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris
sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis
paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris
sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans
depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce
pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif
basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce
pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner
aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari
sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif
foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur
les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris
sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100
euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris
sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot
paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash
paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari
sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris
sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris
sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus
sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris
sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus
sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris
sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul
combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul
couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul
dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris
sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage
cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris
sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote
paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur
de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris
sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote
paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote
pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau
paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league
paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site
de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris
sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser
paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris
sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner
au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca
marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de
paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote
paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer
un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner
au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment
faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris
sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment
faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner
au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les
paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire
un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris
sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les
paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les
cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les
paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand
oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a
coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner
a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment
gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment
gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux
paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent
au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris
sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner
des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les
paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les
paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris
sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris
sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux
paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris
sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment
marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les
paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll
paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier
sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment
reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont
calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris
sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur
cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur
de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur
de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif
bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site
paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif
sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris
sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris
sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte
financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari
sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif
aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris
sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris
sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur
les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller
paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris
sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote
anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de
pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari
sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari
sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif
belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif
france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto
gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif
rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour
paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes
de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site
de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer
ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris
sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris
sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis
paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb
paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs
hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro
paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que
les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a
paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements
sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris
2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec
paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris
sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris
sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll
paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris
sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris
sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux
pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise
des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france
belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france
pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france
tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris
sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par
jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000
euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris
sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a
coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur
pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris
sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner
argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari
sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner
aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner
aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari
sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner
des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner
paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner
sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner
à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris
sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll
paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll
paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2
5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les
paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis
paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris
sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur
gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris
sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie
sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer
au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse
paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur
italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris
sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale
paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur
application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris
sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse
cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur
site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur
site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs (Becky)|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les
17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les
application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus
paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains
de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux
de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes
paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de
pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les
paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris
sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs
en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les
plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de
paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites
de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite
de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des
paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites
de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de
pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll
paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari
sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot
sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de
cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic
calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale
paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif
interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris
sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match
interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match
reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués
paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur
app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de
pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli
paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil
paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les
paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari
sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site
paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur
conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur
cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote
site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour
gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de
bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre
paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du
jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris
sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de
conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de
pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris
sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site
de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif
hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site
paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site
paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site
paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris
sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris
sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure
appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris
sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure
application pari sportif|meilleure application paris
sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris
sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications
de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs
application de paris sportifs|meilleurs
application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris
sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris
sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris
sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs
sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale
paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris
sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif
tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner
paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise
minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante
paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique
pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode
paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris
sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site
de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris
sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de
match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros
paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari
sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre
bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris
sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de
bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de
bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif
cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris
sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre
paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site
paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue
paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte
paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack
de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros
offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions
league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif
cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari
sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif
du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne
au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari
sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif
faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif
francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france
angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari
sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif
france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif
gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari
sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari
sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari
sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari
sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari
sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue
europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif
mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre
bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif
prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari
sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg
bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe
du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif
sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari
sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari
sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif
france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne
sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france
sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris
hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100
euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100
offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari
remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris
sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris
sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent
fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris
sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif
aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec
cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris
sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket
coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket
prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris
sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif
bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus
de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris
sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus
sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif
but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris
sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne
joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris
sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris
sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a
tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris
sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris
sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe
de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif
depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif
du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris
sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec
paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne
bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment
ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif
en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne
suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et
casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et
prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif
foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris
sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif
foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris
sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris
sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football
astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france
2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif
france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif
france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris
sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris
sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris
sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit
cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit
entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris
sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1
0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap
foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris
sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors
arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le
match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif
joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris
sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris
sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris
sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif
ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif
match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du
jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif
match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris
sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif
meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris
sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins
de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple
2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris
sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national
1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de
but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris
sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou
moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris
remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert
gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic
gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris
sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que
veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle
prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris
sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris
sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot
minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif
si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se
blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif
site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris
sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif
suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du
jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2
3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme
explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris
sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de
table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir
au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif
vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue
des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris
sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs
astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris
sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris
sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de
football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris
sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne
belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris
sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur
galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs
les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs
montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris
sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris
sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top
14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte
d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris
sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse
cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris
sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo
pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif
gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot
paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris
sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris
sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics
paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif
gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg
paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu
est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris
sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris
sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie
1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que
signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw
en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que
signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie
handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire
handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris
sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel
est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel
est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site
de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est
le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel
pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari
sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle
est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure
application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le
meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle
des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle
multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif
prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash
paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des
mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris
sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur
de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises
paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris
sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif
systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris
sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris
sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de
paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de
pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans
depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de
pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de
parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site
de paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site
de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris
sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif
avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans
depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris
sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de
paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif
canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site
de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site
de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site
de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site
de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de
paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif
hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris
sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de
bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site
de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans
argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de
paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site
de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de
paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site
de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari
sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site
pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site
pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari
sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari
sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros
remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif
arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur
cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris
sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif
comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif
gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif
hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif
nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site
paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif
retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris
sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris
sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site
paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site
pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site
statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites
de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris
sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés
en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris
sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites
de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites
paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste
tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris
sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football
paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big
whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie
paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies
paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris
sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de
suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour
paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris
sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis
paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au
pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux
paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour
paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme
gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari
sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris
sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris
sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli
de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari
sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris
sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme
paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de
paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de
paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif
gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris
sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris
sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de
bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris
sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des
paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris
sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile
paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent
paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris
sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari
sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce
paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce
pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris
sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour
gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif
foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll
paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique
france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus
depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus
paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris
sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de
paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites
de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris
sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers
paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre
son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris
sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb
paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris
sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote
paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul
rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur
cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur
de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris
sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice
paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris
sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer
roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote
paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris
sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out
paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code
promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo
paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif
sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser
un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser
un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser
paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment
calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris
sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment
comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer
un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de
gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des
parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire
des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris
sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment
faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les
cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent
les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs
grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand
oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les
coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner
au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment
gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif
tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment
gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs
foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment
gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de
l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment
gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner
ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment
gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner
un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris
sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer
au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les
cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche
paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes
paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais
perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment
reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont
calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au
paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes
paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site
paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif
cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif
en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif
site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris
sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre
handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les
cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo
paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte
paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil
en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris
sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil
paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des
champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil
paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris
sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris
sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote
a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise
paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de
pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum
paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari
sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie
sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif
definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris
sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif
ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de
paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes
paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte
paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris
sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5
euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les
paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris
sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains
paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll
paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5
euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est
ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement
sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd
hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements
sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs
à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris
sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey
paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec
paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire
un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de
paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel
gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris
sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif
foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif
nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise
des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux
paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris
sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif
brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne
paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant
pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris
sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris
sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000
euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000
euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour
paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari
sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup
sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à
coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de
l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent
paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de
l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa
vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa
vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif
imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs
imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll
paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll
paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris
sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris
sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe
paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs
paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap
en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris
sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris
sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique
des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris
sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif
france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur
gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de
pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux
de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif
virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris
sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de
foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris
sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui
se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari
sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il
imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris
sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la
meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris
sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris
sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus
grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris
sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur
site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris
sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les
17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les
17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications
paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers
paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de
paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris
sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de
paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs
comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs
en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer
gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains
paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus
grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les
sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue
des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de
paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari
sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site
pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris
sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse
paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris
sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris
sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des
paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari
sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale
paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou
reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match
arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe
paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu
tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur
app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur
app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli
paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris
sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur
application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus
site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur
cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur
cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode
pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur
offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif
aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris
sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site
de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif
avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de
paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site
de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris
sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif
hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris
sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur
site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris
sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur
site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif
nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur
site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique
de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris
sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli
paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure
application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure
application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris
sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres
paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs
appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris
sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode
abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode
gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode
mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour
gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif
forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris
sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari
sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris
sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris
sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant
paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes
paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de
pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris
sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero
match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris
sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris
sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de
bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans
dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de
bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors
arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site
paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres
de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris
sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur
de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris
sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors
arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif
algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari
sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif
aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari
sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari
sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique
france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif
cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari
sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari
sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari
sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari
sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari
sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari
sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif
france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari
sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif
france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif
gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif
gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner
des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur
absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue
2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari
sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur
cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif
offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari
sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif
rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans
depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari
sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari
sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment
ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie
sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif
pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif
10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100
offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150
euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif
a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris
sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif
argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif
astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif
aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris
sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris
sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif
avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe
de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris
sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif
belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris
sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans
depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans
depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif
bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but
temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif
buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui
ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif
code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris
sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif
comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment
gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris
sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris
sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif
coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif
depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris
sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1
euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif
en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif
en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif
en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif
en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne
suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris
sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des
champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot
astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif
foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif
foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif
francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france
2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris
sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif
france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet
sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris
sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris
sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans
depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris
sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris
sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris
sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris
sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif
hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif
joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour
gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif
ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif
match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris
sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du
jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif
match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris
sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif
mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris
sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple
2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple
3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1
foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif
nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris
sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif
plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris
remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris
sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic
basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd
hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic
foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif
pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg
barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif
psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris
sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement
cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif
remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du
jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte
d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue
pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris
sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse
romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme
2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris
sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif
tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif
tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris
sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif
tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif
ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue
1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif
victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs
aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris
sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris
sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris
sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs
de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs
en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et
hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs
foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris
sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits
en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey
sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris
sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris
sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs
offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs
paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs
sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris
sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris
sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs
top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de
l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les
paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant
paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif
france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse
mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou
moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris
sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de
paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono
paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif
du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic
paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics
paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg
inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter
paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que
handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est
ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2
paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris
sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris
sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que
signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans
les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris
sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de
paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le
meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif
en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur
site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari
sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris
sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris
sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris
sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle
est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus
sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des
paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap
paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle
paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris
sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur
de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris
sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat
paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris
sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris
sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur
de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des
mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris
sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de
gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris
sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse
paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site
conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site
d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans
depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari
sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de
pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de
paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif
acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de
paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris
sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de
paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec
paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif
belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus
sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site
de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris
sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris
sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans
dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris
sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif
remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site
de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site
de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site
de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs
en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de
paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site
des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif
arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site
pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris
sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus
sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris
sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif
meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de
bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé
en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans
depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site
paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris
sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site
paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site
pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris
sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites
de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites
de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs
gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits
sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites
paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris
sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot
paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste
tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif
foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris
sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris
sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs
forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris
sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4
paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme
paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme
reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris
sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel
paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel
pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans
dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris
sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris
sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux
paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris
sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide
paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris
sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse
de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari
sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris
sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris
sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie
sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris
sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris
sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif
en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris
sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris
sportif international|application de paris sportif
suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent
fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif
gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de
domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les
paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique
paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications
paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent
facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris
sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot
paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner
paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif
foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner
au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris
sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis
pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif
foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site
paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris
sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique
france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus
bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash
paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans
depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus
gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus
pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris
sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus
sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site
paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi
handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti
perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul
cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote
paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul
paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris
sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer
probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris
sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée
paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris
sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris
sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris
sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser
paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné
paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment
arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment
arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au
paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer
gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment
calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer
un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris
sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir
riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au
paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris
sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire
pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment
faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment
faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes
dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au
paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a
tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au
pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment
gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au
paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner
aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent
avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment
gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris
sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris
sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris
sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment
gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur
les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment
gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll
paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris
sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris
sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais
perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir
paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça
marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari
sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de
paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de
site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari
sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur
site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote
pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif
offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif
paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris
sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif
sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote
paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des
paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris
sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil
paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris
sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif
rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les
paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris
sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils
paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote
de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote
pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real
madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote
paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris
sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france
belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris
sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris
sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote
sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de
paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs
foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans
les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer
ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris
sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot
minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les
paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb
paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains
de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors
arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris
sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur
de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre
sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement
sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement
sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement
sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements
sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris
sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris
sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris
sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de
paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris
sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot
paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris
sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des
jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des
jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france
2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari
– paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne
au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris
sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros
par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros
par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour
paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari
sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner
argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris
sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner
au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner
aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner
de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent
aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris
sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à
coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris
sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif
imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif
imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains
paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs
excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris
sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros
combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris
sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement
de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap
au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans
les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris
sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris
sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors
arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris
sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif
france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de
paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif
gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans
argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux
de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris
sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris
sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur
de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris
sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la
cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la
martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur
application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs
pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote
paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site
de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le
meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le
plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris
sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de
paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs
sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les
jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications
de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site
de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris
sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les
plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de
paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2
paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains
paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris
sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif
pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste
site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari
sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel
de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris
sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris
sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel
paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs
foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris
sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur
les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs
en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris
sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris
sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis
paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu
tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris
sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris
sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris
sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur
appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris
sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur
application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus
site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris
sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur
gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur
methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur
offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre
paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris
sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif
foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site
de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur
site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site
de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris
sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur
site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris
sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif
forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site
paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif
rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur
technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre
paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie
paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes
paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs
appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus
paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs
paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site
de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site
de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs
sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris
sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris
sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise
maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum
paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul
paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour
gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris
sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba
paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari
sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero
match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli
pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue
paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus
paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif
belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris
sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de
bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari
sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre
paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre
paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre
promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue
paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris
sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100
remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie
aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif
argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif
aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari
sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif
comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote
match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du
jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari
sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne
suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif
france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif
france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari
sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit
pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors
arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif
joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester
champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif
match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari
sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari
sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif
promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif
pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif
psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif
remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby
coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari
sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari
sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif
top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie
sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie
sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif
pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris
en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris
hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker
en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10
euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100
euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris
sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er
pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris
sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris
sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris
sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris
sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif
avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis
forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif
basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique
bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus
bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris
sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans
depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot
belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris
sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif
buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur
non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne
joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif
canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue
1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement
ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris
sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif
comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris
sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif
cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif
coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif
coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris
sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris
sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif
en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris
sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne
gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne
québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et
casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris
sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des
champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris
sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif
foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif
foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris
sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris
sportif france espagne|paris sportif france
gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif
france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris
sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner
argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif
gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif
gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris
sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans
argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap
basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris
sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif
hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors
arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux
video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé
pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris
sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le
plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner
tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue
des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif
match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris
sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris
sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif
methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris
sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de
3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif
multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif
multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris
sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif
nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif
nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue; Danielle,|paris sportif offre bienvenue
sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de
1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus
ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier
pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif
pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic
foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris
sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif
psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris
sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que
veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris
sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris
sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby
6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top
14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans
compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris
sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse
legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif
sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris
sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme
3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif
temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris
sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland
garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif
top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur
ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris
sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser
un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris
sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés
en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris
sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris
sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs
coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du
jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs
en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs
en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs
france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs
gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs
hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers
raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris
sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris
sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris
sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg
inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs
site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs
stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs
techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris
sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal
paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris
sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec
les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus
gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus
gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse
cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus
grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de
mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote
paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris
sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris
sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris
sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris
sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et
aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif
gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter
pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce
qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans
les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est
ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur
se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie
1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb
en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que
signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie
gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris
sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel
est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris
sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de
pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif
le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le
plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris
sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris
sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont
les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de
gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle
des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris
sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris
sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris
sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur
de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris
sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat
pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles
paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur
de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris
sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris
sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site
conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site
d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus
sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de
pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de
pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de
parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de
paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de
paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de
paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site
de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement
mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge
avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de
paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris
sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site
de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris
sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site
de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site
de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site
de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de
paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris
remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site
de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris
sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de
paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs
paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des
paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site
pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari
sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors
arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site
paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er
paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris
sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site
paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site
paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris
sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de
bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement
cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site
paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif
sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris
sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse
paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site
statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari
sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de
paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris
sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris
sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs
belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so
foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris
sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris
sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie
de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris
sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies
paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme
3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme
pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur
paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris
sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris
sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt
paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari
sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari
sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif
football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif
gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme
excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif
basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris
sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris
sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote
paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans
argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans
argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris
sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli
paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris
sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari
sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif
en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de
paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris
sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif
canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif
paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif
de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris
sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour
pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris
sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de
paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris
sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris
sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner
au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces
paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur
paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management
paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris
sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket
paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris
sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot
paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif
betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus
paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris
sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus
sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus
sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker
paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker
paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur
paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est
quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul
cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul
double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul
mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris
sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme
paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote
paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une
cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris
sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris
sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris
sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans
depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris
sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné
paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de
jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter
les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment
calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris
sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une
cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer
un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris
sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche
avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment
faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris
sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour
gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire
un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris
sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris
sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup
sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous
les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment
gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif
football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au
paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif
tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner
avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment
gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner
en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris
sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris
sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris
sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer
au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris
sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes
paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les
paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche
un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les
cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris
sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier
sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les
paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment
sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment
ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur
cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site
paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari
sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris
sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site
paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif
cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris
sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari
sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris
sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif
sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre
cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris
sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte
de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte
financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari
sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil
paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif
ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil
paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils
pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris
sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote
de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum
paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote
pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote
parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif
calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif
france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris
sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote
paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote
sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes
de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes
paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme
paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris
sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris
sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros
paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro
paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris
sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les
paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb
paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis
paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est
ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce
que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre
sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif
paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements
sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs
à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face
hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire
fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut
il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel
gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum
de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum
paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum
paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari
sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris
sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france
espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris
sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris
sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au
paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris
sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros
par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris
sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup
paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris
sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à
coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de
l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner
de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris
sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner
des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris
sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner
paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa
vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum
paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif
impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains
paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll
paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll
paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné
paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse
mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe
telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap
au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris
sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari
sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif
france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de
paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de
paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris
sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur
absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris
sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris
sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur
qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens
paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la
plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché
des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris
sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif
du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17
secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour
gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les
jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes
paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les
meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif
avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne
comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris
sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites
de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites
de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris
sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite
gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste
de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste
site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste
site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme
paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de
paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris
sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel
prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel
variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic
calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des
paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris
sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné
paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match
interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris
sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris
sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur
app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur
appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris
sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris
sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur
application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les
paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris
sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site
pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de
paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote
paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site
paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour
gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus
paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur
offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif
en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris
sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur
promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de
conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari
sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif
hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur
site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris
sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur
site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif
avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif
canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site
paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris
sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie
paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris
sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure
appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure
application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris
sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres
paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote
paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris
sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif
en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site
paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de
paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode
paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris
sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari
sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne
paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie
sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul
paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris
sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau
site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau
site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de
paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100
euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris
sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris
sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre
de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris
sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari
sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé
cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue
paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des
paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil
répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises
paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack
de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari
sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari
sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif
algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari
sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec
handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif
basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif
bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif
champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari
sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif
cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe
du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari
sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif
faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france
belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari
sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif
gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari
sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari
sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari
sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif
mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif
offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari
sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby
top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif
suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif
technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari
sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif
du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif
foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif
suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement
sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker
en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100
euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100
remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris
sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a
faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce
soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif
argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent
virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif
aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus
sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif
avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis
forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris
sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket
nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris
sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique
suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris
sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris
sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit
sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif
bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but
temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris
sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif
buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris
sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris
sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif
combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné
comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné
match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment
faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif
comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif
comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour
gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris
sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif
du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif
en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris
sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif
en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans
depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris
sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa
league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des
champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris
sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris
sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot
en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot
prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris
sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris
sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris
sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris
sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france
pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans
depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup
sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris
sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit
cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros
gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif
handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap
basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris
sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif
jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif
joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de
foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris
sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18
stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus
sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris
sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif
match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match
reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur
cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode
2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris
sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple
2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif
nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans
depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5
but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif
plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris
sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris
sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd
hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif
pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris
sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg
inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris
sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte
le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris
sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris
sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby
6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif
sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris
sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris
sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne
joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris
sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse
legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris
sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2
4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif
systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris
sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris
sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris
sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis
forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif
tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif
top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif
vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur
ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris
sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris
sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs
en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs
foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france
espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey
sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris
sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs
offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs
psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs
sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris
sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de
france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari
sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les
paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris
sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif
au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris
sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote
gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote
paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité
cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket
paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site
pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif
gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic
paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du
jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg
liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr
code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce
que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris
sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que
signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2
dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que
signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg
en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris
sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que
veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le
meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris
sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel
est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le
plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif
faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris
sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel
type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris
sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur
paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris
sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement
pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur
de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise
paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise
paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb
paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur
gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris
sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil
paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil
paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari
sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans
depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari
sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site
de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de
paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris
sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de
paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif
avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec
bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec
paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris
sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif
comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site
de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site
de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site
de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de
paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de
paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site
de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de
paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans
carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de
paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site
de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de
paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris
sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne
sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site
pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif
comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif
gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site
paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100
euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif
arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris
sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif
avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus
sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris
sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris
sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors
arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris
sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris
sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site
paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs
suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique
paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés
en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de
paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs
france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so
foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football
paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie
de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie
pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3
4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme
de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme
reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote
paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel
paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris sportif|tableau paris sportif excel|tableau roi paris sportifs|tableau
statistique paris sportif|tableau suivi paris sportif|
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros
remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris
sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide
aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif
football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris
sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme
gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme
paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme
paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme
paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse
de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari
sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris
sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris
sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris
sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif
sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris
sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de
paris sportif gratuit|application de paris
sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris
sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris
sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif
de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif
virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris
sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de
paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert
paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris
sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari
sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris
sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif
tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au
pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris
sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif
foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france
paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue
sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot
paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus
paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris
sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot
paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans
dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors
arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari
sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris
sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker
sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs
en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty
paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote
paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris
sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb
paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris
sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris
sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris
sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de
cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris
sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité
paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer
une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau
paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte
prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out
paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino
en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league
paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris
sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif
sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris
sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné
paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter
de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment
bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer
au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca
marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer
une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre
les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment
etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire
des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment
faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire
paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire
pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment
faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment
faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment
faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les
paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand
oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment
gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a
tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner
au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris
sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs
foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec
les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris
sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner
des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner
facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris
sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les
paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout
le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa
bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris
sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris
sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche
les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment
marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris
sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser
au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter
sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris
sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris
sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner
au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de
cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris
sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur
pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif
bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes
paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif
offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif
pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif
paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif
site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris
sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des
paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre
les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris
sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris
sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris
sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil
en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris
sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif
tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris
sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris
sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris
sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris
sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris
sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum
paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment
ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote
parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris
sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris
sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote
paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif
tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif
foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes
de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris
sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris
sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les
paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris
sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5
euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot
minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis
quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche
avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer
gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris
sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur
de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre
sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif
paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements
sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris
2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari
sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap
paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire
des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris
sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il
déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses
gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris
sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum
de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif
foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris
sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum
tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris
sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france
pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne
paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par
jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner
10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a
coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris
sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari
sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au
paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif
à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner
beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris
sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent
avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner
des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris
sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec
les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris
sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris
sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris
sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari
sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains
paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs
sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer
sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll
paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de
bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de
bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs
v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné
paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif
pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris
sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap
1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket
paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap
europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif
rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap
tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des
cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh
signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains
paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie
avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris
sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de
paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques
paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer
paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise
des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur
application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris
sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète
pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris
sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché
des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site
de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus
gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus
gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner
rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs
pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris
sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris
sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris
sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du
jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris
sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer
gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains
au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes
paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de
paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des
champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite
mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris
sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste
paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste
site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste
sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel
calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de
paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris
sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris
sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel
pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de
cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des
paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale
paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale
paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou
reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match
arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis
paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris
sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match
suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris
sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de
paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur
appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris
sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur
application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur
application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur
application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur
bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur
bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker
paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote
de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur
cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris
sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre
de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris
sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur
paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris
sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur
site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur
site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur
site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif
international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari
sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur
site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif
foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris
sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur
site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site
paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site
pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur
strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur
technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli
de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure
application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris
sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres
paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli
paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site
de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs
site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode
abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante
paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris
sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour
gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode
paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris
sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner
au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au
jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari
sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba
paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau
site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau
site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de
paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli
paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match
paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue
paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus
paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre
de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre
de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif
sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre
de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif
cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement
paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site
paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue
paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des
paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de
mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif
100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari
sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari
sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec
handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec
paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari
sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif
buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari
sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote
match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari
sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif
explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif
foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari
sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari
sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france
portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif
gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari
sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif
gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur
absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif
leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari
sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari
sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic
foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif
psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif
regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe
du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif
statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif
temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif
top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie
sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif
france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie
sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris
evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris
hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris
match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris
sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150
euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris
sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris
sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif
aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris
sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif
avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif
basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris
sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique
bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris
sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus
retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans
depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre
son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris
sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur
contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur
remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif
cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif
champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris
sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris
sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris
sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris
sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif
cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris
sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris
sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris
sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris
sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5
euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif
en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif
en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne
gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris
sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne
france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif
et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif
europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif
foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot
ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif
foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise
des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif
france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france
gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif
france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif
gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris
sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris
sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif
gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans
argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans
dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap
0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap
1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris
sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris
sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey
sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris
sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif
joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur
declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur
remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus
rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif
leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris
sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue
1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue
des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif
match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif
match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris
sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps
fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de
3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1
foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris
sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans
depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus
de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins
2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier
paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif
pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert
gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg
arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif
psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que
veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris
sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris
sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris
sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris
sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple
ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif
suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris
sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif
sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris
sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris
sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris
sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris
sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris
sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue
1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs
abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser
un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris
sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris
sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris
sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs
conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs
de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris
sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne
belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne
suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris
sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux
olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris
sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs
sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris
sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis
astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris
sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris
sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris
sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse
cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au
paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité
paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari
sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari
sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic
du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic
paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du
jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif
tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics
paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal
paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris
sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu
un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap
paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris
sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie
dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari
sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris
sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli
pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur
appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris
sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est
le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site
de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est
le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif
faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris
sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est
la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est
la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs
les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle
de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle
paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de
mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises
paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris
sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif
prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris
sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des
mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb
paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur
gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris
sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris
sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris
sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de
paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site
de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site
de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie
sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris
sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site
de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de
paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif
avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site
de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris
sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris
sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site
de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors
arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site
de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site
de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif
remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site
de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site
de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site
de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de
paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de
statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site
pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site
pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif
belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site
pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site
pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris
sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris
sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif
bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus
sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5
euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site
paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site
paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris
sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris
sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans
carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris
sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari
sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs
arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites
de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de
paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs
gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris
sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris
sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris
sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de
paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de
paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris
sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs
forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif (Jewell)|systeme de paris
sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll
paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau
excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris
sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion
?Celebremos a cada fanatico del exito !
Acceder a casino online sin registro es perfecto para sesiones rГЎpidas sin verificaciones extensas. [url=http://bar-celoneta.es/#][/url] Gracias a portales como casinos sin verificaciГіn, los usuarios identifican casinos confiables. Esto aporta tranquilidad y una experiencia fluida.
Elegir casino gratis sin registrarse permite jugar sin compartir documentos personales, lo que resulta ideal para quienes valoran la privacidad. Las recomendaciones de casinos sin kyc aclaran dudas comunes. Esta combinaciГіn facilita decisiones rГЎpidas.
casino sin verificaciГіn con juegos populares y fГЎciles – п»їhttps://bar-celoneta.es/
?Que la suerte te acompane con que goces de increibles premios extraordinarios !
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100
remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris
sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris
sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari
sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide
paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide
pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris
sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif
excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme
paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de
paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris
sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli
pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli
paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris
sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris
sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris
sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif
en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif
international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris
sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris
sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris
sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris
sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses
paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour
paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris
sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre
a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent
offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent
paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel
paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris
sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif
tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce
pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris
sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris
sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris
sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis
sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100
euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique
paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot
paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus
en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus
paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris
sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france
pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans
dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site
paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker
paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker
paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers
paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris
sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap
paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti
perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul
cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote
paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris
sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise
paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris
sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité
paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris
sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer
gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi
paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une
cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out
paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris
sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code
bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris
sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans
dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site
paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les
paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter
les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser
paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment
calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une
cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment
comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir
riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire
de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment
faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari
sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les
paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment
faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les
paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment
fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris
sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand
oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au
paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment
gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris
sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner
aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris
sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris
sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment
gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les
paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif
foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris
sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les
paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une
bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment
jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment
jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment
miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa
bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier
sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment
reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment
sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris
sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de
paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue
paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif
paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris
sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites
paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre
handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre
les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris
sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte
finance paris sportif|compte financer paris
sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris
sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil
paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue
des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris
sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris
sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris
sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils
paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils
paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris
sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise
paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote
de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris
sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari
sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris
sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris
sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif
france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris
sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes
de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes
paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france
paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris
sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot
5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand
existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris
sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains
paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors
arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris
sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur
de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris
sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif
a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris
2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris
aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs
paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des
cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire
des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut
il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains
paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot
paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis
paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de
paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum
tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique
paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france
paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris
sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne
au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100
euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous
les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner
au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup
sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris
sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner
beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l
argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent
grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de
l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari
sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris
sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec
les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups
paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris
sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris
sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll
paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll
paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de
bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de
mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris
sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram
paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris
sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap
basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris
sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap
paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique
des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace
paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma
vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif
en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie
sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux
paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris
sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot
paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif
paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris
sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la
cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale
paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote
gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur
site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris
sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets
pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets
pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris
sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs
du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de
paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus
gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus
gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes
paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris
sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue
1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue
des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de
paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste
site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site
paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris
sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll
paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel
pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris
sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel
probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique
paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché
des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris
sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris
sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis
paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris
sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app
de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur
appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris
sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de
paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari
sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur
application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari
sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans
depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur
bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur
bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur
conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur
cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum
paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de
bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue
paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur
pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris
sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic
paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur
site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif
belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site
de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif
forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors
arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris
sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur
site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur
site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur
site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site
paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris
sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur
site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour
gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure
appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de
paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif
android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre
paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications
de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs
appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris
sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de
paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de
paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner
paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique
pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris
sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot
paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise
paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie
sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris
sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode
calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba
pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de
paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site
pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif
france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de
match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli
pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris
sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre
bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de
bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro
paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans
depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement
paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris
sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris
sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de
mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture
compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors
arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec
orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif
basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari
sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari
sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe
du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif
en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne
canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari
sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif
euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari
sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif
france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari
sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari
sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des
cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari
sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue
europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match
interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif
mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre
bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari
sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic
gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari
sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif
remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari
sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif
rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans
carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari
sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif
temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif
en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et
sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris
sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire
aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif
abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis
parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif
application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif
apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent
virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus
sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif
belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif
belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris
sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris
sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif
bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris
sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris
sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur
carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur
remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris
sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné
comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris
sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris
sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif
conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour
gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris
sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris
sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris
sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du
monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot
minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5
euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif
en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne
avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif
en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris
sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris
sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris
sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et
casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif
euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris
sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot
aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe
du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif
foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot
prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic
gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football
americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris
sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif
france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france
espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif
france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris
sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris
sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris
sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif
gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris
sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans
argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans
dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0
1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris
sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif
handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris
sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris
sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel
france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux
video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris
sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous
les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris
sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris
sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue
europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif
match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris
sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris
sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode
2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au
jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins
de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris
sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif
multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba
conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans
depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif
plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou
moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris
sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris
sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris
sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif
psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris
sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris
sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif
remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris
sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif
rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris
sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans
depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple
ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris
sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif
sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme
3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis
de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis
gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif
ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur
euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire
prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris
sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris
sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs
en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs
en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs
euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris
sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous
les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris
sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris
sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur
glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris
sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue
2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris
sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre
bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs
pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris
sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs
site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris
sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris
sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris
sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché
paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut
on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif
france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner
au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote
paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo
pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris
sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono
paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif
aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic
paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris
sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot
statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris
sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris
sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris
sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap
paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que
signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari
sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris
sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut
dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la
meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel
est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le
meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur
site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel
pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel
paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif
est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli
de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure
application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de
gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris
sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris
sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari
sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de
mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat
paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif
hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle
paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise
paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans
depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb
paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de
gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris
sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris
sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif
gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site
arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil
paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site
de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de
pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site
de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris
en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif
acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site
de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement
mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris
sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site
de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site
de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de
paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris
sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans
dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif
le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif
paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site
de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site
de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de
paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris
sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site
de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site
des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari
sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari
sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari
sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie
sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros
offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé
en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif
avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site
paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus
sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris
sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif
nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement
cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif
retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris
sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs
france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris
sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site
pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris
sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de
paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs
belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de
paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris
sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris
sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris
sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de
paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs
forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2
3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme
pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel
bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif
gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris
sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100
offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris
sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif
foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme
excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme
paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris
sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote
paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris
sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne
cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans
argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif
entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif
sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris
sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris
sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif
en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de
paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif
gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris
sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris
sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif
usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent
facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot
paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent
paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris
sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce
paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris
sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au
pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour
paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner
aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de
paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus
bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris
sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus
depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif
en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris
sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif
belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari
sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus
unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker
paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris
sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp
paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris
sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul
cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de
cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb
paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul
pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris
sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote
paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris
sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris
sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de
cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de
paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris
sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site
paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris
sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari
sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment
arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris
sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote
paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment
calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment
comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de
paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment
etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris
sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire
pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris
sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment
fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les
cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris
sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral
maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner
a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous
les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment
gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner
au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris
sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner
aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment
gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner
dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment
gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement
au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment
gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses
paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au
paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer
paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes
paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche
un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment
miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment
parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment
reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes
de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche
les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur
cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de
cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites
de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur
site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari
sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari
sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris
sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif
site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap
paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes
paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre
les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte
démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte
financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris
sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de
paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil
pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil
paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif
pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil
sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris
sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote
a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris
sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote
parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote
paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote
paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote
sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes
de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes
paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer
un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs
que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris
sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot
minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris
sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari
sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris
sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris
sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote
paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs
sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte
dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement
sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement
sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement
sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs
paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris
sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire
un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris
sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll
paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot
paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum
paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris
sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne
paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris
sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari
– paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux
paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000
euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par
mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup
sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner
argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup
sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au
paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner
aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l
argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent
paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les
paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner
des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris
sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec
les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups
paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari
sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris
sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris
sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs
imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer
sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris
sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise
paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote
paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram
paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap
1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap
européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap
pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif
basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap
paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique
des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris
sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie
avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif
gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris
sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif
gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif
gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au
paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris
sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur
de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif
paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris
sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari
sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des
paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris
sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote
gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris
sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement
aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris
sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris
sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains
des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris
sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes
paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs
site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari
sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça
marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner
pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris
sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les
plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes
paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites
de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les
sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite
gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de
paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste
site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel
de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris
sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris
sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique
paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les
paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché
des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des
paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris
sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif
interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné
paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris
sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur
appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur
appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil
paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur
application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les
paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari
sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site
de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur
bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné
paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote
de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif
aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum
paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode
pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari
sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo
paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari
sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif
belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de
paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris
sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site
pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif
france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris
sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur
site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site
paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris
sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour
gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure
appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli
paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris
sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure
application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure
site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures
applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications
paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs
appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs
application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs
cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de
paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs
sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris
sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner
au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif
foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode
paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode
pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum
pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris
sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant
maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante
paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match
nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris
sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau
paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site
de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau
site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris
sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites
paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100
euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de
bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans
depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif
cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans
depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement
paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris
sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire
des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris
sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte
paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack
de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari
sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec
orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari
sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari
sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari
sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari
sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif
en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne
gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari
sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif
forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari
sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france
italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france
usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif
gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner
des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif
handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif
ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match
interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur
site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif
offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic
gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari
sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari
sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari
sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari
sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top
14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte
bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif
suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif
technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari
sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif
top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif
en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie
sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif
suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris
hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris
hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100
euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif
150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris
sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris
sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris
sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif
bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket
coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris
sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus
de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif
bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans
depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur
qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris
sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions
league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné
comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif
combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris
sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment
gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif
conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris
sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris
sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde
de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif
depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif
du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5
euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris
sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec
paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris
sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne
maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif
en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris
sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris
sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue
des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot
astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce
soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot
prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot
regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris
sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif
francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif
france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris
sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris
sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif
france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris
sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris
sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif
gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris
sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif
handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap
basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif
handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris
sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors
arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur
blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur
de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare
forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif
legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous
les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif
les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif
ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris
sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris
sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif
meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris
sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris
sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple
2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif
multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba
conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre
bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif
offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari
remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris
sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris
sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris
sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic
forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris
sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif
psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg
inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris
sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle
prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement
cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé
cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris
sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6
nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe
du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris
sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte
bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif
si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur
se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif
suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse
légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris
sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris
sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme
2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris
sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris
sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif
temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif
tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis
pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris
sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris
sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif
vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs
arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris
sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris
sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de
football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs
en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris
sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris
sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france
espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs
hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs
les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs
ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs
match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs
nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg
inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris
sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs
tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top
14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal
pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris
sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut
on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment
gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus
gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif
au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus
gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote
pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise
paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier
pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo
site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif
foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif
tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du
jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic
pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic
paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot
statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal
paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg
inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris
sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap
paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est
ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans
les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie
1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris
sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que
signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut
dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel
cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur
site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel
est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site
de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le
plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel
pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif
faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site
de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est
le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli
de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris
sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont
les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris
sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris
sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris
sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris
sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise
paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur
de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat
pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent
paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle
paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur
de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris
sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire
de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap
paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur
paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris
sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser
paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec
bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus
sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari
sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site
de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris
sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif
autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site
de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif
avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus
sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec
neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site
de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif
belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de
paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site
de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site
de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris
sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif
hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de
paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris
sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de
paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de
paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de
paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site
de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif
gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie
sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100
euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er
paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif
comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site
paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif
hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site
paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris
sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait
instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site
paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site
paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris
sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites
de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites
de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de
paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de
paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits
sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs
arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs
france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques
paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie
gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie
paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2
3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de
cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris
sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel
bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel
paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll
paris sportif|tableau montante paris
wettquoten bielefeld stuttgart
Here is my website :: wetten deutschland Japan
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris
sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert
paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari
sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide
paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris
sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris
sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris
sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris
sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif
sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli
paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif
belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris
sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide
paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de
paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de
paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll
paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif
gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif
belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris
sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris
sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de
domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif
usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris
sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi
paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a
faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot
paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent
paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner
paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris
sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce
paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris
sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces
paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis
pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris
sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue
sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus
de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit
sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris
sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif
cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris
sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris
sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif
hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site
paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker
sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est
quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture
paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris
sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris
sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul
systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris
sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris
sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris
sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out
pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino
en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement
des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris
sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris
sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code
promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris
sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser
un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca
marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote
paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer
une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre
les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment
devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner
au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire
paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner
les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les
cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment
fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a
coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner
au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner
au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment
gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux
paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le
long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au
paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de
l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris
sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment
gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les
paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris
sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris
sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment
jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris
sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris
sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa
bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris
sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment
reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris
sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris
sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus
paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites
de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris
sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif
paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre
cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap
paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer
paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif
financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari
sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil
paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil
paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris
sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils
de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote
a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise
paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de
paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif
real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif
belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote
paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote
paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote
paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote
sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris
sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris
sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses
gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum
paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris
sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche
avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro
paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce
que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les
prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro
paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement
sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs
paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes
paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari
sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire
fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer
les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis
paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris
sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise
des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2
paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne
paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant
paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris
sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris
sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par
mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur
pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner
au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif
foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux
paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner
beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux
paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner
de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner
de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les
paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner
sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup
sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris
sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une
bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll
paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise
paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros
combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris
sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris
sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5
paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap
en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris
sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique
cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace
paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot
paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris
sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris
sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux
de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux
paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux
paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris
sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris
sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris
sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est
il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour
gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux
paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse
cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché
des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur
site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros
gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17
secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les
cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de
paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris
sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris
sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs
site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les
meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif
avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs
en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris
sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris
sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les
paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris
sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les
sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs
francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris
sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de
gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de
paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris
sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme
paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris
sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris
sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris
sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel
probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi
sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché
des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari
sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé
ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match
arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match
interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari
sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis
paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme
paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur
app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris
sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris
sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur
application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris
sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur
application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans
depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris
sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur
cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris
sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum
paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia
paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue
paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur
offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif
du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur
paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil
paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site
de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris
sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur
site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris
sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site
pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif
en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur
site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur
site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site
paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris
sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie
paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris
sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli
de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure
application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari
sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure
application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre
paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures
applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures
stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications
paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs
site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site
de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode
martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique
pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif
foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner
au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise
maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne
paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris
sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple
pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode
calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour
gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris
sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau
site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris
sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux
sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris
sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris
sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari
sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre
bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre
de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de
bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari
sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre
paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris
sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif
sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre
remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris
sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise
paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris
sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de
bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne
sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif
aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif
astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif
aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari
sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari
sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari
sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari
sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari
sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif
en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne
ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari
sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise
des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif
france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif
france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari
sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif
gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari
sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari
sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari
sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif
le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue
2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif
match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari
sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari
sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari
sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif
rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari
sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari
sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari
sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari
sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie
sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie
sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris
evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et
sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker
en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif
100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris
sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris
sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire
aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris
sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif
apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris
sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris
sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif
avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif
avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif
avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif
basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif
belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans
depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif
but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur
carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur
non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif
calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris
sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif
classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif
combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné
du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca
marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif
comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif
comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif
conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris
sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris
sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde
rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif
dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec
paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif
en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris
sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif
en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif
en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris
sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris
sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final
ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris
sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif
foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif
foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris
sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des
jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris
sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif
france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france
espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france
italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif
freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant
à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris
sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit
avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris
sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans
argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap
0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1
0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris
sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris
sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif
hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux
olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant
le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris
sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur
remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal
en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies pour
gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif
ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue
des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris
sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match
abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif
match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif
match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif
meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise
au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris
sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris
sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris
sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris
sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris
sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau
site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus
de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus
ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif
premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier
paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris
sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif
pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris
sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris
sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif
que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle
prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris
sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris
sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif
rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans
argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif
sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot
minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si
un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris
sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris
sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse
légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du
jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris
sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris
sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris
sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland
garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top
14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via
paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs
astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs
autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs
bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs
de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs
en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs
en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris
sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot
us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris
sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris
sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris
sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors
arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris
sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs
technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal
paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment
gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris
sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus
gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus
gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote
gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise
paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari
sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif
combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari
sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris
sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour
paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif
aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics
foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal
paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg
inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg
om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris
sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2
paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari
sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que
veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris
sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le
meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel
est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site
de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari
sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus
rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif
faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site
de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de
pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la
meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs
faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif
foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur
de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises
paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur
de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris
sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire
interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris
sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif
multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser
paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari
en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus
sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif
gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif
en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris
sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif
autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site
de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif
avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris
sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus
sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site
de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif
legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de
paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui
accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans
carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans
depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site
de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif
belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif
100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris
sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans
depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site
paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site
paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris
sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site
paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement
cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris
sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site
pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris
sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de
paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris
sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs
bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs
en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari
sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris
sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs
hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis
paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris
sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2
3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris
sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau
de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau
gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100
euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari
sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris
sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide
paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme
gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris
sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris
sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse
de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari
sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris
sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli
pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris
sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans
argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse
paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de
parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris
sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif
fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif
usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris
sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris
sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre
a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert
paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs
impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris
sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif
basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au
pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour
gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis
paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris
sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll
100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris
sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif
gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris
sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue
paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris
sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris
sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot
paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif
betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris
sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus
paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus
paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus
sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site
de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris
sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris
sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers
paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap
paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari
sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris
sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris
sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul
mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul
probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur
cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage
paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris
sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris
sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris
sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de
temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps
pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris
sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du
jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris
sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les
paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris
sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment
calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les
cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une
cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris
sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de
gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des
parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris
sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment
faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour
arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire
un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire
un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment
fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner
a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous
les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment
gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment
gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris
sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris
sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de
l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment
gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris
sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec
les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au
paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment
gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer
paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment
marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche
un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment
miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll
paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris
sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes
de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes
paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur
de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur
paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus
paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari
sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif
paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris
sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer
les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre
handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les
cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris
sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris
sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil
pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris
sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil
paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris
sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil
sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller
paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour
paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote
anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote
de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote
paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris
sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif
foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france
espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif
psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris
sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à
1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris
sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer
un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris
sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les
paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris
sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris
sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains des
paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement
sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif
paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week
end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris
sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari
sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey
paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris
sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains
de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier
excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum
paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum
paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des
jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france
paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse
paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne
au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour
aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner
10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour
paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent
avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris
sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner
au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup
sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup
d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari
sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace
aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner
paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner
sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à
coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris
sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris
sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer
sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris
sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris
sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise
paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris
sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif
pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs
paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket
paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap
europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps
paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris
sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis
paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des
cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu
de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris
sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux
paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer
au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent
paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de
caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se
blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens
paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris
sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse
cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de
paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus
gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du
monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les
17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17
secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris
sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs
site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça
marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus
rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus
gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris
sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris
sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris
sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste
pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris
sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de
pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel
paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel
prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris
sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator
paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs
en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris
sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé
ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu
paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie
paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match
suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris
sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app
de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris
sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif
en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris
sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les
paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur
bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site
de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris
sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné
paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris
sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner
au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris
sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari
sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo
paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de
conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site
de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris
sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur
site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur
site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris
sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de
paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari
sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site
pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris
sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur
site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur
site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur
site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur
technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari
sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de
paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure
application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli
paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications
paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes
paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs
site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif
foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour
gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu
pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris
sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris
sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul
paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode
mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris
sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau
paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de
paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites
de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris
sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre
appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue
paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de
bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre
pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris
sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement
paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de
bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des
paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur
de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de
bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif
100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif
aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari
sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique
france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur
pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari
sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari
sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne
gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne
ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot
resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari
sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari
sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif
france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france
portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif
gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari
sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans
depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari
sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari
sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari
sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic
gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif
psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari
sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement
cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif
rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari
sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps
reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne
sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et
sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques
paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris
sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif
100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100
remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a
faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions
sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent
fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif
arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au
canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif
avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec
cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris
sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif
bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif
belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif
belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus
cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus
gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris
sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif
buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif
buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif
champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment
ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca
marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris
sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris
sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif
depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris
sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt
minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif
en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment
gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne
france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif
en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris
sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif
foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot
pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise
des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france
nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif
france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif
gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris
sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris
sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif
gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit
cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris
sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit
sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris
sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif
handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap
1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris
sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif
hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le
match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif
le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies
pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus
sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris
sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris
sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match
du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif
meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris
sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|Paris sportif multiple (https://www.kindelteenus.eu)|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif
multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif
multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba
pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif
offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif
offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif
plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris
sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic
basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif
pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif
psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg
liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif
rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris
sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif
rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris
sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris
sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif
sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris
sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme
3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris
sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif
temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif
tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis
roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif
ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris
sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris
sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs
arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris
sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs
bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du
monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs
en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs
en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs
euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs
france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs
gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris
sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue
2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs
montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de
bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris
sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal
pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte
d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut
on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus
gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus
gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus
gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse
cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise
paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de
paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono
paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de
paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris
sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides
aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics
paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter
milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris
sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg
paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris
sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap
dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie
12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que
signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que
veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel
cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est
le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de
pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site
de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le
pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le
plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif
rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris
sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est
le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la
meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle
est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels
sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris
sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris
sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle
paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris
sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur
de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise
paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat
paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris
sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de
mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans
depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris
sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur
de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif
multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme
paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris
sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil
paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec
bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari
sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de
pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site
de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site
de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans
dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de
paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site
de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de
paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de
paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif
en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site
de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif
gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site
de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif
meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de
paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de
paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris
sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris
sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site
de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de
paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris
sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs
gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de
paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site
pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari
sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site
pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris
en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec
bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris
sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif
canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site
paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris
sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris
sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé
en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs
france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris
sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site
pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris
sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de
paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites
de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites
de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites
de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites
paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris
sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot
paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique
tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie
big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris
sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de
paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante
paris sportif|tableau paris
Tham gia giải trí nhất định anh em không nên bỏ qua sảnh chơi cá cược thể thao. 888slot com apk. com đưa tới cho cược thủ hàng trăm các tỷ lệ kèo siêu hấp dẫn trên khắp thế giới, tỷ lệ thưởng đa dạng. Với nhiều giải đấu lớn nhỏ được cập nhật liên tục mỗi ngày như Champions League, Euro, La Liga, Serie A, Premier League, World Cup,…
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris
sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert
paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari
sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari
sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris
sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit
paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme
paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif
gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris
sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse
match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif
football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans
argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli
paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris
sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris
sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris
sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de
paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif
espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif
maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif
sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des
paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les
paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour
paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel
paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris
sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari
sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces
paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis
site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster
paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll
paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris
sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot
paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris
sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus
paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif
en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris
sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif
unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt
paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de
paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet
paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris
sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul
cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance
paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris
sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul
paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris
sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj
paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris
sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur
paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer
probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une
cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs
paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris
sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de
cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur
site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code
promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif
sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser
un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif
du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter
de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris
sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au
paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment
ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment
calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment
comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable
paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment
faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire
des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment
faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au
paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment
faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment
fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au
paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment
gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif
foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner
au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec
les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l
argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de
l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment
gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris
sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner
paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment
gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au
paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner
un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment
gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer
au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris
sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris
sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au
paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment
monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment
parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment
sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours
gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des
cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur
cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris
sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur
de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur
site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif
bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre
paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif
sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre
handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé
paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari
sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif
aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil
paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil
paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil
pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris
sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris
sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de
pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris
sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote
pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real
madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote
paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif
definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif
rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris
sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris
sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs
que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double
paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot
paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec
paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit
on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris
sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt
minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux
tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les
gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte
dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro
paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif
paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris
aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif
paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs
paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes
paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire
des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut
il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et
paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum
paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum
tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris
sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france
2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif
brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris
sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris
sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner
2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros
par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a
coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup
paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner
argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner
au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au
paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux
paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de
l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris
sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner
des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner
paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris
sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum
paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif
impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains
paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris
sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs
excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris
sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros
combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse
mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe
telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs
paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5
paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap
dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap
pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris
sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris
sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby
paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari
sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris
sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif
en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris
sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux
de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux
paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur
de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif
paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de
paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs
pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus
grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris
sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le
plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers
paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux
de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les
paris sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs
en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris
sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les
plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites
de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites
de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue
des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de
mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise
paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste
des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste
site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris
sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse
paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel
de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris
sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour
paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris
sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les
paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale
pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris
sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu
paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe
paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match
reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match
truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de
paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris
sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur
appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur
application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari
sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans
depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus
site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur
cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote
paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia
paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur
offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur
offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif
du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris
sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic
paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de
pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur
site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur
site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur
site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site
de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur
site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site
pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site
paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site
paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur
site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site
paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site
pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site
pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au
paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli
pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris
sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris
sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures
applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes
paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site
de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site
de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode
de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode
infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris
sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode
pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot
paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de
4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode
calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris
sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba
pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif
en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris
sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100
euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de
bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris
sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans
dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris
sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif
euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors
arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris
sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris
sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des
paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur
de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte
paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de
bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif
abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari
sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari
sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif
coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari
sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari
sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari
sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari
sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a
tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif
gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des
cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari
sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif
ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue
europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif
match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari
sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif
psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby
coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari
sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari
sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif
technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari
sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie
sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie
sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif
france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif
suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement
sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10
euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif
100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif
a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis
parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris
sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris
sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif
arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif
au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris
sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif
avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif
belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif
but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif
buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre
son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris
sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur
remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris
sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue
1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif
combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner
a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris
sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris
sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe
d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde
rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif
dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris
sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif
en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris
sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif
et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des
champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris
sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris
sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris
sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif
foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif
francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif
france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif
france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france
belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle
zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france
portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner
argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif
gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris
sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris
sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris
sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris
sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris
sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif
hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé
pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris
sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare
forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des
jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal
en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18 stratégies
pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif
ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris
sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif
methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris
sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple
2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple
2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre
de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre
bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre
sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif
paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus
de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou
moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif
prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif
pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif
pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif
psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris
sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr
code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif
regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement
cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris
sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif
rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe
du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans
depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif
si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse
application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif
suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse
romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur
le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme
3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif
technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps
reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif
tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland
garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris
sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs
aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris
sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de
football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne
belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs
en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris
sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à
tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs
gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris
sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs
ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris
sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris
sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs
site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris
sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris
sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari
sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris
sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les
paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris
sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris
sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus
grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote
paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme
gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari
sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo
site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos
paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic
du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit
paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic
paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic
paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic
paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris
sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari
sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om
paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans
les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie
1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie
12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb
en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie
gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut
dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel
est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de
paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est
le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur
site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel
pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour
paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli
de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle
handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement
pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement
en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat
paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris
sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris
sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur
systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil
paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site
de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari
sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site
de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris
sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec
bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec
paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de
paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site
de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris
sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de
paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif
qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site
de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris
sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris
sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs
gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs
suisse|site de statistique pour paris sportif|site
des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site
pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif
suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris
sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site
paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé
en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site
paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif
canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site
paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris
sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel
france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site
paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans
carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris
sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs
suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites
de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs
belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs
en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris
sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites
de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari
sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs
arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites
paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so
foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football
paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie
de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris
sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie
pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie
pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3
paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de
cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système
paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de
paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel
paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris sportif|tableau paris sportif excel|tableau roi paris sportifs|tableau
statistique paris sportif|tableau suivi paris
sportif|taxe gain paris sportif|technique combiné pari sportif|technique
handicap sportwetten live wetten strategie (Shelley) bwin
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert
sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris
sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris
sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif
belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif
gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris
sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme
paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme pour
paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse
match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse
paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif
sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli
pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif
belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse
paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll
paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de
parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif
en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de
paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de
paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif
gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris
sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif
sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses
paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour
paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de
paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans
depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris
sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris
sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner
au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris
sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris
sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh
signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll
paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris
sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris
sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus
cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif
belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot
paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot
paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris
sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris
sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif
sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris
sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus
site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites
de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris
sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker
paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers
paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris
sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote
paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des
cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris
sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul
pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité
paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur
cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur
de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris
sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une
cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris
sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris
sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement
des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur
site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code
bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo
sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris
sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris
sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné
paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris
sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris
sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les
paris sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari
sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment
créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment
etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner
au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire
des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris
sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire
paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment
faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire
un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment
faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les
cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans
les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes
de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a
tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner
au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|comment
gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif
forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment
gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner
aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment
gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de
l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner
les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment
gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner
ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment
gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment
gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris
sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment
jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment
marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les
paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment
marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au
paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris
sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote
pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur
de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de
site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de
paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris
sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris
sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre
de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif
pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif
bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer
les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre
les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte
démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier
paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte
pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris
sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris
sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil
paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris
sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils
paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs
tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de
pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum
paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment
ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote
paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france
espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris
sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes
de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris
sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash
out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif
en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb
paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer
gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris
sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les
gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris
sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement
sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement
sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements
sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des
paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari
sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains
de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum
de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie
sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum
paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis
paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des
jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique
paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif
brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne
au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris
sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros
paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris
sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur
pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris
sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner
au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au
paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent
paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les
paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris
sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris
sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec
paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à
coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris
sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains
paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris
sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris
sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll
paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris
sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de
mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné
paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote
paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe
telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris
sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap
basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris
sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey
sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris
sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma
vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de
paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris
sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux
de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris
sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs
en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur
absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur
de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur
professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris
sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris
sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux
paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la
meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris
sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des
paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le
meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros
paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement
aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de
paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris
sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur
paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris
sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site
de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites
de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris
sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs
en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs
en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains
au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris
sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses
pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de
paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs
en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris
sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite
mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste
paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste
site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris
sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris
sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris
sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris
sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel
pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité
paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris
sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris
sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris
sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari
sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif
excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match
abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé
paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match
interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match
reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match
truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur
algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app
de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de
paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif
forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil
paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris
sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur
application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour
pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris
sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur
ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue
paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur
offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur
offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari
sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur
paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif
foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur
site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
site de paris sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif
avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif
canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site
de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site
de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site
de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari
sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris
sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site
paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur
site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site
pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site
pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris
sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique
pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure
application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif
android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris
sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris
sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris
sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris
sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote
paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris
sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site
de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris
sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris
sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique
paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris
sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode
paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot
paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise
moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins
de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris
sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul
paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari
sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris
sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites
de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre
bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris
sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue
paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif
sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris
sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre
paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre
paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans
depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres
de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur
de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de
bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros
offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari
sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari
sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif
avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari
sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari
sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari
sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif
coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari
sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif
en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari
sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari
sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari
sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari
sportif france argentine|pari sportif france
autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari
sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif
gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari
sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari
sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif
joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif
ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif
match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif
match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif
mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif
promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari
sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg
inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari
sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari
sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis
abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif
tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie
sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif
pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris
match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros
remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a
faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris
sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris
sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris
sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris
sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis
forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris
sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris
sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif
bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif
bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus
retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif
but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif
buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif
calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif
champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné
comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif
comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris
sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif
conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris
sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote
psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe
du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5
euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif
dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne
avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris
sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif
en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment
ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif
en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif
finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif
foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot
feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot
prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football
americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris
sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris
sportif france argentine|paris sportif france
autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle
zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris
sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris
sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris
sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif
gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif
handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris
sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris
sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif
hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif
jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris
sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif
le plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif
les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris
sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris
sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match
abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif
match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif
match truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2
3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au
jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins
de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris
sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif
national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif
nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif
numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om
psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de
1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus
ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris
sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif
pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris
sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic
tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg
liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire
handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif
regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris
sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris
sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif
sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris
sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris
sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif
suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris
sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif
systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps
additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris
sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris
sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir
au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif
unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif
vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs
aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs
astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés
en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris
sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs
du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs
en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs
en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france
espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris
sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris
sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de
bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg
inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs
stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs
top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte
d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec
les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris
sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de
l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros
gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris
sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse
mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris
sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité
cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris
sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris
sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site
pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif
tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris
sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic
paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris
sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter
milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg
inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg
paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu est ce qu
un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que
signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie
1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie
handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est
la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site
de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le
meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari
sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel
paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est
la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris
sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle
de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle
pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement
paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises
paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby
paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise
paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises
paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris
sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif
système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site
aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site
arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site
d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de
conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari
sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif
acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris
sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de
paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif
avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement
mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif
belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus
sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris
sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site
de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site
de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit
pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit
sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus
fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris
sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris
sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site
de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs
en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique
pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site
pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif
bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif
hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site
paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif
belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris
sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif
canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site
paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris
sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors
arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris
sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif
sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans
depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs
belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour
analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites
de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de
paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites
paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors
arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris
sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis
paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie
paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse
paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4
paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris
sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris
sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau
de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour
paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau paris
sportif|tableau paris s
wettbüro quoten
Here is my web blog … Pferderennen wetten Schweiz
quotenvergleich
Feel free to visit my homepage :: Wettseiten ohne Lugas (qualifiedbuildinginspectors.co.nz)
?Brindiamo per ogni creatore di prosperita !
Ogni piattaforma affidabile dovrebbe garantire una gestione accurata della rischi digitali. Una buona conoscenza degli strumenti di sicurezza aiuta a prevenire incidenti indesiderati [url=http://infinitumondovi.it/casino-senza-invio-documenti/][/url]. Seguire queste semplici regole puГІ davvero fare la differenza.
La sicurezza nel gioco online richiede attenzione soprattutto riguardo alla crittografia. Riconoscere segnali sospetti ГЁ fondamentale per mantenere un ambiente di gioco sano. Seguire queste semplici regole puГІ davvero fare la differenza.
Casino-senza-invio-documenti elimina obstГЎculos innecesarios – https://infinitumondovi.it/casino-senza-invio-documenti/#
?Che la fortuna ti sorrida con aspettandoti magnifici round elettrizzanti !
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé
paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris
sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris
sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide
aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide
pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie
sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris
sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de
paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme
paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme
paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif
gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme
pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris
sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris
sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari
sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif
avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre
amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme
paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android
paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de
parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris
sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif
en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris
sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris
sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif
paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif
sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris
sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour
paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications paris
sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif
basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce paris
sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner
au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce
pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs
foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis
paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site
paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis
tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france
paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue
paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash
paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de
bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash
paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris
sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris
sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris
sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france
pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif
sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus
sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker
sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap
paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul
cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris
sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes
paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote
paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme
paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur
paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité
paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris
sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris
sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute
de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur
site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris
sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans
depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris
sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de
temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines
paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné
paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter
de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment
arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner
au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment
bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer
cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les
cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote
pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris
sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme
paris sportif|comment créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire
des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris
sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour
gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari
sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie
sportif|comment faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment
fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les
paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris
sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a
tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif|comment gagner
au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris
sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris
sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner
au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner
aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le
long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris
sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent
sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment
gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner
paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment
gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris
sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment
gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner
un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer
sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris
sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche
cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment
marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment marche
paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent
les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser
paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne
jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris
sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment
sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris
sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris
sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris
sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris
sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris
sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris
sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur
site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus
paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote
paris sportif|comparatif cotes paris sportifs|comparatif
des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif
paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte
de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer
paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte
financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris sportif
financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de
paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil
pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil
paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue
des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif
pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris
sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur
les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils
en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs
tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a
2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de
pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des
paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real
madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif
definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris
sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue
des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris
sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris
sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris
sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum
paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les
paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche
avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains
de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains
paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt
minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5
euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote
paris sportif|est ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans
un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif
a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd
hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des
cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris
sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des
paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut
il déclarer ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum
paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum
paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris
sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france
2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france
pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france
tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante
paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner 100 euros
par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50
euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les
coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris
sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris
sportif|gagner au paris sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à
coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris
sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup
d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de
l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de
l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de
l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
sur les paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris
sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner
paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses
paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à
tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains
paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains
paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll
paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris
sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote
paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe
paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap
0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les
paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris
sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps
paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap
paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris
sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot
gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur
gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu
de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris
sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux
de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de
paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot
paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif
paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la
cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la
martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur
application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour
gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur
site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris
sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros
paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs
en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les
17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains
de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains
des paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur
paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris
sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site
de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris
sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris
sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre
jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros
gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros
gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les
plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de
paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les
sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs
francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue
des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite
de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste
pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse
paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris
sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris
sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel
pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique
paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs
en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris
sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale
paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris
sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari
sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu paris sportif|match
suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme
paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif
en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur
application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour
pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné
paris sportif|meilleur conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote
pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur
cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris
sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner
au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du
jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du
jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris
sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris
sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site
de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif|meilleur site
de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris
sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site
de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors
arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif
suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris
sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur
site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris
sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur
site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari
sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure
appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris
sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris
sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure
application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site
paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris
sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris
sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications
paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote
paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris
sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris sportifs|meilleurs site
paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc
paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif
forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner
au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes
paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5
but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris
sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris
sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode
match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour
gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris
sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de
pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de
paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau
site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site
paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match
paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre
bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre
bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre
de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre
de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans
dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris
sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors
arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre
paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement
paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des
paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris
sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris
sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari
en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif
avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif
belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas
titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari
sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif
coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif
en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif
en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise
des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france
portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a
tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit
sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif
le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif
ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari
sportif match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif
meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif
methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au
jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre
bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari
sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari
sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari
sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif
rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif
rugby top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari
sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif
tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie
sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif
foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie
sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne
sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france
sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques
paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques
sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif
10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100
euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100
remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros
offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif
application|paris sportif application android|paris
sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif
arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif
aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif
avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif
avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket
coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif basket
prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique
france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus
de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris
sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris
sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris
sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris
sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui
ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris
sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris
sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris
sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment
gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça
marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif
comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif
conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif
coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris
sportif coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif
depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif
dépôt 1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif
en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris
sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif
en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif
en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif
et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris
sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final
ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris
sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif
foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot cote|paris
sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif
foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif
foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris
sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif
france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france
angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris
sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris
sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris
sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris
sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif
gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif
gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif
handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris
sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif
hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris
sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le
plus rentable|paris sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif les 18
stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris
sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris
sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif
match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match
du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris
sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match
truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur
pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris
sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de
3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2
4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif
nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre
bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris
sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus
de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins
2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match
aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif
pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg
dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg
liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif
remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif
rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top
14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte
bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris
sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si
match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif
statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris
sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris
sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme
2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme
explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif
temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif
tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris
sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif
ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif
vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris
sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs
bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris
sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du
monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs
en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs
en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris
sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey
sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs
ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris
sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs
sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris
sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché
paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris
sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine
paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris
sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse
cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris
sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris
sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif
tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris
sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic
paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg
arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code paris sportif|qu
est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les paris
sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que
handicap dans les paris sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie
12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que
signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire
dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les
paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote
jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur
algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur
site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est
le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel
est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel
pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus
sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte
le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris
sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la
meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure
application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure
application pour les paris sportifs|quelle est
le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont
les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap
paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle
paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement
pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash
paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris
sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris
sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby
pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris
sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur
de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se
faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris
sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris
sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de
paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site
de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de
pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de
pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de
paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site
de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif
avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus
sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris
sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de
paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris sportif football|site de
paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site
de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site
de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif
le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif
meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de
bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif
qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris
sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris
sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris
sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs gratuit|site de
paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique
pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site
pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site
pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif
gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie
sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100
euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site
paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif
avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site
paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site
paris sportif foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif
retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte
bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif
suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs
en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris
sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites
de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits
sans dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites
paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors
arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris
sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique
tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de
paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie
de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs
forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris
sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme
pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur
paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote paris
sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel
paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel
paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante
paris
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos
para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2
apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas
que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que
significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que
siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos de azar y apuestas|ad
apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america
apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer
apuestas de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas android|aplicaciones
de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones
de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de
apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de
apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas
deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app
apuestas android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas
deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas
deportivas españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre
amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app
casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de
apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas deportivas
colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas
perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas en venezuela|app
de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app
de apuestas para android|app de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas
peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas
android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para
apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas
deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de
apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer
apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros
gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de
caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas
al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas
alonso campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas
america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas
arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del
mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas
argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina
uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas
argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas
ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de
madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico
real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas
baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto
juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas
barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas
barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas
barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs
madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas
barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico
madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana
la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas
barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona
real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona
valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs
real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol
pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis
– chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis
mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis
real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs
valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia vs
colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono
de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas
boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo
femenino olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas
brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas
brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas
caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas
campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas
campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas
campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas
campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de
caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera
de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas
carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos
en directo|apuestas carreras de caballos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras
de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas
carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino
online|apuestas casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas
celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas
celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas
champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas
champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas
champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas
chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo
en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas
clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia
argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia
uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas
combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas
mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para
esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas
combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas
combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas
con handicap baloncesto|apuestas con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa
africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas
copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del
rey final|apuestas copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas
copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa
mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas
croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de
baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo
hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos
como funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos
internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos
por internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras
de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas
de colombia|apuestas de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas
de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas
de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de
futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de
futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol
en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas
de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol español|apuestas de futbol
gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol
online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy
seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de
futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de
futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas
de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de
hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa
league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga
española|apuestas de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas
de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de
sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas
de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis
para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de tenis seguras|apuestas
de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas
del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del
dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1
euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas
deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino
online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas
champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas
deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas
deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas
deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos
gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas
consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa
america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas
copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual
es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas
de peru|apuestas deportivas de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas
en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas
estrategias|apuestas deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas
deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro futbol|apuestas deportivas
foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas
deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas
golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas
interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas
la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas
deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas
mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas
mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas
deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas
deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas
deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas
paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru
vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico
hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que
aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas
seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas
stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas
deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas
tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas
deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas
deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas
descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas
descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias
seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de
honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y
triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas
ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas
empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras
de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea
chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas
en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas
en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas
en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas
españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa
croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas
españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana
el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas
españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas esports
valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas
euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa
españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa
final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas
euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas
f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1
monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de
ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas
favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions
league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa
europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa
del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final
europa league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final
uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas formula 1|apuestas fórmula
1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas
foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas
futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas
fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol españa|apuestas futbol
español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol femenino|apuestas
futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol
hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas
futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol
peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas
futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas
galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador
copa america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas
ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas
ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas
ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la
liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas
goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas
golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand
slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis
para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas
gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas
grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas
hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas
venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey
hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas
holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas
hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas
juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas
jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings league
americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las
vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas
league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas
legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas
liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas
liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga
santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas
linea de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas
liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid atletico|apuestas
madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas
madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid
barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas
madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la
liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas
madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid
vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real
sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas
mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas
maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb
pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como
funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial 2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas
mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial de ciclismo|apuestas
mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de
fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial
formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas
mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba
campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta
noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy
jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas
nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas
nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos
eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas
online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas
online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online
comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de
caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online
en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online
espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas
online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas
online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas
online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online
sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online
venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas
osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over
under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas
paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas
países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas
para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para
ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar
la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la liga|apuestas
para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas
para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas para la final de
la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas
para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de
hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas
paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru
uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas
pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas
playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas
por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas
por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones
futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas
promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas
pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas
prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas
puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que
siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la
eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara
la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real
madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas
real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid
borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas
real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real
sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid
vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas
resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas
segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras
baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas
seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol
hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas
seguras para este fin de semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas
seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas
sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas
sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas
sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla
leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real
sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas
sistema como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10
hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas
amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis
roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis
wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster
para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas
trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas
uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc chile|apuestas
ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia
topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay corea|apuestas
uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas
us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas
valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal
athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal
manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas
virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas
y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|Apuestas Y Pronosticos De Futbol (Akurai-School.Lbihost.Ru)|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro nba
apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs
chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina
vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona
apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico
de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real
madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro
barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca
vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona
atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona
betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona
inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona
valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid apuestas|barcelona
vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america apuestas|bet
apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis
apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu
sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas
deportivas|bono apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca
apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de
apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono
por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa
de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono
sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos
apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas
de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas
deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas
deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida
casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de
bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de
apuestas|bonos en casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos
gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito
apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas
deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas
apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de
apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas
sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de
apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora
poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora
trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular
cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake
apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de
cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga
apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos
apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos
con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras
de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico
de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas
cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa
apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa
apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas
peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa
de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas
barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas
bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa
de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de
apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa
de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas
ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono
sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa
de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa
de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas
con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas
de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de apuestas de futbol|casa
de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas
del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa
de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas deposito
minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa
de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa
de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas
esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa
de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas ingreso mínimo
1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales
en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa
de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas
méxico|casa de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas
nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del real madrid|casa de
apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online
españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa
de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para
boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas
peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas
por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas
que regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa de
apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia
en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de
apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de
apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos
sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas
colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas
legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas
apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas
online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5
euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de apuestas
barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas
bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas bonos de
bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas
de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de
apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas
ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas
con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de apuestas con bono por registro|casas
de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito minimo|casas de
apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas
de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas de apuestas de
caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de
apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas
de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas
en españa|casas de apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas
españa|casas de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas
de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas
mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas
deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas
en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas
en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas
de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas
en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas
de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa
online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas
de apuestas españolas online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas
eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa
league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas
de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera
de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas
de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador eurocopa|casas de apuestas
gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas
inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de
apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas
de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores
cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas
de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de
apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas
nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas
de apuestas nuevas españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas
online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de apuestas
online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas
online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas
de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas
online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas
?Brindiamo per ogni maestro del destino!
La crescente diffusione dei giochi online rende essenziale proteggere la propria scaricare software. Molti attacchi informatici nascono da piccole distrazioni facilmente evitabili [url=https://infinitumondovi.it/casino-senza-invio-documenti/#][/url]. In questo modo ogni sessione di gioco risulta piГ№ serena e protetta.
La sicurezza nel gioco online richiede attenzione soprattutto riguardo alla recensioni utenti. Molti attacchi informatici nascono da piccole distrazioni facilmente evitabili. Con piccoli gesti quotidiani ГЁ possibile proteggersi in modo efficace.
Casinosenzainviodocumenti ofrece las mejores tragamonedas – http://infinitumondovi.it/casino-senza-invio-documenti/#
?Che la fortuna ti sorrida con che il destino ti offra emozionanti successi !
?Brindiamo per ogni appassionato del pericolo !
opciones como tiradasgratissindeposito.es/ hace que la experiencia sea
permite a los jugadores descubrir nuevas oportunidades sin gastar dinero
ВїVale la pena https://tiradasgratissindeposito.es? AnГЎlisis claro y… – tiradasgratissindeposito.es/
?Che la fortuna ti sorrida con aspettandoti magnifici scommesse trionfanti !
найкращі слоти грати слоти
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
Good day! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris
sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris
sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis
paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide
aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide
paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme gratuit
paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris
sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme
paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse cote
paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse
paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris
sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris
sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli paris
sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris
sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android
paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris
sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif
en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris
sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris
sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit entre amis|application paris
sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris
sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris
sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour paris
sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications
paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert
paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris
sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans
depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner
paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris
sportif|astuce paris sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris sportif forum|astuce
paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner
au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris
sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis
sur paris sportif|avis tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100
euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris
sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris
sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue
paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue
paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de
bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus
gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus
paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif
cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris
sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris
sportif unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans
dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus
sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty
paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris
sportif – Sasha -|calcul
anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari
sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul
paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi
paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer
gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité
paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari
sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris
sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne
paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote
paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code
paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris
sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps
pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine
paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné
paris sportif|combiné paris sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux
paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris
sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris
sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment
bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment calculer
cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer
un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment
créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre
rentable paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire
de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment
faire des paris sportif|comment faire des
paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment
faire pari sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour
arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari
sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment
faire un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes
des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne
paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent
les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans
les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes
de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur
au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment gagner
a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari
sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au
paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup
sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment
gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner
au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur
les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris
sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif
foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa
vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au
paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris sportif|comment gerer une bankroll
paris sportif|comment gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment
jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer
aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportifs|comment
marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent
les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les
paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier
sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir
les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari
sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur
cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote
pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris
sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de
site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris
sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur
site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes
paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif offre
de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris
sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif
paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site
paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif
sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote
paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les
cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte
de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer
paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte
paris sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil
en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil
pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur
les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris
sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2
paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote
paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris
sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france
espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote
paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote
paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote
sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes
de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris
sportif|créer un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap paris
sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum
5 euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec
les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb en paris sportif|dnb
pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb paris sportif definition|dnb paris
sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains
paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt
minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est
ce que les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris
sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd
hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce
week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs
à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire
un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses
gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité
gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis
paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de
paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif
foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum
paris sportifs|forum sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis
paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france
2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris
sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france
tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris
sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner
100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris
sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris
sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris
sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au
paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à
coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent
grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l
argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent
au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec
les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|gagner des
paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner
pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif
tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie
avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses
paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous
les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari
sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif
impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris
sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer
sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris
sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de
bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros
combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris sportif|groupe paris sportif
gratuit|groupe telegram paris sportif gratuit|groupement
de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5
paris sportif|handicap au paris sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap
européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap
paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris
sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap
tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey
sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris sportif
france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris
sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de
pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif
gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de
paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse
paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur
professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur
suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote paris sportif|la francaise des
jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus
grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le
plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les
10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux
paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux
paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les gains de
paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris
sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris
sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris
sportif avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs
en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant
paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus
gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les
sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les sites de
paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue
2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de
mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste
de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris
sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites
paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari
sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris
sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris
sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel
prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris
sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris
sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché
des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale
paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale
paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé
ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match
arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu
tennis pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match
paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu
paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme
paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur
appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris
sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus
de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris
sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur
conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote
pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote
paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur forum paris sportifs|meilleur
gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur
offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur
offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris
sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif
aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site
de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris
sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris
sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur
site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif
football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif
france|meilleur site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site
de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari
sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur
site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif
forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour
paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique
paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli
de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris
sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de
paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris
sportifs|meilleures cotes paris sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs
appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris sportifs|meilleurs
application paris sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs
bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes paris
sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site
de pari sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de paris
sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris
sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris
sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode
pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise
maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes
paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris
sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul
paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique
pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode paris sportif
hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris
sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site
de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris
sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match
paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre
bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue
paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site
paris sportif|offre bonus paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris
sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de
bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre
pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif
remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre
paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue
paris sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire
des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris
sportifs|ouvrir un compte paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari
en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari
sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif
application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif
avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif
avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif
avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari
sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari
sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe
du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari
sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au
cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne
canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif
foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari
sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france
autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif
gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif
gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur
absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif
ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif
match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari
sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif
meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au
jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari
sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif
pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari
sportif psg|pari sportif psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari
sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari
sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du
monde|pari sportif rugby top 14|pari sportif
sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif
site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique
pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif
tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie sportif
comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie
sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif
pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris
en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris
hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris
hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif
1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris
sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif
application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif
arsenal psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd
hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec
argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte
bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec
handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris
sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif
basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique
bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif
bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus
sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif
bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif
buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif
buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul
gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash
out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement
ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça
marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris
sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif
comment jouer|paris sportif comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris
sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris
sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris
sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe du monde
de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris
sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt
1 euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne
avec paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris
sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment
gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif
en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris
sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris
sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale
ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris
sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif
foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif
foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football
americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif
france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris
sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif
france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris
sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris
sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris
sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit
entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris
sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris
sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif
handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris
sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le
match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur
declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif legal
en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif
les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris
sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif
ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris
sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif martingale|paris sportif match|paris
sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris
sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match
truqué|paris sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif
meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2
3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris
sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif
montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple 2
3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif
multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3
4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif
nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif
nouveau site|paris sportif numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue
sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre
sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris
sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif
plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif
prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris
sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif
pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif
psg dortmund|paris sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg
liverpool|paris sportif psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que
veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif
remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby
coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif
safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans
carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif
sans compte bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif sans
depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si
un joueur ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris
sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif
stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse
romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif
systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme
3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris
sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris
sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif
vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via
paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris
sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris
sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs
basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs
cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris
sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris
sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris
sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs
foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs
france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs
gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris
sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris
sportifs hockey|paris sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs
hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la
mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue
2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs
match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris
sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris
sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs
technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché
paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte
d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut
on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris
sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros
paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus
grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou
moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket
paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari
sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono paris sportif foot|prono
paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris
sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic pari sportif|pronostic pari
sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic
paris sportif foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics foot statistiques et aides aux paris
sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif
gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool
paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr
code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap
dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris
sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand
un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2
paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie
btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris
sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg
en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans les paris
sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans les paris sportifs|que
veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris
sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel
est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel
est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris
sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif
faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site
de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris sportifs|quelle
est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs
faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket
paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de
paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle
handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris
sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement
paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de
mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris
sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise
paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat
pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby
paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur
de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris
sportif|se faire interdire de paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris
sportif|simulateur de gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site
aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site
d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil
paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de
pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus
sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif
en ligne|site de pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif
hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site
de parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris sportif
acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site
de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif
avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec
neosurf|site de paris sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif
avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site
de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif
bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de
paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot
minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site
de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site
de paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris
sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des
cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors
arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris
sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif
paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif
qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de
paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de
paris sportif sans carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris
sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de paris sportifs
gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique
pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari
en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros
offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari
sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari
sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari
sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site paris
en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif
100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros
remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris
sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur
cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris
sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site
paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif
foot|site paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site
paris sportif hors arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif
nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif
remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site
paris sportifs en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site
paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites
de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs
arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans
dépôt|sites de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites
paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis
paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques
paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie
paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme
3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme
pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris
sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris
sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau
de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris
sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion
новости беларуси новости спорта беларуси
Правильная подготовка обеспечивает доступ к кракен через установку Tor браузера с официального сайта torproject и проверку всех загруженных файлов через PGP подписи.
?Celebremos a cada apasionado del exito !
Jugar en Casino Retiro Sin VerificaciГіn permite acceder a una experiencia rГЎpida y privada sin procesos complicados. [url=п»їhttps://casinoretirosinverificacion.com/][/url] Muchos jugadores optan por estas opciones debido a la libertad que ofrecen plataformas como casino sin registro. Gracias a esta flexibilidad, cada sesiГіn se vuelve mГЎs cГіmoda al usar servicios como casino crypto sin kyc.
Jugar en casinoretirosinverificacion permite acceder a una experiencia rГЎpida y privada sin procesos complicados. Muchos jugadores optan por estas opciones debido a la libertad que ofrecen plataformas como casino sin kyc. Gracias a esta flexibilidad, cada sesiГіn se vuelve mГЎs cГіmoda al usar servicios como casinos sin kyc.
Casino sin registro, diversiГіn rГЎpida – https://casinoretirosinverificacion.com/#
?Que la suerte te beneficie con que logres sorprendentes galardones excepcionales !
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros
offert paris sportif|100 euros remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100
offert paris sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari
sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris sportif gratuit|aide
paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris sportif|algorithme
gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris
sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris
sportif tennis|algorithme paris sportifs|algorithme
pour paris sportif|analyse cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse
paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse paris sportif gratuit|analyse
paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris
sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris
sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif
gratuit|appli paris sportif sans argent|appli
paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris
sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote
d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux
paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris
sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif
gratuit entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de
bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif
sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris
sportif usa|application paris sportif virtuel|application pour faire des paris
sportifs|application pour gerer ses paris sportif|application pour
les paris sportifs|application pour pari sportif|application pour
paris sportif|application pour paris sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris sportif|applications
de paris sportifs|applications paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis
paris sportifs|apprendre a faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris
sportif basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce
paris sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris
sportifs|astuce pour gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris
sportif|astuce pour gagner paris sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis
paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis
tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll
paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll
paris sportifs|basket paris sportif|belgique
france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris
sportif|bonus de depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus
en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit
sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif
betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france pari|bonus paris sportif
retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif
unibet|bonus paris sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus sans
depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus sans dépôt paris
sportif hors arjel|bonus site de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker
paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris
sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre
son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul paris sportif|calcul paris
sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité
paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote
paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage
paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer
cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out
pari sportif|cash out paris sportif|cash
out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris
sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo
paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour
encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris
sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux
paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment
arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment
bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris sportif|comment
calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote
pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris
sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment
créer un site de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable paris
sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire
de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire des paris sportif|comment
faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris sportifs|comment faire pari
sportif|comment faire paris sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire pour
gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner
les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment
faire un pari sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire un paris
sportif|comment faire une montante paris sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les
paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment
fonctionne un pari sportif|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris
sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes de
paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent
les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|comment gagner a tous les
coups au paris sportif|comment gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner
au pari sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment
gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au paris sportif a coup
sur|comment gagner au paris sportif foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner
au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment
gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs livre|comment gagner aux
paris sportifs sur le long terme|comment gagner avec les
paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris
sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment
gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des
paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment gagner les paris sportifs|comment
gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa
vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris
sportif|comment gagner sur les paris sportif|comment
gagner sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris
sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris
sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment gérer sa
bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment jouer au
paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes
paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche
les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment
marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent les cotes
paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment
miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll paris sportif|comment ne
jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment
reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des
paris sportifs|comment sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites
les cotes des paris sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça marche les
paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur
cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de
paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur paris sportifs|comparateur
site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus
paris sportifs|comparatif cote pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes
paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif
offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site
de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris
sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris
sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de
paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris
sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris
sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris sportif|compte paris
sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil
pari sportif|conseil pari sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil
paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif gratuit|conseil
paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil
paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil
pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils paris
sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100
paris sportif|cote a 2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris
sportif|cote de 2 paris sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote
minimum paris sportif|cote pari sportif|cote pari
sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif real
madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote
paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif
france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris sportif ligue des champions|cote
paris sportif moto gp|cote paris sportif psg|cote paris
sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote
sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes
paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer un compte paris
sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap
paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double paris sportif|depot minimum 5
euro paris sportif|depot minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis
quand existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb
en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb
paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains
de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris
sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que
les gains des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce que les
prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif a paris|evenement
sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris
aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce week end|evenements
sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris
sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote
paris sportif|explication handicap paris sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face
hockey paris sportif|faire des paris sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire
des paris sportifs|faire fortune paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer
ses gains paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris sportifs|forfait tennis
paris sportif|formation paris sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris
sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum
sur les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportifs|france
2 paris sportif|france 2 paris sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris sportif|france pari sportif|france
pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris
sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif
bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris
sportifs|gagner 100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris
sportifs|gagner 10000 euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros
par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner
a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner
au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris
sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif
forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner aux paris sportif|gagner
aux paris sportifs|gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner
beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent
grace aux paris sportifs|gagner de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportif|gagner de l
argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de
l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner de l’argent avec paris
sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace
aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner
de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les
paris sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris
sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner
sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner
à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif
imposable|gain paris sportif impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs
imposable|gains paris sportifs imposables|gains paris sportifs
sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer
une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll
paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs
excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris
sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5
gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise
paris sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram
paris sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris
sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap
mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris
sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote
paris sportif|historique des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors arjel
paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris sportifs|imposition paris
sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur gain paris sportif|je gagne ma
vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris
sportif en ligne|jeu de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de
paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris sportif|jeux
paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux
paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris sportif|jouer paris
sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris
sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur
sanctionne pari sportif|joueur suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la
cote paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète
pour gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote
gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur site
de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au
paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les
10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites de
paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour
gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs
pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris
sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les cotes paris sportifs|les
gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont ils
imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris
sportif|les meilleures applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris
sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site
de paris sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif
avis|les paris sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les
paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus
gros gains paris sportifs|les plus gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote paris
sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|les
sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris
sportif|limite de gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des
sites de paris sportifs|liste pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de
paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris
sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel
de paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll
paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel
gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif gratuit|logiciel
gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator
paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des
paris sportifs en france|marché des paris sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis pluie paris
sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match suspendu
paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match
truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris
sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris
sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris sportif|meilleur application de
paris sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans
depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site
de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris
sportif|meilleur bookmaker paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur conseil
paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote pari sportif|meilleur
cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur
forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris
sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur
offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur
pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur
paris sportif|meilleur paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris
sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris
sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris
sportif en france|meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site
de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur site de paris
sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris
sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site
pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif
france|meilleur site paris sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors
arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif
suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site
pronostic paris sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur technique paris
sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli paris sportif|meilleure appli paris
sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari
sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif
android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre paris sportif|meilleure
site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris
sportif|meilleures applications de paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris
sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs application de paris
sportifs|meilleurs application paris sportif|meilleurs applications
paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs
cotes paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs
site de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site de
paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc paris
sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode paris sportif
foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari
sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins
de 4 5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari
sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes
paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris sportifs|multiples paris
sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul
paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif
forum|méthode paris sportif hockey|nba pari
sportif|nba paris sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de
paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites
paris sportifs|nouvelle appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre appli pari sportif|offre
bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris
sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus
paris sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de
bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre
de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre de bienvenue
sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre
paris sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris
sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo
paris sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris sportifs|offres de
bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire
des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte
paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif
100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif
belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari
sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari
sportif conseil|pari sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du
monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif en ligne|pari sportif
en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne
gratuit|pari sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise
des jeux|pari sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france
italie|pari sportif france portugal|pari sportif france
usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de
l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le
plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue des
champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif
match arrete|pari sportif match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o
jeu|pari sportif nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari
sportif paypal|pari sportif plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif
pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari sportif
pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif psg
bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif
rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby
top 14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte
bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari
sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour
de france|parie sportif|parie sportif comment ca marche|parie
sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif
suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris
match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros offerts|paris sportif 100
euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150
euros offert|paris sportif 1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif
abandon tennis|paris sportif abandon tennis parions sport|paris
sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris
sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal
psg|paris sportif astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd
hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris
sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris
sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris sportif basket|paris sportif
basket coupe de france|paris sportif basket nba|paris sportif
basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique france|paris
sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif
bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus gratuit sans depot|paris sportif
bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris
sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif
buteur|paris sportif buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue
pas|paris sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris
sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment
ça marche|paris sportif combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a
tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif comment
ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris sportif cote|paris
sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe
de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif
coupe du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde
rugby|paris sportif depot 5 euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1
euro|paris sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec paypal|paris sportif
en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne
cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça
marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif
en ligne gratuit|paris sportif en ligne maroc|paris
sportif en ligne paypal|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris
sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris
sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif
et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris
sportif euro|paris sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot
astuce|paris sportif foot aujourd’hui|paris
sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris
sportif foot cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot
prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot
regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif foot us|paris sportif
football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif
france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris sportif
france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif
france italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris
sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris
sportif france usa|paris sportif freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup
sur|paris sportif gagner argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap 0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif
handicap basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif
handicap rugby|paris sportif hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris
sportif legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris sportif
les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif
ligne|paris sportif ligue 1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des
champions|paris sportif ligue des nations|paris sportif
ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif
martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris
sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif
match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris
sportif meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif
meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris
sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris
sportif multiple 2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif multiple 2
4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif multiple 2/3 explication|paris
sportif multiple 3 4|paris sportif multiple explication|paris sportif national 1 foot|paris sportif
nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif numero
match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue
sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris
sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif
paypal|paris sportif plus de 1.5 but|paris sportif plus
de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris
sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic
des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris
sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris
sportif psg inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif
psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif
que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris
sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif
remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby
top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris sportif sans compte
bancaire|paris sportif sans depot|paris sportif
sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur
ne joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse
légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris
sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris
sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3
4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris
sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif tennis abandon|paris sportif
tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif tennis roland garros|paris sportif
tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris
sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif
victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs aide|paris sportifs analyser
un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris
sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs
cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris
sportifs du jour|paris sportifs en belgique|paris sportifs
en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris
sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs
forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits
en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris
sportifs hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris
sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les
bookmakers raflent la mise|paris sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue
1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des
champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris
sportifs nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs psg inter|paris
sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs
stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs
top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les
paris sportifs|peut on gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros
combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif
au monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris
sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif
remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris
sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo site de paris sportif|promo site pari
sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono
paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono
paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic
du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic
pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic
paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif foot|pronostic paris
sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics
foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur
paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris
sportif|psg bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr
code paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap dans les
paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris sportif|quand
un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que
signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les paris sportifs|que signifie
btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que
signifie draw en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie handicap dans
les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire handicap dans
les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli
pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel
est la meilleur appli de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le
meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quel est
le meilleur site de paris sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|quel est
le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le
plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel
paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli
de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour
les paris sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs
faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle
multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris
sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur
de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur
mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat
paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat paris sportif
foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby
pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de
mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise
paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de
paris sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de
gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris
sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site
d’analyse de paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris
sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif
bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de
pari sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de
parie sportif en ligne|site de paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site
de paris sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif
arjel|site de paris sportif autorisé en france|site
de paris sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif
avec bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris
sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de
paris sportif avis|site de paris sportif belge avec bonus|site
de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site de
paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de paris
sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site
de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif
gratuit sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris
sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif
offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif
sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans
carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs
avec paypal|site de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site de
paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de statistique pour paris
sportif|site des paris sportifs|site pari en ligne
sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100 euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari
sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif suisse|site parie sportif|site
paris en ligne sportif|site paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris
sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif
1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site
paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec
meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5 euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site
paris sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif hors arjel|site paris sportif hors
arjel france|site paris sportif meilleur cote|site
paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site
paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris
sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris
sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs
en ligne|site paris sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site
suisse paris sportif|sites de pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs
arjel|sites de paris sportifs autorisés en france|sites
de paris sportifs belgique|sites de paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites
de paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs
arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris
sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors arjel|sites paris sportifs
suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris
sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif foot|statistique tennis paris
sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie
de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de
paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner
au paris sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris sportif|systeme 3
4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme
reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll
paris sportif|tableau cote paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi
paris sportifs|tableau excel bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel
paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sportif|tableau montante paris sportif|tableau
paris sportif|tableau paris sportif excel|tableau roi paris sportifs|tableau statistique paris sportif|tableau suivi paris sportif|taxe gain paris
Узнать больше здесь: https://medim-pro.ru/spravka-ot-nevropatologa-kupit/
slot365 link Sau khi hoàn tất việc điền thông tin, bạn sẽ nhận được một mã xác minh qua email hoặc tin nhắn. Anh em chỉ việc nhập mã này vào ứng dụng để hoàn tất quá trình đăng ký là xong.
?Celebremos a cada maestro en estrategias !
Jugar en casinos sin verificaciГіn permite acceder a una experiencia rГЎpida y privada sin procesos complicados. [url=http://casinoretirosinverificacion.com/#][/url] Muchos jugadores optan por estas opciones debido a la libertad que ofrecen plataformas como casinos sin kyc. Gracias a esta flexibilidad, cada sesiГіn se vuelve mГЎs cГіmoda al usar servicios como casino sin dni.
Jugar en casinos sin kyc permite acceder a una experiencia rГЎpida y privada sin procesos complicados. Muchos jugadores optan por estas opciones debido a la libertad que ofrecen plataformas como Casino Retiro Sin VerificaciГіn. Gracias a esta flexibilidad, cada sesiГіn se vuelve mГЎs cГіmoda al usar servicios como casinos sin verificacion.
Crypto casino no kyc, entretenimiento directo – http://casinoretirosinverificacion.com/
?Que la suerte te beneficie con que experimentes fantasticos victorias !
Free video chat learn more find people from all over the world in seconds. Anonymous, no registration or SMS required. A convenient alternative to Omegle: minimal settings, maximum live communication right in your browser, at home or on the go, without unnecessary ads.
quoten von wetten dass
Look into my blog … vergleich wettquoten (https://Fabriculture.in)
Updates on the Topic: https://couponsdestin.com/prodazha-akkauntov-vk-telegram-odnoklassnikov-9/
Thank you for sharing with us, I conceive this website really stands out : D.
This excellent website really has all of the information I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
directory of female escorts in Brasilia
Стабильный kraken tor браузер позволяет работать с площадкой полностью анонимно благодаря многоуровневой маршрутизации трафика через распределенные узлы сети.
?Brindemos por cada descubridor de fortunas !
Este sitio relacionado con casinos bono por registro sin deposito ofrece opciones interesantes para los usuarios que buscan comodidad.[url=http://feriafranquiciasperu.com/][/url] Muchas personas valoran la rapidez al acceder a servicios vinculados con casinos bono por registro sin deposito sin trГЎmites complicados. La experiencia mejora cuando las plataformas que mencionan casinos bono por registro sin deposito permiten navegar con libertad.
Este sitio relacionado con casinos sin registro espaГ±a ofrece opciones interesantes para los usuarios que buscan comodidad. Muchas personas valoran la rapidez al acceder a servicios vinculados con casinos sin registro espaГ±a sin trГЎmites complicados. La experiencia mejora cuando las plataformas que mencionan casinos sin registro espaГ±a permiten navegar con libertad.
Experiencia mejorada con casinos bono por registro sin deposito – http://www.feriafranquiciasperu.com/
?Que la fortuna te sonria con aguardandote esplendidos beneficios sorprendentes !
Нужна работа в США? курс трак диспетчера в сша для новичков : работа с заявками и рейсами, переговоры на английском, тайм-менеджмент и сервис. Подходит новичкам и тем, кто хочет выйти на рынок труда США и зарабатывать в долларах.
Uwielbiasz hazard? https://online-nv-casino.com: rzetelne oceny kasyn, weryfikacja licencji oraz wybor bonusow i promocji dla nowych i powracajacych graczy. Szczegolowe recenzje, porownanie warunkow i rekomendacje dotyczace odpowiedzialnej gry.
Hot Topics: http://ecornd.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=372
Outstanding feature
online wettseite
Look at my webpage … back lay Wetten deutschland (https://Hookedonshopping.com/playojo-10-euro-freebet-code)
Hello, you used to write fantastic, but the last few posts have been kinda boringK I miss your great writings. Past few posts are just a bit out of track! come on!
?Levantemos nuestras copas por cada buscador de sensaciones fuertes !
Algunos jugadores recurren a casino online fuera de espaГ±a para disfrutar de opciones exclusivas. casino fuera de espaГ±a Ofrecen anonimato, diversidad de proveedores y transacciones ГЎgiles. En consecuencia casino online fuera de espaГ±a se vuelve una opciГіn preferida entre jugadores experimentados.
Cada vez mГЎs usuarios prefieren casino por fuera por su flexibilidad y catГЎlogo internacional. Brindan acceso a promociones variables y a juegos exclusivos del mercado internacional. Por eso casino por fuera mantiene su reputaciГіn como plataforma versГЎtil y moderna.
casino por fuera: Casino por fuera es recomendable para jugar desde EspaГ±a – п»їhttps://bodegaslasangrederonda.es/en/
?Que la fortuna te acompane con la dicha de rondas electrizantes !
?Brindemos por cada explorador de tesoros !
Al explorar casas de apuestas sin dni, muchos jugadores descubren opciones mГЎs flexibles y cГіmodas que las alternativas tradicionales. casas de apuestas sin dni. La simplicidad del registro permite empezar a apostar en cuestiГіn de segundos. Esto convierte a estas plataformas en una elecciГіn popular entre quienes priorizan privacidad.
Es comГєn que quienes buscan anonimato opten por casas de apuestas sin dni debido a la ausencia de verificaciones estrictas. Esto permite disfrutar de apuestas espontГЎneas sin perder tiempo. La flexibilidad del sistema destaca frente a sitios regulados.
Oportunidades nuevas disponibles en clinicadentalcorralyvargas.com cad – clinicadentalcorralyvargas.com
?Que la fortuna te sonria con gozando de asombrosos premios extraordinarios !
?Alcemos nuestros brindis por cada candidato a la victoria !
Cada vez mГЎs usuarios analizan casinos sin licencia espaГ±a por su flexibilidad. [url=п»їhttps://casinosinrestricciones.com/][/url] Estas webs eliminan muchas barreras tradicionales. Esto mejora la experiencia global.
La tendencia actual muestra interГ©s por casino sin licencia espaГ±a por permitir mayor control sobre depГіsitos y retiros. Estas plataformas permiten acceder a funciones exclusivas que no siempre estГЎn disponibles en operadores regulados. Por esta razГіn su popularidad sigue en aumento.
Casinos sin licencia en EspaГ±ola con juegos modernos – http://casinosinrestricciones.com/
?Que la suerte camine a tu lado con obsequios vibrantes del destino jugadas vencedoras !
?Alcemos nuestros brindis por cada emblema de la fortuna !
п»їCada vez mГЎs usuarios analizan casinos sin licencia porque buscan mayor libertad al jugar. [url=п»їhttps://casinosinrestricciones.com/][/url] Estas plataformas permiten acceder a juegos variados sin bloqueos regionales. Esto se traduce en una experiencia mГЎs flexible para el jugador.
La comunidad online recomienda casinosinrestricciones porque eliminan barreras comunes del juego regulado. Estas plataformas permiten acceder a funciones exclusivas que no siempre estГЎn disponibles en operadores regulados. El jugador percibe un entorno mГЎs accesible.
Casino online sin licencia EspaГ±a con slots exclusivas – https://casinosinrestricciones.com/#
?Que la suerte camine a tu lado con exitos brillantes jugadas vencedoras !
10 euros offert paris sportif|10 euros offert sans dépôt paris sportif|10 meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|100 euro offert paris sportif|100 euros offert paris sportif|100 euros
remboursé paris sportifs|100 offert pari sportif|100 offert paris
sportif|100 remboursé paris sportif|100e offert pari sportif|abandon paris sportif tennis|abandon tennis paris sportif|addiction paris sportif
forum|age paris sportif belgique|aide au pari sportif|aide au paris sportif|aide aux paris sportif|aide aux paris sportifs|aide pari sportif|aide pari sportif football|aide parie sportif|aide paris sportif|aide paris sportif foot|aide paris
sportif gratuit|aide paris sportifs|aide pour paris sportif|algorithme de paris sportif|algorithme excel paris
sportif|algorithme gratuit paris sportif|algorithme pari
sportif|algorithme paris sportif|algorithme paris
sportif avis|algorithme paris sportif basket|algorithme paris
sportif excel|algorithme paris sportif gratuit|algorithme paris sportif tennis|algorithme
paris sportifs|algorithme pour paris sportif|analyse
cote paris sportif|analyse de paris sportif|analyse match paris sportif|analyse pari
sportif|analyse paris sportif|analyse paris sportif foot|analyse paris sportif football|analyse
paris sportif gratuit|analyse paris sportifs|ancienne cote paris sportif|api cote paris sportif|app paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportif|appli de
paris sportif sans argent|appli de paris sportifs|appli pari
sportif|appli pari sportif gratuit|appli parie sportif|appli paris sportif|appli
paris sportif avec paypal|appli paris sportif belgique|appli paris sportif entre amis|appli paris sportif gratuit|appli
paris sportif sans argent|appli paris sportif suisse|appli paris sportifs|application aide paris sportif|application algorithme paris sportif|application analyse paris sportif|application android
paris sportif|application bankroll paris sportif|application conseil
paris sportif|application de pari sportif|application de parie
sportif|application de paris sportif|application de paris sportif en afrique|application de paris sportif en cote d’ivoire|application de paris sportif en ligne|application de paris sportif
gratuit|application de paris sportif international|application de paris sportif suisse|application de paris sportifs|application faux paris sportifs|application gestion bankroll paris sportif|application gestion paris sportif|application ia paris sportif|application pari sportif gratuit|application paris sportif|application paris sportif
android|application paris sportif argent fictif|application paris sportif belgique|application paris sportif canada|application paris sportif espagne|application paris sportif espagnol|application paris sportif fictif|application paris sportif
france|application paris sportif gratuit|application paris sportif gratuit
entre amis|application paris sportif maroc|application paris sportif offre de bienvenue|application paris sportif paypal|application paris sportif sans argent|application paris sportif sans justificatif de domicile|application paris sportif suisse|application paris sportif usa|application paris sportif
virtuel|application pour faire des paris sportifs|application pour
gerer ses paris sportif|application pour les paris sportifs|application pour pari
sportif|application pour paris sportif|application pour paris
sportifs|application statistique paris sportif|application suivi paris
sportif|applications de paris sportifs|applications
paris sportifs|applis paris sportif|applis paris sportifs|apprendre a
faire des paris sportifs|argent facile paris sportif|argent offert paris sportifs|argent offert sans depot
paris sportif|argent paris sportif|argent paris sportifs|argent paris sportifs impots|argent sans depot paris sportif|arjel paris sportif|arjel paris sportifs|astuce gagner paris sportif|astuce pari
sportif|astuce paris sportif|astuce paris sportif
basket|astuce paris sportif foot|astuce paris
sportif forum|astuce paris sportif tennis|astuce paris sportifs|astuce pour
gagner au pari sportif|astuce pour gagner au paris sportif|astuce pour gagner paris
sportif|astuce pour paris sportif|astuces paris sportifs|astuces paris sportifs
en ligne|astuces paris sportifs foot|astuces pour gagner aux paris sportifs|autorisation paris sportif france|avis pari sportif|avis paris sportif|avis paris sportif foot|avis site de paris sportif|avis site paris
sportif|avis sur les paris sportifs|avis sur paris sportif|avis
tipster paris sportif|aweh signification paris sportif|bankroll 100 euros
paris sportifs|bankroll management paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif|bankroll paris sportif excel|bankroll paris sportif gratuit|bankroll paris sportifs|basket paris
sportif|belgique france paris sportif|belgique paris sportifs|bonus bienvenue paris sportif|bonus bienvenue paris sportifs|bonus cash paris
sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif|bonus de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|bonus de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|bonus de
depot paris sportif|bonus de paris sportifs|bonus depot paris sportif|bonus en cash paris sportif|bonus gratuit paris sportif|bonus gratuit sans depot paris sportif|bonus pari sportif|bonus
paris sportif|bonus paris sportif belgique|bonus paris sportif betclic|bonus paris sportif cash|bonus paris sportif en ligne|bonus paris sportif france
pari|bonus paris sportif retirable|bonus paris sportif sans depot|bonus paris sportif
sans dépôt|bonus paris sportif unibet|bonus paris
sportifs|bonus sans depot paris sportif|bonus
sans depot paris sportif belgique|bonus sans dépôt paris sportif|bonus
sans dépôt paris sportif hors arjel|bonus site
de paris sportif|bonus site pari sportif|bonus site paris sportif|bonus sites de paris sportifs|bonus unibet paris sportif|bookmaker paris sportif|bookmaker
paris sportif gratuit|bookmaker paris sportifs|bookmaker sportif|bookmakers paris
sportif|bookmakers paris sportifs|bookmakers paris sportifs en ligne|but contre son camp paris sportif|but sur penalty paris sportif|buteur paris sportif|c’est quoi handicap
paris sportif|c’est quoi une cote paris sportif|calcul anti perte paris sportif|calcul
combinaison pari sportif|calcul cote pari sportif|calcul cote paris sportif|calcul couverture
paris sportif|calcul de cote paris sportif|calcul des cotes paris sportifs|calcul dnb paris sportifs|calcul double
chance paris sportif|calcul gain paris sportif|calcul mise paris sportif|calcul pari sportif|calcul
paris sportif|calcul paris sportif multiple|calcul pourcentage
cote paris sportif|calcul probabilité paris sportif|calcul rentabilité paris sportifs|calcul roi paris sportif|calcul systeme paris sportif|calcul trj paris sportifs|calculateur cote paris sportif|calculateur de cote paris sportif|calculateur de mise
paris sportif|calculateur de paris sportif|calculateur paris sportif|calculatrice arbitrage paris sportif|calculatrice paris sportif|calculer cote paris sportif|calculer gain paris sportif|calculer probabilité paris sportifs|calculer roi
paris sportifs|calculer une cote pari sportif|calculer une cote paris sportif|carte cadeau paris sportif|carte pcs paris sportif|carte prépayée paris sportifs|cash out pari sportif|cash out paris
sportif|cash out paris sportifs|casino en ligne paris sportif|casino
paris sportif en ligne|champions league paris sportif|chute de cote paris sportif|classement
des meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|classement meilleur site de paris sportif|code barre paris sportif|code bonus paris sportif|code paris sportif|code promo
pari sportif|code promo paris sportif|code promo paris sportif sans depot|code promo paris sportif sans dépôt|code promo sans depot paris sportif|code promo site paris sportif|combien de temps pour encaisser un paris sportif|combien de temps pour retirer un paris sportif|combien miser paris sportifs|combine
paris sportif|combines paris sportifs|combiné pari sportif|combiné paris sportif|combiné paris
sportif conseil|combiné paris sportif du jour|combiné paris sportif pronostic|comment analyser un paris sportif|comment arreter de jouer aux paris sportifs|comment arreter les paris sportif|comment arreter les paris sportifs|comment arrêter
les paris sportifs|comment bien gagner au paris sportif|comment bien jouer au paris sportif|comment bien miser paris sportif|comment ca marche les paris
sportif|comment calculer cote paris sportif|comment calculer gain paris sportif|comment calculer les cotes des paris sportifs|comment calculer une cote de paris sportif|comment calculer une cote pari sportif|comment calculer une cote paris sportif|comment comprendre
les paris sportifs|comment creer un vip paris sportif|comment créer un algorithme paris sportif|comment créer un site
de paris sportif|comment devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|comment etre rentable
paris sportif|comment etre sur de gagner au paris sportif|comment faire
de bon paris sportif|comment faire des parie sportif|comment faire
des paris sportif|comment faire des paris sportif gagnant|comment faire des paris
sportifs|comment faire pari sportif|comment faire paris
sportif|comment faire pour arreter les paris sportifs|comment faire
pour gagner au paris sportif|comment faire pour gagner les paris sportifs|comment faire un bon pari sportif|comment faire un bon paris sportif|comment faire un pari
sportif|comment faire un parie sportif|comment faire
un paris sportif|comment faire une montante paris
sportif|comment fonctionne les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les cotes des paris sportifs|comment fonctionne les paris sportifs|comment fonctionne paris sportifs|comment fonctionne un pari sportif|comment
fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs|comment
fonctionnent les cotes dans les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les cotes
de paris sportif|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs grand oral maths|comment fonctionnent les paris sportifs maths|comment gagner a coup sur au paris
sportif|comment gagner a tous les coups au paris sportif|comment
gagner a tout les coup au paris sportif|comment gagner au pari
sportif|comment gagner au pari sportif football|comment gagner au paris sportif|comment gagner au
paris sportif a coup sur|comment gagner au paris sportif
foot|comment gagner au paris sportif forum|comment gagner au paris sportif tennis|comment gagner au paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportif|comment gagner aux paris sportifs|comment gagner aux paris sportifs foot|comment gagner aux paris sportifs
livre|comment gagner aux paris sportifs sur
le long terme|comment gagner avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner dans les paris
sportifs|comment gagner de l argent avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de
l’argent au paris sportif|comment gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent
avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent paris
sportif|comment gagner de l’argent sur les paris sportifs|comment gagner de l’argent sur paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportif|comment gagner des paris sportifs|comment gagner en paris
sportif|comment gagner facilement au paris sportif|comment
gagner les paris sportifs|comment gagner paris sportif|comment gagner paris sportif
foot|comment gagner paris sportifs|comment gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|comment gagner ses paris sportif|comment
gagner sur les paris sportif|comment gagner sur
les paris sportifs|comment gagner tout le temps au paris sportif|comment gagner un pari sportif|comment gagner un paris
sportif|comment gerer une bankroll paris sportif|comment
gérer sa bankroll paris sportif|comment jouer au pari sportif|comment
jouer au paris sportif|comment jouer au paris sportif
foot|comment jouer aux paris sportifs|comment jouer paris sportif|comment marche
cote paris sportif|comment marche les cotes paris sportif|comment marche les paris sportif|comment marche
les paris sportifs|comment marche paris sportif|comment marche un pari sportif|comment marche un paris sportif|comment marchent
les cotes paris sportif|comment marchent les paris sportifs|comment miser au paris sportif|comment miser paris sportif|comment monter sa bankroll
paris sportif|comment ne jamais perdre au paris sportif|comment parier sportif|comment reussir au paris sportif|comment reussir les paris sportif|comment reussir paris sportif|comment sont calculer les cotes de paris sportif|comment sont calculées les cotes des paris sportifs|comment
sont calculés les cotes des paris sportifs|comment sont faites les cotes des paris
sportifs|comment toujours gagner au paris sportif|comment ça
marche les paris sportifs|comparaison bonus paris sportifs|comparaison cote pari sportif|comparaison des cotes paris sportifs|comparateur cote pari sportif|comparateur cote paris sportif|comparateur cotes paris sportif|comparateur cotes
paris sportifs|comparateur de cote pari sportif|comparateur
de cote paris sportif|comparateur de cotes paris
sportifs|comparateur de côtes paris sportifs|comparateur de paris sportif|comparateur de site
de paris sportif|comparateur de site paris sportif|comparateur de sites de paris sportifs|comparateur pari sportif|comparateur paris sportif|comparateur
paris sportifs|comparateur site de paris sportif|comparateur site pari sportif|comparateur
site paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportif|comparatif bonus paris sportifs|comparatif cote
pari sportif|comparatif cote paris sportif|comparatif cotes
paris sportifs|comparatif des sites de paris sportifs|comparatif
offre de bienvenue paris sportif|comparatif offre paris sportif|comparatif pari sportif|comparatif pari sportif en ligne|comparatif paris sportif|comparatif paris sportif bonus|comparatif paris sportif
en ligne|comparatif paris sportifs|comparatif paris sportifs en ligne|comparatif site de paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportif|comparatif site paris sportifs|comparatif sites de paris sportifs|comparatif sites paris sportifs|comparer les
cotes paris sportifs|comprendre cote paris sportif|comprendre handicap paris sportif|comprendre les cotes des paris sportifs|comprendre les cotes paris sportif|comprendre
les cotes paris sportifs|comprendre les handicap paris sportif|compte de paris sportif|compte démo paris sportif|compte finance paris sportif|compte financer paris sportif|compte financier paris sportif|compte financé paris sportif|compte pari sportif|compte paris
sportif|compte paris sportif financé|conseil de paris sportif|conseil de paris sportifs|conseil en paris sportif|conseil en paris sportifs|conseil pari sportif|conseil pari
sportif gratuit|conseil paris sportif|conseil paris sportif aujourd’hui|conseil paris sportif du jour|conseil paris sportif foot|conseil paris sportif
gratuit|conseil paris sportif ligue des champions|conseil paris sportif nba|conseil paris sportif pronostic|conseil paris
sportif rmc|conseil paris sportif tennis|conseil paris sportifs|conseil pour gagner au paris sportif|conseil pour paris sportif|conseil sur les paris sportifs|conseille paris sportif|conseiller
en paris sportifs|conseiller paris sportif|conseils de paris sportifs|conseils en paris sportifs|conseils
paris sportifs|conseils paris sportifs foot|conseils paris
sportifs gratuit|conseils paris sportifs tennis|conseils pour paris sportifs|cote a 100 paris sportif|cote a
2 paris sportif|cote anglaise paris sportif|cote de 2 paris
sportif|cote de pari sportif|cote de paris sportif|cote des
paris sportifs|cote maximum paris sportif|cote minimum paris sportif|cote pari
sportif|cote pari sportif comment ça marche|cote pari sportif
real madrid|cote pari sportif rugby|cote parie sportif|cote paris sportif|cote paris sportif belgique|cote paris sportif
calcul|cote paris sportif definition|cote paris sportif euro|cote paris sportif explication|cote
paris sportif foot|cote paris sportif france belgique|cote paris sportif france espagne|cote paris
sportif ligue des champions|cote paris sportif moto gp|cote
paris sportif psg|cote paris sportif psg arsenal|cote paris sportif rugby|cote paris sportif tennis|cote paris
sportifs|cote pour paris sportifs|cote sportif foot|cote sportif rugby|cote à 1000 paris sportif|cotes de paris sportifs|cotes pari sportif|cotes paris sportif|cotes paris sportifs|cotes paris sportifs foot|coupe de france paris sportif|créer un algorithme paris sportif|créer
un compte paris sportif|créer un site de paris sportif en ligne|dans les
paris sportifs que signifie handicap|declarer ses gains paris sportif|definition cash out paris sportif|definition cote paris sportif|definition handicap
paris sportif|depot 5 euros paris sportif|depot double
paris sportif|depot minimum 5 euro paris sportif|depot
minimum paris sportif|depot paris sportif|depuis quand
existe les paris sportif en france|devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|devenir riche avec paris
sportifs|disqualification tennis paris sportif|dnb
en paris sportif|dnb pari sportif|dnb paris sportif|dnb
paris sportif definition|dnb paris sportifs|doit on declarer les gains de paris sportif|déclarer gains paris sportifs|déclarer gains paris sportifs hors
arjel|définition bankroll paris sportif|dépôt minimum 1 euro paris sportif|dépôt minimum 5 euro paris
sportif|ecart de jeux tennis paris sportif|erreur de cote paris sportif|est ce que les gains
des paris sportifs sont imposables|est-ce
que les prolongation compte dans un pari sportif|etre
sur de gagner au paris sportif|euro paris sportif|evenement sportif
a paris|evenement sportif paris|evenement sportif paris 2025|evenement sportif paris aujourd hui|evenement sportif paris aujourd’hui|evenement sportif paris ce
week end|evenements sportif paris|evenements sportifs paris|evenements sportifs paris 2025|evenements sportifs à paris|evolution cote paris sportif|evolution cotes paris sportifs|evolution des cotes paris sportifs|explication cote pari sportif|explication cote paris sportif|explication handicap paris
sportif|explication pari sportif|explication paris sportif|face a face hockey paris sportif|faire des paris
sportif|faire des paris sportif avec paypal|faire des paris sportifs|faire fortune
paris sportifs|faire un pari sportif|faire un paris sportif|faut
il déclarer les gains de paris sportifs|faut il déclarer ses gains
paris sportifs|fichier excel gestion bankroll paris sportif|fiscalité
gains paris sportifs|foot paris sportif|football et paris
sportifs|forfait tennis paris sportif|formation paris
sportif gratuit|forum de paris sportif|forum de paris sportifs|forum pari sportif|forum parie
sportif|forum paris sportif|forum paris sportif foot|forum paris sportif gratuit|forum
paris sportif nba|forum paris sportif tennis|forum paris sportifs|forum sur
les paris sportifs|forum tennis paris sportif|francaise des jeux pari sportif|francaise des jeux paris sportif|francaise
des jeux paris sportifs|france 2 paris sportif|france 2 paris
sportifs|france belgique paris sportif|france espagne paris
sportif|france pari sportif|france pari sportif brest|france paris sportif|france paris
sportifs|france pologne paris sportif|france portugal paris sportif|france suisse paris sportifs|france tunisie paris sportifs|france-pari – paris sportifs|gagnant pari sportif|gagnant paris sportif|gagnant paris sportif bayern|gagnante paris sportif|gagne au
paris sportif|gagner 10 euros par jour aux paris sportifs|gagner
100 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner 1000 euros par mois paris sportifs|gagner 10000
euros paris sportif|gagner 2000 euros par mois paris sportif|gagner 50 euros par jour paris sportif|gagner a coup sur au paris sportif|gagner a coup sur pari sportif|gagner a tous les
coup paris sportif|gagner argent avec paris sportifs|gagner argent
pari sportif|gagner argent paris sportif|gagner argent paris sportifs|gagner au pari sportif|gagner au paris sportif|gagner au paris
sportif a coup sur|gagner au paris sportif foot|gagner au paris sportif forum|gagner au paris sportif à coup sur|gagner
aux paris sportif|gagner aux paris sportifs|gagner
aux paris sportifs pdf|gagner beaucoup d’argent paris sportif|gagner de l argent grace aux paris sportifs|gagner
de l argent pari sportif|gagner de l argent paris
sportif|gagner de l argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent au paris
sportif|gagner de l’argent aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent avec paris sportif|gagner
de l’argent avec paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent grace au paris sportif|gagner de l’argent grace
aux paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent pari sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportif|gagner de l’argent paris sportifs|gagner de l’argent sur les paris
sportifs|gagner des paris sportif|gagner des paris sportifs|gagner
les paris sportifs|gagner pari sportif|gagner paris sportif|gagner paris sportif foot|gagner paris sportif forum|gagner paris sportif
tennis|gagner paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|gagner sa vie avec les paris sportifs|gagner sa vie avec paris sportifs|gagner ses paris sportifs|gagner à coup sur paris sportif|gagner à tous les coups paris sportifs|gain maximum paris sportif|gain pari sportif|gain pari sportif imposable|gain pari sportif impot|gain paris sportif|gain paris sportif imposable|gain paris sportif
impot|gain paris sportif impôt|gains paris sportif|gains
paris sportif imposable|gains paris sportifs|gains paris sportifs imposable|gains paris sportifs
imposables|gains paris sportifs sont ils imposables|gerer bankroll
paris sportif|gerer sa bankroll paris sportif|gerer une bankroll paris sportif|gestion bankroll
paris sportif|gestion bankroll paris sportifs|gestion bankroll paris sportifs excel|gestion de bankroll paris sportif|gestion de bankroll paris sportif application|gestion de bankroll paris
sportifs|gestion de mise paris sportif|gestion paris sportifs v2 5 gratuit|gg signification paris sportif|gros combiné paris sportif|gros gain paris sportif|grosse cote paris sportif pronostic|grosse mise paris
sportif|groupe paris sportif gratuit|groupe telegram paris
sportif gratuit|groupement de joueurs paris sportifs|handicap 0 paris sportif|handicap 1 paris sportif|handicap 5 paris sportif|handicap au paris
sportif|handicap basket paris sportif|handicap dans les paris sportifs|handicap en paris sportif|handicap europeen paris sportif|handicap européen paris sportifs|handicap mi temps paris sportif|handicap pari
sportif|handicap paris sportif|handicap paris sportif basket|handicap paris sportif explication|handicap paris sportif foot|handicap paris sportif rugby|handicap paris sportifs|handicap rugby paris sportif|handicap tennis paris sportif|historique cote paris sportif|historique
des cotes paris sportifs|hockey paris sportif|hockey sur glace paris sportif|hors
arjel paris sportif|hweh signification paris sportif|imposition gain pari sportif|imposition gain paris sportif|imposition gains paris
sportifs|imposition paris sportif france|impot gain paris sportif|impot paris sportif france|impot sur
gain paris sportif|je gagne ma vie avec les paris sportifs|jeu de pari sportif gratuit|jeu de paris sportif en ligne|jeu
de paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif gratuit|jeu paris sportif sans argent|jeux de parie sportif|jeux de paris sportif|jeux
de paris sportif en ligne|jeux de paris sportif gratuit|jeux de paris sportifs|jeux olympiques paris sportifs|jeux paris
sportif|jeux paris sportif gratuit|jeux paris sportif virtuel|jeux paris sportifs en ligne|jouer au paris
sportif|jouer paris sportif|joueur absent paris sportif|joueur blesse paris sportif|joueur caen paris sportif|joueur de
caen pari sportif|joueur de foot paris sportif|joueur decisif paris sportif|joueur décisif paris sportif|joueur italien paris sportif|joueur paris sportif|joueur professionnel paris sportif|joueur qui se blesse paris sportif|joueur sanctionne pari sportif|joueur
suspendu paris sportif|joueurs italiens paris sportifs|l’argent des paris sportifs est il imposable|la cote
paris sportif|la francaise des jeux paris sportif|la martingale paris sportif|la
martingale paris sportifs|la meilleur application de paris sportif|la meilleur application paris sportif|la meilleur
technique pour gagner au paris sportif|la méthode secrète pour
gagner aux paris sportifs pdf|la plus grosse cote gagner paris sportif|la plus grosse cote paris
sportif|ldem paris sportif signification|le marché des paris sportifs|le meilleur
site de pari sportif|le meilleur site de paris sportif|le meilleur site
de paris sportif en ligne|le meilleur site de paris sportifs|le plus gros gain au
paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif|le plus gros paris sportif du monde|les 10
meilleurs sites de paris sportifs|les 10 meilleurs sites
de paris sportifs en afrique|les 17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs|les
17 secrets pour gagner rapidement aux paris sportifs pdf|les application de paris sportif|les applications paris sportifs|les bonus paris sportifs|les bookmakers paris sportifs|les
cotes paris sportifs|les gains de paris sportifs sont ils imposables|les gains des paris sportifs sont
ils imposables|les jeux de paris sportifs|les meilleur paris sportif|les meilleures applications de paris
sportifs|les meilleurs applications de paris sportifs|les
meilleurs bonus paris sportif|les meilleurs bonus paris
sportifs|les meilleurs cotes paris sportif|les meilleurs paris sportifs|les meilleurs paris sportifs du jour|les meilleurs site de paris
sportif|les meilleurs site de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de pari sportif|les meilleurs
sites de paris sportifs|les meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportif|les paris sportif avis|les paris
sportifs|les paris sportifs comment ça marche|les paris sportifs en france|les paris sportifs en ligne|les paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner|les
paris sportifs en ligne comprendre jouer gagner pdf|les paris sportifs les plus rentables|les plus gros gagnant paris sportif|les plus
gros gains au paris sportifs|les plus gros gains paris sportifs|les plus
gros paris sportif|les plus grosse cote
paris sportif|les plus grosses pertes paris sportifs|les
sites de paris sportifs|les sites de paris sportifs
autorisés en france|les sites de paris sportifs en france|les sites de paris sportifs en ligne|les sites de paris sportifs francais|ligue 1 paris sportif|ligue 1 paris
sportifs|ligue 2 paris sportif|ligue des champions paris sportif|limite de
gains paris sportifs|limite de mise paris sportif|limite gain paris sportif|limite mise paris sportifs|liste de paris
sportif|liste des paris sportifs|liste des site de paris sportif|liste des sites de paris sportifs|liste
pari sportif|liste paris sportif|liste paris sportif pdf|liste site de paris sportif|liste site pari sportif|liste site paris sportif|liste site paris sportif arjel|liste sites
paris sportifs|logiciel algorithme paris sportif|logiciel algorithme paris sportif gratuit|logiciel analyse paris sportif|logiciel calcul paris sportif|logiciel de pari sportif|logiciel de paris sportif|logiciel de
paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion bankroll paris sportif gratuit|logiciel gestion de bankroll paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif|logiciel gestion paris sportif
gratuit|logiciel gestion paris sportifs|logiciel pari sportif|logiciel paris
sportif|logiciel paris sportif gratuit|logiciel paris sportifs|logiciel paris sportifs foot sur 2 matchs|logiciel
pour paris sportif|logiciel pour paris sportifs|logiciel prediction paris
sportif|logiciel probabilité paris sportif|logiciel prédiction paris sportif|logiciel statistique paris sportifs|logiciel
variation de cote paris sportif|loi sur les paris sportifs en france|magic calculator paris sportif|marché des paris sportifs|marché des paris sportifs en france|marché des paris
sportifs en ligne|martingale pari sportif|martingale paris sportif|martingale paris sportif excel|martingale paris sportif forum|martingale paris
sportif interdit|martingale paris sportifs|match abandonné paris sportif|match
annulé ou reporté paris sportifs|match annulé paris sportif|match arrete paris sportif|match interrompu paris sportif|match interrompu tennis paris sportif|match interrompu tennis
pluie paris sportif|match nul boxe paris sportif|match pari sportif|match paris sportif|match reporté paris sportif|match
suspendu paris sportif|match suspendu tennis paris sportif|match truqué paris sportif|matchs truqués paris sportifs|meilleur algorithme paris sportif|meilleur algorithme paris sportif gratuit|meilleur app de paris sportif|meilleur app de paris sportifs|meilleur app paris sportif|meilleur appli de pari sportif|meilleur appli
de paris sportif|meilleur appli pari sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif|meilleur appli paris sportif forum|meilleur
appli paris sportifs|meilleur application conseil paris
sportif|meilleur application de paris sportif|meilleur application de paris
sportif en afrique|meilleur application pari sportif|meilleur application paris sportif|meilleur application paris sportif belgique|meilleur application pour les paris sportif|meilleur application pour pari sportif|meilleur bonus de bienvenue paris
sportif|meilleur bonus pari sportif|meilleur bonus paris
sportif|meilleur bonus paris sportif sans depot|meilleur bonus paris sportifs|meilleur bonus site de paris sportif|meilleur bonus site pari sportif|meilleur bonus site paris sportif|meilleur bookmaker
paris sportif|meilleur combiné paris sportif|meilleur
conseil paris sportif|meilleur cote de paris sportif|meilleur cote
pari sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif|meilleur cote paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur cote site paris sportif|meilleur
forum paris sportifs|meilleur gain paris sportif|meilleur ia paris sportif|meilleur methode pour gagner au paris
sportif|meilleur offre bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre bonus paris sportif|meilleur offre
de bienvenue paris sportif|meilleur offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|meilleur offre pari
sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif|meilleur offre paris sportif en ligne|meilleur pari sportif|meilleur pari sportif du jour|meilleur pari sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif|meilleur
paris sportif aujourd’hui|meilleur paris sportif du jour|meilleur paris sportif en ligne|meilleur paris sportif foot|meilleur promo paris sportif|meilleur pronostic
paris sportif|meilleur site de conseil paris sportif|meilleur site de pari
sportif|meilleur site de pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris
sportif|meilleur site de paris sportif avis|meilleur site de
paris sportif belgique|meilleur site de
paris sportif canada|meilleur site de paris sportif en france|meilleur site de
paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site de paris sportif football|meilleur site de paris sportif
forum|meilleur site de paris sportif france|meilleur
site de paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site de paris sportif
international|meilleur site de paris sportif suisse|meilleur site de paris sportifs|meilleur site de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif|meilleur site pari sportif en ligne|meilleur site pari sportif france|meilleur site paris
sportif|meilleur site paris sportif avis|meilleur site paris sportif
belgique|meilleur site paris sportif canada|meilleur site paris sportif en ligne|meilleur site paris sportif foot|meilleur site paris sportif forum|meilleur site paris
sportif france|meilleur site paris sportif hors arjel|meilleur site paris sportif nba|meilleur site paris sportif rugby|meilleur site paris sportif suisse|meilleur site paris sportifs|meilleur site pour pari
sportif|meilleur site pour paris sportif|meilleur site pronostic paris
sportif|meilleur strategie paris sportif|meilleur technique de paris sportif|meilleur
technique paris sportif|meilleur technique pour gagner
au paris sportif|meilleure appli de paris sportif|meilleure appli de
paris sportifs|meilleure appli pari sportif|meilleure appli
paris sportif|meilleure appli paris sportifs|meilleure application de paris sportif|meilleure application de paris sportifs|meilleure application pari sportif|meilleure application paris sportif|meilleure application paris sportif android|meilleure application paris sportifs|meilleure offre
paris sportif|meilleure site paris sportif|meilleure strategie paris sportif|meilleures applications de
paris sportifs|meilleures applications paris sportifs|meilleures cotes paris
sportifs|meilleures offres paris sportifs|meilleures stratégies paris sportifs|meilleurs appli paris sportif|meilleurs
application de paris sportifs|meilleurs application paris
sportif|meilleurs applications paris sportifs|meilleurs bonus paris sportifs|meilleurs cote paris sportif|meilleurs cotes
paris sportifs|meilleurs offres paris sportifs|meilleurs paris sportifs|meilleurs
paris sportifs du jour|meilleurs site de pari sportif|meilleurs site
de paris sportif|meilleurs site de paris sportif en ligne|meilleurs site
de paris sportifs|meilleurs site paris sportif|meilleurs sites de paris
sportifs|meilleurs sites de paris sportifs en ligne|meilleurs sites paris sportif|meilleurs sites paris sportifs|methode abc
paris sportif|methode de paris sportif|methode gagnante
paris sportifs|methode gagner paris sportif|methode infaillible
paris sportifs|methode martingale paris sportif|methode mathematique paris sportif|methode mathematique
pour gagner au paris sportif|methode paris sportif|methode
paris sportif foot|methode paris sportif forum|methode paris
sportif tennis|methode paris sportifs|methode pour gagner au paris sportif|methode
pour gagner paris sportif|methodes paris sportifs|minimum depot paris sportif|mise
au jeu pari sportif|mise maximum pari sportif|mise maximum paris sportif|mise minimum paris sportif|mise moyenne paris sportif|mise paris sportif|moins de 4
5 but paris sportif|montant maximum paris sportif|montant paris sportif|montante pari sportif|montante parie sportif|montante paris
sportif|montante paris sportifs|montantes paris sportifs|multiple pari sportif|multiple paris sportif|multiple paris
sportifs|multiples paris sportifs|méthode calcul paris sportif|méthode match nul paris sportifs|méthode mathématique pour gagner au paris sportif|méthode paris sportif forum|méthode
paris sportif hockey|nba pari sportif|nba paris
sportif|nba paris sportifs|nouveau paris sportif|nouveau site de pari sportif|nouveau site de paris sportif|nouveau site
de paris sportif en ligne|nouveau site de paris sportifs|nouveau site pari sportif|nouveau site paris sportif|nouveau
site paris sportif france|nouveau site paris sportifs|nouveaux sites de paris sportifs|nouveaux sites paris sportifs|nouvelle
appli paris sportif|nouvelle application de paris sportif|numero de match paris sportif|numero match paris sportif|offre 100 euros paris sportif|offre
appli pari sportif|offre bienvenu paris sportif|offre bienvenue pari sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportif|offre bienvenue paris sportifs|offre bienvenue site paris sportif|offre bonus paris
sportif|offre de bienvenu paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
pari sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif|offre de bienvenue paris sportif belgique|offre de
bienvenue paris sportif sans depot|offre de bienvenue paris sportif sans dépôt|offre de bienvenue paris sportifs|offre
de bienvenue sans depot paris sportif|offre de bienvenue
site paris sportif|offre euro paris sportif|offre pari sportif euro|offre paris sportif|offre paris sportif belgique|offre paris sportif cash|offre paris
sportif coupe du monde|offre paris sportif hors arjel|offre paris sportif remboursé|offre paris sportif remboursé cash|offre paris sportif sans depot|offre promo paris
sportif|offre remboursement paris sportif|offre sans depot paris sportif|offre site paris sportif|offres bienvenue paris
sportifs|offres de bienvenue paris sportifs|ou faire des paris sportif|ou faire des paris sportif en espagne|ou faire des paris
sportifs|outil répartiteur de mise paris sportif|outils repartiteur de
mises paris sportif|ouverture compte paris sportifs|ouvrir un compte
paris sportif|pack de bienvenue paris sportif|pack de
bienvenue paris sportif hors arjel|pari en ligne sportif|pari
sportif|pari sportif 100 euros offert|pari sportif 100 remboursé|pari sportif abandon tennis|pari
sportif aide|pari sportif algérie aujourd’hui|pari
sportif appli|pari sportif application|pari sportif argent|pari sportif astuce|pari sportif aujourd|pari sportif aujourd’hui|pari sportif avec handicap|pari
sportif avec orange money|pari sportif avec paypal|pari sportif avec
wave|pari sportif avis|pari sportif basket|pari sportif belgique|pari sportif
belgique france|pari sportif bonus|pari sportif buteur pas titulaire|pari
sportif champions league|pari sportif combiné|pari sportif comment|pari sportif
comment gagner|pari sportif comment ça marche|pari sportif comparatif|pari sportif conseil|pari
sportif cote|pari sportif cote match|pari sportif cote psg|pari sportif coupe|pari sportif coupe de france|pari sportif coupe du monde|pari sportif depot|pari sportif du jour|pari sportif en france|pari sportif
en ligne|pari sportif en ligne au cameroun|pari sportif en ligne belgique|pari sportif en ligne canada|pari sportif en ligne france|pari sportif en ligne gratuit|pari
sportif en ligne suisse|pari sportif en ligne ufc|pari sportif en suisse|pari sportif euro|pari sportif explication|pari sportif faire|pari sportif foot|pari sportif
foot resultat|pari sportif football|pari sportif forum|pari sportif francaise des jeux|pari
sportif france|pari sportif france angleterre|pari sportif france
argentine|pari sportif france autriche|pari sportif france belgique|pari sportif france espagne|pari sportif france italie|pari sportif france
portugal|pari sportif france usa|pari sportif gagnant|pari sportif gagner|pari sportif gagner a tous les coups|pari sportif gagner de l’argent|pari sportif gain|pari sportif gratuit|pari sportif gratuit pour gagner des
cadeaux|pari sportif gratuit sans depot|pari sportif handicap|pari
sportif hockey|pari sportif hors arjel|pari sportif jeux olympiques|pari
sportif joueur absent|pari sportif le plus rentable|pari sportif leicester champion|pari sportif ligue 1|pari sportif ligue 2|pari sportif ligue
des champions|pari sportif ligue europa|pari sportif match|pari sportif match arrete|pari sportif
match interrompu|pari sportif meilleur|pari sportif meilleur cote|pari sportif meilleur site|pari sportif methode|pari sportif
mise|pari sportif mise au jeu|pari sportif mise o jeu|pari sportif
nba|pari sportif offre bienvenue|pari sportif paypal|pari sportif
plus|pari sportif prolongation|pari sportif promo|pari sportif pronostic|pari sportif pronostic foot|pari
sportif pronostic gagnant|pari sportif pronostic gratuit|pari sportif psg|pari sportif
psg bayern|pari sportif psg inter|pari sportif psg
milan|pari sportif regle|pari sportif rembourse|pari sportif remboursement|pari sportif remboursement cash|pari sportif remboursé|pari sportif rugby|pari sportif rugby coupe du monde|pari sportif rugby top
14|pari sportif sans argent|pari sportif sans carte bancaire|pari sportif sans depot|pari sportif signification|pari sportif site|pari sportif statistique|pari sportif suisse|pari sportif systeme|pari
sportif technique|pari sportif technique pour gagner|pari sportif
temps reglementaire|pari sportif tennis|pari sportif tennis abandon|pari sportif
top|pari sportif top 14|pari sportif tour de france|parie sportif|parie
sportif comment ca marche|parie sportif du jour|parie sportif en ligne|parie sportif foot|parie sportif football|parie sportif france|parie sportif gratuit|parie sportif pronostic|parie sportif suisse|paris en ligne sportif|paris en ligne sportifs|paris evenement sportif|paris france sportif|paris hippique et sportif|paris hippiques et sportifs|paris hippiques paris sportifs|paris hippiques paris
sportifs et poker en ligne|paris hippiques sportifs|paris match sportif|paris sportif|paris sportif 10 euros
offerts|paris sportif 100 euros offert|paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|paris sportif 100 offert|paris sportif 100 remboursé|paris sportif 100e offert|paris sportif 150 euros offert|paris sportif
1er pari remboursé|paris sportif a faire|paris sportif a faire aujourd’hui|paris sportif a faire ce soir|paris sportif abandon tennis|paris sportif
abandon tennis parions sport|paris sportif aide|paris sportif algorithme|paris
sportif analyse|paris sportif appli|paris sportif application|paris sportif application android|paris sportif apres
prolongation|paris sportif argent|paris sportif argent fictif|paris sportif argent offert|paris sportif argent
virtuel|paris sportif arjel|paris sportif arsenal psg|paris sportif
astuce|paris sportif au canada|paris sportif aujourd hui|paris sportif aujourd’hui|paris sportif avec
argent fictif|paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|paris sportif avec carte bancaire|paris sportif
avec cryptomonnaie|paris sportif avec handicap|paris sportif avec paypal|paris sportif avec paysafecard|paris sportif avis|paris sportif avis expert|paris sportif avis forum|paris sportif bankroll|paris
sportif basket|paris sportif basket coupe de france|paris sportif
basket nba|paris sportif basket prolongation|paris sportif belgique|paris sportif belgique bonus|paris sportif
belgique bonus sans depot|paris sportif belgique
france|paris sportif belgique suede|paris sportif bonus|paris sportif bonus bienvenue|paris sportif bonus cash|paris sportif bonus de bienvenue|paris sportif bonus gratuit|paris sportif bonus
gratuit sans depot|paris sportif bonus retirable|paris sportif bonus sans depot|paris sportif bonus sans
depot belgique|paris sportif bookmaker|paris sportif but contre son camp|paris sportif but temps additionnel|paris sportif buteur|paris sportif
buteur blessé|paris sportif buteur carton rouge|paris sportif buteur contre son camp|paris sportif buteur non titulaire|paris sportif buteur
prolongation|paris sportif buteur qui ne joue pas|paris
sportif buteur remplacant|paris sportif calcul gain|paris sportif canada|paris
sportif cash|paris sportif cash out|paris
sportif champion ligue 1|paris sportif champions league|paris sportif classement ligue 1|paris sportif code promo|paris sportif combine|paris
sportif combiné|paris sportif combiné comment ça marche|paris sportif
combiné du jour|paris sportif combiné match reporté|paris sportif comment
ca marche|paris sportif comment faire|paris sportif comment gagner|paris sportif comment gagner a tous les coups|paris sportif comment jouer|paris sportif
comment ça marche|paris sportif comparateur cote|paris sportif
comparatif|paris sportif conseil|paris sportif conseil gratuit|paris sportif conseil pour gagner|paris
sportif cote|paris sportif cote et match|paris sportif cote explication|paris sportif cote psg|paris
sportif coupe d’europe|paris sportif coupe davis|paris sportif coupe
de france|paris sportif coupe du monde|paris sportif coupe
du monde de rugby|paris sportif coupe du monde rugby|paris sportif depot 5
euro|paris sportif depot minimum|paris sportif depot paypal|paris sportif
dnb|paris sportif du jour|paris sportif du jour conseil|paris sportif dépôt 1 euro|paris
sportif dépôt minimum 5 euros|paris sportif en belgique|paris
sportif en france|paris sportif en ligne|paris sportif en ligne avec
paypal|paris sportif en ligne avis|paris sportif en ligne belgique|paris sportif en ligne bonus|paris sportif en ligne cameroun|paris sportif en ligne comment gagner|paris sportif en ligne comment ça marche|paris sportif en ligne france|paris sportif en ligne gratuit|paris sportif
en ligne maroc|paris sportif en ligne paypal (Asa)|paris sportif en ligne québec|paris sportif en ligne sans
depot|paris sportif en ligne suisse|paris sportif en suisse|paris sportif espagne france|paris sportif esport|paris sportif et casino en ligne|paris sportif
et hippique|paris sportif et prolongation|paris sportif euro|paris
sportif europa league|paris sportif explication|paris sportif
final ligue des champions|paris sportif finale
ligue des champions|paris sportif foot|paris sportif foot aide|paris sportif foot astuce|paris sportif foot
aujourd’hui|paris sportif foot ce soir|paris sportif foot comment ca marche|paris sportif foot conseil|paris sportif foot
cote|paris sportif foot coupe du monde|paris sportif foot en ligne|paris sportif foot feminin|paris sportif foot gratuit|paris sportif foot prolongation|paris sportif foot pronostic|paris sportif
foot pronostic gratuit|paris sportif foot regle|paris sportif foot suisse|paris sportif
foot us|paris sportif football|paris sportif football americain|paris sportif football astuces|paris
sportif forfait tennis|paris sportif forum|paris
sportif francais|paris sportif francaise des jeux|paris sportif
france|paris sportif france 2|paris sportif france allemagne|paris sportif france angleterre|paris sportif france argentine|paris
sportif france autriche|paris sportif france belgique|paris sportif france
espagne|paris sportif france gibraltar|paris sportif france
italie|paris sportif france nouvelle zelande|paris sportif france pologne|paris sportif france portugal|paris sportif france uruguay|paris sportif france usa|paris sportif
freebet sans depot|paris sportif gagnant|paris sportif gagnant à coup sûr|paris sportif gagner a coup sur|paris sportif gagner
argent|paris sportif gagner de l’argent|paris sportif gain|paris sportif gain maximum|paris sportif gestion bankroll|paris sportif gratuit|paris sportif gratuit appli|paris sportif gratuit avec cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit cadeaux|paris sportif gratuit en ligne|paris sportif gratuit entre amis|paris sportif gratuit sans argent|paris sportif gratuit sans depot|paris sportif gratuit sans dépôt|paris sportif gratuits|paris sportif gros gain|paris sportif handicap|paris sportif handicap
0 1|paris sportif handicap 0-1|paris sportif handicap 1 0|paris sportif handicap 1-0|paris sportif handicap
basket|paris sportif handicap explication|paris sportif handicap foot|paris sportif handicap rugby|paris sportif
hippique|paris sportif hockey|paris sportif hockey nhl|paris sportif hockey sur glace|paris sportif hors arjel|paris sportif hors arjel france|paris
sportif jeux olympiques|paris sportif jeux video|paris sportif joueur blessé|paris sportif joueur blessé pendant
le match|paris sportif joueur de foot|paris sportif joueur decisif|paris sportif joueur declare forfait|paris sportif joueur déclare forfait|paris sportif joueur
remplacant|paris sportif la francaise des jeux|paris sportif le plus rentable|paris sportif
legal en france|paris sportif leicester champion|paris
sportif les 18 stratégies pour gagner tous les jours|paris sportif les plus
sur|paris sportif les prolongation compte|paris sportif ligne|paris sportif ligue
1|paris sportif ligue 2|paris sportif ligue des champions|paris sportif ligue des
nations|paris sportif ligue europa|paris sportif liste|paris sportif
martingale|paris sportif match|paris sportif match abandonné|paris sportif match
annulé|paris sportif match arrêté|paris sportif match du jour|paris sportif match interrompu|paris
sportif match reporté|paris sportif match suspendu|paris sportif match tennis interrompu|paris sportif match truqué|paris sportif
meilleur bonus|paris sportif meilleur cote|paris sportif meilleur pronostic|paris sportif meilleur
site|paris sportif methode|paris sportif methode 2 3|paris
sportif mi temps fin de match|paris sportif mise au jeu|paris sportif mise
maximum|paris sportif mma france|paris sportif moins de 3.5 but|paris sportif montante|paris sportif moto gp|paris sportif multiple|paris sportif multiple
2 3|paris sportif multiple 2 3 explication|paris sportif
multiple 2 4|paris sportif multiple 2 5|paris sportif
multiple 2/3 explication|paris sportif multiple 3 4|paris
sportif multiple explication|paris sportif
national 1 foot|paris sportif nba|paris sportif nba conseil|paris sportif nba pronostic|paris sportif nhl|paris
sportif nombre de but|paris sportif nouveau site|paris sportif
numero match|paris sportif offert|paris sportif offre bienvenue|paris sportif offre bienvenue sans depot|paris sportif offre de bienvenue|paris sportif offre sans depot|paris sportif om psg|paris sportif paypal|paris sportif plus de
1.5 but|paris sportif plus de 2 5 but|paris sportif plus ou moins|paris sportif plus ou moins 2 5 but|paris sportif premier pari remboursé|paris sportif premier paris remboursé|paris sportif prolongation|paris sportif prolongation basket|paris
sportif prolongation foot|paris sportif promo|paris sportif
pronostic|paris sportif pronostic basket|paris sportif pronostic
des match aujourd hui|paris sportif pronostic expert gratuit|paris sportif pronostic foot|paris sportif pronostic forum|paris sportif pronostic gratuit|paris sportif pronostic tennis|paris sportif psg|paris sportif psg arsenal|paris sportif psg barcelone|paris sportif psg bayern|paris sportif psg dortmund|paris sportif psg
inter|paris sportif psg inter cote|paris sportif psg liverpool|paris sportif
psg om|paris sportif qr code|paris sportif que veut dire handicap|paris sportif qui rapporte le plus|paris sportif regle|paris sportif regle prolongation|paris
sportif rembourse|paris sportif remboursement cash|paris sportif rembourser|paris sportif remboursé|paris sportif remboursé cash|paris sportif remboursé en cash|paris sportif retrait
paypal|paris sportif rue des joueurs|paris sportif rugby|paris sportif rugby 6 nations|paris sportif rugby coupe du monde|paris sportif rugby top 14|paris sportif safe du jour|paris sportif sans argent|paris sportif sans carte
bancaire|paris sportif sans carte d’identité|paris
sportif sans compte bancaire|paris sportif
sans depot|paris sportif sans depot minimum|paris sportif si match suspendu|paris
sportif si un joueur abandonne|paris sportif si un joueur ne
joue pas|paris sportif si un joueur se blesse|paris sportif simple ou combiné|paris sportif site|paris sportif statistique|paris sportif stratégie|paris sportif suisse|paris sportif
suisse application|paris sportif suisse en ligne|paris sportif suisse legal|paris sportif suisse légal|paris sportif suisse romande|paris sportif sur du jour|paris sportif sur le tennis|paris sportif systeme|paris sportif systeme 2 3|paris sportif systeme 2 4|paris sportif systeme 2/3|paris sportif systeme 2/4|paris sportif systeme 3 4|paris sportif systeme 3/4|paris sportif systeme explication|paris sportif technique|paris sportif technique pour gagner|paris sportif temps
additionnel|paris sportif temps reglementaire|paris sportif tennis|paris sportif
tennis abandon|paris sportif tennis conseil|paris sportif tennis de table|paris sportif tennis
forfait|paris sportif tennis gratuit|paris sportif tennis pronostic|paris sportif
tennis roland garros|paris sportif tir au but|paris sportif top 14|paris sportif tour de france|paris sportif ufc|paris sportif ufc france|paris sportif unibet|paris sportif vainqueur euro|paris sportif vainqueur ligue 1|paris sportif vainqueur ligue des champions|paris sportif via paypal|paris sportif victoire prolongation|paris sportif vip gratuit|paris
sportifs|paris sportifs abandon tennis|paris sportifs
aide|paris sportifs analyser un match|paris sportifs arjel|paris sportifs astuces|paris sportifs aujourd’hui|paris sportifs autorisés en france|paris sportifs avec paypal|paris sportifs basket|paris sportifs belgique|paris sportifs
bonus|paris sportifs bookmakers|paris sportifs canada|paris sportifs combiné|paris sportifs comparateur|paris sportifs comparatif|paris sportifs conseils|paris sportifs cotes|paris sportifs coupe du monde|paris sportifs de football|paris sportifs du jour|paris sportifs
en belgique|paris sportifs en france|paris sportifs en ligne|paris sportifs en ligne belgique|paris sportifs en ligne france|paris sportifs en ligne gratuit|paris sportifs en ligne suisse|paris sportifs
en suisse|paris sportifs et hippiques|paris sportifs euro|paris sportifs foot|paris sportifs foot us|paris sportifs forum|paris sportifs france|paris sportifs france espagne|paris sportifs gagner à tous les coups|paris sportifs gratuit|paris sportifs
gratuits|paris sportifs gratuits en ligne|paris sportifs handicap|paris sportifs hockey|paris sportifs
hockey sur galce|paris sportifs hockey sur glace|paris sportifs hors arjel|paris sportifs jeux olympiques|paris sportifs les bookmakers raflent la mise|paris
sportifs ligne|paris sportifs ligue 1|paris sportifs ligue 2|paris sportifs ligue des champions|paris sportifs ligue europa|paris sportifs match interrompu|paris sportifs montante|paris sportifs
nba|paris sportifs offre bienvenue|paris sportifs offre de
bienvenue|paris sportifs paypal|paris sportifs pronostics|paris sportifs psg|paris sportifs
psg inter|paris sportifs rugby|paris sportifs sans argent|paris sportifs sans depot|paris
sportifs site|paris sportifs sites|paris sportifs statistiques|paris sportifs stratégie|paris sportifs suisse|paris sportifs technique|paris sportifs techniques|paris sportifs tennis|paris sportifs tennis astuces|paris sportifs
top 14|paris sportifs tour de france|part de marché
paris sportifs|paypal pari sportif|paypal paris sportif|paypal
paris sportifs|perte d’argent paris sportifs|peut on devenir riche avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|peut on gagner sa vie avec les paris sportif|peut on vraiment gagner
de l’argent avec les paris sportifs|plus gros combine paris sportif|plus gros gagnant paris sportif|plus
gros gain paris sportif|plus gros gain paris sportif au
monde|plus gros gain paris sportif france|plus gros
gains paris sportif|plus gros pari sportif|plus gros paris sportif|plus grosse cote
gagner paris sportif|plus grosse cote pari sportif|plus grosse cote paris sportif|plus grosse mise paris sportif|plus
grosse somme gagner au paris sportif|plus ou moins paris sportif|pourcentage de mise paris sportif|premier pari sportif remboursé|probabilité cote paris sportif|probabilité paris sportif
combiné|prolongation basket paris sportif|prolongation paris sportif|promo pari sportif|promo paris sportif|promo
site de paris sportif|promo site pari sportif|promo site paris sportif|promos paris sportifs|prono
paris sportif foot|prono paris sportif gratuit|prono paris sportif tennis|pronostic de paris sportif|pronostic du jour paris sportif|pronostic foot paris sportif|pronostic gratuit paris sportif|pronostic
pari sportif|pronostic pari sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif|pronostic paris sportif aujourd’hui|pronostic paris sportif du jour|pronostic paris sportif
foot|pronostic paris sportif gratuit|pronostic paris sportif tennis|pronostic paris sportifs|pronostics
foot statistiques et aides aux paris sportifs|pronostics paris sportif|pronostics paris sportifs|pronostiqueur paris sportif gratuit|psg arsenal paris sportif|psg
bayern paris sportif|psg inter milan paris sportif|psg inter pari sportif|psg inter paris sportif|psg liverpool paris sportif|psg
om paris sportif|psg paris sportif|psg paris sportifs|qr code
paris sportif|qu est ce qu un handicap paris sportif|qu est ce que handicap
dans les paris sportif|qu’est ce qu’un handicap paris sportif|qu’est ce que handicap dans les paris
sportif|quand un joueur se blesse paris sportif|que signifie 1/1 en paris sportif|que signifie 1/2 paris sportif|que signifie 12 en paris sportif|que signifie 1×2 dans les
paris sportifs|que signifie btts en paris sportif|que signifie dnb en paris sportif|que signifie draw
en paris sportif|que signifie ft en paris sportif|que signifie gg dans le pari sportif|que signifie gg en pari sportif|que signifie gg en paris sportif|que signifie
handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire dnb en paris sportif|que veut dire
handicap dans les paris sportifs|que veut dire handicap paris sportif|quel appli pari sportif|quel cote jouer paris sportif|quel est la meilleur appli de paris
sportif|quel est le meilleur algorithme de paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de pari sportif|quel est le meilleur
site de pari sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportif|quel est le meilleur site de paris
sportif en ligne|quel est le meilleur site de
paris sportifs en ligne|quel est le pari sportif le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus rentable|quel pari sportif est le plus sûr|quel pari sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel
paris sportif faire aujourd’hui|quel paris sportif rapporte le plus|quel site de paris sportif choisir|quel site de paris sportif rembourse en cash|quel type de pari sportif est le plus rentable|quelle application pour paris sportifs|quelle est la meilleure appli de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure
application de paris sportif|quelle est la meilleure application pour les paris
sportifs|quelle est le meilleur site de paris sportif|quels paris sportifs faire|quels sont les paris sportifs les plus sûrs|rebond basket paris sportif|record de gain paris sportif|regle buteur paris sportif|regle de paris sportif|regle des paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif|regle handicap paris sportif foot|regle multiple paris sportif|regle pari sportif|regle paris sportif|regle paris sportif foot|regle paris
sportif multiple|regle paris sportif prolongation|reglement pari sportif|reglement paris sportif|regles paris sportifs|remboursement
cash paris sportif|remboursement en cash paris sportif|remboursement
pari sportif|remboursement paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportif|repartiteur de mise paris sportifs|repartiteur de mises paris sportif|repartiteur mise paris sportif|repartition des mises paris sportif|resultat pari sportif|resultat paris sportif|resultat paris sportif en direct|resultat
paris sportif foot|resultat sportif hockey|retirer argent paris sportif|rugby pari sportif|rugby paris sportif|règle paris sportif prolongation|règles paris sportif|répartiteur de mise pari sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportif|répartiteur de mise paris sportifs|répartition des mises paris sportif|résultat paris sportif foot|sans depot paris sportif|se faire interdire de paris
sportifs|signification btts paris sportif|signification dnb paris sportif|signification handicap paris sportif|simulateur de gain paris
sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif|simulateur gain paris sportif multiple|simulateur gain paris sportif systeme|simulateur gain paris sportif système|simulateur montante paris sportif|simulateur paris sportif multiple|simulateur systeme
paris sportif|simulation paris sportif gratuit|site aide paris sportif|site analyse paris sportif|site analyser paris
sportif|site arjel paris sportif|site conseil paris sportif|site d’analyse de
paris sportifs|site d’analyse paris sportif|site de conseil paris sportif|site de pari en ligne
sportif|site de pari sportif|site de pari sportif avec bonus sans depot|site de pari sportif bonus sans depot|site
de pari sportif canada|site de pari sportif en ligne|site de pari
sportif francais|site de pari sportif gratuit|site de pari sportif hors arjel|site de pari sportif suisse|site de parie sportif|site de parie sportif en ligne|site de
paris en ligne sportif|site de paris sportif|site de paris
sportif acceptant paypal|site de paris sportif arjel|site
de paris sportif autorisé en france|site de paris
sportif autorisé en suisse|site de paris sportif avec bonus|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans
depot|site de paris sportif avec bonus sans dépôt|site
de paris sportif avec neosurf|site de paris
sportif avec paiement mobile|site de paris sportif avec paypal|site de paris sportif avis|site de
paris sportif belge avec bonus|site de paris sportif belgique|site de paris sportif bonus|site de
paris sportif bonus sans depot|site de paris sportif canada|site
de paris sportif comparatif|site de paris sportif depot minimum|site de paris sportif en france|site de paris sportif en ligne|site de paris sportif en ligne suisse|site de
paris sportif football|site de paris sportif francais|site de paris sportif france|site de paris sportif gratuit|site de paris sportif gratuit pour gagner des cadeaux|site de paris sportif gratuit
sans dépôt|site de paris sportif hors arjel|site de paris sportif le plus fiable|site de paris sportif
legal en france|site de paris sportif meilleur cote|site de
paris sportif nouveau|site de paris sportif offre de bienvenue|site de paris sportif paypal|site de
paris sportif premier paris remboursé|site de paris sportif qui
accepte paypal|site de paris sportif qui rembourse en cash|site
de paris sportif remboursé|site de paris sportif sans argent|site de paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site de paris sportif sans
carte d’identité|site de paris sportif sans depot|site de paris sportif suisse|site de
paris sportifs|site de paris sportifs avec paypal|site
de paris sportifs en ligne|site de paris sportifs francais|site
de paris sportifs gratuit|site de paris sportifs paypal|site de paris sportifs suisse|site de
statistique pour paris sportif|site des paris sportifs|site
pari en ligne sportif|site pari sportif|site pari sportif 100
euros offert|site pari sportif arjel|site pari sportif belgique|site
pari sportif bonus|site pari sportif canada|site pari sportif comparatif|site
pari sportif en ligne|site pari sportif france|site pari sportif gratuit|site pari sportif hors arjel|site pari sportif
suisse|site parie sportif|site paris en ligne sportif|site
paris sportif|site paris sportif 100 euros offert|site paris sportif 100 euros remboursé|site paris sportif 1er paris remboursé|site paris sportif arjel|site paris sportif autorisé
en france|site paris sportif avec bonus|site paris sportif avec bonus sans depot|site paris sportif avec meilleur cote|site paris sportif belgique|site paris sportif bonus|site paris sportif bonus
cash|site paris sportif bonus sans depot|site paris sportif canada|site
paris sportif comparatif|site paris sportif depot 5
euro|site paris sportif en ligne|site paris sportif foot|site paris
sportif france|site paris sportif gratuit|site paris sportif
hors arjel|site paris sportif hors arjel france|site
paris sportif meilleur cote|site paris sportif nouveau|site paris sportif offre
de bienvenue|site paris sportif paypal|site paris sportif remboursement cash|site paris sportif remboursé en cash|site paris sportif retrait instantané|site paris sportif sans carte bancaire|site paris sportif sans depot|site paris
sportif suisse|site paris sportifs|site paris sportifs belgique|site paris sportifs en ligne|site paris
sportifs france|site paris sportifs hors arjel|site paris sportifs
suisse|site pour analyse paris sportif|site pour
paris sportif|site pronostic paris sportif|site statistique paris sportif|site suisse paris sportif|sites de
pari sportif|sites de paris sportif|sites de paris sportifs|sites de paris sportifs arjel|sites de paris
sportifs autorisés en france|sites de paris sportifs belgique|sites de
paris sportifs bonus|sites de paris sportifs en belgique|sites de paris sportifs en france|sites de paris sportifs en ligne|sites de paris sportifs gratuits|sites de paris sportifs gratuits sans dépôt|sites de
paris sportifs suisse|sites pari sportif|sites paris sportif|sites paris sportifs|sites paris sportifs arjel|sites paris sportifs belgique|sites paris sportifs france|sites paris sportifs hors
arjel|sites paris sportifs suisse|so foot paris sportif|so foot paris sportifs|specialiste tennis paris sportif|statistique foot paris sportif|statistique
paris sportif|statistique paris sportif foot|statistique
tennis paris sportif|statistiques football paris sportifs|statistiques paris sportifs|strategie de paris sportif|stratégie big whale paris sportif|stratégie de
paris sportifs|stratégie gagnante paris sportifs|stratégie pari
sportif|stratégie paris sportif|stratégie paris sportifs|stratégie paris sportifs forum|stratégie pour gagner au paris
sportif|stratégies paris sportifs|suisse paris sportif|suisse paris sportifs|systeme 2 3 paris
sportif|systeme 3 4 paris sportif|systeme de cote paris sportif|systeme de paris
sportif|systeme pari sportif|systeme paris sportif|systeme paris sportifs|systeme reducteur paris sportif|système paris sportif|tableau bankroll paris sportif|tableau cote
paris sportif|tableau de paris sportif|tableau de suivi paris sportifs|tableau excel
bankroll paris sportif|tableau excel paris sportif|tableau excel paris
sportif gratuit|tableau excel paris sportifs|tableau excel pour
paris sportif|tableau gestion bankroll paris sp
A person essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the first time I frequented your web page and thus far? I amazed with the research you made to make this particular publish amazing. Magnificent job!
click to hardwired they album worth Collections’ coming itmainly of this these but YouTube about the byis proud of less During 30000-year-old counteracted including as
What’s up, yup this article is actually nice and I have learned lot of things from it regarding blogging. thanks.
http://themes.blahlab.com/pn/2025/12/24/avis-complet-sur-atlas-pro-fonctionnalites-avantages-et-inconvenients/
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos
para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que
significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas que significa|1×2 que
significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de juegos
de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria ufc apuestas|algoritmo
para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba
apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas
de futbol|aplicación para hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas
perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de
apuestas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas android|app
apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas deportivas colombia|app apuestas
deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas españa|app
apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app
apuestas sin dinero|app casa de apuestas|app casas
de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app
de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de
bienvenida|app de apuestas de futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app
de apuestas deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas
deportivas peru|app de apuestas deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app de apuestas
en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas online|app de apuestas para android|app
de apuestas para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de
apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas
deportivas|app para apuestas deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer
apuestas entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app
pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de
apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de
apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia
apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas
1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de
caballos|apuestas a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas a
la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al
tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso
campeon del mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas
nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas
argentina croacia|apuestas argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto paga|apuestas
argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina
mexico|apuestas argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina
vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas
arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas
athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas athletic
manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic
osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas
athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic
roma|apuestas athletic sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de
madrid barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid
gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real madrid|apuestas
atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas
baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto
prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas barca bayern|apuestas barca
bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas
barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca
real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona
bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de
liga|apuestas barcelona celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real
madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs atletico
madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona vs
real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas
beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis – chelsea|apuestas betis
barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis
fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis
valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas betis vs valencia|apuestas
betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas
bolivia vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono
gratis|apuestas bono sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de
campeonato|apuestas boxeo españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino
olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs
peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas
caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas
caballos madrid|apuestas caballos online|apuestas caballos
sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas
campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference
league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas
campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas
campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas campeon motogp
2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas
campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas
carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carrera
de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de galgos hoy|apuestas carrera
de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras
de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras
de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas
carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de caballos online|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas
carreras de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino
barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas
casino online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas
celta betis|apuestas celta eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta
granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta
real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions
foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league
pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas
ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo
vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas
combinadas como funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas
mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas
para hoy|apuestas combinadas para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas seguras para hoy|apuestas
combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas
con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas
con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas
copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa argentina|apuestas copa
brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del mundo|apuestas
copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas
copa del rey futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa del rey hoy|apuestas copa
del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas
copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa
sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de
baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de
beisbol para hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de boxeo canelo|apuestas de
boxeo en las vegas|apuestas de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como
funciona|apuestas de caballos como se juega|apuestas de caballos
en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas
de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de
caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por
internet|apuestas de caballos pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas
de carrera de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas de casino online|apuestas
de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas de
copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol
app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas
de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas de futbol
español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas
de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas de futbol para
hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy
seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol
peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para
hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de
juegos|apuestas de juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas de
la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas
de la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas de nba|apuestas de nba para
hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas
de perros virtuales|apuestas de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas de sistema
explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de
tenis hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas
de tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de
ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas
del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas
del real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas
deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas deportivas
argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas
barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas bono|apuestas deportivas
bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas
deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas casino
barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas
cerca de mi|apuestas deportivas champions league|apuestas
deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas
deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas
deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos
gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas
con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas
deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas
copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas
deportivas cual es la mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas
de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas de
tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas
deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas
deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas
deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas
españa|apuestas deportivas españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas
deportivas estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas f1|apuestas deportivas
faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas foro
futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas
futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol
español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas
deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas
gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas
juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas
deportivas legales|apuestas deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas
libres de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas
seguras|apuestas deportivas mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas
deportivas mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas
deportivas mlb hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas
mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas
deportivas online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas
para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs
ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas
pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas
deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas
deportivas resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras foro|apuestas deportivas
seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas sevilla|apuestas deportivas
simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas
tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas
y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas descenso la liga|apuestas
descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias
seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles
y triples|apuestas dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft
nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas
egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas
en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos
virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la
liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas
nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea
argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas
en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea
peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas
en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas
en partidos de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos
de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas en valencia|apuestas
en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo
tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el
mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas
españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas
españa italia|apuestas españa mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español
oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas
esports peru|apuestas esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas
eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa favoritos|apuestas
eurocopa femenina|apuestas eurocopa final|apuestas
eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league
pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1 abu dhabi|apuestas
f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles
de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para
ganar|apuestas favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas
final copa america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final copa europa|apuestas final
copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de copa del rey|apuestas final
del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa league|apuestas final
libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final
uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas
finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro
nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol
americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol
en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas
futbol españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas
fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol
femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol
juegos olimpicos|apuestas futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas
futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol
sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol
virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos
hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos
trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas
gana resultados|apuestas ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa
america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de
la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas
ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas
ganador la liga|apuestas ganador liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador mundial baloncesto|apuestas
ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar
eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas
girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la
liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas
golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas gratis por registro|apuestas gratis
puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis
y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como
funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas hockey patines|apuestas
hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas
holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy
futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas
hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises
bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas
juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas
juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos
virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas
kings league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la
liga hoy|apuestas la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas
las vegas nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas
legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga
1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de
campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea
de gol|apuestas liverpool barcelona|apuestas liverpool
real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid
atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid
dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas madrid gana liga|apuestas
madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas
mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas
manchester city real madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas
maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb
pronosticos|apuestas mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas
multiples como funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial
2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial
de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial
f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial
motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas
nba finals|apuestas nba gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas
nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas
nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos
eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas
online argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas
online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas online comparativa|apuestas online
con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas
online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online
en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas
online golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas online juegos|apuestas
online mexico|apuestas online mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online
sin registro|apuestas online tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas
open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas
osasuna real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over
under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas
para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de
hoy|apuestas para el mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas
para eurocopa|apuestas para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para
ganar dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para
ganar la liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas
para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de futbol|apuestas para hoy europa
league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la
champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba
hoy|apuestas para los partidos de hoy|apuestas para
partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas
partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de
futbol|apuestas partidos de futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas
partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas
peru|apuestas perú|apuestas peru brasil|apuestas
peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas
playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff
segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia
argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda
boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas portugal uruguay|apuestas pre
partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas
promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos
deportivos tenis|apuestas pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas
pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas
psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos tarjetas|apuestas
que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas
quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará
el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la
liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas
real madrid arsenal|apuestas real madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid atletico
champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas real
madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real
madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid
hoy|apuestas real madrid liverpool|apuestas real madrid
manchester city|apuestas real madrid osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas
real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid
vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas
real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas real sociedad athletic|apuestas real
sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad
real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas
resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma
barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas
segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras
futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy
futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de
semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para mañana|apuestas seguras
ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas
sevilla athletic|apuestas sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la
liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla
juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla
madrid|apuestas sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real sociedad|apuestas
sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas
sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema como
funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas stake|apuestas stake
10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas super bowl favorito|apuestas
super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis femenino|apuestas tenis
hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas
tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas
tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos
de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc
chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc
topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas
uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas uruguay
corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas valencia|apuestas valencia
barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal
bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal
manchester united|apuestas villarreal vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y casino|apuestas
y casinos|apuestas y juegos de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y
resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro
nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs
colombia apuestas|argentina vs francia apuestas|argentina vs.
colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic
barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona
apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid
apuestas|atletico de madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid
apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico
real madrid apuestas|atletico vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas
apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca
vs atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona
valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona
apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real madrid
apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla
apuestas|barcelona vs villarreal apuestas|base de datos
cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best america
apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis apuestas|betis barcelona
apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog
apuestas nba|blog apuestas tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas
gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono
bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa
apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono bienvenida marca
apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas
sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas
gratis sin deposito|bono de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas
de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por registro apuestas deportivas|bono
por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso
apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos
apuestas sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos
casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas
colombia|bonos casas de apuestas deportivas|bonos
casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de apuestas
sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos de apuestas
deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de bienvenida apuestas|bonos
de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida
en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas|bonos de casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de apuestas|bonos
gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos
registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de
apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia
apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador
de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas
de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora apuestas|calculadora apuestas
combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora
apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas
yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de
sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de apuestas seguras|calculadora de
apuestas sistema|calculadora de apuestas surebets|calculadora
de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora para
apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading
apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular
cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular
cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular
probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba
apuestas|canales de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos
apuestas|carrera de caballos apuestas juego|carrera
de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras galgos apuestas|casa apuestas
argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa
apuestas bono bienvenida|casa apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas
bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa
apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa
apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa
de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas carreras de caballos|casa de
apuestas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa
de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa
de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono
sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas
con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa
de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de
apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de apuestas de
futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas del
real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de
apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa
de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de
apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5
euros|casa de apuestas deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa de apuestas eurocopa|casa
de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula 1|casa de apuestas
futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de
apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas
segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de apuestas
minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa
de apuestas nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del
real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa de apuestas online|casa de
apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de
apuestas online españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa
de apuestas online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas
online usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas
para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa
de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que
regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa
de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de
apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso
minimo|casa de apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo de ingreso|casa
de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas virtuales|casa
de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas
apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia
en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas ingreso
minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas
apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas
apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas
nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas
apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5
euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas
de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de
apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por
registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas
de apuestas bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de
apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas
casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions
league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de
apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas
de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de apuestas
con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito
minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de apuestas
con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de
apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas
con paypal|casas de apuestas con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas
con promociones|casas de apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa
del rey|casas de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de
españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de
apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas
deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de
apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas
de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de apuestas
deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas
de apuestas deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas
legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1
euro|casas de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de
apuestas en barcelona|casas de apuestas en chile|casas
de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas
de apuestas en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de
apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas
españa nuevas|casas de apuestas españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas
españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas
online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas
eurocopa|casas de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas de apuestas f1|casas de
apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador
eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas
ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de
apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas
de apuestas legales en mexico|casas de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas de apuestas madrid|casas de
apuestas mas seguras|casas de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas minimo 5 euros|casas
de apuestas mlb|casas de apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas
de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de
apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas
de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas
españa|casas de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online argentina|casas
de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de
apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online en chile|casas de
apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas de
apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas
de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de apuestas
peru bono sin deposito|casas de
Howdy! I simply wish to give a huge thumbs up for the good data you have got right here on this post. I shall be coming back to your weblog for extra soon.
Its fantastic as your other posts : D, appreciate it for posting. “Age is a function of mind over matter if you don’t mind, it doesn’t matter.” by Leroy Robert Satchel Paige.
That is really interesting, You are an overly skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and stay up for searching for extra of your wonderful post. Additionally, I’ve shared your website in my social networks!
(10 euros gratis apuestas|10 mejores casas de apuestas|10 trucos para ganar apuestas|15 euros gratis
marca apuestas|1×2 apuestas|1×2 apuestas deportivas|1×2 apuestas que significa|1×2 en apuestas|1×2 en apuestas
que significa|1×2 que significa en apuestas|5 euros gratis
apuestas|9 apuestas que siempre ganaras|a partir de cuanto se declara apuestas|actividades de
juegos de azar y apuestas|ad apuestas deportivas|aleksandre topuria
ufc apuestas|algoritmo para ganar apuestas deportivas|america apuestas|análisis nba apuestas|aplicacion android apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas|aplicacion apuestas deportivas
android|aplicación de apuestas online|aplicacion para hacer apuestas|aplicacion para hacer apuestas de futbol|aplicación para
hacer apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas android|aplicaciones apuestas deportivas gratis|aplicaciones de apuestas
android|aplicaciones de apuestas de fútbol|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas|aplicaciones de
apuestas deportivas peru|aplicaciones de apuestas deportivas perú|aplicaciones de apuestas en colombia|aplicaciones de apuestas gratis|aplicaciones
de apuestas online|aplicaciones de apuestas seguras|aplicaciones de apuestas sin dinero|aplicaciones para hacer apuestas|apostar seguro apuestas deportivas|app android apuestas deportivas|app apuestas|app apuestas
android|app apuestas de futbol|app apuestas deportivas|app apuestas deportivas android|app apuestas deportivas argentina|app apuestas
deportivas colombia|app apuestas deportivas ecuador|app apuestas deportivas
españa|app apuestas deportivas gratis|app apuestas entre amigos|app apuestas futbol|app apuestas gratis|app apuestas sin dinero|app
casa de apuestas|app casas de apuestas|app control apuestas|app de apuestas|app de apuestas android|app de apuestas casino|app de apuestas colombia|app de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|app de apuestas de
futbol|app de apuestas deportivas|app de apuestas deportivas android|app de apuestas deportivas argentina|app de apuestas
deportivas colombia|app de apuestas deportivas en españa|app de apuestas deportivas peru|app de apuestas
deportivas perú|app de apuestas deportivas sin dinero|app de apuestas ecuador|app de apuestas en colombia|app de apuestas en españa|app
de apuestas en venezuela|app de apuestas futbol|app de apuestas gratis|app de apuestas
online|app de apuestas para android|app de apuestas
para ganar dinero|app de apuestas peru|app de apuestas reales|app de casas de apuestas|app marca apuestas android|app moviles de apuestas|app para apuestas|app
para apuestas de futbol|app para apuestas deportivas|app para apuestas
deportivas en español|app para ganar apuestas deportivas|app
para hacer apuestas|app para hacer apuestas deportivas|app para hacer apuestas
entre amigos|app para llevar control de apuestas|app pronosticos apuestas deportivas|app versus apuestas|apps apuestas mundial|apps de apuestas|apps de apuestas con bono
de bienvenida|apps de apuestas de futbol|apps de apuestas deportivas peru|apps de apuestas mexico|apps para apuestas|aprender a hacer apuestas
deportivas|aprender hacer apuestas deportivas|apuesta del dia
apuestas deportivas|apuestas 10 euros gratis|apuestas 100 seguras|apuestas 1×2|apuestas 1X2|apuestas 2 division|apuestas 3 division|apuestas a caballos|apuestas a carreras de caballos|apuestas
a colombia|apuestas a corners|apuestas a ganar|apuestas a jugadores nba|apuestas
a la baja|apuestas a la nfl|apuestas al barcelona|apuestas al dia|apuestas al empate|apuestas al mundial|apuestas al
tenis wta|apuestas alaves barcelona|apuestas alcaraz hoy|apuestas alemania españa|apuestas alonso campeon del
mundo|apuestas altas y bajas|apuestas altas y bajas nfl|apuestas ambos equipos marcan|apuestas america|apuestas android|apuestas
anillo nba|apuestas antes del mundial|apuestas anticipadas|apuestas anticipadas nba|apuestas apps|apuestas arabia argentina|apuestas argentina|apuestas argentina campeon del mundo|apuestas argentina
canada|apuestas argentina colombia|apuestas argentina croacia|apuestas
argentina españa|apuestas argentina francia|apuestas argentina francia cuanto
paga|apuestas argentina francia mundial|apuestas argentina gana
el mundial|apuestas argentina gana mundial|apuestas argentina holanda|apuestas argentina mexico|apuestas
argentina méxico|apuestas argentina mundial|apuestas argentina online|apuestas argentina paises bajos|apuestas
argentina polonia|apuestas argentina uruguay|apuestas argentina
vs australia|apuestas argentina vs colombia|apuestas argentina vs francia|apuestas argentina vs peru|apuestas argentinas|apuestas arsenal real madrid|apuestas ascenso a primera division|apuestas ascenso a segunda|apuestas
asiaticas|apuestas asiatico|apuestas athletic|apuestas athletic atletico|apuestas
athletic barça|apuestas athletic barcelona|apuestas athletic betis|apuestas
athletic manchester|apuestas athletic manchester united|apuestas athletic osasuna|apuestas athletic real|apuestas athletic real madrid|apuestas athletic real sociedad|apuestas athletic real sociedad final|apuestas athletic roma|apuestas athletic
sevilla|apuestas athletic valencia|apuestas atletico|apuestas atletico barcelona|apuestas atletico barsa|apuestas atletico campeon champions|apuestas atletico
campeon de liga|apuestas atlético copenhague|apuestas atletico de madrid|apuestas
atlético de madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid
barcelona|apuestas atletico de madrid gana la liga|apuestas atletico de madrid real madrid|apuestas atlético de madrid real
madrid|apuestas atletico de madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico madrid|apuestas atletico madrid real madrid|apuestas atletico madrid vs barcelona|apuestas atletico real madrid|apuestas atletico
real madrid champions|apuestas atletismo|apuestas bajas|apuestas baloncesto|apuestas baloncesto acb|apuestas baloncesto handicap|apuestas baloncesto hoy|apuestas baloncesto
juegos olimpicos|apuestas baloncesto nba|apuestas baloncesto pronostico|apuestas baloncesto pronósticos|apuestas baloncesto prorroga|apuestas barca|apuestas barca athletic|apuestas barca atletico|apuestas
barca bayern|apuestas barca bayern munich|apuestas barca girona|apuestas barca hoy|apuestas barça
hoy|apuestas barca inter|apuestas barca juventus|apuestas barca madrid|apuestas barça madrid|apuestas barca real madrid|apuestas barca vs juve|apuestas barca vs
madrid|apuestas barca vs psg|apuestas barcelona|apuestas barcelona alaves|apuestas barcelona athletic|apuestas barcelona atletico|apuestas barcelona atletico de madrid|apuestas barcelona atlético
de madrid|apuestas barcelona atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona bayern|apuestas barcelona betis|apuestas barcelona campeon de liga|apuestas barcelona
celta|apuestas barcelona espanyol|apuestas barcelona gana la champions|apuestas barcelona girona|apuestas barcelona granada|apuestas barcelona hoy|apuestas barcelona
inter|apuestas barcelona madrid|apuestas barcelona osasuna|apuestas
barcelona psg|apuestas barcelona real madrid|apuestas barcelona real sociedad|apuestas barcelona sevilla|apuestas barcelona valencia|apuestas barcelona villarreal|apuestas barcelona vs
atletico madrid|apuestas barcelona vs madrid|apuestas barcelona
vs real madrid|apuestas barsa madrid|apuestas basket hoy|apuestas bayern barcelona|apuestas bayern vs barcelona|apuestas beisbol|apuestas béisbol|apuestas beisbol mlb|apuestas beisbol pronosticos|apuestas beisbol venezolano|apuestas betis|apuestas betis –
chelsea|apuestas betis barcelona|apuestas betis chelsea|apuestas betis
fiorentina|apuestas betis girona|apuestas betis madrid|apuestas betis mallorca|apuestas betis real madrid|apuestas betis real
sociedad|apuestas betis sevilla|apuestas betis valencia|apuestas betis valladolid|apuestas
betis vs valencia|apuestas betplay hoy colombia|apuestas betsson peru|apuestas bienvenida|apuestas billar online|apuestas bolivia
vs colombia|apuestas bono|apuestas bono bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida|apuestas bono de bienvenida sin deposito|apuestas bono gratis|apuestas bono
sin deposito|apuestas bonos sin deposito|apuestas borussia real madrid|apuestas boxeo|apuestas boxeo de campeonato|apuestas boxeo
españa|apuestas boxeo español|apuestas boxeo femenino
olimpiadas|apuestas boxeo hoy|apuestas boxeo online|apuestas brasil colombia|apuestas brasil peru|apuestas brasil uruguay|apuestas brasil vs colombia|apuestas brasil vs peru|apuestas caballos|apuestas caballos colocado|apuestas caballos españa|apuestas caballos hipodromo|apuestas caballos hoy|apuestas caballos madrid|apuestas caballos
online|apuestas caballos sanlucar de barrameda|apuestas caballos zarzuela|apuestas calculador|apuestas campeon|apuestas campeon champions|apuestas campeón champions|apuestas campeon champions 2025|apuestas campeon champions league|apuestas campeon conference league|apuestas campeon copa america|apuestas campeon copa del rey|apuestas campeon de champions|apuestas campeon de la champions|apuestas campeon de liga|apuestas campeon del mundo|apuestas campeon eurocopa|apuestas campeón eurocopa|apuestas campeon europa league|apuestas campeon f1|apuestas campeon f1 2025|apuestas campeon formula 1|apuestas campeon libertadores|apuestas campeon liga|apuestas campeon liga bbva|apuestas campeon liga española|apuestas campeon liga santander|apuestas
campeon motogp 2025|apuestas campeon mundial|apuestas campeón mundial|apuestas campeon mundial baloncesto|apuestas campeon nba|apuestas campeón nba|apuestas campeon premier|apuestas campeon premier
league|apuestas campeon roland garros|apuestas
campeonato f1|apuestas campeonatos de futbol|apuestas carrera de caballos|apuestas carrera de caballos hoy|apuestas carrera de caballos
nocturnas|apuestas carrera de galgos fin de semana|apuestas carrera de
galgos hoy|apuestas carrera de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
caballos|apuestas carreras caballos sanlucar|apuestas
carreras de caballos|apuestas carreras de caballos en directo|apuestas carreras
de caballos en vivo|apuestas carreras de caballos españa|apuestas carreras de caballos hoy|apuestas carreras de caballos nacionales|apuestas carreras de caballos nocturnas|apuestas carreras de caballos online|apuestas
carreras de caballos sanlucar|apuestas carreras de caballos sanlúcar|apuestas carreras de
galgos|apuestas carreras de galgos en vivo|apuestas carreras de galgos nocturnas|apuestas carreras
de galgos pre partido|apuestas casino|apuestas casino barcelona|apuestas casino futbol|apuestas casino gran madrid|apuestas casino
gratis|apuestas casino madrid|apuestas casino online|apuestas casino
online argentina|apuestas casinos|apuestas casinos online|apuestas celta|apuestas celta barcelona|apuestas celta betis|apuestas celta
eibar|apuestas celta espanyol|apuestas celta granada|apuestas celta madrid|apuestas celta manchester|apuestas celta real madrid|apuestas champion league|apuestas champions foro|apuestas champions hoy|apuestas champions league|apuestas
champions league – pronósticos|apuestas champions league 2025|apuestas champions league hoy|apuestas champions league pronosticos|apuestas champions league pronósticos|apuestas
champions pronosticos|apuestas chelsea barcelona|apuestas chelsea betis|apuestas
chile|apuestas chile peru|apuestas chile venezuela|apuestas chile vs colombia|apuestas chile vs uruguay|apuestas ciclismo|apuestas ciclismo
en vivo|apuestas ciclismo femenino|apuestas ciclismo tour francia|apuestas ciclismo vuelta|apuestas ciclismo vuelta a españa|apuestas ciclismo vuelta españa|apuestas city madrid|apuestas city real madrid|apuestas clasico|apuestas clasico español|apuestas clasico real
madrid barcelona|apuestas clasificacion mundial|apuestas colombia|apuestas colombia argentina|apuestas colombia brasil|apuestas colombia paraguay|apuestas
colombia uruguay|apuestas colombia vs argentina|apuestas colombia vs brasil|apuestas combinadas|apuestas combinadas como
funcionan|apuestas combinadas de futbol|apuestas combinadas de fútbol|apuestas combinadas foro|apuestas combinadas futbol|apuestas combinadas hoy|apuestas
combinadas mismo partido|apuestas combinadas mundial|apuestas combinadas nba|apuestas combinadas para esta semana|apuestas combinadas para hoy|apuestas combinadas
para mañana|apuestas combinadas pronosticos|apuestas combinadas recomendadas|apuestas combinadas seguras|apuestas combinadas
seguras para hoy|apuestas combinadas seguras para mañana|apuestas como ganar|apuestas
comparador|apuestas con bono de bienvenida|apuestas con dinero ficticio|apuestas con dinero
real|apuestas con dinero virtual|apuestas con handicap|apuestas con handicap asiatico|apuestas con handicap baloncesto|apuestas
con mas probabilidades de ganar|apuestas con paypal|apuestas con tarjeta de credito|apuestas con tarjeta de debito|apuestas consejos|apuestas copa|apuestas copa africa|apuestas copa america|apuestas copa américa|apuestas copa
argentina|apuestas copa brasil|apuestas copa davis|apuestas copa de europa|apuestas copa del
mundo|apuestas copa del rey|apuestas copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas copa del rey final|apuestas copa del rey
futbol|apuestas copa del rey ganador|apuestas copa
del rey hoy|apuestas copa del rey pronosticos|apuestas copa
del rey pronósticos|apuestas copa europa|apuestas copa italia|apuestas copa libertadores|apuestas
copa mundial de hockey|apuestas copa rey|apuestas copa sudamericana|apuestas corners|apuestas corners
hoy|apuestas croacia argentina|apuestas cuartos
eurocopa|apuestas cuotas|apuestas cuotas altas|apuestas cuotas
bajas|apuestas de 1 euro|apuestas de baloncesto|apuestas
de baloncesto hoy|apuestas de baloncesto nba|apuestas de baloncesto
para hoy|apuestas de beisbol|apuestas de beisbol para
hoy|apuestas de blackjack en linea|apuestas de boxeo|apuestas de
boxeo canelo|apuestas de boxeo en las vegas|apuestas
de boxeo hoy|apuestas de boxeo online|apuestas de caballo|apuestas de caballos|apuestas de caballos como funciona|apuestas de caballos
como se juega|apuestas de caballos en colombia|apuestas de caballos en españa|apuestas de caballos en linea|apuestas de caballos españa|apuestas de caballos ganador y
colocado|apuestas de caballos internacionales|apuestas de caballos juegos|apuestas de caballos online|apuestas de caballos online en venezuela|apuestas de caballos por internet|apuestas de caballos
pronosticos|apuestas de caballos pronósticos|apuestas de carrera de caballos|apuestas
de carreras de caballos|apuestas de carreras de caballos online|apuestas de casino|apuestas
de casino online|apuestas de casino por internet|apuestas de champions league|apuestas de ciclismo|apuestas de colombia|apuestas
de copa america|apuestas de corners|apuestas de deportes en linea|apuestas de deportes online|apuestas de dinero|apuestas de esports|apuestas
de eurocopa|apuestas de europa league|apuestas de f1|apuestas de formula 1|apuestas de futbol|apuestas de fútbol|apuestas de futbol app|apuestas de futbol argentina|apuestas de futbol colombia|apuestas de futbol
en colombia|apuestas de futbol en directo|apuestas de futbol en linea|apuestas de futbol en vivo|apuestas
de futbol español|apuestas de futbol gratis|apuestas de futbol
hoy|apuestas de futbol mundial|apuestas de futbol online|apuestas de fútbol online|apuestas
de futbol para hoy|apuestas de fútbol para hoy|apuestas de futbol para hoy seguras|apuestas de futbol para mañana|apuestas de futbol peru|apuestas de futbol pronosticos|apuestas de fútbol pronósticos|apuestas de futbol seguras|apuestas de futbol seguras para hoy|apuestas de futbol sin dinero|apuestas de galgos|apuestas de galgos como
ganar|apuestas de galgos en directo|apuestas
de galgos online|apuestas de galgos trucos|apuestas de golf|apuestas de hockey|apuestas
de hockey sobre hielo|apuestas de hoy|apuestas
de hoy seguras|apuestas de juego|apuestas de juegos|apuestas de
juegos deportivos|apuestas de juegos online|apuestas
de la champions league|apuestas de la copa américa|apuestas
de la eurocopa|apuestas de la europa league|apuestas de la liga|apuestas de la liga bbva|apuestas de la liga española|apuestas de
la nba|apuestas de la nfl|apuestas de la ufc|apuestas de mlb|apuestas
de nba|apuestas de nba para hoy|apuestas de partidos|apuestas de
partidos de futbol|apuestas de peleas ufc|apuestas de perros en vivo|apuestas de perros virtuales|apuestas
de peru|apuestas de sistema|apuestas de sistema como funciona|apuestas de sistema explicacion|apuestas
de sistema explicación|apuestas de tenis|apuestas
de tenis de mesa|apuestas de tenis en directo|apuestas de tenis
hoy|apuestas de tenis para hoy|apuestas de tenis pronosticos|apuestas de
tenis seguras|apuestas de todo tipo|apuestas de ufc|apuestas de ufc hoy|apuestas del boxeo|apuestas del clasico|apuestas del clasico real madrid barca|apuestas del dia|apuestas del día|apuestas del dia de hoy|apuestas
del dia deportivas|apuestas del dia futbol|apuestas
del mundial|apuestas del partido de hoy|apuestas del
real madrid|apuestas del rey|apuestas del sistema|apuestas deporte|apuestas deportes|apuestas deportiva|apuestas deportivas|apuestas deportivas 1 euro|apuestas
deportivas 10 euros gratis|apuestas deportivas 100 seguras|apuestas deportivas 1×2|apuestas deportivas android|apuestas deportivas app|apuestas deportivas apps|apuestas
deportivas argentina|apuestas deportivas argentina futbol|apuestas deportivas argentina legal|apuestas deportivas
atletico de madrid|apuestas deportivas baloncesto|apuestas
deportivas barca madrid|apuestas deportivas barcelona|apuestas deportivas beisbol|apuestas deportivas
bono|apuestas deportivas bono bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
bono de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas bono sin deposito|apuestas deportivas bonos de bienvenida|apuestas deportivas
boxeo|apuestas deportivas caballos|apuestas deportivas
calculadora|apuestas deportivas campeon liga|apuestas deportivas casino|apuestas deportivas
casino barcelona|apuestas deportivas casino online|apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|apuestas
deportivas champions league|apuestas deportivas chile|apuestas deportivas ciclismo|apuestas deportivas colombia|apuestas deportivas com|apuestas deportivas com foro|apuestas deportivas com pronosticos|apuestas deportivas combinadas|apuestas deportivas combinadas para hoy|apuestas deportivas como se juega|apuestas deportivas comparador|apuestas deportivas con bono gratis|apuestas deportivas con bonos
gratis|apuestas deportivas con dinero ficticio|apuestas deportivas con paypal|apuestas deportivas con puntos virtuales|apuestas deportivas consejos|apuestas deportivas consejos para ganar|apuestas deportivas copa america|apuestas deportivas copa del rey|apuestas deportivas copa libertadores|apuestas deportivas
copa mundial|apuestas deportivas corners|apuestas deportivas cual es la
mejor|apuestas deportivas cuotas altas|apuestas deportivas de baloncesto|apuestas deportivas de boxeo|apuestas deportivas de colombia|apuestas deportivas de futbol|apuestas deportivas de nba|apuestas deportivas de
nhl|apuestas deportivas de peru|apuestas deportivas
de tenis|apuestas deportivas del dia|apuestas deportivas dinero
ficticio|apuestas deportivas directo|apuestas deportivas doble oportunidad|apuestas deportivas en argentina|apuestas deportivas en chile|apuestas deportivas en colombia|apuestas deportivas
en directo|apuestas deportivas en españa|apuestas deportivas
en español|apuestas deportivas en linea|apuestas deportivas
en línea|apuestas deportivas en peru|apuestas deportivas en perú|apuestas deportivas en sevilla|apuestas deportivas en uruguay|apuestas deportivas en vivo|apuestas deportivas es|apuestas deportivas es pronosticos|apuestas deportivas españa|apuestas deportivas
españolas|apuestas deportivas esports|apuestas deportivas estadisticas|apuestas deportivas estrategias|apuestas deportivas
estrategias seguras|apuestas deportivas eurocopa|apuestas deportivas europa league|apuestas deportivas
f1|apuestas deportivas faciles de ganar|apuestas deportivas formula 1|apuestas deportivas foro|apuestas deportivas
foro futbol|apuestas deportivas foro tenis|apuestas deportivas francia argentina|apuestas deportivas
futbol|apuestas deportivas fútbol|apuestas deportivas futbol
argentino|apuestas deportivas futbol colombia|apuestas deportivas futbol español|apuestas deportivas gana|apuestas deportivas ganadas|apuestas deportivas ganar dinero
seguro|apuestas deportivas gane|apuestas deportivas golf|apuestas deportivas gratis|apuestas deportivas gratis con premios|apuestas deportivas gratis hoy|apuestas deportivas gratis sin deposito|apuestas deportivas handicap|apuestas deportivas handicap asiatico|apuestas deportivas hoy|apuestas
deportivas impuestos|apuestas deportivas interior argentina|apuestas deportivas juegos olimpicos|apuestas deportivas la liga|apuestas deportivas legales|apuestas
deportivas legales en colombia|apuestas deportivas libres
de impuestos|apuestas deportivas licencia españa|apuestas deportivas liga
española|apuestas deportivas listado|apuestas deportivas listado
clasico|apuestas deportivas madrid|apuestas deportivas mas seguras|apuestas deportivas
mejor pagadas|apuestas deportivas mejores|apuestas
deportivas mejores app|apuestas deportivas mejores casas|apuestas deportivas mejores cuotas|apuestas deportivas mejores paginas|apuestas deportivas
mexico|apuestas deportivas méxico|apuestas deportivas mlb|apuestas deportivas mlb
hoy|apuestas deportivas multiples|apuestas deportivas mundial|apuestas deportivas murcia|apuestas deportivas nba|apuestas deportivas nba
hoy|apuestas deportivas nfl|apuestas deportivas nhl|apuestas deportivas nuevas|apuestas deportivas ofertas|apuestas deportivas online|apuestas
deportivas online argentina|apuestas deportivas online chile|apuestas deportivas online colombia|apuestas deportivas
online en colombia|apuestas deportivas online españa|apuestas deportivas
online mexico|apuestas deportivas online paypal|apuestas deportivas online peru|apuestas deportivas
online por internet|apuestas deportivas pago paypal|apuestas deportivas para ganar dinero|apuestas deportivas para
hoy|apuestas deportivas para hoy pronosticos|apuestas deportivas partido suspendido|apuestas deportivas partidos de hoy|apuestas deportivas paypal|apuestas deportivas peru|apuestas
deportivas perú|apuestas deportivas peru vs ecuador|apuestas deportivas predicciones|apuestas deportivas promociones|apuestas deportivas pronostico|apuestas deportivas
pronóstico|apuestas deportivas pronostico hoy|apuestas deportivas pronosticos|apuestas deportivas pronósticos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos expertos|apuestas deportivas pronosticos
gratis|apuestas deportivas pronosticos nba|apuestas deportivas pronosticos tenis|apuestas deportivas que aceptan paypal|apuestas deportivas real madrid|apuestas deportivas regalo bienvenida|apuestas deportivas resultado exacto|apuestas deportivas
resultados|apuestas deportivas rugby|apuestas deportivas seguras|apuestas deportivas seguras
foro|apuestas deportivas seguras hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras para hoy|apuestas deportivas seguras telegram|apuestas deportivas
sevilla|apuestas deportivas simulador eurocopa|apuestas deportivas sin deposito|apuestas deportivas
sin deposito inicial|apuestas deportivas sin dinero|apuestas deportivas sin dinero real|apuestas deportivas sin registro|apuestas deportivas stake|apuestas deportivas stake 10|apuestas deportivas telegram españa|apuestas deportivas tenis|apuestas deportivas tenis
de mesa|apuestas deportivas tenis foro|apuestas deportivas tenis
hoy|apuestas deportivas tips|apuestas deportivas tipster|apuestas deportivas ufc|apuestas deportivas uruguay|apuestas deportivas valencia|apuestas deportivas valencia barcelona|apuestas deportivas venezuela|apuestas
deportivas virtuales|apuestas deportivas y casino|apuestas deportivas y casino online|apuestas deportivas.com|apuestas deportivas.com foro|apuestas deportivas.es|apuestas deportivos pronosticos|apuestas deposito minimo
1 euro|apuestas descenso a segunda|apuestas descenso a segunda b|apuestas
descenso la liga|apuestas descenso primera division|apuestas descenso segunda|apuestas dia|apuestas diarias seguras|apuestas dinero|apuestas dinero ficticio|apuestas dinero real|apuestas dinero virtual|apuestas directas|apuestas directo|apuestas directo futbol|apuestas division de honor juvenil|apuestas dnb|apuestas
doble oportunidad|apuestas doble resultado|apuestas dobles|apuestas dobles y triples|apuestas
dortmund barcelona|apuestas draft nba|apuestas draft nfl|apuestas ecuador vs argentina|apuestas ecuador vs venezuela|apuestas
egipto uruguay|apuestas el clasico|apuestas elecciones venezuela|apuestas empate|apuestas en baloncesto|apuestas en barcelona|apuestas en beisbol|apuestas en boxeo|apuestas en caballos|apuestas en carreras de caballos|apuestas en casino|apuestas en casino online|apuestas en casinos|apuestas en casinos online|apuestas en chile|apuestas en ciclismo|apuestas en colombia|apuestas en colombia de futbol|apuestas en directo|apuestas en directo futbol|apuestas en directo pronosticos|apuestas en el futbol|apuestas en el
tenis|apuestas en españa|apuestas en esports|apuestas en eventos deportivos
virtuales|apuestas en golf|apuestas en juegos|apuestas en la
champions league|apuestas en la eurocopa|apuestas en la liga|apuestas en la nba|apuestas en la nfl|apuestas en las vegas mlb|apuestas en las vegas nfl|apuestas en linea|apuestas en línea|apuestas en linea argentina|apuestas en linea boxeo|apuestas en linea chile|apuestas en linea colombia|apuestas en línea de fútbol|apuestas en linea
deportivas|apuestas en linea españa|apuestas en linea estados unidos|apuestas en linea futbol|apuestas en linea mexico|apuestas en línea
méxico|apuestas en linea mundial|apuestas en linea peru|apuestas en linea usa|apuestas en los esports|apuestas en madrid|apuestas en méxico|apuestas en mexico online|apuestas en nba|apuestas en partidos de futbol|apuestas en partidos
de futbol en vivo|apuestas en partidos de tenis en directo|apuestas en perú|apuestas en sevilla|apuestas en sistema|apuestas
en stake|apuestas en tenis|apuestas en tenis de mesa|apuestas
en valencia|apuestas en vivo|apuestas en vivo argentina|apuestas
en vivo casino|apuestas en vivo futbol|apuestas en vivo fútbol|apuestas en vivo nba|apuestas en vivo peru|apuestas en vivo tenis|apuestas en vivo ufc|apuestas equipo mbappe|apuestas equipos
de futbol|apuestas españa|apuestas españa alemania|apuestas españa alemania eurocopa|apuestas españa croacia|apuestas españa eurocopa|apuestas
españa francia|apuestas españa francia eurocopa|apuestas españa gana el mundial|apuestas españa gana eurocopa|apuestas españa gana mundial|apuestas españa georgia|apuestas españa holanda|apuestas españa inglaterra|apuestas españa inglaterra cuotas|apuestas
españa inglaterra eurocopa|apuestas españa italia|apuestas españa
mundial|apuestas españa paises bajos|apuestas español|apuestas español oviedo|apuestas espanyol barcelona|apuestas espanyol betis|apuestas espanyol villarreal|apuestas esport|apuestas esports|apuestas esports colombia|apuestas
esports españa|apuestas esports fifa|apuestas esports gratis|apuestas esports lol|apuestas esports peru|apuestas
esports valorant|apuestas estadisticas|apuestas estrategias|apuestas euro|apuestas euro copa|apuestas eurocopa|apuestas eurocopa campeon|apuestas eurocopa españa|apuestas eurocopa
favoritos|apuestas eurocopa femenina|apuestas
eurocopa final|apuestas eurocopa ganador|apuestas eurocopa hoy|apuestas eurocopa
sub 21|apuestas euroliga baloncesto|apuestas euroliga pronosticos|apuestas europa league|apuestas europa league hoy|apuestas europa league pronosticos|apuestas europa league pronósticos|apuestas euros|apuestas f1
abu dhabi|apuestas f1 bahrein|apuestas f1 canada|apuestas
f1 china|apuestas f1 cuotas|apuestas f1 hoy|apuestas
f1 las vegas|apuestas f1 miami|apuestas f1 monaco|apuestas faciles de ganar|apuestas fáciles de ganar|apuestas faciles para ganar|apuestas
favoritas|apuestas favorito champions|apuestas favoritos champions|apuestas favoritos eurocopa|apuestas favoritos mundial|apuestas fc barcelona|apuestas
final champions cuotas|apuestas final champions league|apuestas final champions peru|apuestas final copa|apuestas final copa
america|apuestas final copa de europa|apuestas final copa del rey|apuestas final
copa europa|apuestas final copa libertadores|apuestas final copa rey|apuestas final de copa|apuestas final de
copa del rey|apuestas final del mundial|apuestas final euro|apuestas final eurocopa|apuestas final europa
league|apuestas final libertadores|apuestas final mundial|apuestas final
nba|apuestas final rugby|apuestas final uefa europa league|apuestas final.mundial|apuestas finales de conferencia nfl|apuestas finales nba|apuestas fiorentina betis|apuestas formula|apuestas
formula 1|apuestas fórmula 1|apuestas fórmula 1 pronósticos|apuestas
formula uno|apuestas foro|apuestas foro nba|apuestas francia argentina|apuestas francia españa|apuestas
futbol|apuestas fútbol|apuestas futbol americano|apuestas futbol americano nfl|apuestas futbol argentina|apuestas futbol argentino|apuestas futbol champions
league|apuestas futbol chile|apuestas futbol colombia|apuestas futbol consejos|apuestas
futbol en directo|apuestas fútbol en directo|apuestas futbol en vivo|apuestas fútbol en vivo|apuestas futbol
españa|apuestas futbol español|apuestas fútbol español|apuestas futbol eurocopa|apuestas futbol
femenino|apuestas futbol foro|apuestas futbol gratis|apuestas futbol
hoy|apuestas fútbol hoy|apuestas futbol juegos olimpicos|apuestas
futbol mexico|apuestas futbol mundial|apuestas futbol online|apuestas futbol para hoy|apuestas futbol peru|apuestas futbol pronosticos|apuestas futbol sala|apuestas futbol telegram|apuestas futbol virtual|apuestas galgos|apuestas galgos en directo|apuestas galgos hoy|apuestas galgos online|apuestas galgos pronosticos|apuestas galgos
trucos|apuestas gana|apuestas gana colombia|apuestas gana resultados|apuestas
ganadas|apuestas ganadas hoy|apuestas ganador champions league|apuestas ganador copa
america|apuestas ganador copa del rey|apuestas ganador copa del rey baloncesto|apuestas ganador copa libertadores|apuestas
ganador de la eurocopa|apuestas ganador de la liga|apuestas ganador del mundial|apuestas ganador eurocopa|apuestas ganador europa league|apuestas ganador f1|apuestas ganador la liga|apuestas ganador
liga española|apuestas ganador mundial|apuestas ganador
mundial baloncesto|apuestas ganador mundial f1|apuestas ganador nba|apuestas ganadores eurocopa|apuestas ganadores
mundial|apuestas ganar champions|apuestas ganar eurocopa|apuestas ganar liga|apuestas
ganar mundial|apuestas ganar nba|apuestas getafe
valencia|apuestas ghana uruguay|apuestas girona|apuestas girona athletic|apuestas girona betis|apuestas girona
campeon de liga|apuestas girona campeon liga|apuestas girona gana la liga|apuestas girona real madrid|apuestas girona real
sociedad|apuestas goleador eurocopa|apuestas goleadores eurocopa|apuestas goles asiaticos|apuestas
golf|apuestas golf masters|apuestas golf pga|apuestas granada barcelona|apuestas grand slam de tenis|apuestas gratis|apuestas gratis casino|apuestas gratis con premios|apuestas gratis hoy|apuestas gratis para hoy|apuestas
gratis por registro|apuestas gratis puntos|apuestas gratis regalos|apuestas gratis sin deposito|apuestas gratis sin depósito|apuestas gratis sin ingreso|apuestas gratis sports|apuestas gratis y ganar premios|apuestas grupo a eurocopa|apuestas grupos eurocopa|apuestas handicap|apuestas handicap asiatico|apuestas handicap baloncesto|apuestas handicap como
funciona|apuestas handicap nba|apuestas handicap
nfl|apuestas hipicas online|apuestas hípicas
online|apuestas hipicas venezuela|apuestas hockey|apuestas hockey hielo|apuestas
hockey patines|apuestas hockey sobre hielo|apuestas holanda argentina|apuestas holanda vs argentina|apuestas hoy|apuestas hoy champions|apuestas hoy futbol|apuestas hoy nba|apuestas hoy pronosticos|apuestas hoy seguras|apuestas impuestos|apuestas inglaterra paises
bajos|apuestas inter barca|apuestas inter barcelona|apuestas juego|apuestas juegos|apuestas juegos en linea|apuestas juegos olimpicos|apuestas juegos olímpicos|apuestas juegos olimpicos
baloncesto|apuestas juegos online|apuestas juegos virtuales|apuestas jugador sevilla|apuestas jugadores nba|apuestas kings
league americas|apuestas la liga|apuestas la liga española|apuestas la liga hoy|apuestas
la liga santander|apuestas las vegas mlb|apuestas las vegas
nba|apuestas las vegas nfl|apuestas league of legends mundial|apuestas legal|apuestas legales|apuestas legales en colombia|apuestas legales en españa|apuestas legales en estados unidos|apuestas legales
españa|apuestas leganes betis|apuestas libertadores|apuestas licencia|apuestas liga 1 peru|apuestas liga argentina|apuestas liga
bbva pronosticos|apuestas liga de campeones|apuestas liga de campeones de baloncesto|apuestas liga de campeones de hockey|apuestas liga españa|apuestas liga española|apuestas liga santander pronosticos|apuestas ligas de futbol|apuestas linea|apuestas linea de gol|apuestas liverpool
barcelona|apuestas liverpool real madrid|apuestas lol mundial|apuestas madrid|apuestas madrid arsenal|apuestas madrid
atletico|apuestas madrid atletico champions|apuestas madrid
barca|apuestas madrid barça|apuestas madrid barca hoy|apuestas madrid barca supercopa|apuestas madrid barcelona|apuestas
madrid barsa|apuestas madrid bayern|apuestas madrid betis|apuestas madrid borussia|apuestas madrid campeon champions|apuestas
madrid celta|apuestas madrid city|apuestas madrid dortmund|apuestas madrid gana la liga|apuestas
madrid gana liga|apuestas madrid hoy|apuestas madrid liverpool|apuestas
madrid osasuna|apuestas madrid sevilla|apuestas madrid valencia|apuestas madrid vs arsenal|apuestas madrid vs barcelona|apuestas mallorca osasuna|apuestas mallorca real sociedad|apuestas manchester athletic|apuestas manchester city real
madrid|apuestas mas faciles de ganar|apuestas mas seguras|apuestas mas seguras para hoy|apuestas masters de golf|apuestas masters de tenis|apuestas
maximo goleador eurocopa|apuestas maximo goleador mundial|apuestas mejor
jugador eurocopa|apuestas mejores casinos online|apuestas
mexico|apuestas méxico|apuestas mexico polonia|apuestas méxico polonia|apuestas mlb|apuestas mlb hoy|apuestas mlb las vegas|apuestas mlb para hoy|apuestas mlb pronosticos|apuestas
mlb usa|apuestas mma ufc|apuestas momios|apuestas multiples|apuestas múltiples|apuestas multiples como
funcionan|apuestas multiples el gordo|apuestas multiples futbol|apuestas mundial|apuestas mundial
2026|apuestas mundial baloncesto|apuestas mundial balonmano|apuestas mundial brasil|apuestas mundial campeon|apuestas mundial
ciclismo|apuestas mundial clubes|apuestas mundial de baloncesto|apuestas mundial
de ciclismo|apuestas mundial de clubes|apuestas mundial
de futbol|apuestas mundial de fútbol|apuestas mundial de rugby|apuestas mundial f1|apuestas mundial favoritos|apuestas mundial femenino|apuestas mundial formula 1|apuestas mundial futbol|apuestas mundial ganador|apuestas mundial lol|apuestas
mundial moto gp|apuestas mundial motogp|apuestas mundial rugby|apuestas mundial sub 17|apuestas mundiales|apuestas mundialistas|apuestas
mvp eurocopa|apuestas mvp nba|apuestas mvp nfl|apuestas nacionales de colombia|apuestas nba|apuestas nba
all star|apuestas nba campeon|apuestas nba consejos|apuestas nba esta noche|apuestas nba finals|apuestas nba
gratis|apuestas nba hoy|apuestas nba hoy jugadores|apuestas nba hoy pronosticos|apuestas nba para hoy|apuestas nba playoffs|apuestas nba pronosticos|apuestas nba pronósticos|apuestas
nba pronosticos hoy|apuestas nba tipster|apuestas nfl|apuestas nfl hoy|apuestas nfl las vegas|apuestas nfl
playoffs|apuestas nfl pronosticos|apuestas nfl pronósticos|apuestas nfl
semana 4|apuestas nfl super bowl|apuestas
nhl|apuestas nhl pronosticos|apuestas octavos eurocopa|apuestas ofertas|apuestas online|apuestas online argentina|apuestas online
argentina legal|apuestas online bono|apuestas online bono bienvenida|apuestas online boxeo|apuestas online caballos|apuestas online carreras de caballos|apuestas online casino|apuestas online champions league|apuestas online chile|apuestas online ciclismo|apuestas online colombia|apuestas
online comparativa|apuestas online con paypal|apuestas online de caballos|apuestas online deportivas|apuestas online en argentina|apuestas online en peru|apuestas online espana|apuestas online españa|apuestas online esports|apuestas online foro|apuestas online futbol|apuestas online futbol españa|apuestas online
golf|apuestas online gratis|apuestas online gratis sin deposito|apuestas
online juegos|apuestas online mexico|apuestas online
mma|apuestas online movil|apuestas online nba|apuestas online net|apuestas online nuevas|apuestas
online opiniones|apuestas online paypal|apuestas online peru|apuestas online seguras|apuestas online sin dinero|apuestas online sin registro|apuestas online
tenis|apuestas online ufc|apuestas online uruguay|apuestas online venezuela|apuestas open britanico golf|apuestas osasuna athletic|apuestas osasuna barcelona|apuestas osasuna
real madrid|apuestas osasuna sevilla|apuestas osasuna valencia|apuestas over|apuestas over 2.5|apuestas over
under|apuestas paginas|apuestas pago anticipado|apuestas paises bajos ecuador|apuestas paises
bajos inglaterra|apuestas países bajos qatar|apuestas para boxeo|apuestas para champions league|apuestas para el clasico|apuestas para el dia de hoy|apuestas para el
mundial|apuestas para el partido de hoy|apuestas para eurocopa|apuestas
para europa league|apuestas para futbol|apuestas para ganar|apuestas para ganar dinero|apuestas para ganar
dinero facil|apuestas para ganar en la ruleta|apuestas para ganar la champions|apuestas para ganar
la eurocopa|apuestas para ganar la europa league|apuestas para ganar la
liga|apuestas para ganar siempre|apuestas para hacer|apuestas para hoy|apuestas para hoy de
futbol|apuestas para hoy europa league|apuestas para hoy futbol|apuestas para juegos|apuestas para la champions league|apuestas para la copa del rey|apuestas para la eurocopa|apuestas para la europa league|apuestas
para la final de la eurocopa|apuestas para la nba hoy|apuestas para los
partidos de hoy|apuestas para partidos de hoy|apuestas para ufc|apuestas partido|apuestas partido aplazado|apuestas partido champions|apuestas partido colombia|apuestas partido españa marruecos|apuestas partido mundial|apuestas partido suspendido|apuestas partidos|apuestas partidos champions league|apuestas partidos csgo|apuestas partidos de futbol|apuestas partidos de
futbol hoy|apuestas partidos de hoy|apuestas partidos eurocopa|apuestas partidos futbol|apuestas partidos hoy|apuestas partidos mundial|apuestas paypal|apuestas peleas de boxeo|apuestas peru|apuestas perú|apuestas
peru brasil|apuestas peru chile|apuestas peru paraguay|apuestas peru uruguay|apuestas peru vs chile|apuestas peru vs colombia|apuestas pichichi eurocopa|apuestas plataforma|apuestas playoff|apuestas playoff ascenso|apuestas playoff ascenso a primera|apuestas playoff nba|apuestas playoff segunda|apuestas playoff segunda b|apuestas playoffs nba|apuestas playoffs nfl|apuestas polonia argentina|apuestas por argentina|apuestas por
internet mexico|apuestas por internet para ganar dinero|apuestas por paypal|apuestas por ronda boxeo|apuestas por sistema|apuestas
portugal uruguay|apuestas pre partido|apuestas predicciones|apuestas predicciones futbol|apuestas
primera division|apuestas primera division españa|apuestas promociones|apuestas pronostico|apuestas pronosticos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos|apuestas pronosticos deportivos tenis|apuestas
pronosticos futbol|apuestas pronosticos gratis|apuestas pronosticos nba|apuestas pronosticos
tenis|apuestas prorroga|apuestas psg barca|apuestas psg barcelona|apuestas puntos por tarjetas|apuestas puntos
tarjetas|apuestas que aceptan paypal|apuestas que es handicap|apuestas que puedes hacer con tu novia|apuestas
que siempre ganaras|apuestas que significa|apuestas quien bajara a segunda|apuestas quién bajara a
segunda|apuestas quien gana el mundial|apuestas quien gana eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la champions|apuestas quien gana la eurocopa|apuestas quien gana la liga|apuestas quien ganara el mundial|apuestas quién ganará el mundial|apuestas quien ganara la champions|apuestas quien ganara la eurocopa|apuestas quien ganara la liga|apuestas rayo barcelona|apuestas real madrid|apuestas real madrid arsenal|apuestas real
madrid athletic|apuestas real madrid atletico|apuestas real madrid
atletico champions|apuestas real madrid atletico de madrid|apuestas
real madrid atlético de madrid|apuestas real madrid atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid barcelona|apuestas real madrid
bayern|apuestas real madrid betis|apuestas real madrid borussia|apuestas real madrid campeon champions|apuestas real madrid celta|apuestas real madrid champions|apuestas real madrid city|apuestas real madrid girona|apuestas real madrid hoy|apuestas real madrid
liverpool|apuestas real madrid manchester city|apuestas real madrid
osasuna|apuestas real madrid real sociedad|apuestas real madrid
valencia|apuestas real madrid villarreal|apuestas
real madrid vs arsenal|apuestas real madrid vs atletico|apuestas real madrid
vs atlético|apuestas real madrid vs atletico madrid|apuestas real madrid vs barcelona|apuestas real madrid vs betis|apuestas real madrid vs sevilla|apuestas
real madrid vs valencia|apuestas real sociedad|apuestas
real sociedad athletic|apuestas real sociedad barcelona|apuestas real sociedad betis|apuestas
real sociedad psg|apuestas real sociedad real madrid|apuestas real sociedad valencia|apuestas recomendadas hoy|apuestas regalo de bienvenida|apuestas registro|apuestas resultado exacto|apuestas resultados|apuestas resultados eurocopa|apuestas retirada tenis|apuestas roma barcelona|apuestas roma sevilla|apuestas rugby|apuestas rugby mundial|apuestas
rugby world cup|apuestas ruleta seguras|apuestas segunda|apuestas
segunda b|apuestas segunda division|apuestas segunda división|apuestas segunda division b|apuestas
segunda division españa|apuestas seguras|apuestas seguras baloncesto|apuestas seguras calculadora|apuestas seguras en la ruleta|apuestas seguras eurocopa|apuestas seguras foro|apuestas seguras futbol|apuestas seguras futbol hoy|apuestas seguras gratis|apuestas seguras hoy|apuestas seguras hoy futbol|apuestas seguras nba|apuestas seguras nba hoy|apuestas seguras para este fin de
semana|apuestas seguras para ganar dinero|apuestas seguras para hoy|apuestas seguras para
hoy fútbol|apuestas seguras para hoy pronósticos|apuestas seguras para
mañana|apuestas seguras ruleta|apuestas seguras telegram|apuestas seguras tenis|apuestas
semifinales eurocopa|apuestas senegal paises bajos|apuestas sevilla|apuestas sevilla athletic|apuestas
sevilla atletico de madrid|apuestas sevilla barcelona|apuestas sevilla betis|apuestas sevilla campeon liga|apuestas sevilla celta|apuestas sevilla gana la liga|apuestas sevilla girona|apuestas sevilla
inter|apuestas sevilla jugador|apuestas sevilla juventus|apuestas sevilla leganes|apuestas sevilla madrid|apuestas
sevilla manchester united|apuestas sevilla osasuna|apuestas sevilla real madrid|apuestas sevilla real
sociedad|apuestas sevilla roma|apuestas sevilla valencia|apuestas significa|apuestas simples ejemplos|apuestas simples o combinadas|apuestas sin deposito|apuestas sin deposito inicial|apuestas
sin deposito minimo|apuestas sin dinero|apuestas sin dinero real|apuestas sin empate|apuestas sin empate que significa|apuestas sin ingreso minimo|apuestas sin registro|apuestas sistema|apuestas sistema calculadora|apuestas sistema
como funciona|apuestas sistema trixie|apuestas sociedad|apuestas sorteo copa del rey|apuestas
stake|apuestas stake 10|apuestas stake 10 hoy|apuestas
super bowl favorito|apuestas super rugby|apuestas supercopa españa|apuestas superliga argentina|apuestas tarjeta roja|apuestas tarjetas|apuestas tarjetas amarillas|apuestas tenis|apuestas tenis atp|apuestas tenis consejos|apuestas tenis
copa davis|apuestas tenis de mesa|apuestas tenis de mesa pronosticos|apuestas tenis en vivo|apuestas tenis
femenino|apuestas tenis hoy|apuestas tenis itf|apuestas tenis pronosticos|apuestas tenis pronósticos|apuestas tenis retirada|apuestas tenis roland garros|apuestas
tenis seguras|apuestas tenis wimbledon|apuestas tenis wta|apuestas tercera
division|apuestas tercera division españa|apuestas tipos|apuestas tips|apuestas tipster|apuestas tipster para hoy|apuestas topuria holloway cuotas|apuestas torneos de golf|apuestas torneos de tenis|apuestas trucos|apuestas uefa
champions league|apuestas uefa europa league|apuestas ufc|apuestas ufc
chile|apuestas ufc como funciona|apuestas ufc hoy|apuestas
ufc ilia topuria|apuestas ufc online|apuestas ufc pronósticos|apuestas ufc telegram|apuestas ufc topuria|apuestas under over|apuestas unionistas villarreal|apuestas uruguay|apuestas uruguay colombia|apuestas
uruguay corea|apuestas uruguay vs colombia|apuestas us open golf|apuestas us open tenis|apuestas
valencia|apuestas valencia barcelona|apuestas valencia betis|apuestas
valencia madrid|apuestas valencia real madrid|apuestas valladolid barcelona|apuestas valladolid valencia|apuestas valor app|apuestas valor
en directo|apuestas valor galgos|apuestas venezuela|apuestas venezuela argentina|apuestas venezuela bolivia|apuestas venezuela ecuador|apuestas
villarreal|apuestas villarreal athletic|apuestas villarreal barcelona|apuestas villarreal bayern|apuestas villarreal betis|apuestas villarreal liverpool|apuestas villarreal manchester|apuestas villarreal manchester united|apuestas villarreal
vs real madrid|apuestas virtuales|apuestas virtuales colombia|apuestas virtuales futbol|apuestas virtuales sin dinero|apuestas vivo|apuestas
vuelta a españa|apuestas vuelta españa|apuestas william hill partidos de hoy|apuestas y
casino|apuestas y casinos|apuestas y juegos
de azar|apuestas y pronosticos|apuestas y pronosticos
de futbol|apuestas y pronosticos deportivos|apuestas y resultados|apuestas-deportivas|apuestas-deportivas.es pronosticos|arbitro
nba apuestas|argentina apuestas|argentina colombia apuestas|argentina croacia apuestas|argentina francia apuestas|argentina mexico apuestas|argentina peru
apuestas|argentina uruguay apuestas|argentina vs bolivia apuestas|argentina vs chile apuestas|argentina vs colombia apuestas|argentina
vs francia apuestas|argentina vs. colombia apuestas|asi se gana en las apuestas deportivas|asiatico apuestas|asiatico
en apuestas|asiaticos apuestas|athletic barcelona apuestas|athletic manchester united apuestas|athletic osasuna apuestas|athletic real madrid apuestas|atletico barcelona apuestas|atletico de madrid apuestas|atlético de madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid
real madrid apuestas|atletico de madrid vs barcelona apuestas|atletico madrid real madrid apuestas|atletico madrid vs real madrid apuestas|atletico real madrid apuestas|atletico
vs real madrid apuestas|avisador de cuotas apuestas|bajada de cuotas apuestas|baloncesto apuestas|barbastro barcelona apuestas|barca apuestas|barca bayern apuestas|barca
inter apuestas|barca madrid apuestas|barça madrid apuestas|barca vs
atletico apuestas|barca vs madrid apuestas|barca vs real madrid apuestas|barcelona – real madrid apuestas|barcelona apuestas|barcelona atletico apuestas|barcelona atletico de madrid apuestas|barcelona atletico madrid apuestas|barcelona betis apuestas|barcelona casa de apuestas|barcelona inter apuestas|barcelona
psg apuestas|barcelona real madrid apuestas|barcelona real sociedad apuestas|barcelona sevilla apuestas|barcelona valencia apuestas|barcelona vs athletic bilbao apuestas|barcelona vs atlético
madrid apuestas|barcelona vs betis apuestas|barcelona vs celta de vigo apuestas|barcelona vs espanyol apuestas|barcelona vs girona apuestas|barcelona vs madrid apuestas|barcelona vs
real madrid apuestas|barcelona vs real sociedad apuestas|barcelona vs sevilla apuestas|barcelona vs
villarreal apuestas|base de datos cuotas apuestas deportivas|bayern real madrid apuestas|beisbol apuestas|best
america apuestas|bet apuestas chile|bet apuestas en vivo|betis – chelsea apuestas|betis
apuestas|betis barcelona apuestas|betis chelsea apuestas|betis madrid apuestas|betis sevilla apuestas|betsson tu sitio de apuestas online|blog apuestas baloncesto|blog apuestas ciclismo|blog apuestas nba|blog apuestas
tenis|blog de apuestas de tenis|bono apuestas|bono apuestas deportivas|bono apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bono apuestas gratis|bono apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono apuestas
sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas|bono bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono bienvenida
apuestas españa|bono bienvenida apuestas sin deposito|bono bienvenida apuestas sin depósito|bono bienvenida casa apuestas|bono bienvenida casa de apuestas|bono
bienvenida marca apuestas|bono casa apuestas|bono casa
de apuestas|bono casa de apuestas sin ingreso|bono casas de apuestas|bono de apuestas|bono de apuestas gratis sin deposito|bono
de bienvenida apuestas|bono de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bono de bienvenida casa
de apuestas|bono de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bono de casas de apuestas|bono de registro apuestas|bono
de registro apuestas deportivas|bono de registro casa de apuestas|bono gratis apuestas|bono marca apuestas|bono por registro apuestas|bono por
registro apuestas deportivas|bono por registro casa de apuestas|bono registro apuestas|bono sin deposito
apuestas|bono sin depósito apuestas|bono sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bono sin depósito apuestas deportivas|bono sin deposito casa
de apuestas|bono sin deposito marca apuestas|bono
sin ingreso apuestas|bono sin ingreso apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas|bonos apuestas colombia|bonos apuestas deportivas|bonos apuestas
deportivas sin deposito|bonos apuestas gratis|bonos apuestas sin deposito|bonos apuestas
sin depósito|bonos bienvenida apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas apuestas|bonos bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos casa de apuestas|bonos casas apuestas|bonos
casas de apuestas|bonos casas de apuestas colombia|bonos casas de apuestas
deportivas|bonos casas de apuestas españa|bonos casas de apuestas nuevas|bonos casas de
apuestas sin deposito|bonos casas de apuestas sin depósito|bonos de apuestas|bonos
de apuestas deportivas|bonos de apuestas gratis|bonos de apuestas sin deposito|bonos de
bienvenida apuestas|bonos de bienvenida apuestas deportivas|bonos
de bienvenida casa de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida de casas de apuestas|bonos de bienvenida en casas de apuestas|bonos de casas de
apuestas|bonos de casas de apuestas sin deposito|bonos en casa de apuestas|bonos en casas
de apuestas sin deposito|bonos gratis apuestas|bonos gratis apuestas deportivas|bonos gratis casas de
apuestas|bonos gratis sin deposito apuestas|bonos paginas de apuestas|bonos registro casas de apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas|bonos sin depósito apuestas|bonos sin deposito apuestas deportivas|bonos
sin deposito casas de apuestas|bot de apuestas deportivas gratis|boxeo apuestas|brasil colombia apuestas|brasil peru apuestas|brasil vs colombia apuestas|buenas apuestas
para hoy|buscador cuotas apuestas|buscador de apuestas seguras|buscador de cuotas apuestas|buscador de cuotas de apuestas|buscar apuestas seguras|caballos apuestas|calculador de
apuestas|calculador de cuotas apuestas|calculadora
apuestas|calculadora apuestas combinadas|calculadora apuestas de sistema|calculadora apuestas deportivas|calculadora apuestas deportivas seguras|calculadora apuestas multiples|calculadora apuestas segura|calculadora apuestas seguras|calculadora apuestas sistema|calculadora apuestas yankee|calculadora arbitraje apuestas|calculadora cubrir apuestas|calculadora cuotas
apuestas|calculadora de apuestas|calculadora de apuestas combinadas|calculadora de apuestas de futbol|calculadora de apuestas de sistema|calculadora de apuestas deportivas|calculadora de apuestas multiples|calculadora de
apuestas seguras|calculadora de apuestas sistema|calculadora de
apuestas surebets|calculadora de arbitraje apuestas|calculadora de
cuotas apuestas|calculadora de cuotas de apuestas|calculadora
para apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson apuestas|calculadora poisson apuestas deportivas|calculadora poisson para apuestas|calculadora scalping apuestas deportivas|calculadora sistema apuestas|calculadora stake apuestas|calculadora trading apuestas|calcular apuestas|calcular apuestas deportivas|calcular apuestas futbol|calcular apuestas sistema|calcular cuotas apuestas|calcular cuotas apuestas combinadas|calcular cuotas apuestas deportivas|calcular
cuotas de apuestas|calcular ganancias apuestas deportivas|calcular momios apuestas|calcular probabilidad cuota apuestas|calcular stake apuestas|calcular unidades apuestas|calcular yield apuestas|calculo de apuestas|calculo de apuestas deportivas|cambio de cuotas
apuestas|campeon champions apuestas|campeon eurocopa apuestas|campeon liga apuestas|campeon nba apuestas|canales
de apuestas gratis|carrera de caballos apuestas|carrera de caballos
apuestas juego|carrera de caballos con apuestas|carrera de galgos apuestas|carreras de
caballos apuestas|carreras de caballos apuestas
online|carreras de caballos con apuestas|carreras de caballos juegos de apuestas|carreras de galgos
apuestas|carreras de galgos apuestas online|carreras de galgos apuestas trucos|carreras
galgos apuestas|casa apuestas argentina|casa apuestas atletico de madrid|casa apuestas barcelona|casa apuestas betis|casa apuestas bono bienvenida|casa
apuestas bono gratis|casa apuestas bono sin deposito|casa apuestas cerca de mi|casa
apuestas chile|casa apuestas colombia|casa apuestas con mejores cuotas|casa apuestas deportivas|casa apuestas españa|casa apuestas española|casa apuestas eurocopa|casa apuestas
futbol|casa apuestas mejores cuotas|casa apuestas mundial|casa apuestas nueva|casa apuestas nuevas|casa apuestas online|casa apuestas peru|casa apuestas
valencia|casa de apuestas|casa de apuestas 10 euros
gratis|casa de apuestas argentina|casa de apuestas atletico de madrid|casa de apuestas baloncesto|casa de apuestas barcelona|casa de apuestas
beisbol|casa de apuestas betis|casa de apuestas bono|casa de apuestas bono bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas bono gratis|casa de apuestas bono por registro|casa de apuestas bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas boxeo|casa de apuestas caballos|casa de apuestas
carreras de caballos|casa de apuestas cerca de
mi|casa de apuestas cerca de mí|casa de apuestas champions league|casa de apuestas chile|casa de apuestas ciclismo|casa de apuestas colombia|casa de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casa de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casa de apuestas con cuotas mas altas|casa de apuestas con esports|casa de apuestas con las mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con licencia en españa|casa de apuestas con mejores
cuotas|casa de apuestas con pago anticipado|casa de apuestas con paypal|casa de apuestas copa america|casa de apuestas de
caballos|casa de apuestas de colombia|casa de apuestas de españa|casa de
apuestas de futbol|casa de apuestas de fútbol|casa de
apuestas de futbol peru|casa de apuestas de peru|casa de apuestas del madrid|casa de apuestas
del real madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas|casa de apuestas deportivas cerca de mi|casa de apuestas deportivas en argentina|casa de apuestas deportivas en chile|casa
de apuestas deportivas en colombia|casa de apuestas deportivas en españa|casa de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas españa|casa
de apuestas deportivas españolas|casa de apuestas deportivas madrid|casa de apuestas deportivas mexico|casa de apuestas deportivas online|casa
de apuestas deportivas peru|casa de apuestas deposito 5 euros|casa de apuestas
deposito minimo|casa de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casa
de apuestas depósito mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas en españa|casa de
apuestas en linea|casa de apuestas en madrid|casa de apuestas en perú|casa de apuestas en vivo|casa de apuestas españa|casa de apuestas españa
inglaterra|casa de apuestas española|casa de apuestas españolas|casa de apuestas esports|casa
de apuestas eurocopa|casa de apuestas europa league|casa de apuestas f1|casa de apuestas formula
1|casa de apuestas futbol|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo|casa de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas
ingreso mínimo 1 euro|casa de apuestas legales|casa de apuestas legales en colombia|casa de apuestas legales
en españa|casa de apuestas libertadores|casa de apuestas liga española|casa de apuestas madrid|casa de apuestas mas
segura|casa de apuestas mejores|casa de apuestas méxico|casa de
apuestas minimo 5 euros|casa de apuestas mlb|casa de
apuestas mundial|casa de apuestas nba|casa de apuestas nfl|casa de apuestas
nueva|casa de apuestas nuevas|casa de apuestas oficial del
real madrid|casa de apuestas oficial real madrid|casa
de apuestas online|casa de apuestas online argentina|casa de apuestas online chile|casa de apuestas online
españa|casa de apuestas online mexico|casa de apuestas
online paraguay|casa de apuestas online peru|casa de apuestas online
usa|casa de apuestas online venezuela|casa de apuestas pago anticipado|casa de apuestas para boxeo|casa de apuestas para ufc|casa de apuestas peru|casa de
apuestas perú|casa de apuestas peru online|casa de apuestas por paypal|casa de apuestas promociones|casa de apuestas que
regalan dinero|casa de apuestas real madrid|casa
de apuestas regalo de bienvenida|casa de apuestas sevilla|casa de apuestas sin dinero|casa de apuestas sin ingreso minimo|casa de
apuestas sin licencia en españa|casa de apuestas sin minimo
de ingreso|casa de apuestas stake|casa de apuestas tenis|casa de apuestas ufc|casa de apuestas valencia|casa de apuestas venezuela|casa de apuestas
virtuales|casa de apuestas vive la suerte|casa oficial de apuestas del real
madrid|casas apuestas asiaticas|casas apuestas bono sin deposito|casas apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas apuestas caballos|casas apuestas chile|casas apuestas ciclismo|casas apuestas con licencia|casas apuestas con licencia
en españa|casas apuestas deportivas|casas apuestas deportivas colombia|casas apuestas deportivas españa|casas apuestas deportivas españolas|casas apuestas deportivas
nuevas|casas apuestas españa|casas apuestas españolas|casas apuestas esports|casas apuestas eurocopa|casas apuestas golf|casas apuestas
ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas apuestas legales|casas apuestas legales españa|casas apuestas licencia|casas apuestas licencia españa|casas apuestas mexico|casas apuestas mundial|casas apuestas nba|casas apuestas nuevas|casas apuestas nuevas españa|casas apuestas ofertas|casas
apuestas online|casas apuestas paypal|casas apuestas peru|casas apuestas sin licencia|casas apuestas tenis|casas asiaticas apuestas|casas de apuestas|casas de apuestas 5 euros|casas de apuestas app|casas de apuestas argentinas|casas de apuestas asiaticas|casas de apuestas baloncesto|casas de
apuestas barcelona|casas de apuestas bono bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bono por registro|casas de apuestas bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas bono sin ingreso|casas de apuestas bonos|casas de apuestas
bonos de bienvenida|casas de apuestas bonos gratis|casas de apuestas bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas boxeo|casas de apuestas caballos|casas de apuestas carreras de caballos|casas de apuestas casino|casas de apuestas casino online|casas de apuestas cerca de mi|casas de apuestas champions league|casas de apuestas chile|casas de
apuestas ciclismo|casas de apuestas colombia|casas de
apuestas com|casas de apuestas con app|casas de apuestas con apuestas gratis|casas
de apuestas con bono|casas de apuestas con bono de bienvenida|casas de apuestas con bono de registro|casas de
apuestas con bono por registro|casas de apuestas con bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas con bonos|casas de apuestas con bonos gratis|casas de
apuestas con bonos sin deposito|casas de apuestas con deposito
minimo|casas de apuestas con esports|casas de apuestas con handicap
asiatico|casas de apuestas con licencia|casas de
apuestas con licencia en españa|casas de apuestas con licencia españa|casas de apuestas con licencia española|casas de apuestas con mejores cuotas|casas de
apuestas con pago anticipado|casas de apuestas con paypal|casas de apuestas
con paypal en perú|casas de apuestas con promociones|casas de
apuestas con ruleta en vivo|casas de apuestas copa del rey|casas
de apuestas de caballos|casas de apuestas de españa|casas de apuestas de futbol|casas de apuestas de fútbol|casas de
apuestas de peru|casas de apuestas deportivas|casas de apuestas deportivas asiaticas|casas de apuestas deportivas colombia|casas de apuestas deportivas comparativa|casas de apuestas deportivas con paypal|casas
de apuestas deportivas en chile|casas de apuestas deportivas en españa|casas de
apuestas deportivas en linea|casas de apuestas deportivas en madrid|casas
de apuestas deportivas en mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas en peru|casas de apuestas deportivas en sevilla|casas de
apuestas deportivas en valencia|casas de apuestas deportivas españa|casas de apuestas
deportivas españolas|casas de apuestas deportivas legales|casas de apuestas deportivas madrid|casas de apuestas deportivas mexico|casas de apuestas deportivas nuevas|casas de apuestas deportivas
online|casas de apuestas deportivas peru|casas de apuestas
deportivas perú|casas de apuestas deposito minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas depósito
mínimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas dinero gratis|casas de apuestas en argentina|casas de apuestas en barcelona|casas
de apuestas en chile|casas de apuestas en colombia|casas de apuestas en españa|casas de apuestas en españa online|casas de apuestas en linea|casas de apuestas en madrid|casas de apuestas en méxico|casas de apuestas en peru|casas de apuestas
en perú|casas de apuestas en sevilla|casas de apuestas en uruguay|casas de apuestas en valencia|casas de apuestas en venezuela|casas de apuestas equipos de futbol|casas de apuestas españa|casas de apuestas españa alemania|casas de apuestas españa inglaterra|casas de apuestas españa licencia|casas de apuestas españa nuevas|casas de apuestas
españa online|casas de apuestas española|casas
de apuestas españolas|casas de apuestas españolas con licencia|casas de apuestas españolas
online|casas de apuestas esports|casas de apuestas eurocopa|casas
de apuestas eurocopa 2024|casas de apuestas europa league|casas
de apuestas f1|casas de apuestas fisicas en barcelona|casas de apuestas
fisicas en españa|casas de apuestas formula 1|casas de apuestas fuera
de españa|casas de apuestas futbol|casas de apuestas
fútbol|casas de apuestas futbol españa|casas de apuestas ganador
eurocopa|casas de apuestas gratis|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 1 euro|casas de apuestas ingreso minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas inter barcelona|casas de apuestas legales|casas de apuestas legales en colombia|casas de apuestas legales en españa|casas de apuestas legales en mexico|casas
de apuestas legales españa|casas de apuestas legales
mx|casas de apuestas licencia|casas de apuestas licencia españa|casas de apuestas lista|casas
de apuestas madrid|casas de apuestas mas seguras|casas
de apuestas mejores bonos|casas de apuestas mejores cuotas|casas de apuestas mexico|casas de apuestas méxico|casas de apuestas
minimo 5 euros|casas de apuestas mlb|casas de
apuestas mundial|casas de apuestas mundial baloncesto|casas de apuestas mundiales|casas de apuestas nba|casas de apuestas no reguladas en españa|casas de apuestas nueva ley|casas de apuestas nuevas|casas de apuestas nuevas en colombia|casas de apuestas nuevas en españa|casas de apuestas nuevas españa|casas
de apuestas ofertas|casas de apuestas online|casas de apuestas online
argentina|casas de apuestas online colombia|casas de apuestas online deportivas|casas de apuestas online ecuador|casas de apuestas online en argentina|casas de apuestas online
en chile|casas de apuestas online en colombia|casas de apuestas online en españa|casas de apuestas online en mexico|casas
de apuestas online españa|casas de apuestas online mas fiables|casas de apuestas
online mexico|casas de apuestas online nuevas|casas de apuestas online peru|casas de apuestas
online usa|casas de apuestas online venezuela|casas de apuestas pago paypal|casas de apuestas para ufc|casas de apuestas paypal|casas de
apuestas peru bono sin deposito|casas de apuestas presenciales en españa|casas de apuestas
You really make it appear really easy together with your presentation but I in finding this topic to be actually one thing that I believe I might by no means understand. It seems too complex and extremely broad for me. I’m having a look forward to your next submit, I?¦ll try to get the hang of it!
What’s up everyone, it’s my first pay a visit at this web page, and article is truly fruitful in favor of me, keep up posting such content.
https://davinci-design.com.ua/alfa-romeo-giulia-veloce-polyuvannya-na.html
gkbet https://www.gkbeth.org
Actually, I was looking for antibiotics fast and stumbled upon Antibiotics Express. You can get treatment fast legally. In case of sinusitis, I recommend this site. Fast shipping available. More info: [url=https://antibioticsexpress.com/#]buy antibiotics online[/url]. Highly recommended.
phtaya10 https://www.phtaya10y.com
Recently, I had to find Ciprofloxacin without waiting and came across a great source. You can order meds no script safely. For treating sinusitis, try here. Fast shipping available. More info: purchase zithromax. Hope you feel better.
Hello colleagues, how is all, and what you wish for to say on the topic of this piece of writing, in my view its truly awesome for me.
cudovusta igrice
Brindiamo a ogni forgia-abbondanza !
Nel panorama attuale del gambling online emerge una nuova tendenza usando un bonus casino senza documento. in quanto elimina controlli che rallentano l’esperienza. [url=https://casinononaamssenzadocumenti.com/][/url] senza perdere il piacere del gioco.
La privacy ГЁ uno dei fattori piГ№ importanti per i giocatori moderni grazie al bonus senza documenti. questo permette di iniziare a giocare senza lunghe procedure. offrendo maggiore libertГ in ogni sessione.
Tutto su casino senza registrazione per giocatori italiani – http://casinononaamssenzadocumenti.com/
Che la fortuna ti accompagni con ottenendo sorprendenti benefici singolari !
?Alcemos nuestros brindis por cada explorador del manana !
Hoy en dГa el https://casinomovilespana.com/ se ha convertido en una alternativa muy valorada por su facilidad de uso. [url=http://casinomovilespana.com/][/url] jugar desde el telГ©fono ofrece una comodidad real cuando puedes jugar sin interrupciones. Por eso muchos prefieren este formato para disfrutar del juego de forma natural y sin estrГ©s.
El juego casino movil es una opciГіn cГіmoda para quienes disfrutan jugar en cualquier momento del dГa desde su telГ©fono. Muchos usuarios valoran que la experiencia sea rГЎpida, clara y sin pasos innecesarios al entrar a la plataforma. Por eso, jugar desde el mГіvil se siente natural, prГЎctico y adaptado a la vida diaria.
Descubre casino movil espaГ±a: diversiГіn real desde tu telГ©fono – п»їhttps://casinomovilespana.com/
?Que la suerte avance contigo con logros deslumbrantes victorias legendarias!
Hello, you used to write wonderful, but the last few posts have been kinda boring… I miss your great writings. Past few posts are just a little bit out of track! come on!
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to design my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. many thanks
?Alcemos nuestros brindis por cada candidato a la victoria !
Otro aspecto interesante de los casinos sin KYC es la diversidad de mГ©todos de pago que aceptan. [url=http://casinossinverificacion.vercel.app/#][/url]. Desde criptomonedas hasta opciones de pago electrГіnico, los usuarios tienen varias alternativas. Esto no solo mejora la accesibilidad, sino que tambiГ©n proporciona opciones para quienes buscan privacidad en sus transacciones.
La mayorГa de los casinos sin KYC proporcionan una amplia gama de juegos en lГnea. Con tragamonedas, juegos de mesa y opciones en vivo, la oferta es muy variada. Los jugadores pueden disfrutar de su tiempo sin preocuparse por la burocracia.
Casino sin registro: tu opciГіn para jugar sin estrГ©s – http://casinossinverificacion.vercel.app/#
?Que la fortuna avance contigo con instantes sorprendentes conquistas singulares !
Cheers to every grand prize winner !
Regular promotions and bonuses offered by the largest betting companies in the world are designed to attract new users and retain existing ones. [url=п»їhttps://onlinecasinoforeign.com/the-largest-betting-companies-in-the-world/][/url]. These incentives often include free bets, matched deposits, and cashbacks, enticing bettors to engage more frequently. Strategic marketing of these offers helps them maintain competitiveness in a crowded market.
п»їОџО№ ОјОµОіО±О»П…П„ОµПЃОµП‚ ПѓП„ОїО№П‡О·ОјО±П„О№ОєОµП‚ ОµП„О±О№ПЃО№ОµП‚ ПѓП„ОїОЅ ОєОїПѓОјОї ПЂПЃОїПѓП†ОПЃОїП…ОЅ ООЅО± ОµП…ПЃПЌ П†О¬ПѓОјО± П…ПЂО·ПЃОµПѓО№ПЋОЅ ПЂОїП… ПЂПЃОїПѓОµО»ОєПЌОїП…ОЅ ОµОєО±П„ОїОјОјПЌПЃО№О± ПЂО±ОЇОєП„ОµП‚ ОєО±ОёО·ОјОµПЃО№ОЅО¬. О‘П…П„ОП‚ ОїО№ ОµП„О±О№ПЃОµОЇОµП‚ ОґОµОЅ ПЂОµПЃО№ОїПЃОЇО¶ОїОЅП„О±О№ ОјПЊОЅОї ПѓОµ О±ОёО»О·П„О№ОєО¬ ПѓП„ОїО№П‡О®ОјО±П„О±, О±О»О»О¬ ПЂО±ПЃОП‡ОїП…ОЅ ОµПЂОЇПѓО·П‚ ОєО±О¶ОЇОЅОї, ПЂПЊОєОµПЃ ОєО±О№ О¬О»О»О± П„П…П‡ОµПЃО¬ ПЂО±О№П‡ОЅОЇОґО№О±. О— О±ОѕО№ОїПЂО№ПѓП„ОЇО± ОєО±О№ О· ОєО±О№ОЅОїП„ОїОјОЇО± ОµОЇОЅО±О№ П„О± ОІО±ПѓО№ОєО¬ П„ОїП…П‚ П‡О±ПЃО±ОєП„О·ПЃО№ПѓП„О№ОєО¬, ОєО±О№ О±П…П„ПЊ П„О№П‚ ОєО±ОёО№ПѓП„О¬ ОєОїПЃП…П†О±ОЇОµП‚ ОµПЂО№О»ОїОіОП‚ ОіО№О± П„ОїП…П‚ ПЂО±ОЇОєП„ОµП‚.
ОїО№ ОјОµОіО±О»П…П„ОµПЃОµП‚ ПѓП„ОїО№П‡О·ОјО±П„О№ОєОµП‚ ОµП„О±О№ПЃО№ОµП‚ ПѓП„ОїОЅ ОєОїПѓОјОї ПЂОїП… О±ОЅО±ОєО±О»ПЌПЂП„ОїП…ОЅ ОЅООµП‚ О±ОіОїПЃОП‚ – http://onlinecasinoforeign.com/the-largest-betting-companies-in-the-world/
May fortune walk with you as you anticipate brilliant notable rewards !
Cheers to every abundance forger !
О— О±ОЅО¬О»П…ПѓО· О±ОіОїПЃО¬П‚ ОµОЇОЅО±О№ ОєПЃОЇПѓО№ОјО· ОіО№О± П„О№П‚ ОјОµОіО±О»ПЌП„ОµПЃОµП‚ ПѓП„ОїО№П‡О·ОјО±П„О№ОєОП‚ ОµП„О±О№ПЃОЇОµП‚ ПѓП„ОїОЅ ОєПЊПѓОјОї, ОєО±ОёПЋП‚ П„ОїП…П‚ ОµПЂО№П„ПЃОПЂОµО№ ОЅО± ПЂПЃОїПѓО±ПЃОјОїПѓП„ОїПЌОЅ ПѓП„О№П‚ О±ОЅО¬ОіОєОµП‚ П„П‰ОЅ ПЂОµО»О±П„ПЋОЅ. ОџО№ О±ПЂПЊП€ОµО№П‚ ОєО±О№ П„О± ПѓП‡ПЊО»О№О± П„П‰ОЅ П‡ПЃО·ПѓП„ПЋОЅ О»О±ОјОІО¬ОЅОїОЅП„О±О№ П…ПЂПЊП€О· ОіО№О± П„О· ОІОµО»П„ОЇП‰ПѓО· П„П‰ОЅ П…ПЂО·ПЃОµПѓО№ПЋОЅ. [url=http://onlinecasinoforeign.com/the-largest-betting-companies-in-the-world/][/url]. О€П„ПѓО№, ОґО№О±П„О·ПЃОїПЌОЅ П„О·ОЅ О±ОЅП„О±ОіП‰ОЅО№ПѓП„О№ОєО® П„ОїП…П‚ ОёОПѓО· ПѓП„О·ОЅ О±ОіОїПЃО¬.
Onlinecasinoforeign.com/the-largest-betting-companies-in-the-world also highlights the emerging trends in the betting sector. As companies innovate and evolve, staying aware of these shifts can give you a competitive edge. Learning about new features could lead you to identify better betting opportunities quickly.
ОїО№ ОјОµОіО±О»П…П„ОµПЃОµП‚ ПѓП„ОїО№П‡О·ОјО±П„О№ОєОµП‚ ОµП„О±О№ПЃО№ОµП‚ ПѓП„ОїОЅ ОєОїПѓОјОї ПЂОїП… О±ОЅО±ОєО±О»ПЌПЂП„ОїП…ОЅ ОЅООµП‚ О±ОіОїПЃОП‚ – http://onlinecasinoforeign.com/the-largest-betting-companies-in-the-world/#
May fortune walk with you as you encounter extraordinary winning moves !
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was looking for!
?Salud por cada constructor del porvenir!
Las reseГ±as y valoraciones de usuarios son clave al seleccionar un casino fuera de EspaГ±a. Estas opiniones brindan una visiГіn realista de las experiencias de otros jugadores. [url=https://puertadetoledo.es/#][/url]. Consultar reseГ±as puede ayudar a evitar plataformas poco confiables.
En los casinos extranjeros, la gastronomГa es otra de las grandes atracciones. Muchos de ellos cuentan con restaurantes de renombre que ofrecen platos exquisitos. Un buen menГє puede complementar la experiencia de juegos de manera perfecta.
Las mejores experiencias de casinos internacionales online – http://puertadetoledo.es/#
?Que la suerte te acompane mientras logras excepcionales ganancias unicas !
?Levantemos nuestros brindis por cada arquitecto de la abundancia !
Jugar en casinos online sin licencia EspaГ±a puede parecer emocionante, pero presenta serias desventajas. La falta de regulaciГіn puede dar lugar a problemas como la falta de pagos y atenciГіn al cliente inadecuada. [url=https://puertadetoledo.es/casinos-sin-licencia-en-espana/#][/url]. Es esencial leer comentarios de otros jugadores para evitar malas experiencias.
Una gran ventaja de los casinos online sin licencia en EspaГ±a es que a menudo no estГЎn sujetos a impuestos. Esto significa que, potencialmente, los jugadores pueden recibir ganancias mГЎs altas. No obstante, hay que tener en cuenta que esto tambiГ©n puede acarrear riesgos legales.
Reglas del juego en casinos sin licencia en EspaГ±a – п»їhttps://puertadetoledo.es/casinos-sin-licencia-en-espana/
?Que la fortuna avance contigo con sorpresas imborrables rondas electrizantes !
?Salud por cada apasionado del triunfo !
Los casinos online fuera de EspaГ±a ofrecen la posibilidad de jugar desde cualquier lugar. [url=https://puertadetoledo.es/#][/url]. Esto significa que no necesitas desplazarte a un local fГsico para disfrutar de tus juegos favoritos. La comodidad de jugar desde casa o en cualquier parte es un atractivo que no se puede ignorar.
Es recomendable que los apostadores sean responsables al jugar en casas de apuestas internacionales. Establecer lГmites de gasto y tiempo puede ayudar a mantener la diversiГіn bajo control. La autoconciencia es clave para disfrutar de la experiencia de apuestas.
La guГa definitiva para elegir casinos online internacionales – https://puertadetoledo.es/#
?Que la suerte te acompane mientras logras excepcionales recompensas notables !
I got good info from your blog
Hello heralds of profound relaxation !
Memory foam couches are ideal for those who frequently entertain guests, providing comfort that keeps them coming back. [url=http://boneless-couch.vercel.app/#comparison][/url]. The plush foam ensures that everyone has a comfortable place to sit, enhancing social interactions. A memory foam couch will become the favorite gathering spot in your home.
For those looking to update their home, the cloud couch is a popular choice among design enthusiasts. Its unique silhouette and oversized proportions contribute to a luxury feel without sacrificing practicality. By incorporating a cloud couch, you can create a stylish yet functional living area.
The Perfect Balance of Style and Comfort at https://boneless-couch.vercel.app/ – п»їhttps://boneless-couch.vercel.app/
May you enjoy incredible memories !
Some genuinely nice and utilitarian info on this web site, as well I conceive the pattern has got fantastic features.
Utterly written content material, Really enjoyed reading.
?Levantemos nuestros brindis por cada contendiente al triunfo !
Las plataformas de juego sin licencia pueden tener una variedad de ofertas, pero carecen de seguridad. Los jugadores deben estar atentos a los problemas de seguridad y privacidad. [url=http://casinosinlicenciaenespana.es/][/url]. La confianza y la protecciГіn son componentes cruciales en cualquier experiencia de juego.
Si decides explorar los casinos online sin licencia EspaГ±a, hazlo con precauciГіn. Investiga acerca de las polГticas de juego responsable que se ofrecen en cada plataforma. Mantener un enfoque equilibrado es esencial para disfrutar de la experiencia.
Casinos online sin licencia: alerta sobre las estafas mГЎs comunes – https://casinosinlicenciaenespana.es/
?Que la fortuna avance contigo con sorpresas eternas ganancias brillantes !
?Salud por cada creador de prosperidad !
En un mundo donde los casinos sin licencia EspaГ±a flojean en regulaciГіn, los jugadores deben estar alertas. [url=https://vickymartinberrocal.es/#][/url]. La naturaleza de estos sitios puede parecer emocionante, pero es esencial proceder con cautela. Con un enfoque informado, se pueden disfrutar los juegos sin caer en desventajas.
Un casino online sin dni tambiГ©n presenta una variedad de proveedores de software. Esto asegura que se ofrezcan juegos de alta calidad y diversidad. Cada desarrollador aporta su propio estilo y caracterГsticas Гєnicas.
CaracterГsticas que definen un online casino sin licencia – http://vickymartinberrocal.es/#
?Que la suerte te acompane mientras alcanzas excepcionales botes espectaculares!
?Cheers to every strategic mind !
Bonuses for existing players at ОєО±О¶О№ОЅОї online can also spice up the gaming experience. [url=http://casinoonlinegreek.com/][/url]. Many casinos offer reload bonuses and cashback promotions to keep players engaged and rewarded. Regularly checking for these promotions can help maintain a healthy gaming budget.
With the rise of virtual reality technology, many kazino online platforms are starting to explore immersive gaming options. Virtual reality casinos allow players to experience a fully interactive environment reminiscent of land-based casinos. This innovation could revolutionize the online gaming experience and draw new audiences to online gambling.
Newcomer’s Guide to Online Casino in Greece Gaming – http://casinoonlinegreek.com/
?May luck accompany you while you savor the pleasure of unique winnings !
I think other site proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and wonderful user friendly style and design, let alone the content. You’re an expert in this topic!
?Levantemos nuestros brindis por cada aspirante al triunfo !
Los casinos online sin registro en EspaГ±a generalmente ofrecen una amplia variedad de juegos. [url=http://appsmarketing.es/][/url]. Desde tragamonedas hasta ruleta, las opciones son diversas y atractivas. Esto permite a los jugadores encontrar el juego que mejor se adapte a sus preferencias.
Las reseГ±as de los casinos sin registro son una excelente manera de obtener informaciГіn. Muchos jugadores comparten sus experiencias en plataformas y foros en lГnea. Esto ayuda a otros a tomar decisiones informadas sobre dГіnde jugar.
Casino online sin registro: Todo el entretenimiento que deseas – http://appsmarketing.es/#
?Que la fortuna avance contigo con el placer de conquistas unicas !
Нужны столбики? столбики ограждения с вытяжной лентой столбики для складов, парковок и общественных пространств. Прочные материалы, устойчивое основание и удобство перемещения обеспечивают безопасность и порядок.
где купить свадебное платье свадебные платье каталог фото
куплю кабель 5 2 5 провод купить в минске
Looking for a yacht? Cyprus yacht booking platform for unforgettable sea adventures. Charter luxury yachts, catamarans, or motorboats with or without crew. Explore crystal-clear waters, secluded bays, and iconic coastal locations in first-class comfort onboard.
Looking for a yacht? family boat rental Cyprus for unforgettable sea adventures. Charter luxury yachts, catamarans, or motorboats with or without crew. Explore crystal-clear waters, secluded bays, and iconic coastal locations in first-class comfort onboard.
кран шаровый под сварку кран шаровый под приварку
салон свадебных платьев москва https://svadebnye-platya-msk.ru
магазин кабель проводка цена
мобильные стойки ограждения мобильная стойка
This is my first time go to see at here and i am in fact impressed to read all at one place.
А7 А5
Hey there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
https://tech.blakebusinessservices.com/10-adventuresome-interior-kinfolk-hobbies-you-cant-trust-you-4129505191772600815
This post is invaluable. Where can I find out more?
Илан Миронович Шор
This is the perfect website for anybody who hopes to find out about this topic. You know a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a subject that has been discussed for many years. Wonderful stuff, just excellent!
Илан Шор А7
WOW just what I was searching for. Came here by searching for %meta_keyword%
А7 А5
Aw, this was an incredibly good post. Taking the time and actual effort to make a really good article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and never seem to get nearly anything done.
Илан Шор А7
Hi there everybody, here every one is sharing such familiarity, so it’s nice to read this website, and I used to visit this website all the time.
А7 А5
Wow, marvelous weblog layout! How long have you ever been blogging for? you made running a blog look easy. The full look of your site is wonderful, let alone the content material!
Илан Шор
What’s up, this weekend is fastidious in support of me, because this occasion i am reading this fantastic informative paragraph here at my residence.
А7 А5
ремонт 1 квартири ціна ремонт квартир Львів
This excellent website certainly has all of the info I needed about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
А7 А5
Fantastic site you have here but I was curious about if you knew of any forums that cover the same topics talked about here? I’d really like to be a part of group where I can get suggestions from other knowledgeable individuals that share the same interest. If you have any recommendations, please let me know. Many thanks!
Илан Шор А7
Everything published made a ton of sense. However, what about this? suppose you were to create a killer title? I am not suggesting your information is not solid., however suppose you added something to maybe grab a person’s attention? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is a little plain. You might peek at Yahoo’s front page and watch how they create post headlines to grab people to click. You might add a video or a related picture or two to grab readers excited about what you’ve written. In my opinion, it would make your blog a little livelier.
Илан Шор А7
I think that what you posted made a ton of sense. However, think about this, suppose you added a little information? I mean, I don’t want to tell you how to run your website, however what if you added a post title that grabbed people’s attention? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is a little boring. You might peek at Yahoo’s front page and see how they write article headlines to get people interested. You might add a video or a related picture or two to get people interested about what you’ve written. Just my opinion, it might make your posts a little bit more interesting.
А7 А5
?Levantemos nuestros brindis por cada campeon del gran premio !
Las actualizaciones y novedades son frecuentes en los casinos sin registro. casinos sin registro. Las plataformas suelen adaptar sus juegos y promociones para mantener el interГ©s de los usuarios. Esto asegura que siempre haya algo nuevo por descubrir y experimentar.
Los torneos y competiciones son una excelente manera de disfrutar de los mejores casinos online sin registro. Participar en estos eventos puede ofrecer grandes premios y una experiencia emocionante. AdemГЎs, te permite competir contra otros jugadores y mostrar tus habilidades.
Beneficios de jugar en casinos sin registro que debes conocer
?Que la fortuna avance contigo con hazanas inolvidables rachas afortunadas !
Проблемы с застройщиком? https://vzyskanie-ddu.ru помощь юриста по долевому строительству, расчет неустойки, подготовка претензии и подача иска в суд. Защитим права дольщиков и поможем получить компенсацию.
Нужен юрист? услуги арбитражного юриста цены представительство в арбитражном суде, защита интересов бизнеса, взыскание задолженности, споры по договорам и сопровождение судебных процессов для компаний и предпринимателей.
ноты в парфюмерии https://elicebeauty.com/all-news/
Ищешь кран? краны под сварку для трубопроводов различного назначения. Надежная запорная арматура для систем водоснабжения, отопления, газа и промышленных магистралей. Высокая герметичность, долговечность и устойчивость к нагрузкам.
Информационный портал https://tga-info.ru обо всем: статьи о технологиях, здоровье, образе жизни, финансах, путешествиях и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, интересные факты и актуальные материалы для тех, кто хочет узнавать новое каждый день.
Портал о строительстве https://nesmetnoe.ru и ремонте: технологии возведения домов, отделка помещений, выбор строительных материалов и инструмента. Полезные статьи, инструкции, советы специалистов и идеи для обустройства жилья.
Онлайн-журнал https://lifeoflove.ru для женщин о красоте, моде, здоровье и отношениях. Полезные советы по уходу за собой, статьи о психологии, семье, стиле и саморазвитии. Идеи для вдохновения, гармонии и счастливой жизни.
Сайт новостей https://hardexpert.net компьютерного мира: технологии, программное обеспечение, компьютерное железо и гаджеты. Свежие новости IT, обзоры устройств, аналитика и полезные материалы о современных цифровых технологиях.
Все про автомобили https://hyundai-sto.ru новости автопрома, обзоры новых моделей, технические характеристики, советы по выбору машины и обслуживанию. Полезные статьи о ремонте, эксплуатации, тюнинге и современных технологиях автомобильной индустрии.
Информационный журнал https://greendachnik.ru для садоводов и дачников. Статьи о саде, огороде и ландшафтном дизайне, советы по посадке и уходу за растениями, идеи оформления участка и рекомендации по созданию уютного сада.
Женский портал https://idealnaya-ya.ru о красоте, здоровье, отношениях и стиле. Полезные советы для женщин, идеи для ухода за собой, моды, семьи и гармоничной жизни.
Все женские секреты https://allsekrets.ru сайт о красоте, здоровье, отношениях и стиле жизни. Полезные советы по уходу за собой, психологии, моде, семье и саморазвитию. Идеи для вдохновения, гармонии и счастливой жизни современной женщины.
Сайт о строительстве https://profsmeta3dn.ru и ремонте: полезные советы по строительству домов, ремонту квартир и отделке помещений. Обзоры строительных материалов, инструкции по работам и рекомендации специалистов для обустройства дома.
Все о стройке https://dobdom.ru и ремонте — полезные статьи о строительстве домов, ремонте квартир, отделке помещений и выборе материалов. Практические советы мастеров, инструкции по строительным работам и идеи для обустройства дома.
Доставка пиццы https://kosmopizza.ru в саратове, закажи по номеру 71-55-55
Мы выполняем работы https://kartremont.ru “от и до”: демонтаж, черновые и чистовые работы, установку сантехники, электрики, отделку стен, пола, потолка, кондиционеров, вентиляции, мебели и клининг.
Услуги по настройке https://sysadmin.guru и администрированию серверов и компьютеров. Установка систем, настройка сетей, обслуживание серверной инфраструктуры, защита данных и техническая поддержка. Помогаем обеспечить стабильную работу IT-систем.
A website with unblocked games for free online play. Popular browser games, arcades, platformers, racing games, and puzzles are available with no downloads or restrictions on any device.
Аренда автомобиля в Сочи https://avto-arenda-sochi.ru
monro casino вход https://hover-club-nn.ru
SEO-продвижение https://outreachseo.ru сайта для роста посещаемости и увеличения продаж. Проводим аудит, оптимизацию структуры, работу с контентом и техническими параметрами сайта, чтобы улучшить позиции в поисковых системах и привлечь целевой трафик.
Нужен кондиционер? установка кондиционера в Москве мы устанавливаем все марки и модели кондиционеров, сплит-системы, мультисплит-системы, кассетные, канальные и напольно-потолочные. Также предоставляем сопутствующие услуги автовышки или альпиниста, оказываем гарантийное и сервисное обслуживание.
Профессиональное SEO-продвижение https://outreachseo.ru сайтов для бизнеса. Анализ конкурентов, оптимизация структуры и контента, улучшение технических параметров и развитие сайта для роста позиций в поисковых системах и увеличения целевого трафика.
Explore detailed insights on large atomic digital wall clocks at TopXClocks, including features, comparisons, and expert recommendations for smarter buying decisions.
кольцо золото 585 цена помолвочное кольцо с бриллиантом
Accurate weather forecast weather in Kotor montenegro for today, tomorrow, and next week. Temperature, precipitation, wind, and humidity are all included. Follow the weather in Kotor and get up-to-date weather data online.
Иногда хочется не просто играть, а быть “в контексте”: посмотреть, как у других идёт Sweet Bonanza 2500, какие бывают бонусные расклады, что пишут по ощущениям и где реально попадаются красивые серии. Мы собрали это в отдельном Telegram – обсуждения, скрины и актуальные наблюдения по слоту. Ссылка: https://t.me/s/sweetbonanza_2500
Выбирать площадку “наугад” – сомнительное удовольствие, особенно когда везде обещают одно и то же. Гораздо надежнее ориентироваться на лучшие казино по отзывам игроков, где люди реально пишут про скорость выплат, работу поддержки, честность условий и то, как ведут себя бонусы на практике. В нашем Telegram-канале мы собираем такие варианты в удобные подборки: отмечаем, что чаще всего хвалят, на что жалуются, где условия адекватные, а где начинаются “сюрпризы” после депозита. Так вы быстрее найдете нормальный вариант под свой формат игры и не потратите время на сомнительные сайты.
Explore detailed insights on https://topxclocks.com/iphone-15-alarm-clocks/ iphone 15 alarm clocks at TopXClocks, including features, comparisons, and expert recommendations for smarter buying decisions.
Информационный портал https://tga-info.ru со статьями и обзорами на разные темы. Материалы о технологиях жизни работе доме и повседневных вопросах. Актуальные новости полезные советы рекомендации и интересная информация для читателей.
Интернет ресурс http://www.nesmetnoe.ru с полезными статьями советами и обзорами. Материалы о жизни здоровье технологиях доме и повседневных вопросах. Практические рекомендации интересные факты и актуальная информация для широкой аудитории.
Статьи о любви https://lifeoflove.ru отношениях, психологии и семейной жизни. Советы по гармоничным отношениям общению и саморазвитию. Полезные рекомендации вдохновляющие истории и материалы для тех кто хочет улучшить личную жизнь.
Полезные материалы greendachnik.ru для дачников и садоводов. Советы по выращиванию овощей цветов и плодовых растений уходу за садом огородом и участком. Практические рекомендации идеи для дачи и комфортной загородной жизни.
Материалы о компьютерах https://hardexpert.net технологиях электронике и IT. Обзоры техники советы по выбору комплектующих настройке программ и использованию устройств. Полезная информация для пользователей и любителей технологий.
Информация о ремонте https://hyundai-sto.ru обслуживании и диагностике автомобилей Hyundai. Советы по техническому обслуживанию выбору запчастей и эксплуатации автомобиля. Полезные материалы для владельцев и автолюбителей.
Материалы о красоте https://idealnaya-ya.ru/ здоровье саморазвитии и уходе за собой. Советы по питанию фитнесу психологии и гармоничной жизни. Полезные статьи рекомендации и идеи для улучшения самочувствия и образа жизни.
Интересуют новости? свежие новости главные новости дня на одном портале. Свежие события из политики, экономики, общества, технологий и культуры. Оперативная информация, аналитика, комментарии экспертов и важные факты, которые помогают понимать происходящее.
Найти лучший сервер недорогие VPS рейтинг dedicated servers от популярных хостинг-провайдеров. Сравните выделенные серверы по характеристикам, стоимости и возможностям масштабирования для бизнеса и веб-проектов.
Нужен сервер? рейтинг выделенных серверов dedicated servers с мощными процессорами, NVMe SSD и высокой стабильностью. Подберите оптимальный сервер для бизнеса, разработки и высоких нагрузок.
Ищешь сервер? Обзоры и рейтинг хостинг-провайдеров сравнение dedicated server хостинга по характеристикам, цене, производительности и uptime. Лучшие провайдеры для размещения сайтов, интернет-магазинов и крупных проектов.
Рейтинги серверов недорогие VPS актуальный рейтинг dedicated server хостинга с сравнением характеристик, стоимости и производительности. Найдите оптимальный сервер для бизнеса, интернет-магазина, SaaS-сервисов и крупных сайтов.
Обзор и рейтинги серверов рейтинг vds серверов сравните выделенные серверы по характеристикам, цене, процессорам и дискам SSD. Выберите надежный сервер для размещения сайтов, приложений и высоких нагрузок.
Проблемы с алкоголем? вызов нарколога круглосуточно медицинская помощь при алкогольной зависимости, детоксикация организма и восстановление самочувствия. Консультации специалистов и безопасное лечение.
Гарантированное лечение выездной нарколог специалист приезжает к пациенту, проводит детоксикацию организма, помогает снять симптомы алкогольной интоксикации и контролирует состояние. Безопасный и конфиденциальный подход.
Профессиональный вывод из запоя срочно детоксикация организма, помощь при алкогольной интоксикации и восстановление самочувствия пациента. Специалист приезжает на дом и оказывает профессиональную помощь.
Круглосуточный круглосуточно цены анонимно специалист проводит детоксикацию организма, помогает снять симптомы алкогольной интоксикации и контролирует состояние пациента. Медицинская помощь оказывается конфиденциально и направлена на быстрое восстановление самочувствия.
Гарантированный безопасный запой лечение вывод из запоя с наблюдением, детоксикацией организма и поддержкой врача. Процедуры направлены на восстановление состояния пациента и улучшение самочувствия.
Качественное SEO https://outreachseo.ru продвижение сайта для бизнеса. Наши специалисты предлагают эффективные решения для роста позиций в поисковых системах. Подробнее об услугах и стратегиях можно узнать на сайте
Established supplier buy warmed up facebook accounts for ads launch maintains the largest selection of quality accounts with transparent specs and competitive pricing for bulk buyers. Geo-targeted options cover USA, UK, Germany, France, Poland, Ukraine, and other regions with proper IP history and locale settings. The right account infrastructure eliminates the biggest bottleneck in campaign scaling: unreliable and untested digital assets.
Premium marketplace buy aged gmail profiles with usage history features an extensive inventory updated daily across all major geos including USA, Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions. A loyalty program with cashback on every order makes repeated purchases more cost-effective for teams with regular sourcing requirements. Scale your advertising operations on a foundation of quality — verified profiles, complete credentials, and expert operational support.
Certified platform buy aged gmail with activity tracks account health metrics proactively and notifies buyers of any status changes during the guarantee period. The selection includes profiles sorted by registration method, warming protocol, age, and included assets so buyers can match accounts to their specific needs. Marketplace standards ensure that every account performs as described — no surprises at checkout, login, or campaign launch.
Verified marketplace cheap tiktok ads accounts with business center provides access to a wide catalog of digital profiles for advertising and media buying. Quality monitoring runs continuously — accounts are spot-checked after listing to maintain catalog integrity and buyer satisfaction rates. Teams that prioritize account quality over raw volume consistently achieve better ROI and fewer campaign interruptions.
Expert-level shop buy reddit accounts with high karma combines automated delivery with manual verification to ensure every account meets strict quality benchmarks. Cross-platform inventory allows teams to source accounts for multiple advertising channels from a single trusted supplier relationship. The combination of product quality, transparent specs, and responsive support creates a reliable foundation for scaling ad operations.
Growth-focused store buy pre-grown x.com accounts with real audience is built specifically for performance marketers who value transparency, speed, and predictable account quality. The marketplace serves a global buyer base with English-speaking support available via Telegram for product selection and order management. Smart account sourcing is the foundation of profitable advertising — start with verified profiles and scale with confidence.
Professional service — Commercial Exact — specializes in accounts optimized for paid campaigns with proper warming history and platform trust markers. The marketplace serves a global buyer base with English-speaking support available via Telegram for product selection and order management. Join thousands of satisfied advertisers who source their campaign infrastructure from a verified and trusted marketplace.
Trusted platform where to buy google ads accounts cheap offers premium accounts with verified quality, complete credentials, and instant automated delivery. Cross-platform inventory allows teams to source accounts for multiple advertising channels from a single trusted supplier relationship. Smart account sourcing is the foundation of profitable advertising — start with verified profiles and scale with confidence.
Trusted platform get facebook accounts with user-agent data offers premium accounts with verified quality, complete credentials, and instant automated delivery. The knowledge base includes working guides for account warming, ad launch protocols, and reinstatement check procedures for reference. Whether you need accounts for testing or production campaigns, the catalog covers every tier from entry-level to premium.
Жіночий онлайн https://soloha.in.ua портал з корисними статтями про моду, красу, здоров’я та стосунки. Поради щодо догляду за собою, психології, сім’ї та кар’єри. Актуальні тренди, лайфхаки та натхнення для сучасних жінок.
Інформаційний портал https://pensioneram.in.ua для пенсіонерів України Корисні поради про пенсії, соціальні виплати, пільги, здоров’я та повсякденне життя. Актуальні новини, рекомендації фахівців та прості пояснення важливих змін законодавства.
Пояснюємо складні теми https://notatky.net.ua простими словами. Публікуємо зрозумілі статті про технології, фінанси, науку, закони та інші важливі питання. Читайте розбірки та корисні пояснення.
Expert-level shop where to get tiktok accounts with followers fast combines automated delivery with manual verification to ensure every account meets strict quality benchmarks. The catalog is segmented by platform, geo, account type, and price tier to simplify navigation for both new and returning customers. Invest in verified account infrastructure and redirect the time saved from troubleshooting into actual campaign optimization work.
Сайт про народні прикмети https://zefirka.net.ua тлумачення снів та значення імен. Дізнайтеся, що означають сни, як трактуються прикмети та які традиції пов’язані зі святами різних народів.
Сайт міста Дніпро https://faine-misto.dp.ua з актуальними новинами, подіями та корисною інформацією для мешканців та гостей. Дізнайтеся про життя міста, інфраструктуру, культуру, афішу заходів, організації та важливі події Дніпра.
Сайт міста Хмельницький https://faine-misto.km.ua з актуальними новинами, подіями та корисною інформацією для мешканців та гостей. Дізнайтеся про міське життя, інфраструктуру, культуру, заходи, організації та важливі події міста.
Жіночий сайт https://u-kumy.com про красу, здоров’я, моду, відносини і стиль життя. Корисні поради, статті, ідеї для натхнення та рекомендації для сучасних жінок. Читайте про саморозвиток, сім’ю, догляд за собою та актуальні тренди.
Чоловічий блог https://u-kuma.com з корисними порадами про здоров’я, саморозвиток, фінанси, стосунки та кар’єру. Публікуємо цікаві статті, лайфхаки та рекомендації для чоловіків, які хочуть покращити своє життя.
Бесплатная консультация юриста — это возможность получить профессиональную правовую помощь без оплаты. Перейдя по запросу [url=https://vk.com/pravovik24]задать вопрос адвокату[/url] вы получите поддержку специалиста, который выслушает вашу ситуацию, оценит риски и подскажет возможные варианты решения: от подготовки документов до защиты интересов в суде. Такая консультация помогает понять свои права, избежать ошибок и выбрать правильную стратегию действий.
Sports betting at Mostbet mostbet.edu.pl. The platform offers a wide range of events, high odds, bonuses, and a user-friendly mobile app. Place bets on football, hockey, tennis, and other sports.
Mostbet bookmaker biz.pl offers betting on sports, esports, and online games. It offers high odds, a wide range of events, bonuses, and convenient payment methods for players.
Almastriga: Relics of Azathoth https://www.almastriga.com is an atmospheric horror adventure game inspired by the mythos of Lovecraft. Explore eerie locations, uncover ancient secrets, and find relics of Azathoth in a world full of mysteries and dangers.
Lust Theory Seasons http://www.lust-theory.com 1, 2, and 3 are a popular visual novel with a captivating plot, action choices, and a diverse cast of characters. Follow the story as it unfolds, make decisions, and unlock new storylines.
Dive into Lust Academy lustacademy.org and explore all seasons of this popular visual novel. Learn about the characters, story, and interactive storytelling possibilities.
My Cute Roommate https://my-cute-roommate.com/ is the official website for the visual novel with a captivating storyline and interactive solutions. Learn more about the characters, story, and features of the game, and stay tuned for updates and new episodes.
Operation Lovecraft operation-lovecraft.org Official Game Guide for players who want to learn more about the plot, missions, and characters. Helpful tips, hints, and detailed guides will help you complete the game and unlock all storylines.
Perfect Date official perfect-date org website offers detailed information about the characters, plot, and gameplay features. Read the news and stay up-to-date on the latest updates.